Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business School
Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business School
Uploaded by
shanky00720 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
128 views45 pagesOriginal Title
ECGC
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
128 views45 pagesProf Mahesh Kumar Amity Business School
Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business School
Uploaded by
shanky0072Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 45
ECGC
Prof Mahesh Kumar
Amity Business School
profmaheshkumar@rediffmail.com
Introduction
There are two major risks in international
trade:
a) Risk of loss of or damage to the goods.
b) Risk of non-realization of export
proceeds.
The risk of loss of damage of the goods
is covered by general insurers under
marine insurance.
Introduction
Non receipt of export proceeds may
be due to the failure of the buyer to
accept and/or pay for the goods. This
is known as commercial risk.
Such difficulties mat be attributed to
political and economic changes.
The Export Risks Insurance
Corporation (ERIC) was set up by
Government of India in July 1957 to
protect the overseas business from
political and economic changes.
Evolution of ECGC
Initially the task of ERIC was to protect the
overseas business from political and economic
changes.
Apart from this ERIC was also to facilitate the
timely and liberal facilities from banks for overseas
trade.
To give encouragement to the banks to promote
overseas trade ,guarantees were issued in their
favor so as to protect them against failure of the
exporter to repay the bank advance.
Consequently, the ERIC was transformed into
Export Credit and Guarantee Corporation Ltd. In
1964.
ECGC and its administrative
structure
ECGC is a company wholly owned by
GoI.
It functions under the administrative
control of the Ministry of Commerce
and is managed by board of Directors
representing Government, banking,
insurance, trade and industry.
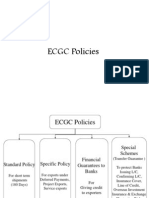
Schemes of ECGC
The functions of ECGC are reflected in the
different schemes it has evolved to protect
the exporter and the exporter’s bank.
Schemes of ECGC for Exporter’s Bank is in the
form of various guarantees issued by them.
a) Packing Credit Guarantee
b) Export Production Finance Guarantee
c) Post-shipment Export Credit Guarantee
d) Export Finance Guarantee
e) Export Performance Guarantee
f) Export Finance (Overseas Lending) Guarantee
g) Transfer Guarantee
ECGC Schemes For Exporters
ECGC provides three kind of schemes to exporters.
a) Whole Turnover policy
1) Standard Policy
2) Small Exporters Policy
b) Factoring
1) Maturity Factoring
c) Specific Policies
1) Specific Shipment policy ( short term)
2) Supply Contracts Policy
3) Exporters ( Specific Buyers ) Policy
4) Export Turnover policy
ECGC Schemes For Exporters
5) Buyer Exposure policy.
6) Consignment Exports Policy
7) Buyer’s Credit
8) Services Policy
9) Construction Works Policy
10) Software Project Policy
11) IT Enabled Services ( Specific Customer) Policy
12) Overseas Investment Insurance
13) Exchange Fluctuation Risk Cover
For Exporters- Whole Turnover
Policy
Standard Policy
The standard policy issued by ECGC are
meant to provide cover for shipments
on short term credit on whole turnover
basis.
The risks covered may be divided into
two categories a) Commercial risk b)
Political risk
For Exporters- Whole Turnover
Policy
Commercial risk covered include:
1) Insolvency of the buyer
2) Buyer’s protracted default to pay for
the goods accepted by him.
3) Buyer’s failure to accept goods
subject to certain conditions.
For Exporters- Whole Turnover
Policy
Political risk covered are:
1) Imposition of restrictions on remittances
by the government in the buyer’s
country or any action which may block
or delay the payment of the exporter.
2) War, revolution or civil disturbances in
the buyer’s country.
3) New import licensing restrictions or
cancellation of a valid import license in
the buyer’s country.
For Exporters- Whole Turnover
Policy
4) Cancellation of export license or imposition
of new export licensing restrictions in India.
5) Payment of additional handling, transport
or insurance charges occasioned by
interruption or diversion of the voyage
which cannot be covered from the buyer;
and
6) Any other cause of loss occurring outside
India, not normally insured by commercial
insurer, and beyond the control of exporter
and/or the buyer.
Risks Not Covered
The following risks are not covered under Standard Policy
1) Commercial disputes raised by the buyer, unless the
exporter obtains a decree from the competent court
of law in the buyer’s country in his favor.
