Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Knowledge Deficit
NCP Knowledge Deficit
Uploaded by
Fatima Dorcas Roxas LabausaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Di HybridDocument6 pagesDi HybridTaheera Khan100% (2)
- ATP-3.2.1 Land TacticsDocument273 pagesATP-3.2.1 Land Tacticsian R100% (16)
- Tratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoDocument22 pagesTratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoAndersonAguiarOdéIfé0% (3)
- API570 Training Book PDFDocument312 pagesAPI570 Training Book PDFRamziAhmed100% (4)
- BPH NCPDocument1 pageBPH NCPJayson BenitezNo ratings yet
- NCP (Icu)Document2 pagesNCP (Icu)jessie_nuñez_263% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Definitio N Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluati ONDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Definitio N Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluati ONOphelia Ross Omaña TutanesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Kay D. Beredo100% (2)
- NCP Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument2 pagesNCP Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDayan CabrigaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- NCP-Caregiver Role StrainDocument3 pagesNCP-Caregiver Role Strainmikee-berredo-997550% (4)
- NCP HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Hypertensionsinister1781% (27)
- OutlookDocument53 pagesOutlookAvi Kense100% (1)
- NCP HPNDocument5 pagesNCP HPNGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPkatrina_velasco_1No ratings yet
- Knowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionDocument2 pagesKnowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care Deficitnor ain b. odingNo ratings yet
- N C PDocument3 pagesN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- NCP Lack of KnowledgeDocument3 pagesNCP Lack of KnowledgeFaye BartianaNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Sheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvDocument2 pagesSheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy Berry100% (1)
- Verbal / Non-Verbal Communication Therapeutic Communication Used Rationale & Feelings of Nurse Evaluate / ResultDocument3 pagesVerbal / Non-Verbal Communication Therapeutic Communication Used Rationale & Feelings of Nurse Evaluate / ResultJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument1 pageSelf Care DeficitWilly EstacionNo ratings yet
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocument1 pageThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- NCP PowerlessnessDocument6 pagesNCP PowerlessnessopxNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Fdar UTIDocument2 pagesFdar UTINickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- NCP Ischemic StrokeDocument3 pagesNCP Ischemic StrokeEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient KnowledgeDocument1 pageNCP Deficient KnowledgeLouie Siazon Vasquez100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HyperthermiaKirby ContaoiNo ratings yet
- Gallstone NCPDocument2 pagesGallstone NCPKelly RiedingerNo ratings yet
- Cad NCPDocument1 pageCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPnictan 140% (1)
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- IMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Document2 pagesIMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Senyorita KHaye67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan BalnkDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan BalnkKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis 3Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis 3Mark Cau Meran100% (2)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPHippocrates Impressionist CostalesNo ratings yet
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocument3 pagesImpaired Verbal CommunicationChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateCarla AlmerolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument20 pagesNursing Care PlanAgustian Ian S0% (1)
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Deficit - RegorDocument3 pagesKnowledge Deficit - RegorAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- NCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainDocument2 pagesNCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainAubrey RecierdoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Suicidal TendencyDocument2 pagesNCP - Suicidal Tendencyяoxel яayмoи eитяeиa100% (5)
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Ang Sakit NG Tiyan Short-Term: Independent: IndependentDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Ang Sakit NG Tiyan Short-Term: Independent: IndependentKate Pedrajas100% (3)
- Ineffective Coping Related To Situational Crises: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesIneffective Coping Related To Situational Crises: Nursing Care PlanJa LoNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument1 pageNCP Knowledge Deficittspears82100% (2)
