Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Controlling and Building Commitment
Controlling and Building Commitment
Uploaded by
Shrey JoshiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Area Manager ChecklistDocument2 pagesArea Manager ChecklistTharun Rao33% (3)
- OTBI DocumentDocument264 pagesOTBI Documentsatyanarayana NVSNo ratings yet
- UE SAP AuditingDocument60 pagesUE SAP AuditingJeffrey CardonaNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Audit ReportDocument39 pagesReal Estate Audit ReportAbdalla NabagNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project ReportDocument50 pagesSummer Internship Project ReportDeepanshu MathurNo ratings yet
- Penyata Akaun: Tarikh Date Keterangan Description Terminal ID ID Terminal Amaun (RM) Amount (RM) Baki (RM) Balance (RM)Document8 pagesPenyata Akaun: Tarikh Date Keterangan Description Terminal ID ID Terminal Amaun (RM) Amount (RM) Baki (RM) Balance (RM)mrbucks100% (1)
- 2 Audit Sistem Informasi - Pertemuan 2Document72 pages2 Audit Sistem Informasi - Pertemuan 2Fikriansyah AdzakiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: An OverviewDocument18 pagesManagerial Accounting: An OverviewFarhan RabbehNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: An OverviewDocument18 pagesManagerial Accounting: An OverviewCartiNo ratings yet
- Horngrenima14e - ch01 Accounting INfo & EthicDocument26 pagesHorngrenima14e - ch01 Accounting INfo & EthicMagnolia KhineNo ratings yet
- الشباتر العاشر مترجم مبادئ إدارةDocument15 pagesالشباتر العاشر مترجم مبادئ إدارةjtgo765No ratings yet
- ISAudit 2010oct18Document239 pagesISAudit 2010oct18Suvojit DeshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 IT Controls Part I: Sarbanes Oxley & IT GovernanceDocument49 pagesChapter 15 IT Controls Part I: Sarbanes Oxley & IT GovernanceDesiree De OcampoNo ratings yet
- 370 13735 EA111 2012 1 1 1 Chapt13Document16 pages370 13735 EA111 2012 1 1 1 Chapt13trnddpattyNo ratings yet
- MGT 420 Uitm Ch08 ControllingDocument27 pagesMGT 420 Uitm Ch08 ControllingAifaa ArinaNo ratings yet
- Internal Financial Controls Sivaram SubramoniamDocument22 pagesInternal Financial Controls Sivaram SubramoniamKRISHNA RAO KNo ratings yet
- Day 13 Feb 15 Chapters 8 and 9 StudentDocument24 pagesDay 13 Feb 15 Chapters 8 and 9 StudentmohebqasNo ratings yet
- Ch08 ControllingDocument27 pagesCh08 ControllingoshafikahNo ratings yet
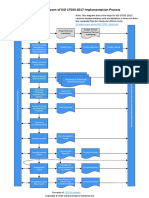
- Diagram of ISO 17025:2017 Implementation ProcessDocument1 pageDiagram of ISO 17025:2017 Implementation ProcessraquelNo ratings yet
- 02 Lean - Advanced Lean - Pull Systems v1Document176 pages02 Lean - Advanced Lean - Pull Systems v1lrff1950No ratings yet
- CIMA Operational Case Study NotesDocument16 pagesCIMA Operational Case Study NotesDuncan MenziesNo ratings yet
- Presentation Part 1Document78 pagesPresentation Part 1charbelNo ratings yet
- IcfrDocument12 pagesIcfrAnupam BaliNo ratings yet
- 7 Step To Lean MFGDocument22 pages7 Step To Lean MFGYusranNo ratings yet
- PP 15 NewDocument49 pagesPP 15 NewStevan PknNo ratings yet
- Poka Yoke PDFDocument62 pagesPoka Yoke PDFmartinNo ratings yet
- The Basis For Business DecisionsDocument13 pagesThe Basis For Business DecisionsmzqaceNo ratings yet
- Oracle Financials Cloud: Expense Report To ReimbursementDocument49 pagesOracle Financials Cloud: Expense Report To Reimbursementsujit nayakNo ratings yet
- Quality Training - Audit PreparationDocument40 pagesQuality Training - Audit PreparationHans PunterNo ratings yet
- Module Training Internal Audit HISDocument38 pagesModule Training Internal Audit HISarieznavalNo ratings yet
- Aawareness On QMSDocument26 pagesAawareness On QMSAnees ArainNo ratings yet
- Iso9001 Revision InfographicDocument1 pageIso9001 Revision InfographicAbdulsalam AlYousefNo ratings yet
- MACC 317 Lesson 8Document20 pagesMACC 317 Lesson 8graceNo ratings yet
- SPPTChap 001Document11 pagesSPPTChap 001saharinshakib7505No ratings yet
