Professional Documents
Culture Documents
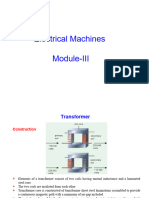
Hah Aha
Hah Aha
Uploaded by
Syafiq KamaruddinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Group 2 Ac Motors Technical ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Ac Motors Technical Reporttristan jeff bautistaNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument27 pagesDC MotorAnonymous AFFiZn100% (2)
- EL221-Electromechanical System Lab 07: D.C. MachineDocument17 pagesEL221-Electromechanical System Lab 07: D.C. MachineMuhammad AreebNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: ConstructionDocument5 pagesElectric Motor: Constructionأحمد صابرNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument5 pagesUntitled DocumentranaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical SystemDocument18 pagesAircraft Electrical SystemAma Serwaa YeboahNo ratings yet
- Define and Differentiate Between AC Generators and DC GeneratorsDocument17 pagesDefine and Differentiate Between AC Generators and DC GeneratorsArafatNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument33 pagesDC MachineAnu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument9 pagesUnit IIIhariNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 DC MotorDocument13 pagesUnit 5 DC MotorSayali HadapNo ratings yet
- BEE R20 - Unit-1 (Ref-2)Document44 pagesBEE R20 - Unit-1 (Ref-2)Dhanush 413No ratings yet
- Uint 4 BEEDocument17 pagesUint 4 BEEshivprakashNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document85 pagesUnit 2Naitik NavyNo ratings yet
- CIA-2 Answer Key1Document11 pagesCIA-2 Answer Key1Electrical & Electroncic Engg HODNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument35 pagesDC Machinehs637717No ratings yet
- Dhiviyansh - Electric MotorsDocument19 pagesDhiviyansh - Electric MotorsDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- Module IIIDocument66 pagesModule IIIUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Machine OperationDocument94 pagesBasic Principles of Machine OperationRashmi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine II: EEEEC11 (3 - 0 - 2) Semester 4Document250 pagesElectrical Machine II: EEEEC11 (3 - 0 - 2) Semester 4sanjoni.jainNo ratings yet
- Presentation On DC GeneratorDocument36 pagesPresentation On DC GeneratorShubham prajeshNo ratings yet
- DC Machine & Ac MachineDocument19 pagesDC Machine & Ac MachineSankara nathNo ratings yet
- DC Drives-AV322-PEDocument15 pagesDC Drives-AV322-PEDarkSIDE FactsNo ratings yet
- Construction of DC GeneratorDocument58 pagesConstruction of DC GeneratorRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines (31-141 Page)Document111 pagesElectrical Machines (31-141 Page)judieNo ratings yet
- Name: Khushi Goyal Class: Xii Project: DC Generator Roll No.Document6 pagesName: Khushi Goyal Class: Xii Project: DC Generator Roll No.Khushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2Dr.Sakthivel SNo ratings yet
- Assignment EET374Document13 pagesAssignment EET374Ayyan MirNo ratings yet
- Basic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorDocument12 pagesBasic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorMaheedhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument18 pagesDC Machinesfmrayan66No ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFDocument29 pagesHTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFVigneshwaran J vNo ratings yet
- EPE491 - Chapter 6 - DC MachinesDocument14 pagesEPE491 - Chapter 6 - DC MachinesMajad RazakNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-Ch2-DcmotorDocument93 pagesElectrical Machines-Ch2-DcmotoradamwaizNo ratings yet
- Dumaguin Facma42l-Elep08 Module4Document7 pagesDumaguin Facma42l-Elep08 Module4Mike DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 and 2Document20 pagesLecture 1 and 2Bonface weitaraNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Simulation StudyDocument10 pagesExperimental and Simulation Studyمحمد عامرNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument43 pagesDC MotorKharlaNo ratings yet
- Construction of DC MotorDocument49 pagesConstruction of DC MotorAvanish Verma100% (1)
- Basic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorDocument15 pagesBasic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorAnonymous QcCCBsNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ac DCDocument10 pagesAssignment Ac DCKamil KhairiNo ratings yet
