Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsCytoplasm - Mitochondria IRFAN
Cytoplasm - Mitochondria IRFAN
Uploaded by
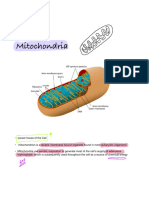
Irfan HidayatThe cytoplasm is the portion of a cell that is enclosed within the cell membrane and contains organelles like mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles found in the cytoplasm that generate ATP and range in size from 0.5 to 10 micrometers. They contain an outer and inner membrane that create five distinct compartments: the outer mitochondrial membrane, intermembrane space, inner mitochondrial membrane, crista space, and matrix. The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins that perform important functions like redox reactions and ATP synthesis.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Histology: Lecture NotesDocument97 pagesHistology: Lecture Notessky100% (4)
- Mitochondrial Structure and Function.Document8 pagesMitochondrial Structure and Function.AnnuNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument10 pagesMitochondriaHanumat SinghNo ratings yet
- THE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaDocument16 pagesTHE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaJoshua DorisNo ratings yet
- Notability NotesDocument5 pagesNotability Notesznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Bot-201Document13 pagesGroup 4 Bot-201Aye ShaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesMitochondrion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaTarun Chowdary100% (1)
- Mitokondria - Kelompok 2Document21 pagesMitokondria - Kelompok 2Miftahul jannahNo ratings yet
- Bio Final AssignmentDocument47 pagesBio Final AssignmentmikhailNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The CellDocument43 pagesStructure and Function of The CellElvie Gutierrez100% (1)
- Cell Physiology-1Document32 pagesCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 BiologyDocument4 pagesCH 6 BiologysophieowensNo ratings yet
- Forest Botany For Forestry StudentsDocument39 pagesForest Botany For Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Cell Lect 2Document16 pagesCell Lect 2sadaffardoosNo ratings yet
- Hum, An CellDocument6 pagesHum, An CellQlife KlinikNo ratings yet
- Biology - MitochondriaDocument9 pagesBiology - MitochondriaAJ IzaguirreNo ratings yet
- The Basic of LifeDocument21 pagesThe Basic of LifeJALAL JAMINo ratings yet
- Cell_physiology by MaifataDocument32 pagesCell_physiology by Maifatastephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Mitochondria: μίτο or mitos thread + χονδρίον or chondrion granuleDocument15 pagesMitochondria: μίτο or mitos thread + χονδρίον or chondrion granuleNitun PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document42 pagesCell Organelles 2James IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-The CellDocument43 pagesLecture 2-The CellMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Biohem NotesDocument118 pagesBiohem Notesdalweravikumar69No ratings yet
- NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURES and ORGANELLESDocument39 pagesNUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURES and ORGANELLESolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- MitochondriaDocument25 pagesMitochondriaaadarshtripathi4218No ratings yet
- The Plant Cell Pharma With Bot&tax Week 4-6Document10 pagesThe Plant Cell Pharma With Bot&tax Week 4-6Katrina CarolasanNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document25 pagesCell 3Rashul ChutaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Proteasome and MitochondriaDocument2 pagesProteasome and MitochondriaVeronica GamosoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMDocument40 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMnomysalihNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesLecture 3 - Cell Structure & Functionlazysadoon09No ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Cellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4Document24 pagesCellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4madhav biyaniNo ratings yet
- Acad Fall08 ThecellDocument13 pagesAcad Fall08 Thecellhassanmusahassan81No ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument3 pagesMitochondriaGood AstraNo ratings yet
- The OrganellesDocument4 pagesThe Organellesabdullah aliNo ratings yet
- Cytology and Basic HistologyDocument71 pagesCytology and Basic HistologyAnonymous JpipMjNo ratings yet
- Intro, Cell, TissueDocument29 pagesIntro, Cell, Tissueanisa930804No ratings yet
- Biology REVIEW FOR CMDocument12 pagesBiology REVIEW FOR CMyangyang804574No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesS PaulNo ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?Document6 pagesUnit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?juan mondaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsDocument5 pagesChapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsFrancis PhimphivongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Structures in A Cell JJDocument25 pagesLesson 6 Structures in A Cell JJGemma WrigleyNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: PratibhapariharDocument38 pagesMitochondria: PratibhapariharPatel BansariNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Cell StructureDocument62 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Cell StructureElyse LeeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Lab Research 7. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument17 pagesLab Research 7. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPamPam10No ratings yet