- PWC - Understanding Internal AuditDocument20 pagesPWC - Understanding Internal AuditISabella ARndorferNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Implement Budgets: BSBFIM601 Manage Finances Session 3Document9 pagesPrepare and Implement Budgets: BSBFIM601 Manage Finances Session 3Tatiana Garcia MendozaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Accounting EnvironmentDocument33 pagesTopic 1 - Accounting EnvironmentdenixngNo ratings yet
- 2021 - KPI For PPB Workshop PDFDocument25 pages2021 - KPI For PPB Workshop PDFParc RizalNo ratings yet
- 02 PrinciplesDocument16 pages02 PrinciplesSarahNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: An OverviewDocument26 pagesManagerial Accounting: An OverviewNgọc MaiNo ratings yet
- KPMG MethodDocument88 pagesKPMG MethodAlexius Julio BrianNo ratings yet
- Lecture ONE Accounting For ManagerDocument30 pagesLecture ONE Accounting For Managermohamed elsabahiNo ratings yet
- Investing and Financing Decisions and The Balance SheetDocument57 pagesInvesting and Financing Decisions and The Balance Sheetd-fbuser-57033070No ratings yet
- Aligning CMMI & ITIL: Where Am I and Which Way Do I Go?Document27 pagesAligning CMMI & ITIL: Where Am I and Which Way Do I Go?Wewe SlmNo ratings yet
- The Controlling Process: Ready NotesDocument26 pagesThe Controlling Process: Ready NotesKazi Shahrin SuchiNo ratings yet
- The Foundation of ControlDocument22 pagesThe Foundation of Controlc00lsidzNo ratings yet
- Oracle Hyperion Financial ManagementDocument45 pagesOracle Hyperion Financial ManagementZaid ShammoutNo ratings yet
- Financial & Managerial Accounting The Basis For Business DecisionsDocument20 pagesFinancial & Managerial Accounting The Basis For Business DecisionssaybilNo ratings yet
- 02 PrinciplesDocument16 pages02 PrincipleszillsmkNo ratings yet
- 2024 PrecISOft EnglishDocument15 pages2024 PrecISOft EnglishJose Carlos Espinoza AlatorreNo ratings yet
- A Strategy For Performance ExcellenceDocument73 pagesA Strategy For Performance ExcellenceHéctor Eduardo CazotNo ratings yet
- ISO-IEC 20000 OverviewDocument13 pagesISO-IEC 20000 OverviewPFEENo ratings yet
- Narrative: You Will Need A Copy of The Book As Future Reference Material For This PresentationDocument33 pagesNarrative: You Will Need A Copy of The Book As Future Reference Material For This PresentationRoifah AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Control: Correction & PreventionDocument13 pagesControl: Correction & PreventionRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Dr. A. Rashid KausarDocument32 pagesPrinciples of Management: Dr. A. Rashid KausarzrdNo ratings yet
- Group 4 3simbDocument19 pagesGroup 4 3simbquen anatasyaNo ratings yet
- Outs Exercises & Workshops Bureau Veritas: Internal AuditDocument3 pagesOuts Exercises & Workshops Bureau Veritas: Internal AuditriaNo ratings yet
- ACC231-PPT-CH1-Week 3Document21 pagesACC231-PPT-CH1-Week 3Crista IyNo ratings yet
- Full Recording Available At:: S4Rjbnco&Feature Youtu - BeDocument60 pagesFull Recording Available At:: S4Rjbnco&Feature Youtu - BeCosta VaggasNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Management Audit (Nov. 6-9, 2023)Document4 pagesCourse Outline - Management Audit (Nov. 6-9, 2023)Camella CandonNo ratings yet
- Week 1 IntroDocument33 pagesWeek 1 IntroRhinndhi SakthyvelNo ratings yet
- A Strategy For Performance ExcellenceDocument19 pagesA Strategy For Performance ExcellenceAshu SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Effective Operations and Controls for the Small Privately Held BusinessFrom EverandEffective Operations and Controls for the Small Privately Held BusinessNo ratings yet
- Auditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlFrom EverandAuditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlNo ratings yet
- Commercial Dispatch Eedition 4-11-19Document12 pagesCommercial Dispatch Eedition 4-11-19The DispatchNo ratings yet
- W - (9) Irs FormDocument4 pagesW - (9) Irs Formjlr7776863100% (19)
- Characteristics of A Good VisionDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of A Good VisionwubeNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae - Andrian PratamaDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae - Andrian PratamaAndrian Pratama SumendapNo ratings yet