2) Causes inherent in the nature of the goods.
3) Buyer’s failure to obtain necessary import or export
authorization from authorities in his country.
4) Insolvency or default of an agent of the exporter or
of the collecting bank.
5) Loss or damage of the goods which can be covered
by commercial insurers.
6) Exchange fluctuations.
Types of Policies
The policy issued may cover risk from
the date of shipment or from the date of
contract and may cover political risk and
commercial risk or only commercial risk.
On this basis policies issued are
classified as
1. Shipment ( Comprehensive Risks) Policy
2. Shipment ( Political Risk ) Policy
3. Contract ( Comprehensive Risk) Policy
4. Contract ( Political Risk ) Policy
Types of Policies
Policy covering the political risk alone
may be preferred if the export is
covered by letter of credit or where the
export is made to an associate concern.
Contract policies, which cover risks
from the date of contract, are issued
only in special cases when the goods
exported are manufactured to non-
standard specifications of a buyer.
Extent of Cover
ECGC’s liability is subject to two limits:
a) Maximum liability: is the limit up to which
ECGC would accept liability for shipments
made during the period of policy.
b) Credit limit: is the limit up to which ECGC
accepts claims in respect of each buyer.
ECGC normally pays 90 percent of the losses
on account of political and commercial risk
Obtaining the Cover
The exporter submits the proposal to
ECGC.
After examination, ECGC sends a letter
stating the terms of its cover and
premium rates.
The policy is issued after the exporter
conveys his consent to the premium
rates and pays the stipulated non
refundable policy fees
Premium
Premium rates are closely related to
the risks involved and vary according
to countries to which goods are
exported and the payment terms.
Reporting Defaults
A monthly declaration of all bills which
remain unpaid for more than 30 days
should be submitted to ECGC in the
prescribed form, indicating action taken
in each case.
Granting extension of time in payment,
converting bills from DP to DA terms or
resale of unaccepted goods at lower
price require the prior approval of ECGC.
Settlement of Claims
A claim will arise when any of the risks insured
under the policy materializes.
If an overseas buyer goes insolvent, the exporter
becomes eligible for claim one after his loss is
admitted to rank against insolvent’s estate or
after four months from the due date, which ever
is earlier.
Claims in case of additional handling, transport or
insurance charges incurred by the exporter
because of interruption or diversion of voyage
outside India are payable after the proof of loss
is furnished.
In all other cases, claim is payable four months
from the date of the event causing the loss.
Small Exporter’s Policy
It is a standard policy issued to exporters
whose anticipated export turnover for next 12
months does not exceeds Rs. 25 lakhs.
This policy differs from standard policy in
following respects:
a) Period of policy: Issued for 12 months as
against 24 months in the case of standard
policy.
b) Minimum premium: The minimum premium
payable is 0.3% of the anticipated turnover
on DP and DA terms of payment, plus 0.10%
of the anticipated turnover on LC terms or Rs.
1000 whichever is higher.
Small Exporter’s Policy
c) Declaration of Shipments: Shipments need
to be declared only twice: in the seventh
month and the thirteenth month.
d) Declaration of overdue payment: Monthly
declaration of all payments overdue be more
than 60 days from the due date, as against 30
days in the case of the standard policy.
e) Percentage of Cover: 95% for loss due to
commercial risk and 100% if due to political
risk.
f) Waiting period for claim: Two months as
against four months in standard policy.
Small Exporter’s Policy
g) Change in terms of payment or extension of
credit period:
1) A small exporter may without the prior approval of
ECGC , convert DP bill into DA bill, provided he has
already obtained suitable credit limit on the buyer
on DA terms.
2) Where the value of the bill is not more than Rs.
3.00 lacs, conversion of DP bills into DA bills is
permitted even if credit limit of buyer has been
obtained on DP terms only, but not more than one
claim can be considered during the policy period on
account of losses arising from such conversions.
3) Due date of payment of a DA bill can be extended,
provided a credit limit from on the DA terms is in
force at the time of such extension.
