Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Days
Days
Uploaded by
shreyansh123Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Days
Days
Uploaded by
shreyansh123Copyright:
Available Formats
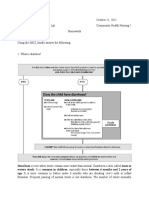
days,
because your immune system will automatically fight the infection.
In the meantime, you can ease your symptoms by following the steps below.
Drink fluids
You can avoid becoming dehydrated by drinking lots of fluids. You are more likely to be
dehydrated if you are also vomiting.
Take small, frequent sips of water or diluted fruit juice. It is especially important that babies and
small children do not become dehydrated. Even if your child vomits, still give them frequent sips
of water. A small amount of fluid is better than none.
If your child shows signs of dehydration (drowsiness, passing little urine, few or no wet nappies,
a dry mouth and tongue, unresponsiveness or glazed eyes) you should contact your GP
immediately.
Rehydration drinks
If you are worried that you are becoming dehydrated, your doctor or pharmacist may advise you
to take rehydration drinks. You can buy sachets of rehydration salts from your pharmacy and add
them to water. They provide the correct balance of water, salt and sugar.
Rehydration drinks do not help to cure diarrhoea, but can prevent or treat dehydration.
Your doctor or pharmacist may also recommend rehydration drinks for your child, if you are
worried they may become dehydrated. Do not use homemade salt or sugar drinks. Always
consult your pharmacist.
Eat as soon as you can
The old advice was to not eat anything for a day or two, but now it is recommended that you eat
foods high in carbohydrates (bread, pasta, rice or potatoes) and other foods as soon as you feel
like it. Salty foods such as soup can help replace salt lost from your system.
If you feel you cannot eat, it shouldn't do you any harm, but make sure you continue drinking
fluids and eat as soon as you are able.
If your child wants to eat, offer soups and foods high in carbohydrates at first. Your child can eat
normally as soon as possible. If your child refuses to eat, continue to offer drinks and wait until
their appetite returns.
Anti-diarrhoea medicines
Anti-diarrhoea drugs such as loperamide can relieve symptoms by slowing down the movement
of bowel contents, and sometimes by increasing water absorption from the gut.
Loperamide can be taken once or twice a day, over a long period. However:
Do not take anti-diarrhoea drugs if there is blood in your stools or if you have a high
temperature (check with your pharmacist).
Do not give anti-diarrhoea drugs to your child.
Continue breastfeeding or bottle-feeding
If you are breastfeeding or bottle-feeding your child and they have diarrhoea, continue if they
will still feed (use their normal-strength feed if they are bottle-fed). Rehydration drinks should
also be given if necessary.
Painkillers
You can take recommended doses of paracetamol or ibuprofen if you have a fever or
headache. Do not take ibuprofen if you are asthmatic, or if you have stomach, liver or kidney
problems.
Liquid paracetamol or ibuprofen can also be given to your child if necessary. Children aged
under 16 should not take aspirin.
You might also like
- Eating Disorder Harm Reduction 4Document1 pageEating Disorder Harm Reduction 4Marle NiklNo ratings yet
- BIOETHICS COMPILE FinalDocument36 pagesBIOETHICS COMPILE Finalshai espejoNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan: What You Need To Know: Discharge InstructionsDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan: What You Need To Know: Discharge Instructionscoral jade cuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Clinical Privileges Department: ICU /NICU /LRDocument3 pagesNursing Clinical Privileges Department: ICU /NICU /LRKUMARJIT SAHA100% (3)
- English Gastroenteritis PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish Gastroenteritis PDFkatyweymNo ratings yet
- Moreless PH DownDocument4 pagesMoreless PH DownjayjonbeachNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Care in Thoracic Surgery A Comprehensive GuideDocument397 pagesPostoperative Care in Thoracic Surgery A Comprehensive GuideΑΘΑΝΑΣΙΟΣ ΚΟΥΤΟΥΚΤΣΗΣ100% (1)
- Epidemiology An IntroductionDocument18 pagesEpidemiology An Introductionfatehatun noorNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013Document9 pagesDiarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013emmi_valentinaNo ratings yet
- Hydration Peds PDFDocument2 pagesHydration Peds PDFMaryNguyenNo ratings yet
- Oral Rehydration Salts 2Document2 pagesOral Rehydration Salts 2William ImpNo ratings yet