- Knitting: Products and Services For The Warp Knitting IndustryDocument16 pagesKnitting: Products and Services For The Warp Knitting IndustryAzm FaisalNo ratings yet
- Circlip External1Document3 pagesCirclip External1ThejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Paper - Overview of Copyright Protection in UgandaDocument10 pagesPaper - Overview of Copyright Protection in Ugandasemwezi100% (2)
- Inventory Custodian Slip 1Document2 pagesInventory Custodian Slip 1Leny Cosep Abis100% (2)
- Study Guide 7 Entrepreneurship 1Document43 pagesStudy Guide 7 Entrepreneurship 1Cathlyne Mejia NatnatNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 School Calendar - Updated 6-15-22Document1 page2022-2023 School Calendar - Updated 6-15-22api-201390630No ratings yet
- HBSP Global SC Decision Record TemplateDocument4 pagesHBSP Global SC Decision Record TemplateIman Christin Wirawan0% (1)
- Raja Guru. P: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesRaja Guru. P: ObjectiveAnonymous 7CVuZbInUNo ratings yet
- UTA's Fair Park StudyDocument49 pagesUTA's Fair Park StudyRobert WilonskyNo ratings yet
- Method of Bank ValuationDocument12 pagesMethod of Bank Valuationhariyanto9999No ratings yet
- SAP SD - Sales Document ControlsDocument4 pagesSAP SD - Sales Document ControlsHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Mathieu FortierDocument14 pagesMathieu Fortierfk8xxpsrgzNo ratings yet
- Blastrac Catalogue 2018 ENG LR2Document122 pagesBlastrac Catalogue 2018 ENG LR2elfigossNo ratings yet
- c1 Salary BenchmarksDocument44 pagesc1 Salary BenchmarkssnhdnebdhNo ratings yet
- The Basic Issues Involved in Design and Operating DecisionsDocument19 pagesThe Basic Issues Involved in Design and Operating DecisionsqamarulislamNo ratings yet
- John Donaldson - DocsDocument46 pagesJohn Donaldson - Docsaiai100% (2)
- Unicorn Start-UpsDocument3 pagesUnicorn Start-UpsRohanNo ratings yet
- Process Mapping PDFDocument21 pagesProcess Mapping PDFShalini SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Types of EntrepreneursDocument3 pagesTypes of EntrepreneursMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAK50% (2)
- Unit: 2: Prepared By: Togadiya JigneshDocument24 pagesUnit: 2: Prepared By: Togadiya JigneshJignesh TogadiyaNo ratings yet
- Banking and Microfinance - IIDocument24 pagesBanking and Microfinance - IIKoyelNo ratings yet
- Foreclosure BrochureDocument6 pagesForeclosure BrochureAnnMarie BelairNo ratings yet
Controlling and Building Commitment
Controlling and Building Commitment
Uploaded by
Shrey JoshiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Controlling and Building Commitment
Controlling and Building Commitment
Uploaded by
Shrey JoshiCopyright:
Available Formats
Controlling and Building
Commitment
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 1
Chapter Objectives
• Analyze the traditional control process
• Compare traditional and commitment-based control
• Discuss diagnostic, boundary, and interactive
control methods
• List unintended behavioral effects of controls
• Understand how belief systems and employee
commitment can expedite control
• Discuss the factors that contribute to employee
commitment
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 2
Setting
The Role of a Target
Control
Measuring
Performance
Why is Control Making
Required? Corrections
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 3
Timing of Controls
Steering Yes-No Post-Action
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 4
Diagnostic
Diagnostic Systems
Systems
Traditional
Traditional Boundary
Boundary Systems
Systems
Interactive
Interactive Systems
Systems
Two Basic
Control
Options
Belief
Belief Systems
Systems
Commitment-
Commitment-
Based
Based
Commitment-Fostering
Commitment-Fostering
Systems
Systems
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 5
Establish Standards
Measure Performance
The Traditional
Control Process
Compare to Standards
Take Corrective Action
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 6