- DC Motor MBZ 2020-21Document31 pagesDC Motor MBZ 2020-21lakshya.santaniNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument33 pagesDC MachineSlim ShaddysNo ratings yet
- D.C Machine: Anati Syahirah Jabatan Kejuruteraan Elektrik UTM Space, KLDocument35 pagesD.C Machine: Anati Syahirah Jabatan Kejuruteraan Elektrik UTM Space, KLAnati Syahirah Binti HedzirNo ratings yet
- Eme Practical PDFDocument68 pagesEme Practical PDFr kNo ratings yet
- Rotating Machines and Transformers Unit 2 DC GENERATOR CLASS NOTESDocument70 pagesRotating Machines and Transformers Unit 2 DC GENERATOR CLASS NOTESSEDHURAJA SNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument14 pagesDC GeneratorGlen DangaranNo ratings yet
- DC Machines: Answer: The DC Generators and DC Motors Have The Same General Construction. in FactDocument9 pagesDC Machines: Answer: The DC Generators and DC Motors Have The Same General Construction. in FacthavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Eee - 7Document30 pagesEee - 7TanvirNo ratings yet
- The Construction of A DC Generator Includes Several Key ComponentsDocument11 pagesThe Construction of A DC Generator Includes Several Key ComponentsMD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet
- Extra Notes DCmotorsDocument19 pagesExtra Notes DCmotorsashikinNo ratings yet
- DC Machine L04Document34 pagesDC Machine L04luckyNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument16 pagesDC GeneratorSK MD WALI ULLAH BULONNo ratings yet
- DC Motors Lecture NotesDocument71 pagesDC Motors Lecture Notesm.investment.kNo ratings yet
- TASK:2: 1.generators and Motors 2.trasnformersDocument24 pagesTASK:2: 1.generators and Motors 2.trasnformersFaiza Tabassam 546-FET/BSEE/F19No ratings yet
- AC GeneratorDocument7 pagesAC Generatoraswardi8756No ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument25 pagesDC MotorsBruceNo ratings yet
- Rotor and Stator Magnetic FieldsDocument4 pagesRotor and Stator Magnetic FieldsJOAO ESTEVAONo ratings yet
- Electric GeneratorDocument7 pagesElectric GeneratorRahul Shivu100% (1)
- DC Generators Jkuat 2024Document10 pagesDC Generators Jkuat 2024sikolia.wanjalaNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument25 pagesDC MachinesAbdallah EssamNo ratings yet
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
Hah Aha
Hah Aha
Uploaded by
Syafiq KamaruddinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hah Aha
Hah Aha
Uploaded by
Syafiq KamaruddinCopyright:
Available Formats
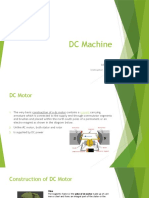
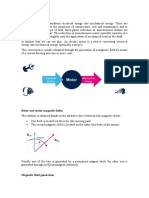
A DC machine can act as a DC generator or DC
DC motor as a generator
If the shaft of a DC motor is turned by an external force, it will produce electromotive force (EMF).
During normal operation, the spinning of the motor produces a voltage, known as counter EMF or back
EMF. The back EMF is the reason that the motor when free-running does not appear to have the same
low electrical resistance as the wire contained in its winding. This is the same EMF that is produced
when the motor is used as a generator
b) Functions of field and armature windings in DC motor.
Field winding
Field winding is also known as energizing winding or exciting coil. The coil energizes the stator, which is
either permanent magnet or electromagnet. Field winding is placed on the stator of the motor. This
winding has more number of turns which generates magnetic flux. The position of the field coils is such
that the outwardly directed or radial component of the magnetic field produced in the air gap to the
stator is approximately sinusoidally distributed around the periphery of the rotor.
Armature winding
Armature is the turning conductor in a DC motor. The conducting coils that wound around the armature
in which voltage is induced, causing it to rotate within a magnetic field. If the wires are damaged or
broken, the armature will not rotate properly.
c) 2 components of a dc motor equivalent circuit
Back-EMF – Back electromotive force is also knows as counter-electromotive force (CEMF). Back
electromotive force is a voltage that occurs in DC motors where there is relative motion between the
armature of the motor and the external magnetic field.