Small
h)ResaleExporter’s
of unacceptedPolicy
goods: If, upon non
acceptance of goods by a buyer, the exporter
sells the goods to an alternate buyer without
obtaining the prior approval of ECGC. The
corporation may consider payment of claims up
to an amount considered reasonable by it,
provided it is satisfied that the exporter did his
best under the circumstances to minimize the
loss.
i) Claims due to loss or damage to goods:
ECGC may also consider payment of claim up
to an amount considered by it as reasonable
where loss is due to loss or damage of goods
due to certain risks which are not normally
included in general/ marine insurance policies.
Specific Policies
Specific Shipment Policy ( Short
Term): Offers to cover one or more
shipments only under a particular
contract. Option is to cover both
commercial and political risk. The
percentage cover is 80%. This policy is
taken by exporters who do not hold
standard policy or even by those holding
it to cover the shipments specifically
permitted to be excluded from the
purview of the Standard Policy.
Specific Policies
Specific Policy for Supply Contracts:
Specific policy for supply contracts covers
exports of commodities for period beyond
180 days. Both contract and shipment
policies ( for both comprehensive and
political risks) are available. Losses that
may be sustained by an exporter at the
pre-shipment stage due to frustration of
contract are covered under this policy.
Specific Policies
Export (Specific Buyer) Policy: Buyer-wise
Policies-Short Term provide cover to Indian
exporters against commercial and political
risks involved in export of goods on short term
credit to a particular buyer. Three types of
policies are available:
a) Buyer-wise (commercial and political risks)
Policy- Short Term
b) Buyer-wise (political risks) Policy- short term.
c) Buyer-wise (insolvency & default of L/C
opening bank and political risks) Policy-Short
Term
Specific Policies
Export Turnover Policy: Turnover policy is a
variation of the standard policy for the benefit
of large exporters who contribute not less than
Rs. 10 lakhs per annum towards premium.
The policy provides additional discount in
premium with an added incentive for
increasing the exports beyond projected
turnover and also offers simplified procedure
for premium remittance and filing of shipment
information. It also provides for higher
discretionary credit limits on overseas buyers.
Specific Policies
Buyer Exposure Policies: Two
types of exposure policies are offered
a) Exposure (Single Buyer) Policy- for
covering the risks on a specified
buyer; and
b) Exposure (Multi Buyer) Policy- for
covering the risks on all buyers.
Specific Policies
Consignment Exports Policy: Indian
exporters are increasingly adopting
consignment exports where the goods are
shipped and held in stocks overseas ready
for sale to overseas buyers. To protect the
Indian exporters from possible losses under
Consignment Policy Cover. There are two
policies for covering consignment export viz.
a) Consignment Exports ( Stock-holding Agent)
b) Consignment Exports ( Global Entity Policy)
Specific Policies
Insurance Cover for Buyer’s Credit and Lines
of Credit:
Credit Buyer’s credit is a loan extended by a
financial institutions or a consortium of financial
institutions, to the buyer for financing a particular
export contract. Under lines of credit, a loan is
extended to government or financial institutions
in the importing country for financing import of
specified item from the lending country. ECGC
has evolved schemes to protect financial
institutions in India which extend these types of
credit for financing exports from India.
Specific Policies
Services Policy: When Indian firms
render services to foreign parties
they would be exposed to payment
risks similar to those involved in
export of goods. Service policy offers
protection to Indian firms against
such payment risks.
Specific Policies
Construction Works Policy: ECGC’s
Construction Works Policy covers civil
construction as well as turnkey projects
involving supplies and services. It
provides cover for all payment that fall
due to the contractor under the contract.
Two types of policies have been evolved
to cover contracts with i) Government
buyers, and b) Private buyers.
Specific Policies
Software Project Policy: These are
special policies for software exporters
in addition to general service policy.
Specific Policies
Overseas Investment Insurance:
ECGC has evolved a scheme to provide
protection for involvement of exporters
in capital participation in overseas
projects. Any investment made by way
of equity capital or untied loan for the
purpose of setting up or expansion of
overseas projects will be eligible for
cover under investment insurance.
Specific Policies
Exchange Fluctuation Risk Cover Schemes:
The Exchange Fluctuation Risk Cover Schemes
are intended to provide a measure of protection
to exporters of capital goods, civil engineering
contractors and consultants who have often to
receive payments over a period of years for
their exports, construction work or services.