- 1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONDocument6 pages1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONOlamide KoleNo ratings yet
- Final Bio VivaDocument49 pagesFinal Bio Vivamanuel ortegaNo ratings yet
- The Body and Its ConstituentsDocument19 pagesThe Body and Its Constituentssantosh s u100% (1)
- Organelles in CellsDocument3 pagesOrganelles in CellsSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Document4 pagesWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Phospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreDocument7 pagesPhospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreCmae VidadNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Week 3: Cells and Tissues-Part 1 Cells - Structure and FunctionDocument27 pagesWeek 3 Week 3: Cells and Tissues-Part 1 Cells - Structure and FunctionJEANNo ratings yet
Cytoplasm - Mitochondria IRFAN
Cytoplasm - Mitochondria IRFAN
Uploaded by
Irfan Hidayat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThe cytoplasm is the portion of a cell that is enclosed within the cell membrane and contains organelles like mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles found in the cytoplasm that generate ATP and range in size from 0.5 to 10 micrometers. They contain an outer and inner membrane that create five distinct compartments: the outer mitochondrial membrane, intermembrane space, inner mitochondrial membrane, crista space, and matrix. The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins that perform important functions like redox reactions and ATP synthesis.
Original Description:
Original Title
Cytoplasm_Mitochondria IRFAN>>>>>>>
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cytoplasm is the portion of a cell that is enclosed within the cell membrane and contains organelles like mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles found in the cytoplasm that generate ATP and range in size from 0.5 to 10 micrometers. They contain an outer and inner membrane that create five distinct compartments: the outer mitochondrial membrane, intermembrane space, inner mitochondrial membrane, crista space, and matrix. The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins that perform important functions like redox reactions and ATP synthesis.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageCytoplasm - Mitochondria IRFAN
Cytoplasm - Mitochondria IRFAN
Uploaded by
Irfan HidayatThe cytoplasm is the portion of a cell that is enclosed within the cell membrane and contains organelles like mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles found in the cytoplasm that generate ATP and range in size from 0.5 to 10 micrometers. They contain an outer and inner membrane that create five distinct compartments: the outer mitochondrial membrane, intermembrane space, inner mitochondrial membrane, crista space, and matrix. The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins that perform important functions like redox reactions and ATP synthesis.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
~Cytoplasm~
enclosed within the cell membrane.
Contains cells of prokaryote organisms (which lack a cell nucleus)
contains organelles, such as mitochondria, which are filled with liquid that is kept separate from
the rest of the cytoplasm by biological membranes
most cellular activities occur
has three major elements; the cytosol, organelles and inclusions.
cytosol is the portion of a cell that is not enclosed within membrane-bound organelles
Organelles are membrane-bound compartments within the cell that have specific functions
The inclusions are small particles of insoluble substances suspended in the cytosol.
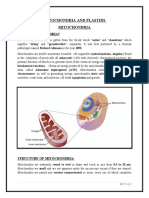
~mitochondria~
range from 0.5 to 10 micrometers (μm) in diameter
sometimes described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the cell's
supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy
he number of mitochondria in a cell varies widely by organism and tissue type
Many cells have only a single mitochondrion, whereas others can contain several thousand
mitochondria
contains outer and inner membranes composed of phospholipid bilayers and proteins. The
two membranes, however, have different properties. Because of this double-membraned
organization, there are five distinct compartments within the mitochondrion. There is the
outer mitochondrial membrane, the intermembrane space (the space between the outer
and inner membranes), the inner mitochondrial membrane, the crista space (formed by
infoldings of the inner membrane), and the matrix (space within the inner membrane).