- Age PDFDocument3 pagesAge PDFDika AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument5 pagesHealth EducationMichellin Lara VergaraNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea and Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesDiarrhea and Acute GastroenteritisAkasa DudungNo ratings yet
- How To Prevent and Treat Diarrhea While You Are TravelingDocument2 pagesHow To Prevent and Treat Diarrhea While You Are TravelingAnu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastroDocument2 pagesGastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastrokatyweymNo ratings yet
- Oral RehydrationDocument23 pagesOral Rehydrationbuttashly125No ratings yet
- Made at Home: ORS Solution A Special Drink For Diarrhoea: ShareDocument4 pagesMade at Home: ORS Solution A Special Drink For Diarrhoea: Sharetayeloluademola103No ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride For Potassium DepletionDocument2 pagesPotassium Chloride For Potassium DepletionWilliam ImpNo ratings yet
- CHWguidelines DiarrheaDocument25 pagesCHWguidelines DiarrheaYurika SastyarinaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For New Diarrhea Treatment Protocols: For Community-Based Healthcare WorkersDocument23 pagesGuidelines For New Diarrhea Treatment Protocols: For Community-Based Healthcare WorkersFebria Valentine AritonangNo ratings yet
- Discharge and Recommendation: - Give Plenty Amount of Water.Document2 pagesDischarge and Recommendation: - Give Plenty Amount of Water.Nestor CabacunganNo ratings yet
- Home Made ORSDocument4 pagesHome Made ORSTrajan AureliusNo ratings yet
- Vomiting and DiarrheaDocument1 pageVomiting and DiarrheaNader AbsiNo ratings yet
- Viral Gastroenteritis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesViral Gastroenteritis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsMars TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Four Rules For Home Treatment of Diarrhoea 4.2.1 Rule 1: Give The Child More Fluids Than UsualDocument3 pagesFour Rules For Home Treatment of Diarrhoea 4.2.1 Rule 1: Give The Child More Fluids Than UsualMaral Bimanti FebrilinaNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument2 pagesHealth EducationPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Q:-Prepare An ORS SolutionDocument2 pagesQ:-Prepare An ORS SolutionRajesh UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- The Health Consequences of DehydrationDocument4 pagesThe Health Consequences of DehydrationJulio AlvesNo ratings yet
- Cold Remedies: What Works, What Doesn't, What Can't HurtDocument2 pagesCold Remedies: What Works, What Doesn't, What Can't HurtCarlos VSNo ratings yet
- The 6 Most Effective Diarrhea RemediesDocument6 pagesThe 6 Most Effective Diarrhea RemediesCatarina Baccay CauilanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledF WoyenNo ratings yet
- ORESOL Is "Oral Glucose-ElectrolyteDocument4 pagesORESOL Is "Oral Glucose-ElectrolyteMichelle ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Poo Passport Part 2 PDF For The Parent and ChildDocument36 pagesPoo Passport Part 2 PDF For The Parent and Childblumhaghel bogdanNo ratings yet
- Course Task #8Document6 pagesCourse Task #8ANGEL MICAH DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea JPNDocument6 pagesDiarrhea JPNShawnNo ratings yet
- Diarrheal Disease (Acute) : Escherichia ColiDocument8 pagesDiarrheal Disease (Acute) : Escherichia ColiFuzoh MfzNo ratings yet
- Oral Rehydration Solutions: Made at Home: Share This Page!Document4 pagesOral Rehydration Solutions: Made at Home: Share This Page!Grace DasNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea - DiarreaDocument6 pagesDiarrhea - DiarreaStephany Burgos SolarteNo ratings yet
- Con FluDocument3 pagesCon FlusnylstlNo ratings yet
- Causes of Vomiting and How To Treat in AdultsDocument8 pagesCauses of Vomiting and How To Treat in Adultsto van quyenNo ratings yet
- When To Use The Master CleanseDocument4 pagesWhen To Use The Master CleanseNzame NkwaNo ratings yet
- Vomiting: Self-Care: HealthDocument2 pagesVomiting: Self-Care: HealthAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNo ratings yet
- Imci Diarrhoea Homework#2Document9 pagesImci Diarrhoea Homework#2Cherub ChuaNo ratings yet
- Prevention of DiseasesDocument27 pagesPrevention of DiseasesDhritismita KalitaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPRic TinNo ratings yet
- Ors Recitation#1Document4 pagesOrs Recitation#1Cherub ChuaNo ratings yet
- David Jockers Symptomatic Digestive Relief GuideDocument24 pagesDavid Jockers Symptomatic Digestive Relief GuideConfidentro BlospotNo ratings yet
- Cat Cure TataeDocument3 pagesCat Cure TataeIsabel Basay OllabanNo ratings yet
- When Illness Reduces Your AppetiteDocument4 pagesWhen Illness Reduces Your AppetiteErick orellanaNo ratings yet