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Assess Men 1Document2 pagesAssess Men 1Jenesis BilogNo ratings yet
- NCP PeregrinoDocument2 pagesNCP PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINONo ratings yet
- NCM 109-NCP - PeregrinoDocument2 pagesNCM 109-NCP - PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINONo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanSiena KaleiNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ReadingDocument3 pagesBenefits of ReadingJoJo TanNo ratings yet
- Famous Filipino AthleteDocument5 pagesFamous Filipino AthleteSandara SarciaNo ratings yet
- MTCR - Missile Technology Control RegimeDocument11 pagesMTCR - Missile Technology Control Regimefernandocwrocha-1No ratings yet
- JaneEyre ExtendedEssayOutlineDocument3 pagesJaneEyre ExtendedEssayOutlineAnonymous w3Gji93No ratings yet
- ACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Document23 pagesACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- Secrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxeDocument480 pagesSecrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxelautaroNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFK Cor100% (1)
- Water-Treatment (Rhen)Document13 pagesWater-Treatment (Rhen)Mark Anthony ReyesNo ratings yet
- TW 05 ZhangDocument9 pagesTW 05 ZhangAhmed ELhefnawyNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Intel ProcessorsDocument4 pagesEvolution of Intel Processors이고양No ratings yet
- Ansi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Document17 pagesAnsi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Boris AguilarNo ratings yet
- What Drivers Are Supplied With KepServer Enterprise 9Document2 pagesWhat Drivers Are Supplied With KepServer Enterprise 9Pipe CastilloNo ratings yet
- Increasing Awareness of Future Teachers About Health, Health Preservation and Health Saving Technologies of Preschool ChildrenDocument4 pagesIncreasing Awareness of Future Teachers About Health, Health Preservation and Health Saving Technologies of Preschool ChildrenResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Sonia Baltodano ResumeDocument1 pageSonia Baltodano Resumesbaltoda100% (2)
- The Talent Company's HR Job Postings in The GTA Report - April 5, 2021Document180 pagesThe Talent Company's HR Job Postings in The GTA Report - April 5, 2021heymuraliNo ratings yet
- Structural Excavation and BackfillDocument3 pagesStructural Excavation and BackfillBillal BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Nicmar / Code OfficeDocument8 pagesAssignment Nicmar / Code OfficeRevanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Switch POE 16 Porturi - Dahua PFS4218-16ET-240-wDocument1 pageSwitch POE 16 Porturi - Dahua PFS4218-16ET-240-wVasiliuNo ratings yet
- Emad 21522379 Type A KWH PDFDocument8 pagesEmad 21522379 Type A KWH PDFEMAD ABDULRAHMAN ABDULLAH HASAN MASHRAH -No ratings yet
- Data AlatDocument29 pagesData AlatRefi Opti faniNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence Research Paper TopicsDocument5 pagesJurisprudence Research Paper TopicsAmandeep MalikNo ratings yet
- Drainage NOTESDocument9 pagesDrainage NOTESAuraNo ratings yet
- Vibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SDocument1 pageVibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SSadettin BağdatlıNo ratings yet
- 555 TimerDocument48 pages555 TimeracidreignNo ratings yet
- Treasure IslandDocument266 pagesTreasure IslandNader HaddadNo ratings yet
NCP Knowledge Deficit
NCP Knowledge Deficit
Uploaded by
Fatima Dorcas Roxas LabausaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Knowledge Deficit
NCP Knowledge Deficit
Uploaded by
Fatima Dorcas Roxas LabausaCopyright:
Available Formats
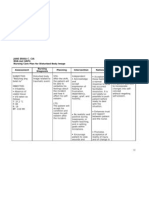
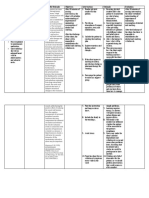
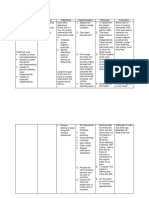
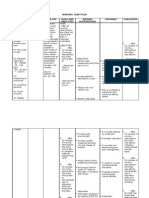
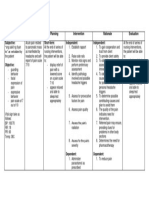
Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale evaluation
Identification
SUBJECTIVE: Risk for prone After 2 hours of
“mataas ba behavior related After 2 hours of INDEPENDENT: nursing
ang bp ko? Ok to lack of nursing interventions, •Define and state the limits of Provides basis for interventions, the
lng ba ‘yon? knowledge about the patient was able desired BP. Explain understanding elevations patient was able
Minsan kasi the disease. to verbalize hypertension and its effect on of BP, and clarifies to verbalize
napapasarap understanding of the the heart, blood vessels, misconceptions and also understanding of
ang kain ko.” disease process and kidney, and brain. understanding that high the disease
treatment regimen. BP can exist without process and
OBJECTIVE: symptom or even when treatment
•Request for feeling well. regimen.
information.
