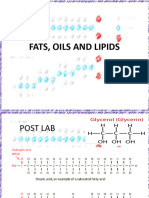
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gel Lotion Pharlab
Gel Lotion Pharlab
Uploaded by
Jes Ong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views1 pageThis document discusses different dosage forms including suspensions, emulsions, aerosols, gels, and lotions. Suspensions contain undissolved particles dispersed in a liquid medium and may exhibit thixotropy, becoming semisolid when undisturbed. Lotions are liquid suspensions or dispersions intended for external application. Methods of preparing suspensions and lotions include trituration, chemical reactions, and using clear solutions. Gels are suspensions where the particle size reaches the colloidal range below 0.5 um.
Original Description:
Original Title
38524763 Gel Lotion Pharlab
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different dosage forms including suspensions, emulsions, aerosols, gels, and lotions. Suspensions contain undissolved particles dispersed in a liquid medium and may exhibit thixotropy, becoming semisolid when undisturbed. Lotions are liquid suspensions or dispersions intended for external application. Methods of preparing suspensions and lotions include trituration, chemical reactions, and using clear solutions. Gels are suspensions where the particle size reaches the colloidal range below 0.5 um.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views1 pageGel Lotion Pharlab
Gel Lotion Pharlab
Uploaded by
Jes OngThis document discusses different dosage forms including suspensions, emulsions, aerosols, gels, and lotions. Suspensions contain undissolved particles dispersed in a liquid medium and may exhibit thixotropy, becoming semisolid when undisturbed. Lotions are liquid suspensions or dispersions intended for external application. Methods of preparing suspensions and lotions include trituration, chemical reactions, and using clear solutions. Gels are suspensions where the particle size reaches the colloidal range below 0.5 um.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Dispersed Phase – cannot combine Character:
- Emulsions - Exhibits thixotrophy
- May contain peppermint oil, sorbitol,
Different dosage forms:
sucrose, saccharin or other suitable
Suspensions preservative and flavorant = not
Emulsions exceeding 0.5%
Aerosols
Gels Thixotrophy – if undisturbed, they may become
Lotion semisolid or gelatinous; if disturbed, they
liquefy
10 – 15 um coarse dispersions
LOTION
0.5 – 10 um fine dispersions
- Liquid suspension or dispersions
1 nm – 0.5um colloidal dispersions
intended for external application to the
body.
- Applied without friction
Aluminum Hydroxide Gel – is an aqueous - More soothing to inflamed areas
suspension or gelatinous precipitate - More effective in contact with infected
surface (Shake well & external)
- Composed of insoluble Al(OH)3 & the - Particles should approach, colloidal
hydrated Al2O3
- Equivalent to about 4% Al2O3 Methods of preparation:
1. Trituration method. Triturating the
PREPARATION # 29 ingredients to smooth paste & then
Aluminum Hydroxide Gel adding the remaining liquid phase
Official Internal a. Calamine Lotion (ZnO and FeO)
High speed mixers &
homogenizers
INGREDIENTS OA CA 2. By chemical reactions
Ammonium Alum 800 g 18 g a. White lotion/ white sulfide
Sodium carbonate 1000 g 15 g ZnSO4+sulfurated potash ZnS
Peppermint Oil 0.01% 0.003 mL
Sodium benzoate 0.1% 0.03 g 3. Clear solution
P.H20, qsad 2000 mL 30 mL a. Dimethisoquin HCl Lotion – in
which the active ingredient is a
water soluble substance
Method: Precipitation
WHY?