- June - Diarrhea AwarenessDocument8 pagesJune - Diarrhea AwarenessMary Jean HernaniNo ratings yet
- READINGSDocument3 pagesREADINGSMary Grace AmbaNo ratings yet
- Treatment in Childhood DiarrhoeaDocument17 pagesTreatment in Childhood DiarrhoeaPrabir Kumar ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Report in NCM 102 ConstipationDocument5 pagesReport in NCM 102 ConstipationErina Erichan OtoNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument2 pagesDiarrheajanna_3No ratings yet
- Basic Training For Barangay Health Workers Calasiao, PangasinanDocument18 pagesBasic Training For Barangay Health Workers Calasiao, Pangasinan700AIDANNo ratings yet
- Ostomy Nutrition Guide - Patient Education Materials - UPMC PDFDocument7 pagesOstomy Nutrition Guide - Patient Education Materials - UPMC PDFkaktushijauNo ratings yet
- Juice & Thoughtsvol.4 Juice Fast & Elimination Nutritional ProgramDocument20 pagesJuice & Thoughtsvol.4 Juice Fast & Elimination Nutritional ProgramThirtythree SpiritsNo ratings yet
- Care For The Child in Hospital: How To Identify and Treat Children Who Need Urgent CareDocument22 pagesCare For The Child in Hospital: How To Identify and Treat Children Who Need Urgent CareDahrren Grace JalonNo ratings yet
- Preparation Instructions For ColonosDocument4 pagesPreparation Instructions For Colonosmonir61No ratings yet
- Constipation Treatment For Infants and ChildrenDocument2 pagesConstipation Treatment For Infants and Childrenapi-559575515No ratings yet
- PatanjaliDocument2 pagesPatanjaliPravin SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument9 pagesDischarge PlanRheynel NietesNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument26 pagesCase StudyGrace Orencia100% (1)
- Wafeequa Dinath Final Paper AdolescentsDocument9 pagesWafeequa Dinath Final Paper AdolescentsIRMA SAFRIANINo ratings yet
- FCP Network ListDocument150 pagesFCP Network Listoscpramod2695No ratings yet
- FinalDocument36 pagesFinalNirali GalaNo ratings yet
- CoccusDocument5 pagesCoccusJay R ChivaNo ratings yet
- Breastcrawl PDFDocument41 pagesBreastcrawl PDFRyan AndarestaNo ratings yet
- The State Nurses Registration CouncilsDocument10 pagesThe State Nurses Registration CouncilsPriyadharshene RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Public Health CatalogDocument36 pagesPublic Health CatalogrrockelNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument11 pagesOtitis MediajessyNo ratings yet
- VAERS Summary 09242021Document12 pagesVAERS Summary 09242021rehankedhenNo ratings yet
- Hospital Diagnostic Center Management SystemDocument23 pagesHospital Diagnostic Center Management SystemBani Amel RanaNo ratings yet
- Moderator (Nurhafizatul)Document12 pagesModerator (Nurhafizatul)nurhafizatul asmakNo ratings yet
- Peer Assessment Rating (Par) Index: ReliabilityDocument5 pagesPeer Assessment Rating (Par) Index: ReliabilityLaween AbdulkhaliqNo ratings yet
- Management of Intractable AspirationDocument49 pagesManagement of Intractable Aspirationekaefka50% (2)
- Occupational Health Hazards and Safety Practices: Industrial Hygiene and SanitationDocument32 pagesOccupational Health Hazards and Safety Practices: Industrial Hygiene and SanitationPhilemon MsangiNo ratings yet
- Hyperbaric Oxygen TherapyDocument30 pagesHyperbaric Oxygen TherapychaiNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Ethics of TBDocument38 pagesGuidance On Ethics of TBRhea Derije100% (1)
- Declaration When Patient Has No Insurance Policy:: PPN Network - Declaration by Patient/Patient'S AttendantDocument1 pageDeclaration When Patient Has No Insurance Policy:: PPN Network - Declaration by Patient/Patient'S AttendantRatheesh TNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pharmacology For Canadian Health Care Practice 2nd Edition LilleyDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Pharmacology For Canadian Health Care Practice 2nd Edition Lilleymoneyedcoronal1ah2y100% (28)
- Treatment of Feline Panleukopenia Virus InfectionDocument8 pagesTreatment of Feline Panleukopenia Virus InfectionDhea SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- BXT-557G Prismax Brochure-Trifold LowRes 10DEC18Document2 pagesBXT-557G Prismax Brochure-Trifold LowRes 10DEC18Ahmed KrayemNo ratings yet
- Field Triage in TraumaDocument12 pagesField Triage in TraumaKABERA RENENo ratings yet
- HEAS 1000 Health HistoryDocument17 pagesHEAS 1000 Health HistoryNirali ParmarNo ratings yet
- Ruffault Et Al., 2016Document22 pagesRuffault Et Al., 2016Mayara HamúNo ratings yet
- Sga 3Document7 pagesSga 3Shane PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Jurisprudence 1Document19 pagesNursing Jurisprudence 1Rodolf Gerone G. MacahilosNo ratings yet