Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Flow Through Heart
Blood Flow Through Heart
Uploaded by
Matthew Alan BrittonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Flow Through Heart
Blood Flow Through Heart
Uploaded by
Matthew Alan BrittonCopyright:
Available Formats
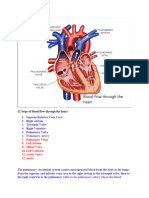
1.
Vena cava-
2. Right atrium
3. Tricuspid valve
4. Right ventricle
5. Semi-lunar valve
6. Pulmonary artery
7. Lungs
8. Back to heart via the pulmonary vein
9. Left atrium
10. Bicuspid valve
11. Left ventricle
12. Semi-lunar valve
13. Aorta
14. Organs in the body
Here is a step-by-step from my university level Anatomy and Physiology II
class:
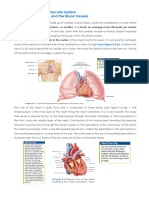
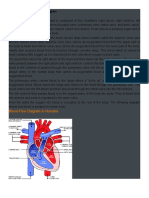
1. The right atrium receives deoxygentated blood from the systemic circuit (the
body ) through the vena cavae (superior and inferior).
2. Blood flows from the right atrium through the right AV valve ( right
atrioventricular valve or tricuspid valve) into the right ventricle.
3. When the right ventricle contracts it pumps blood through the pulmonary semi-
lunar valve to enter the pulmonary trunk which starts the pulmonary circuit.
4. Pulmonary trunk divides into left and right pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary
arteries divide smaller and smaller until they deliver blood to gas exchange sites
of lungs (alveoli).
5. Once blood is oxygentated it flows back to the heart through the right and left
pulmonary veins.
6. Right and left pulmonary veins deliver blood to the left atrium.
7. Blood flows from the left atrium through the left AV valve (aka Mitral or
Bicuspid valve) into the left ventricle.
8. Blood is pumped by the strong left ventricle through the aortic semi-lunar valve
into the ascending aorta.
9. Blood flows through the aortic arch into the descending aorta.
You might also like
- Learn The Anatomy of The HeartDocument3 pagesLearn The Anatomy of The Heartash vldnbr100% (1)
- Biology Study Guide 1 - Blood Flow in The HeartDocument1 pageBiology Study Guide 1 - Blood Flow in The HeartmaryNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 ACTIVITYblood FlowconductionchmabersvalvesDocument29 pagesGROUP 4 ACTIVITYblood FlowconductionchmabersvalvesKarla Katrina SibbalucaNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Through The HeartDocument10 pagesBlood Flow Through The HeartJack MessarosNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentSiti Sumari HarahapNo ratings yet
- Structure of Heart To SendDocument12 pagesStructure of Heart To SendlaibahundekarNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument5 pagesCirculatory System ActivityKeen Jude CaminosNo ratings yet
- Part of The Heart and Its FunctionsDocument1 pagePart of The Heart and Its FunctionsAngelica A TultogNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ReportDocument7 pagesCardiovascular ReportFaith MarfilNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory SystemPuguh HadiNo ratings yet
- Preparation Tasks - Week 6Document7 pagesPreparation Tasks - Week 6Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Q1W2-Lesson 1-2 CIRCULATION OF BLOODDocument40 pagesQ1W2-Lesson 1-2 CIRCULATION OF BLOODKRISTA MAE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Systemapi-297526590No ratings yet
- Cardio VasDocument99 pagesCardio VashellerkittyNo ratings yet
- Rat Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesRat Circulatory SystemAnkit NariyaNo ratings yet
- BingrrisDocument1 pageBingrrisYolanda SaritaNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1johnnatividad445No ratings yet
- Blood Flow Through The Heart AssignmentDocument2 pagesBlood Flow Through The Heart Assignmentvwalker12550No ratings yet
- 3 The Human HeartDocument27 pages3 The Human HeartOlivia MorenteNo ratings yet
- CVS 1 (Physiological Anatomy) .PDF AfraaDocument36 pagesCVS 1 (Physiological Anatomy) .PDF AfraaEra NewNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System LectureDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System LectureMarci MunirNo ratings yet
- TALLER #3 BioinstrumentacionDocument2 pagesTALLER #3 BioinstrumentacionmaNo ratings yet
- Self Study MaterialDocument2 pagesSelf Study MaterialNisha JojanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System +Document14 pagesCardiovascular System +Yasin AbassNo ratings yet
- About The Circulatry System 001Document46 pagesAbout The Circulatry System 001gaboelgaNo ratings yet
- Heart Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesHeart Lecture NotesAsh KetchumNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioAlexandra Duque-David100% (2)
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemCookies AndcreamNo ratings yet
- 8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pages8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMammarahn0No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument32 pagesCardiovascular SystemAugustus Alejandro ZenitNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFDocument11 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFAnonymous e6LINHNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1frenee aradanasNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument6 pagesFetal Circulationkc-orense-1005No ratings yet
- The Anatomy of HeartDocument46 pagesThe Anatomy of HeartPrincess NavarroNo ratings yet
- Heart: StructureDocument11 pagesHeart: StructureKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Basics of The Heart: Katee Beaudry MS 2 - Penn State University College of MedicineDocument24 pagesBasics of The Heart: Katee Beaudry MS 2 - Penn State University College of MedicineAlkhnsa CaifNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Heartrave26No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyJenn YumulNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument3 pagesHeartJEEJANo ratings yet
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDocument3 pagesHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaNo ratings yet
- Heart Structure, Function and Arrhythmias: Elizabeth M. Cherry and Flavio H. FentonDocument15 pagesHeart Structure, Function and Arrhythmias: Elizabeth M. Cherry and Flavio H. Fentonmaurice bertrandNo ratings yet
- List The Chambers/vessels That The Four Valves Connect:: The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac CycleDocument2 pagesList The Chambers/vessels That The Four Valves Connect:: The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac CycleKathiNo ratings yet
- Diagram Human Heart Kel 1Document3 pagesDiagram Human Heart Kel 1Rahma SafitriNo ratings yet
- MY CLASS NOTES - BIOLOGY Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesMY CLASS NOTES - BIOLOGY Circulatory SystemJjongNo ratings yet
- 7.8.heart and VesselsDocument11 pages7.8.heart and Vesselssomebody_maNo ratings yet
- MS Wrep IIDocument51 pagesMS Wrep IIiana-almocera-6970No ratings yet
- Parts of The Human HeartDocument4 pagesParts of The Human HeartKearly Joy VictorioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1Dedi ProbudiNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument25 pages1 Anatomy and PhysiologyMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesELYANNo ratings yet
- Wiki Heart ChamberDocument4 pagesWiki Heart Chamberdgina8800No ratings yet
- Blood Flow DiagramDocument1 pageBlood Flow Diagrambeeluvit81444No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument28 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyeliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- BioDocument4 pagesBioMustofa KamalNo ratings yet
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartFrom EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo ratings yet