Gels – suspension in a water medium of
insoluble drugs e form in hydratwherein the -Solubility permitting liquid therapy
particle size attains or reaches colloidal
dispersions (part. Size < 0.5 um)
You might also like
- Biochem Lab Activity 5Document47 pagesBiochem Lab Activity 5Nafeesa Cadir100% (1)
- PharDose Lab Prep 19-30Document4 pagesPharDose Lab Prep 19-30Angelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- Principles of Formulation & Building Blocks of Hair Care ProductsDocument32 pagesPrinciples of Formulation & Building Blocks of Hair Care Productsnuha100% (6)
- Manuf Lab Prelims Ointment Tablets PDFDocument3 pagesManuf Lab Prelims Ointment Tablets PDFGNCDWNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 KeyDocument3 pagesHomework 6 Keychip_dale100% (1)
- 1ST - Dispensing 1Document3 pages1ST - Dispensing 1Krianne Chris DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Wxs PDFDocument2 pagesWxs PDFoussama22No ratings yet
- EmulsionDocument71 pagesEmulsionKhushboo100% (2)
- PHAR3 LAB - Preparation 22-30Document2 pagesPHAR3 LAB - Preparation 22-30Gerard LeeNo ratings yet
- Incompatibilities: SyllabusDocument16 pagesIncompatibilities: SyllabusRuchitaNo ratings yet
- EmulsionDocument51 pagesEmulsionMasum ParvesNo ratings yet
- L-14 - Ointments, Pastes and JelliesDocument52 pagesL-14 - Ointments, Pastes and Jelliesf20231186No ratings yet
- Chapter-Is Matter Around Us Pure Class - Ix C ChemistryDocument30 pagesChapter-Is Matter Around Us Pure Class - Ix C ChemistryelimentaryNo ratings yet
- Week 14 IncompatibilityDocument18 pagesWeek 14 IncompatibilityTony Jr BalatongNo ratings yet
- Ficha Amb 23Document1 pageFicha Amb 23lourdesNo ratings yet
- EXamples ON LIPIDS PyOSTLABoratoryDocument35 pagesEXamples ON LIPIDS PyOSTLABoratoryedriansamaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical IncompatibilitiesDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical IncompatibilitiesamrhkmhNo ratings yet
- Biochemlab (Lipids)Document18 pagesBiochemlab (Lipids)Apple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Pharm. LinimentsDocument38 pagesPharm. LinimentsDr-Md Abul BarkatNo ratings yet
- Emulsions: Group Number: 02 Course: Physical Pharmacy Course Code: 311Document70 pagesEmulsions: Group Number: 02 Course: Physical Pharmacy Course Code: 311gaurav chauhanNo ratings yet
- Ointment: Presentation By: Ms. Krutika H. PardeshiDocument23 pagesOintment: Presentation By: Ms. Krutika H. PardeshiShumaila QadirNo ratings yet
- Women Institute of Learning AbbottabadDocument15 pagesWomen Institute of Learning AbbottabadRida syedNo ratings yet
- Group Number: 02 Course: Physical Pharmacy Course Code: 311Document70 pagesGroup Number: 02 Course: Physical Pharmacy Course Code: 311poovenmoonoosamyNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormsDocument22 pagesDosage FormsMustafa ShahinNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For LipidsDocument6 pagesQualitative Tests For LipidsCorine RepatoNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Solution and Rate of SolubilityDocument14 pages5.2 Solution and Rate of SolubilityIrfanArmy Musical LoversNo ratings yet
- Phardose 19 31 DiscussionDocument8 pagesPhardose 19 31 DiscussionAnna Patricia Berza100% (1)
- Milk of Magnesia, USP Antacid Cathartic Magnesium Hydroxide, Rolaids, Magnesia MagmaDocument3 pagesMilk of Magnesia, USP Antacid Cathartic Magnesium Hydroxide, Rolaids, Magnesia MagmaKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- PHAR3 LAB Preparation 22 30Document2 pagesPHAR3 LAB Preparation 22 30Eunice AndradeNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics II Lab Exam I ReviewDocument5 pagesPharmaceutics II Lab Exam I Reviewapi-3723612100% (1)