•Assist the patient in •These risk factors have
•V/S taken as identifying modifiable risk been shown to contribute
follows: factors like diet high in to hypertension.
T: 36.5 sodium, saturated fats and
P: 72 cholesterol.
R: 21
BP: 150/90 •Reinforce the importance of •Lack of cooperation is
adhering to treatment common reason for failure
regimen and keeping follow of antihypertensive
up appointments. therapy.
•Suggest frequent position •Decreases peripheral
changes, leg exercises when venous pooling that may
lying down. be potentiated by
vasodilators and
prolonged sitting or
standing.
•Help patient identify sources •Two years on moderate
of sodium intake. low salt diet may be
sufficient to control mild
hypertension.
•Encourage patient to •Caffeine is a cardiac
decrease or eliminate stimulant and may
caffeine like in tea, coffee, adversely affect cardiac
cola and chocolates. function.
•Stress importance of •Alternating rest and
accomplishing daily rest activity increases
periods. tolerance to activity
progression.
DEPENDENT:
•Give due medications •Refer to drug study.
You might also like
- Di HybridDocument6 pagesDi HybridTaheera Khan100% (2)
- ATP-3.2.1 Land TacticsDocument273 pagesATP-3.2.1 Land Tacticsian R100% (16)
- Tratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoDocument22 pagesTratado de Ifa Uso Exclusivo de BabalawoAndersonAguiarOdéIfé0% (3)
- API570 Training Book PDFDocument312 pagesAPI570 Training Book PDFRamziAhmed100% (4)
- BPH NCPDocument1 pageBPH NCPJayson BenitezNo ratings yet
- NCP (Icu)Document2 pagesNCP (Icu)jessie_nuñez_263% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Definitio N Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluati ONDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Definitio N Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluati ONOphelia Ross Omaña TutanesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Kay D. Beredo100% (2)
- NCP Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument2 pagesNCP Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDayan CabrigaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- NCP-Caregiver Role StrainDocument3 pagesNCP-Caregiver Role Strainmikee-berredo-997550% (4)
- NCP HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Hypertensionsinister1781% (27)
- OutlookDocument53 pagesOutlookAvi Kense100% (1)
- NCP HPNDocument5 pagesNCP HPNGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPkatrina_velasco_1No ratings yet
- Knowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionDocument2 pagesKnowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care Deficitnor ain b. odingNo ratings yet
- N C PDocument3 pagesN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- NCP Lack of KnowledgeDocument3 pagesNCP Lack of KnowledgeFaye BartianaNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Sheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvDocument2 pagesSheryl Ann B. Pedines Bsn-IvSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy Berry100% (1)
- Verbal / Non-Verbal Communication Therapeutic Communication Used Rationale & Feelings of Nurse Evaluate / ResultDocument3 pagesVerbal / Non-Verbal Communication Therapeutic Communication Used Rationale & Feelings of Nurse Evaluate / ResultJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument1 pageSelf Care DeficitWilly EstacionNo ratings yet
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocument1 pageThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- NCP PowerlessnessDocument6 pagesNCP PowerlessnessopxNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Fdar UTIDocument2 pagesFdar UTINickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- NCP Ischemic StrokeDocument3 pagesNCP Ischemic StrokeEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient KnowledgeDocument1 pageNCP Deficient KnowledgeLouie Siazon Vasquez100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HyperthermiaKirby ContaoiNo ratings yet
- Gallstone NCPDocument2 pagesGallstone NCPKelly RiedingerNo ratings yet
- Cad NCPDocument1 pageCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPnictan 140% (1)
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- IMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Document2 pagesIMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Senyorita KHaye67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan BalnkDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan BalnkKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis 3Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis 3Mark Cau Meran100% (2)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPHippocrates Impressionist CostalesNo ratings yet