encloses the entire organelle, has a protein-to-phospholipid ratio similar to that of the
eukaryotic plasma membrane
inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins with five types of functions:
1. Those that perform the redox reactions of oxidative phosphorylation
2. ATP synthase, which generates ATP in the matrix
3. Specific transport proteins that regulate metabolite passage into and out of the matrix
4. Protein import machinery.
5. Mitochondria fusion and fission protein
You might also like
- Histology: Lecture NotesDocument97 pagesHistology: Lecture Notessky100% (4)
- Mitochondrial Structure and Function.Document8 pagesMitochondrial Structure and Function.AnnuNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument10 pagesMitochondriaHanumat SinghNo ratings yet
- THE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaDocument16 pagesTHE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaJoshua DorisNo ratings yet
- Notability NotesDocument5 pagesNotability Notesznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Bot-201Document13 pagesGroup 4 Bot-201Aye ShaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesMitochondrion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaTarun Chowdary100% (1)
- Mitokondria - Kelompok 2Document21 pagesMitokondria - Kelompok 2Miftahul jannahNo ratings yet
- Bio Final AssignmentDocument47 pagesBio Final AssignmentmikhailNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The CellDocument43 pagesStructure and Function of The CellElvie Gutierrez100% (1)
- Cell Physiology-1Document32 pagesCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 BiologyDocument4 pagesCH 6 BiologysophieowensNo ratings yet
- Forest Botany For Forestry StudentsDocument39 pagesForest Botany For Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Cell Lect 2Document16 pagesCell Lect 2sadaffardoosNo ratings yet
- Hum, An CellDocument6 pagesHum, An CellQlife KlinikNo ratings yet
- Biology - MitochondriaDocument9 pagesBiology - MitochondriaAJ IzaguirreNo ratings yet
- The Basic of LifeDocument21 pagesThe Basic of LifeJALAL JAMINo ratings yet
- Cell_physiology by MaifataDocument32 pagesCell_physiology by Maifatastephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Mitochondria: μίτο or mitos thread + χονδρίον or chondrion granuleDocument15 pagesMitochondria: μίτο or mitos thread + χονδρίον or chondrion granuleNitun PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document42 pagesCell Organelles 2James IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-The CellDocument43 pagesLecture 2-The CellMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Biohem NotesDocument118 pagesBiohem Notesdalweravikumar69No ratings yet
- NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURES and ORGANELLESDocument39 pagesNUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURES and ORGANELLESolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- MitochondriaDocument25 pagesMitochondriaaadarshtripathi4218No ratings yet
- The Plant Cell Pharma With Bot&tax Week 4-6Document10 pagesThe Plant Cell Pharma With Bot&tax Week 4-6Katrina CarolasanNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document25 pagesCell 3Rashul ChutaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Proteasome and MitochondriaDocument2 pagesProteasome and MitochondriaVeronica GamosoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMDocument40 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMnomysalihNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesLecture 3 - Cell Structure & Functionlazysadoon09No ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Cellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4Document24 pagesCellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4madhav biyaniNo ratings yet
- Acad Fall08 ThecellDocument13 pagesAcad Fall08 Thecellhassanmusahassan81No ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument3 pagesMitochondriaGood AstraNo ratings yet
- The OrganellesDocument4 pagesThe Organellesabdullah aliNo ratings yet
- Cytology and Basic HistologyDocument71 pagesCytology and Basic HistologyAnonymous JpipMjNo ratings yet
- Intro, Cell, TissueDocument29 pagesIntro, Cell, Tissueanisa930804No ratings yet
- Biology REVIEW FOR CMDocument12 pagesBiology REVIEW FOR CMyangyang804574No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesS PaulNo ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?Document6 pagesUnit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?juan mondaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsDocument5 pagesChapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsFrancis PhimphivongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Structures in A Cell JJDocument25 pagesLesson 6 Structures in A Cell JJGemma WrigleyNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: PratibhapariharDocument38 pagesMitochondria: PratibhapariharPatel BansariNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Cell StructureDocument62 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Cell StructureElyse LeeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Lab Research 7. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument17 pagesLab Research 7. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPamPam10No ratings yet
- 1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONDocument6 pages1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONOlamide KoleNo ratings yet
- Final Bio VivaDocument49 pagesFinal Bio Vivamanuel ortegaNo ratings yet
- The Body and Its ConstituentsDocument19 pagesThe Body and Its Constituentssantosh s u100% (1)
- Organelles in CellsDocument3 pagesOrganelles in CellsSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Document4 pagesWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Phospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreDocument7 pagesPhospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreCmae VidadNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Week 3: Cells and Tissues-Part 1 Cells - Structure and FunctionDocument27 pagesWeek 3 Week 3: Cells and Tissues-Part 1 Cells - Structure and FunctionJEANNo ratings yet