Where such payment are to be received in
foreign currency, they are open to exchange
fluctuation risk and the forward exchange
market does not provide cover for such
deferred payments. The cover is available for
payments scheduled over a period of 12 months
or more up to a maximum of 15 years.
Maturity Factoring Facility
Under maturity factoring the factor
initially undertakes only sales ledger
administration and collection functions
involving granting of credit to the
buyer for a period not exceeding 180
days. The factor pays the amount of
each invoice to the client at the end of
the credit term or on the agreed
maturity date.
Benefits to the Banks: Maturity Factoring
Facility
The maturity factoring facility offered by
ECGC does not disturb the existing system of
banking arrangement.
Banks would be able to finance against the
factored bills at zero risk, as they would be
protected even in case where the non-
payment is due to dispute between the
exporter and the buyer.
As the discounting of the bill under the
scheme is to be done by the exporter’s bank
they would not face any hassle in adjusting
advances granted at the packing credit stage.
Benefits to the Exporters: Maturity Factoring
Facility
100% risk protection in respect of transactions
where the buyer accepts the bills/documents
without recourse to the exporter.
Sharing of loss in case of non-acceptance of
goods/documents due to insolvency or
financial difficulty.
Receivable management and sales ledger
maintenance.
Enables the exporter to avail bank finance on
easier terms.
The exporter can avail of the above benefit
without disturbing existing system of banking
arrangement.
Guarantees to Banks
Packing Credit Guarantees: This guarantee
covers advances granted to exporters at the
pre-shipment stage for the purpose of purchase,
manufacture, processing and packing of goods
meant for export against firm contracts of sale,
whether on credit terms or against irrevocable
letters of credit. Advances given by banks to
Indian firms engaged in export of services or to
those which take up construction work abroad
to meet preliminary expenses in connection with
such contracts are also eligible. The guarantee
protects the bank against failure of exporter to
repay the advance because of his insolvency or
protracted default to repay.
Guarantees to Banks
Post Shipment Export Credit
Guarantee: Post Shipment finance
given to exporters by banks through
purchase, negotiation or discount of
export bills or advance against such bills
qualifies for this guarantee. It is
necessary, however, that the exporter
concerned should hold suitable policy of
ECGC to cover the overseas credit risks.
Guarantees to Banks
Export Finance Guarantee: This
guarantee covers post-shipment
advances granted by banks to
exporters against incentive receivable
in the form of cash assistance, duty
drawback etc.
Guarantees to Banks
Export Performance Indemnity: It is
an indemnity which is in nature of a
counter guarantee issued to the
exporter’s bank to protect against losses
that it may suffer on account of
guarantees given by it on behalf of the
exporters. The cover is available for such
guarantees as performance guarantee,
advance money guarantee, retention
money guarantee, guarantee to foreign
bank for finance raised overseas etc.
Guarantees to Banks
Export Finance (Overseas Lending)
Guarantee: If a bank financing an
overseas project provides a foreign
currency loan to the contractor, it can
protect itself from the risk of non-payment
by the contractor by obtaining Export
Finance (Overseas Lending) Guarantee.
Guarantees to Banks
Transfer Guarantee: This guarantee seeks to
safeguard the banks on the confirmation they might
add to letters of credit opened by banks abroad in
favor of Indian exporters. The guarantee covers risks
of
a) insolvency of the opening bank.
b) Failure of the opening bank to pay within four
months from the due date of payment.
c) Operation of law which prevents, restricts or controls
transfer of the amount of the credit to India, in
circumstances outside the control of the opening
bank and the confirming bank
d) Occurrence of war between the country of the
opening bank and India.
e) Occurrence of war, hostilities, civil war, rebellion,
insurrection or other disturbances in the country of
the opening bank.
