Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study - Calcium Carbonate
Drug Study - Calcium Carbonate
Uploaded by
mikErlhOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study - Calcium Carbonate
Drug Study - Calcium Carbonate
Uploaded by
mikErlhCopyright:
Available Formats
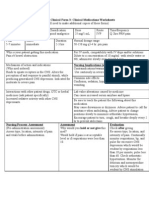
Calcium Carbonate
(1 tab tid)
Classification: Electrolyte replacement or
supplements. Antacid
Desired Dosage: 500 mg (200 mg Ca), 600 mg
(240 mg Ca), 650 mg (260 mg Ca), 667 mg (266.8 mg Ca), 1 g (400
mg Ca), 1.25 mg (500 mg Ca), 1.5 mg (600 mg Ca)
Mode of Action: Essential for nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems. Maintain cell membrane
and capillary permeability. Act as an activator in the transmission of nerve impulses and
contraction of cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscles. It is essential for bone formation
and blood coagulation. It is also used a replacement of calcium in deficiency states. It controls
of hyperphosphatemia in end-stage renal disease without promoting aluminum absorption.
Interactions: Hypercalcemia increases the risk of digoxin toxicity. Chronic use with antacids in
renal insufficiency may lead to milk-alkali syndrome. Ingestion by mouth may decrease the
absorption of orally administered tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, phenytoin, and iron salts.
Excessive amounts may decrease the effects of calcium channel blockers, atenolol. Concurrent
use with diuretics may result in hypercalcemia.
Side Effects:
CNS: syncope, tingling
CV: cardiac arrest, arrythmias, bradycardia
GI: constipation, nausea, vomting
GU: calculi, hypercalciuruia
Local: phlebitis (IV only)
Nursing Responsibilities:
1. Monitor VS especially BP and PR.
2. Obtain ECG result.
3. Asses for heartburn, indigestion, abdominal pain.
4. Monitor serum calcium before treatment.
5. Assess for nausea and vomiting, anorexia, thirst, severe constipation.
You might also like
- 100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of NursingDocument14 pages100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursingshark_tale0488% (43)
- 100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleDocument21 pages100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleAijem Ryan93% (15)
- Drug Study CaptoprilDocument2 pagesDrug Study CaptoprilLyza Pamela T. Vinluan0% (1)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Drugs Affecting Calcium BalanceDocument63 pagesDrugs Affecting Calcium BalanceRd Chandane100% (1)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateRye AnchNo ratings yet
- NaproxenDocument2 pagesNaproxenCharish Jade PaezNo ratings yet
- DemerolDocument1 pageDemerolCassie100% (1)
- Sodium ChlorideDocument1 pageSodium ChlorideMark Christian M. GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyRemedios Bandong100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing (5) - 100 Items - QuestionsDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Nursing (5) - 100 Items - QuestionsmikErlhNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Test IDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Test IRose Ann100% (30)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAl-nazer Azer AlNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument1 pageFerrous SulfateZhyrraRamirezGarcia100% (1)
- Fe SO4Document3 pagesFe SO4CarmellaDawnNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateJoesineNo ratings yet
- Sucralfate PDFDocument2 pagesSucralfate PDFJoshua Christian Penggele100% (1)
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNo ratings yet
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pages1 DrugsPatricia Lucero67% (3)
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument1 pageSodium BicarbonateALbinong VelascoNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NameMichael PalmaNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateMikko EnocNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFerrous Sulfate Drug StudyAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Ferrous SulfateSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Potassium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPotassium Drug StudyNasrah N. Musa100% (2)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateCarla AlmerolNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Ascorbic AcidDocument2 pagesAscorbic AcidJaymark Lambino100% (1)
- Folic AcidDocument2 pagesFolic AcidConn_Casipe_8158100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocument2 pagesCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Metoclopramide (Plasil)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Metoclopramide (Plasil)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Routes Side Effects Co4Ntraindications Nursing Responsibility Brand Name: Inhalation: CoughDocument2 pagesDrug Routes Side Effects Co4Ntraindications Nursing Responsibility Brand Name: Inhalation: CoughChristianne Janella PagadorNo ratings yet