Diagnostic Controls
Management Control System
Sales
Sales Operating
Operating
Budget
Budget Budget
Budget
Income
Income Balance
Balance Cash
Cash
Statement
Statement Sheet
Sheet Budget
Budget
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 7
Example of a Performance Report for
Machinery Department, June 2000
Budget Actual Variance Explanation
Direct labor
$2,107 $2,480 $373 over Overtime work
Supplies
$3,826 $4,200 $374 over Wasted Material
Repairs
$ 402 $ 150 $252 under
Overhead
$ 500 $ 500 $ 0
Total
$6,835 $7,330 $495 over
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 8
Diagnostic Controls
Financial
Financial Ratios Responsibility
Centers
Enterprise Corporate
Resource Planning Scorecards
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 9
Boundary
Controls
Ethical Codes of
Behavior Conduct
Strategies
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 10
Interactive
Controls
Face-to-Face Strategic
Interaction Control
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 11
Behavioral
Gamesmanship
Displacement
The Negative Side of Controls
Operating Attitude
Delays Problems
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 12
Using Belief Systems and
Values to Foster Self-Control
Common Shared Common
Culture Values Goals
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 13
Using Commitment-Building
Systems to Foster Self-Control
• Foster people-first values
• Promote two-way communication
• Build a sense of community
• Communicate a vision
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 14
Using Commitment-Building
Systems to Foster Self-Control
• Practice value-based hiring
• Use financial rewards and profit sharing
• Encourage self-actualizing
©Prentice Hall, 2000 Chapter 15 15
You might also like
- Area Manager ChecklistDocument2 pagesArea Manager ChecklistTharun Rao33% (3)
- OTBI DocumentDocument264 pagesOTBI Documentsatyanarayana NVSNo ratings yet
- UE SAP AuditingDocument60 pagesUE SAP AuditingJeffrey CardonaNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Audit ReportDocument39 pagesReal Estate Audit ReportAbdalla NabagNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project ReportDocument50 pagesSummer Internship Project ReportDeepanshu MathurNo ratings yet
- Penyata Akaun: Tarikh Date Keterangan Description Terminal ID ID Terminal Amaun (RM) Amount (RM) Baki (RM) Balance (RM)Document8 pagesPenyata Akaun: Tarikh Date Keterangan Description Terminal ID ID Terminal Amaun (RM) Amount (RM) Baki (RM) Balance (RM)mrbucks100% (1)
- 2 Audit Sistem Informasi - Pertemuan 2Document72 pages2 Audit Sistem Informasi - Pertemuan 2Fikriansyah AdzakiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: An OverviewDocument18 pagesManagerial Accounting: An OverviewFarhan RabbehNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: An OverviewDocument18 pagesManagerial Accounting: An OverviewCartiNo ratings yet
- Horngrenima14e - ch01 Accounting INfo & EthicDocument26 pagesHorngrenima14e - ch01 Accounting INfo & EthicMagnolia KhineNo ratings yet
- الشباتر العاشر مترجم مبادئ إدارةDocument15 pagesالشباتر العاشر مترجم مبادئ إدارةjtgo765No ratings yet
- ISAudit 2010oct18Document239 pagesISAudit 2010oct18Suvojit DeshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 IT Controls Part I: Sarbanes Oxley & IT GovernanceDocument49 pagesChapter 15 IT Controls Part I: Sarbanes Oxley & IT GovernanceDesiree De OcampoNo ratings yet
- 370 13735 EA111 2012 1 1 1 Chapt13Document16 pages370 13735 EA111 2012 1 1 1 Chapt13trnddpattyNo ratings yet
- MGT 420 Uitm Ch08 ControllingDocument27 pagesMGT 420 Uitm Ch08 ControllingAifaa ArinaNo ratings yet
- Internal Financial Controls Sivaram SubramoniamDocument22 pagesInternal Financial Controls Sivaram SubramoniamKRISHNA RAO KNo ratings yet
- Day 13 Feb 15 Chapters 8 and 9 StudentDocument24 pagesDay 13 Feb 15 Chapters 8 and 9 StudentmohebqasNo ratings yet
- Ch08 ControllingDocument27 pagesCh08 ControllingoshafikahNo ratings yet
- Diagram of ISO 17025:2017 Implementation ProcessDocument1 pageDiagram of ISO 17025:2017 Implementation ProcessraquelNo ratings yet