- PHAR3 LAB Preparation 22 30Document2 pagesPHAR3 LAB Preparation 22 30Jaica Mangurali TumulakNo ratings yet
- Or Purge) Bring Up Mucus and Other Material From The Lungs, Bronchi, and Trachea)Document34 pagesOr Purge) Bring Up Mucus and Other Material From The Lungs, Bronchi, and Trachea)Danica BondocNo ratings yet
- Extemporaneous Dispensing OF:: EmulsionsDocument43 pagesExtemporaneous Dispensing OF:: EmulsionsSidraNo ratings yet
- Prep #29 - Aluminum Hydroxide GelDocument2 pagesPrep #29 - Aluminum Hydroxide GelKirsten Shayne ManingasNo ratings yet
- 22 30Document2 pages22 30Eunice AndradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Suspensions and EmulsionsDocument49 pagesChapter 27 Suspensions and EmulsionsKate Montenegro67% (3)
- 125 - FTSS-2010-handout - Umm Dian 1Document68 pages125 - FTSS-2010-handout - Umm Dian 1Laras TiasNo ratings yet
- Emulsions ExtractivesDocument9 pagesEmulsions ExtractivesPNo ratings yet
- Solution ComplteDocument19 pagesSolution ComplteHn9ub7No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - (I) - ColloidDocument64 pagesChapter 6 - (I) - ColloidezanaNo ratings yet
- Emulzome - Informative NoteDocument1 pageEmulzome - Informative NoteControle de Qualidade Pharma ExpressNo ratings yet
- Emulsions NotesDocument128 pagesEmulsions NotesIntan Najiihah67% (3)
- DefinitionandPreparationofSyrups, Elixirs, LinimentsandLotionsPharmaguideline 1708131932947Document3 pagesDefinitionandPreparationofSyrups, Elixirs, LinimentsandLotionsPharmaguideline 1708131932947pearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- Physical IncompatibilityDocument3 pagesPhysical IncompatibilityRaymarkChanBornales0% (1)
- Is Matter Pure?Document8 pagesIs Matter Pure?Aarti JainNo ratings yet
- Preparation 2: Calcium Hydroxide Topical Solution: Dds LabDocument4 pagesPreparation 2: Calcium Hydroxide Topical Solution: Dds LabKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- C-10 Ointment 2Document90 pagesC-10 Ointment 2Mara Angelica100% (1)
- EmulsionsDocument92 pagesEmulsionsBalu KaminiNo ratings yet
- RX 18-20Document2 pagesRX 18-20milkymilkyNo ratings yet
- Colloid and Surface Science: Nurul Huda BT Abu Bakar 012-7892664 Hudabakar@ump - Edu.myDocument8 pagesColloid and Surface Science: Nurul Huda BT Abu Bakar 012-7892664 Hudabakar@ump - Edu.myAlbert12346No ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument13 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureNANDITA NAYAK BNo ratings yet
- White Paper - Emulsion Breaking TechniquesDocument1 pageWhite Paper - Emulsion Breaking TechniquesRandy SooknananNo ratings yet
- 5.2 (A) Solution, Suspension and Colloid - NotesDocument11 pages5.2 (A) Solution, Suspension and Colloid - NotesWeitze LeeNo ratings yet
- PHT 312 EmulsionDocument48 pagesPHT 312 EmulsionSolomonNo ratings yet
- EmulsionDocument155 pagesEmulsionDivithNo ratings yet
- Semisolid Dosage Forms: Prepared By: Dr. Tara A. AbdullaDocument83 pagesSemisolid Dosage Forms: Prepared By: Dr. Tara A. AbdullaEman Aziz100% (1)
- Solutions, XX ReducedDocument35 pagesSolutions, XX Reducedpharma2013No ratings yet
- LinimentsDocument38 pagesLinimentsabibajo100% (1)
- Simple Homemade Lotion: Easy Homemade Beauty Products For A Silky Soft, Gorgeous And Radiant Looking Skin!From EverandSimple Homemade Lotion: Easy Homemade Beauty Products For A Silky Soft, Gorgeous And Radiant Looking Skin!No ratings yet