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocument3 pagesImpaired Verbal CommunicationChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateCarla AlmerolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument20 pagesNursing Care PlanAgustian Ian S0% (1)
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Deficit - RegorDocument3 pagesKnowledge Deficit - RegorAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- NCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainDocument2 pagesNCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainAubrey RecierdoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Suicidal TendencyDocument2 pagesNCP - Suicidal Tendencyяoxel яayмoи eитяeиa100% (5)
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Ang Sakit NG Tiyan Short-Term: Independent: IndependentDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Ang Sakit NG Tiyan Short-Term: Independent: IndependentKate Pedrajas100% (3)
- Ineffective Coping Related To Situational Crises: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesIneffective Coping Related To Situational Crises: Nursing Care PlanJa LoNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument1 pageNCP Knowledge Deficittspears82100% (2)
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Assess Men 1Document2 pagesAssess Men 1Jenesis BilogNo ratings yet
- NCP PeregrinoDocument2 pagesNCP PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINONo ratings yet
- NCM 109-NCP - PeregrinoDocument2 pagesNCM 109-NCP - PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINONo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanSiena KaleiNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ReadingDocument3 pagesBenefits of ReadingJoJo TanNo ratings yet
- Famous Filipino AthleteDocument5 pagesFamous Filipino AthleteSandara SarciaNo ratings yet
- MTCR - Missile Technology Control RegimeDocument11 pagesMTCR - Missile Technology Control Regimefernandocwrocha-1No ratings yet
- JaneEyre ExtendedEssayOutlineDocument3 pagesJaneEyre ExtendedEssayOutlineAnonymous w3Gji93No ratings yet
- ACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Document23 pagesACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- Secrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxeDocument480 pagesSecrets of A Millionaire Magician DeluxelautaroNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFK Cor100% (1)
- Water-Treatment (Rhen)Document13 pagesWater-Treatment (Rhen)Mark Anthony ReyesNo ratings yet
- TW 05 ZhangDocument9 pagesTW 05 ZhangAhmed ELhefnawyNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Intel ProcessorsDocument4 pagesEvolution of Intel Processors이고양No ratings yet
- Ansi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Document17 pagesAnsi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Boris AguilarNo ratings yet
- What Drivers Are Supplied With KepServer Enterprise 9Document2 pagesWhat Drivers Are Supplied With KepServer Enterprise 9Pipe CastilloNo ratings yet
- Increasing Awareness of Future Teachers About Health, Health Preservation and Health Saving Technologies of Preschool ChildrenDocument4 pagesIncreasing Awareness of Future Teachers About Health, Health Preservation and Health Saving Technologies of Preschool ChildrenResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Sonia Baltodano ResumeDocument1 pageSonia Baltodano Resumesbaltoda100% (2)
- The Talent Company's HR Job Postings in The GTA Report - April 5, 2021Document180 pagesThe Talent Company's HR Job Postings in The GTA Report - April 5, 2021heymuraliNo ratings yet
- Structural Excavation and BackfillDocument3 pagesStructural Excavation and BackfillBillal BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Nicmar / Code OfficeDocument8 pagesAssignment Nicmar / Code OfficeRevanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Switch POE 16 Porturi - Dahua PFS4218-16ET-240-wDocument1 pageSwitch POE 16 Porturi - Dahua PFS4218-16ET-240-wVasiliuNo ratings yet
- Emad 21522379 Type A KWH PDFDocument8 pagesEmad 21522379 Type A KWH PDFEMAD ABDULRAHMAN ABDULLAH HASAN MASHRAH -No ratings yet
- Data AlatDocument29 pagesData AlatRefi Opti faniNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence Research Paper TopicsDocument5 pagesJurisprudence Research Paper TopicsAmandeep MalikNo ratings yet
- Drainage NOTESDocument9 pagesDrainage NOTESAuraNo ratings yet
- Vibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SDocument1 pageVibracord. Vibration Meter Summary Sheet (Graphic) : Record Time: 4 SSadettin BağdatlıNo ratings yet
- 555 TimerDocument48 pages555 TimeracidreignNo ratings yet
- Treasure IslandDocument266 pagesTreasure IslandNader HaddadNo ratings yet