- 02 Lean - Advanced Lean - Pull Systems v1Document176 pages02 Lean - Advanced Lean - Pull Systems v1lrff1950No ratings yet
- CIMA Operational Case Study NotesDocument16 pagesCIMA Operational Case Study NotesDuncan MenziesNo ratings yet
- Presentation Part 1Document78 pagesPresentation Part 1charbelNo ratings yet
- IcfrDocument12 pagesIcfrAnupam BaliNo ratings yet
- 7 Step To Lean MFGDocument22 pages7 Step To Lean MFGYusranNo ratings yet
- PP 15 NewDocument49 pagesPP 15 NewStevan PknNo ratings yet
- Poka Yoke PDFDocument62 pagesPoka Yoke PDFmartinNo ratings yet
- The Basis For Business DecisionsDocument13 pagesThe Basis For Business DecisionsmzqaceNo ratings yet
- Oracle Financials Cloud: Expense Report To ReimbursementDocument49 pagesOracle Financials Cloud: Expense Report To Reimbursementsujit nayakNo ratings yet
- Quality Training - Audit PreparationDocument40 pagesQuality Training - Audit PreparationHans PunterNo ratings yet
- Module Training Internal Audit HISDocument38 pagesModule Training Internal Audit HISarieznavalNo ratings yet
- Aawareness On QMSDocument26 pagesAawareness On QMSAnees ArainNo ratings yet
- Iso9001 Revision InfographicDocument1 pageIso9001 Revision InfographicAbdulsalam AlYousefNo ratings yet
- MACC 317 Lesson 8Document20 pagesMACC 317 Lesson 8graceNo ratings yet
- SPPTChap 001Document11 pagesSPPTChap 001saharinshakib7505No ratings yet
- PWC - Understanding Internal AuditDocument20 pagesPWC - Understanding Internal AuditISabella ARndorferNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Implement Budgets: BSBFIM601 Manage Finances Session 3Document9 pagesPrepare and Implement Budgets: BSBFIM601 Manage Finances Session 3Tatiana Garcia MendozaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Accounting EnvironmentDocument33 pagesTopic 1 - Accounting EnvironmentdenixngNo ratings yet
- 2021 - KPI For PPB Workshop PDFDocument25 pages2021 - KPI For PPB Workshop PDFParc RizalNo ratings yet
- 02 PrinciplesDocument16 pages02 PrinciplesSarahNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: An OverviewDocument26 pagesManagerial Accounting: An OverviewNgọc MaiNo ratings yet
- KPMG MethodDocument88 pagesKPMG MethodAlexius Julio BrianNo ratings yet
- Lecture ONE Accounting For ManagerDocument30 pagesLecture ONE Accounting For Managermohamed elsabahiNo ratings yet
- Investing and Financing Decisions and The Balance SheetDocument57 pagesInvesting and Financing Decisions and The Balance Sheetd-fbuser-57033070No ratings yet
- Aligning CMMI & ITIL: Where Am I and Which Way Do I Go?Document27 pagesAligning CMMI & ITIL: Where Am I and Which Way Do I Go?Wewe SlmNo ratings yet
- The Controlling Process: Ready NotesDocument26 pagesThe Controlling Process: Ready NotesKazi Shahrin SuchiNo ratings yet
- The Foundation of ControlDocument22 pagesThe Foundation of Controlc00lsidzNo ratings yet
- Oracle Hyperion Financial ManagementDocument45 pagesOracle Hyperion Financial ManagementZaid ShammoutNo ratings yet
- Financial & Managerial Accounting The Basis For Business DecisionsDocument20 pagesFinancial & Managerial Accounting The Basis For Business DecisionssaybilNo ratings yet
- 02 PrinciplesDocument16 pages02 PrincipleszillsmkNo ratings yet
- 2024 PrecISOft EnglishDocument15 pages2024 PrecISOft EnglishJose Carlos Espinoza AlatorreNo ratings yet
- A Strategy For Performance ExcellenceDocument73 pagesA Strategy For Performance ExcellenceHéctor Eduardo CazotNo ratings yet
- ISO-IEC 20000 OverviewDocument13 pagesISO-IEC 20000 OverviewPFEENo ratings yet
- Narrative: You Will Need A Copy of The Book As Future Reference Material For This PresentationDocument33 pagesNarrative: You Will Need A Copy of The Book As Future Reference Material For This PresentationRoifah AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Control: Correction & PreventionDocument13 pagesControl: Correction & PreventionRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Dr. A. Rashid KausarDocument32 pagesPrinciples of Management: Dr. A. Rashid KausarzrdNo ratings yet