- Paints & Varnishes Paints & VarnishesDocument26 pagesPaints & Varnishes Paints & VarnishesBhawani Shankar69% (13)
- Eve PI Diagrams v1 4Document6 pagesEve PI Diagrams v1 4Gustavo Alexandre SchefferNo ratings yet
- Anachem Week 2 TransDocument4 pagesAnachem Week 2 TransAnn Frencis Louise PalaoNo ratings yet
- Duratec HPL Features and BenefitsDocument2 pagesDuratec HPL Features and BenefitsAbir MazumderNo ratings yet
- Material Balance and Reaction Kinetics Modeling FoDocument6 pagesMaterial Balance and Reaction Kinetics Modeling Fousman_hafeez86No ratings yet
- SP19 CH117 Exam 1A KEYDocument6 pagesSP19 CH117 Exam 1A KEYharlow6winfield6adamNo ratings yet
- PVC - Polyvinyl ChlorideDocument13 pagesPVC - Polyvinyl ChloridejbertralNo ratings yet
- NPPA1Document3 pagesNPPA1haryroyNo ratings yet
- #1 2 3 Chemistry - Atoms - First-OPDocument188 pages#1 2 3 Chemistry - Atoms - First-OPMutiara Hikmah100% (1)
- Matpr D 20 09686 - R1Document39 pagesMatpr D 20 09686 - R1Omar Al-KubasiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument16 pagesChemistry: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceTan Yong KhaiNo ratings yet
- 5-Hexynoic AcidDocument1 page5-Hexynoic AcidRajasekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Junior High School ScienceDocument4 pagesJunior High School ScienceDoom RefugeNo ratings yet
- Activity: Free Energy: Julius P. Hular Stem 12 BerkelDocument4 pagesActivity: Free Energy: Julius P. Hular Stem 12 BerkelRealyn JerusalemNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The Fifth International Groundwater Conference (IGWC-2012)Document43 pagesProceedings of The Fifth International Groundwater Conference (IGWC-2012)prijucpNo ratings yet
- Why Is Oxygen Absorbed in A Colorless Alkaline Solution of Pyrogallol and Why Does It Turn Dark Brown?Document1 pageWhy Is Oxygen Absorbed in A Colorless Alkaline Solution of Pyrogallol and Why Does It Turn Dark Brown?John WalkerNo ratings yet
- Tic Reinforced AmcDocument27 pagesTic Reinforced AmcarlyNo ratings yet
- New Basic Chemistry 2 Solution (Ideal Solution and Colligative PropertiesDocument83 pagesNew Basic Chemistry 2 Solution (Ideal Solution and Colligative PropertiesRetno Ayu PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plan - Chem - Spring 2022-23 - 17weekDocument3 pagesLecture Plan - Chem - Spring 2022-23 - 17weekreduan sadikNo ratings yet
- Galvanic CorrosionDocument2 pagesGalvanic CorrosionDGWNo ratings yet
- Fluorinated Polymeric Materials: PTFE, FEP, PFA, ETFE: CharacteristicsDocument1 pageFluorinated Polymeric Materials: PTFE, FEP, PFA, ETFE: CharacteristicsrocketvtNo ratings yet
- Methacrylate Structural Adhesives: Plexus MA422 Plexus MA832Document1 pageMethacrylate Structural Adhesives: Plexus MA422 Plexus MA832johnNo ratings yet
- TDS - Glenium 51Document3 pagesTDS - Glenium 51Alexi ALfred H. TagoNo ratings yet
- Metal Art CraftsDocument185 pagesMetal Art CraftsDonald MeikleNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Foam, "Alporas": The Production Process,: Properties and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesAluminum Foam, "Alporas": The Production Process,: Properties and ApplicationsLuis CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Momentive Elastomers Fluorosilicones BrochureDocument8 pagesMomentive Elastomers Fluorosilicones BrochureM J VoraNo ratings yet
- Metal Guard Rust Preventatives PDFDocument2 pagesMetal Guard Rust Preventatives PDFShafnur HamdiNo ratings yet
- NutruentsDocument7 pagesNutruentsPEDRO INFANTE AGUILARNo ratings yet
- CO2 Absorption1Document8 pagesCO2 Absorption1arun manchekarNo ratings yet