You might also like
- SIE Exam Practice Question Workbook: Seven Full-Length Practice Exams (2023 Edition)From EverandSIE Exam Practice Question Workbook: Seven Full-Length Practice Exams (2023 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Case StudyfdffdfDocument3 pagesCase StudyfdffdffreNo ratings yet
- Kims RLCO Trading System DescriptionDocument21 pagesKims RLCO Trading System DescriptionAmol b100% (2)
- Trade Finance ProductsDocument35 pagesTrade Finance ProductsAnkit Malde100% (1)
- Chetan Bhagat - Three Mistakes of My LifeDocument144 pagesChetan Bhagat - Three Mistakes of My LifeGayathri ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Assembly LanguageDocument2 pagesComputer Architecture and Assembly LanguageasifanisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document50 pagesChapter 4Nguyen Hai AnhNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Role of EcgcDocument11 pagesAssignment On Role of EcgcBhawna DagarNo ratings yet
- Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (ECGC)Document36 pagesExport Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (ECGC)tcdarwinNo ratings yet
- Objectives of EcgcDocument28 pagesObjectives of EcgcjamalayajNo ratings yet
- MBA (IB) PART-TIME 2015-18: Financing of International TradeDocument12 pagesMBA (IB) PART-TIME 2015-18: Financing of International TradeAmit HazraNo ratings yet
- Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India LTDDocument7 pagesExport Credit Guarantee Corporation of India LTDAisha SayyadNo ratings yet
- Dr. A.K. Sengupta: Former Dean, Indian Institute of Foreign TradeDocument12 pagesDr. A.K. Sengupta: Former Dean, Indian Institute of Foreign TradeimadNo ratings yet
- Group 6 (Ecgc)Document8 pagesGroup 6 (Ecgc)indu_31No ratings yet
- Export Credit and Guarantee CorporationDocument8 pagesExport Credit and Guarantee CorporationIndrajitNo ratings yet
- A. Commercial RisksDocument9 pagesA. Commercial Riskssumitg2781No ratings yet
- ECGCDocument22 pagesECGCchandran0567No ratings yet
- ECGCDocument46 pagesECGCtrinath1100% (1)
- ECGC PolicyDocument48 pagesECGC Policynikhiljain19743100% (1)
- Export Credit Guarantee Corporation: Submitted To Aparna Jain Mam Class: SYBMSDocument30 pagesExport Credit Guarantee Corporation: Submitted To Aparna Jain Mam Class: SYBMSSnehal ThoratNo ratings yet
- ECGCDocument22 pagesECGCabhi7oct1987No ratings yet
- ECGCDocument16 pagesECGCpoojaishiiiNo ratings yet
- Ecgc Schemes of Export: 1.maturity FactoringDocument5 pagesEcgc Schemes of Export: 1.maturity FactoringRizwan Kondkari0% (1)
- Shipments (Comprehensive Risks) - SCR or Standard PolicyDocument48 pagesShipments (Comprehensive Risks) - SCR or Standard PolicyrabhjainNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 MecibDocument3 pagesChap 12 MecibHe's Rasta She's Purple50% (2)
- ECGCDocument24 pagesECGCDrRuchi GargNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk ManagementDocument15 pagesCredit Risk ManagementRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sanghvi Institute of Management & ScienceDocument19 pagesSanghvi Institute of Management & ScienceFatema MhowwalaNo ratings yet
- Ecgc ProjectDocument4 pagesEcgc ProjectrabharaNo ratings yet
- Export Credit InsuranceDocument43 pagesExport Credit InsuranceAbhishek Soni0% (1)
- Malaysia EXIM Bank Insurance Products For Investment: Commercial Risk - Up To 90% Political & Country Risk - Up To 95%Document9 pagesMalaysia EXIM Bank Insurance Products For Investment: Commercial Risk - Up To 90% Political & Country Risk - Up To 95%Ibnu HerbowoNo ratings yet
- Export Finance and Risk Insurance1Document40 pagesExport Finance and Risk Insurance1api-291598576No ratings yet
- ECGCDocument6 pagesECGCpuja2009No ratings yet
- Export Credit InsuranceDocument9 pagesExport Credit InsuranceSrinivasa KirankumarNo ratings yet
- International Trade Logistics Project: Made By: Group 9Document7 pagesInternational Trade Logistics Project: Made By: Group 9Prathamesh Rajaykumar DahakeNo ratings yet
- What Is ECGCDocument48 pagesWhat Is ECGCShreyans GolchhaNo ratings yet
- Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India LTDDocument22 pagesExport Credit Guarantee Corporation of India LTDrohini_jNo ratings yet