- Group 4 3simbDocument19 pagesGroup 4 3simbquen anatasyaNo ratings yet
- Outs Exercises & Workshops Bureau Veritas: Internal AuditDocument3 pagesOuts Exercises & Workshops Bureau Veritas: Internal AuditriaNo ratings yet
- ACC231-PPT-CH1-Week 3Document21 pagesACC231-PPT-CH1-Week 3Crista IyNo ratings yet
- Full Recording Available At:: S4Rjbnco&Feature Youtu - BeDocument60 pagesFull Recording Available At:: S4Rjbnco&Feature Youtu - BeCosta VaggasNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Management Audit (Nov. 6-9, 2023)Document4 pagesCourse Outline - Management Audit (Nov. 6-9, 2023)Camella CandonNo ratings yet
- Week 1 IntroDocument33 pagesWeek 1 IntroRhinndhi SakthyvelNo ratings yet
- A Strategy For Performance ExcellenceDocument19 pagesA Strategy For Performance ExcellenceAshu SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Effective Operations and Controls for the Small Privately Held BusinessFrom EverandEffective Operations and Controls for the Small Privately Held BusinessNo ratings yet
- Auditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlFrom EverandAuditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlNo ratings yet
- Commercial Dispatch Eedition 4-11-19Document12 pagesCommercial Dispatch Eedition 4-11-19The DispatchNo ratings yet
- W - (9) Irs FormDocument4 pagesW - (9) Irs Formjlr7776863100% (19)
- Characteristics of A Good VisionDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of A Good VisionwubeNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae - Andrian PratamaDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae - Andrian PratamaAndrian Pratama SumendapNo ratings yet
- Knitting: Products and Services For The Warp Knitting IndustryDocument16 pagesKnitting: Products and Services For The Warp Knitting IndustryAzm FaisalNo ratings yet
- Circlip External1Document3 pagesCirclip External1ThejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Paper - Overview of Copyright Protection in UgandaDocument10 pagesPaper - Overview of Copyright Protection in Ugandasemwezi100% (2)
- Inventory Custodian Slip 1Document2 pagesInventory Custodian Slip 1Leny Cosep Abis100% (2)
- Study Guide 7 Entrepreneurship 1Document43 pagesStudy Guide 7 Entrepreneurship 1Cathlyne Mejia NatnatNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 School Calendar - Updated 6-15-22Document1 page2022-2023 School Calendar - Updated 6-15-22api-201390630No ratings yet
- HBSP Global SC Decision Record TemplateDocument4 pagesHBSP Global SC Decision Record TemplateIman Christin Wirawan0% (1)
- Raja Guru. P: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesRaja Guru. P: ObjectiveAnonymous 7CVuZbInUNo ratings yet
- UTA's Fair Park StudyDocument49 pagesUTA's Fair Park StudyRobert WilonskyNo ratings yet
- Method of Bank ValuationDocument12 pagesMethod of Bank Valuationhariyanto9999No ratings yet
- SAP SD - Sales Document ControlsDocument4 pagesSAP SD - Sales Document ControlsHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Mathieu FortierDocument14 pagesMathieu Fortierfk8xxpsrgzNo ratings yet
- Blastrac Catalogue 2018 ENG LR2Document122 pagesBlastrac Catalogue 2018 ENG LR2elfigossNo ratings yet
- c1 Salary BenchmarksDocument44 pagesc1 Salary BenchmarkssnhdnebdhNo ratings yet
- The Basic Issues Involved in Design and Operating DecisionsDocument19 pagesThe Basic Issues Involved in Design and Operating DecisionsqamarulislamNo ratings yet
- John Donaldson - DocsDocument46 pagesJohn Donaldson - Docsaiai100% (2)
- Unicorn Start-UpsDocument3 pagesUnicorn Start-UpsRohanNo ratings yet
- Process Mapping PDFDocument21 pagesProcess Mapping PDFShalini SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Types of EntrepreneursDocument3 pagesTypes of EntrepreneursMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAK50% (2)
- Unit: 2: Prepared By: Togadiya JigneshDocument24 pagesUnit: 2: Prepared By: Togadiya JigneshJignesh TogadiyaNo ratings yet
- Banking and Microfinance - IIDocument24 pagesBanking and Microfinance - IIKoyelNo ratings yet
- Foreclosure BrochureDocument6 pagesForeclosure BrochureAnnMarie BelairNo ratings yet