- Caltrate Plus Drug StudyDocument1 pageCaltrate Plus Drug StudyGrace Donato100% (1)
- Drug Study MgSO4Document1 pageDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyErika ManubayNo ratings yet
- Fe SO4Document2 pagesFe SO4Vincent John Faller93% (14)
- Drug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)mikErlh100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studymecz26No ratings yet
- Drug Study For Mini Case PRESDocument11 pagesDrug Study For Mini Case PRESKevin AliasasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Potassium CitrateDocument3 pagesDrug Study Potassium CitrateDat boiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCyric Jyn Fadul Full100% (2)
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study OxytocinGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- Final Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFinal Drug StudyCherry Lou Correos Tejada100% (2)
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Nacl Drug StudyDocument1 pageNacl Drug StudydyndzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NubainDocument2 pagesDrug Study NubainampalNo ratings yet
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDocument1 pageNifedepine Drug StudyMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Losartan Potassium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Potassium Drug StudyJonieP84100% (4)
- Drug Study OralDocument1 pageDrug Study OralBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMetherginebdumaranNo ratings yet
- CALCIUM METABOLISM RaminDocument42 pagesCALCIUM METABOLISM RaminRamin MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Imbalance 2Document10 pagesFluid Imbalance 2saranya amuNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte JournalDocument10 pagesFluid and Electrolyte JournalAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- CA Vit D MetabolismDocument41 pagesCA Vit D MetabolismPramod N KNo ratings yet
- PhilHealth ClaimForm2Document2 pagesPhilHealth ClaimForm2La Lolls CruzNo ratings yet
- My Collection of Old Currencies in The PhilippinesDocument92 pagesMy Collection of Old Currencies in The PhilippinesmikErlhNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursing Keys2Document15 pages100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursing Keys2Aijem RyanNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of NursingDocument15 pages100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursingshark_tale04No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing KeysDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Nursing KeysAijem Ryan0% (1)
- 15 Item Acls DrillDocument4 pages15 Item Acls DrillVal SolidumNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursing KeysDocument14 pages100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursing KeysMar BleNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of NursingDocument14 pages100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursingshark_tale04100% (2)
- Mental Health: Psychiatric NursingDocument20 pagesMental Health: Psychiatric NursingmikErlh100% (1)
- 15 Item ACLS Drill Answers and RationaleDocument6 pages15 Item ACLS Drill Answers and RationaleAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- 100 Items Comprehensive ExamDocument16 pages100 Items Comprehensive ExamAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Review - BurnsDocument52 pagesIntegumentary System Review - BurnsmikErlhNo ratings yet
- 75 Items MS Random QuestionsDocument16 pages75 Items MS Random QuestionsAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- 60 Item Exam On Cardiovascular DisordersDocument9 pages60 Item Exam On Cardiovascular DisordersAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- PainDocument90 pagesPainmikErlh100% (4)
- Perioperative NursingDocument148 pagesPerioperative NursingBok's TriadNo ratings yet
- CANCERDocument46 pagesCANCERZakie ZapNo ratings yet
- 60 Item Exam On Cardiovascular Disorders With Answers and RationaleDocument15 pages60 Item Exam On Cardiovascular Disorders With Answers and RationaleAijem Ryan100% (2)
- Nursing Care of Client With CancerDocument63 pagesNursing Care of Client With CancermikErlhNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in Oxygenation (Part 2)Document88 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in Oxygenation (Part 2)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in Perception and CoordinationDocument44 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in Perception and CoordinationmikErlhNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in Oxygenation (Part 3)Document103 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in Oxygenation (Part 3)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tranexamic AcidDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Tranexamic AcidmikErlh86% (7)
- Drug Study - Sodium BicarbonateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Sodium BicarbonatemikErlhNo ratings yet