- Export Credit InsuranceDocument50 pagesExport Credit InsuranceGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trade Finance Guru Mantra Part-1Document37 pagesTrade Finance Guru Mantra Part-1sudhir.kochhar3530No ratings yet
- Inbt Finals ReviewerDocument11 pagesInbt Finals ReviewerQuenie SagunNo ratings yet
- Export Promotion: By: Rajeev Kumar Ap NitkDocument24 pagesExport Promotion: By: Rajeev Kumar Ap NitkPriyanka AnejaNo ratings yet
- AbitDocument13 pagesAbitmesfinabera180No ratings yet
- Export FinanceDocument59 pagesExport FinancerazambaNo ratings yet
- Business RiskDocument15 pagesBusiness RiskRuchita SinghNo ratings yet
- ECGCDocument4 pagesECGCTarun GargNo ratings yet
- TFG 2008 CH 5Document2 pagesTFG 2008 CH 5Harpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- From (Akanksha Tambulkar (Akanksha - Tambulkar@gmail - Com) ) - ID (47) - ITLDocument15 pagesFrom (Akanksha Tambulkar (Akanksha - Tambulkar@gmail - Com) ) - ID (47) - ITLMukesh TomarNo ratings yet
- Introduction of EcgcDocument41 pagesIntroduction of Ecgcurmi_patel22100% (3)
- CHPT 2tybcomDocument12 pagesCHPT 2tybcomAnamika SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Export Credit Guarantee Corporation LTDDocument6 pagesExport Credit Guarantee Corporation LTDASHUTOSH GUPTANo ratings yet
- ECGC - Export Specific Buyer PolicyDocument2 pagesECGC - Export Specific Buyer PolicySoundararajan SeeranganNo ratings yet
- II. Trade Finance Methods and Instruments: An Overview: A. IntroductionDocument11 pagesII. Trade Finance Methods and Instruments: An Overview: A. IntroductionSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Ecgc Presentation FinalDocument22 pagesEcgc Presentation FinalMeet BuchNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document18 pagesDay 1amar dihingiaNo ratings yet
- Export Financing in IndiaDocument8 pagesExport Financing in IndiaRohit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Export Credit RaunaqDocument18 pagesExport Credit Raunaqhermandeep5No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: MeaningDocument84 pagesChapter - 1: MeaningManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Export Credit Insurance InformationDocument27 pagesExport Credit Insurance InformationChowdhary Parikshit100% (1)
- Export Finance and Payment Presented by Sri Jintu Borthakur Sri Dipranjal KeotDocument45 pagesExport Finance and Payment Presented by Sri Jintu Borthakur Sri Dipranjal Keotjunet123123No ratings yet
- Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance of State Bank of India (Sbi)Document5 pagesPre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Finance of State Bank of India (Sbi)Rohit OberoiNo ratings yet
- TFG 2008 CH 8Document2 pagesTFG 2008 CH 8anon_344986524No ratings yet
- FPQP Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2024 Edition)From EverandFPQP Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2024 Edition)No ratings yet
- Leonardo Da Vinci - Lost NotebooksDocument130 pagesLeonardo Da Vinci - Lost NotebooksTuyenOnline100% (14)
- Registration FormDocument1 pageRegistration FormasifanisNo ratings yet
- Textile HistoryDocument23 pagesTextile Historyajabrao75% (4)
- Final Export ImportDocument9 pagesFinal Export Importronak sNo ratings yet
- Indian Export Import GuideDocument101 pagesIndian Export Import GuideMEGHANALOKSHA100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document13 pagesChapter 2asifanisNo ratings yet
- DBT STCDocument2 pagesDBT STCasifanisNo ratings yet
- Exim Policy of India 2004Document8 pagesExim Policy of India 2004Jas777100% (3)
- Chapter 7Document27 pagesChapter 7asifanisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1asifanisNo ratings yet
- Prices and Monetary ManagementDocument26 pagesPrices and Monetary ManagementasifanisNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document1 pageChap 12asifanisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document24 pagesChapter 5asifanisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3asifanisNo ratings yet
- Chap 110Document2 pagesChap 110asifanisNo ratings yet
- Mohd Asif Anis: Uttar Prades HDocument2 pagesMohd Asif Anis: Uttar Prades HasifanisNo ratings yet
- AOL Time Warner Final Paper-Marena BronsonDocument26 pagesAOL Time Warner Final Paper-Marena BronsonasifanisNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry Lab - Ii: Course Code: BTF 221 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsDocument1 pageApplied Chemistry Lab - Ii: Course Code: BTF 221 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsasifanisNo ratings yet
- Amended Foreign Trade Policy of India (2004-2009) : ObjectiveDocument1 pageAmended Foreign Trade Policy of India (2004-2009) : ObjectiveasifanisNo ratings yet
- Blade Inc Case Assessment Government On Exchange RateDocument2 pagesBlade Inc Case Assessment Government On Exchange RateNguyễn Linh TrangNo ratings yet
- Auto Loan Application Form - IndividualDocument2 pagesAuto Loan Application Form - IndividualKlarise EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Commercial Banks and MicrofinanceDocument25 pagesCommercial Banks and MicrofinanceNikhil Suresh PareekNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Financial ManagementDocument16 pagesApproaches To Financial Managementarko banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Amar Nath PuttaparthiDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Amar Nath PuttaparthikartheekroyalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2Ritika ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Invoice 197Document2 pagesInvoice 197miroljubNo ratings yet
- Nasdaq Trading Strategy Wealth CreationDocument22 pagesNasdaq Trading Strategy Wealth CreationThembokuhleNo ratings yet
- 2017TAtA Steel Annual ReportDocument8 pages2017TAtA Steel Annual ReportHeadshot's GameNo ratings yet
- Lic Pension PlusDocument10 pagesLic Pension PlustsrajanNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Customer Perception Towards LIC of India in View of Increased Competition by Private Companies A Research Done in 2009Document55 pagesA Comparative Study On Customer Perception Towards LIC of India in View of Increased Competition by Private Companies A Research Done in 2009pratiush0792% (13)
- KA Articles Final List 12022024 ACC-1-2-2-2Document6 pagesKA Articles Final List 12022024 ACC-1-2-2-2Ashok GNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument34 pagesResearch MethodologyAshwani VermaNo ratings yet
- XII Economics Guess Paper - 1Document5 pagesXII Economics Guess Paper - 1kawaljeetsingh121666No ratings yet
- Tle6 q2 Mod1 Familyresourcesneedsandsourcesoffamilyincomeversion 5Document28 pagesTle6 q2 Mod1 Familyresourcesneedsandsourcesoffamilyincomeversion 5Cindy KibosNo ratings yet
- Application Form - Car Park Rental 2023 PDFDocument2 pagesApplication Form - Car Park Rental 2023 PDFRozaimi AdliNo ratings yet
- Home Developmen T Mutual Fund Agency: (HDMF)Document6 pagesHome Developmen T Mutual Fund Agency: (HDMF)Trixie LadesmaNo ratings yet
- Litepaper YpredictDocument1 pageLitepaper YpredictSharon NwozaNo ratings yet
- Girish KurudiDocument4 pagesGirish KurudiDenny CraneNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Mathematics Class 8th Icse CbseDocument5 pagesSample Paper Mathematics Class 8th Icse CbseSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Accounting Final ExamDocument10 pagesAccounting Final ExamMauro ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Examination: Subject CT5 - Contingencies Core TechnicalDocument7 pagesExamination: Subject CT5 - Contingencies Core TechnicalMadonnaNo ratings yet
- BBMF 3083 Exam Paper September 2019Document6 pagesBBMF 3083 Exam Paper September 2019KAR ENG QUAHNo ratings yet
- MYOB Qualification Test: Level BasicDocument7 pagesMYOB Qualification Test: Level BasiculfahNo ratings yet
- Outcome of Board Meeting - Buy-Back of Equity Shares of The Company (Board Meeting)Document2 pagesOutcome of Board Meeting - Buy-Back of Equity Shares of The Company (Board Meeting)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Project Report of Kolhapuri Thushi AlankarDocument9 pagesProject Report of Kolhapuri Thushi AlankarSanyam BugateNo ratings yet
- Wire Transfer Details For Remitting Funds To Your Investment Account With ICICI Bank CanadaDocument2 pagesWire Transfer Details For Remitting Funds To Your Investment Account With ICICI Bank CanadasumalrajNo ratings yet