You might also like
- Group 2 Ac Motors Technical ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Ac Motors Technical Reporttristan jeff bautistaNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument27 pagesDC MotorAnonymous AFFiZn100% (2)
- EL221-Electromechanical System Lab 07: D.C. MachineDocument17 pagesEL221-Electromechanical System Lab 07: D.C. MachineMuhammad AreebNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: ConstructionDocument5 pagesElectric Motor: Constructionأحمد صابرNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument5 pagesUntitled DocumentranaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical SystemDocument18 pagesAircraft Electrical SystemAma Serwaa YeboahNo ratings yet
- Define and Differentiate Between AC Generators and DC GeneratorsDocument17 pagesDefine and Differentiate Between AC Generators and DC GeneratorsArafatNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument33 pagesDC MachineAnu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument9 pagesUnit IIIhariNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 DC MotorDocument13 pagesUnit 5 DC MotorSayali HadapNo ratings yet
- BEE R20 - Unit-1 (Ref-2)Document44 pagesBEE R20 - Unit-1 (Ref-2)Dhanush 413No ratings yet
- Uint 4 BEEDocument17 pagesUint 4 BEEshivprakashNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document85 pagesUnit 2Naitik NavyNo ratings yet
- CIA-2 Answer Key1Document11 pagesCIA-2 Answer Key1Electrical & Electroncic Engg HODNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument35 pagesDC Machinehs637717No ratings yet
- Dhiviyansh - Electric MotorsDocument19 pagesDhiviyansh - Electric MotorsDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- Module IIIDocument66 pagesModule IIIUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Machine OperationDocument94 pagesBasic Principles of Machine OperationRashmi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine II: EEEEC11 (3 - 0 - 2) Semester 4Document250 pagesElectrical Machine II: EEEEC11 (3 - 0 - 2) Semester 4sanjoni.jainNo ratings yet
- Presentation On DC GeneratorDocument36 pagesPresentation On DC GeneratorShubham prajeshNo ratings yet
- DC Machine & Ac MachineDocument19 pagesDC Machine & Ac MachineSankara nathNo ratings yet
- DC Drives-AV322-PEDocument15 pagesDC Drives-AV322-PEDarkSIDE FactsNo ratings yet
- Construction of DC GeneratorDocument58 pagesConstruction of DC GeneratorRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines (31-141 Page)Document111 pagesElectrical Machines (31-141 Page)judieNo ratings yet
- Name: Khushi Goyal Class: Xii Project: DC Generator Roll No.Document6 pagesName: Khushi Goyal Class: Xii Project: DC Generator Roll No.Khushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2Dr.Sakthivel SNo ratings yet
- Assignment EET374Document13 pagesAssignment EET374Ayyan MirNo ratings yet
- Basic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorDocument12 pagesBasic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorMaheedhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument18 pagesDC Machinesfmrayan66No ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFDocument29 pagesHTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFVigneshwaran J vNo ratings yet
- EPE491 - Chapter 6 - DC MachinesDocument14 pagesEPE491 - Chapter 6 - DC MachinesMajad RazakNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-Ch2-DcmotorDocument93 pagesElectrical Machines-Ch2-DcmotoradamwaizNo ratings yet
- Dumaguin Facma42l-Elep08 Module4Document7 pagesDumaguin Facma42l-Elep08 Module4Mike DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 and 2Document20 pagesLecture 1 and 2Bonface weitaraNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Simulation StudyDocument10 pagesExperimental and Simulation Studyمحمد عامرNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument43 pagesDC MotorKharlaNo ratings yet
- Construction of DC MotorDocument49 pagesConstruction of DC MotorAvanish Verma100% (1)
- Basic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorDocument15 pagesBasic Construction and Working of A DC GeneratorAnonymous QcCCBsNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ac DCDocument10 pagesAssignment Ac DCKamil KhairiNo ratings yet
- DC Motor MBZ 2020-21Document31 pagesDC Motor MBZ 2020-21lakshya.santaniNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument33 pagesDC MachineSlim ShaddysNo ratings yet
- D.C Machine: Anati Syahirah Jabatan Kejuruteraan Elektrik UTM Space, KLDocument35 pagesD.C Machine: Anati Syahirah Jabatan Kejuruteraan Elektrik UTM Space, KLAnati Syahirah Binti HedzirNo ratings yet
- Eme Practical PDFDocument68 pagesEme Practical PDFr kNo ratings yet
- Rotating Machines and Transformers Unit 2 DC GENERATOR CLASS NOTESDocument70 pagesRotating Machines and Transformers Unit 2 DC GENERATOR CLASS NOTESSEDHURAJA SNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument14 pagesDC GeneratorGlen DangaranNo ratings yet
- DC Machines: Answer: The DC Generators and DC Motors Have The Same General Construction. in FactDocument9 pagesDC Machines: Answer: The DC Generators and DC Motors Have The Same General Construction. in FacthavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Eee - 7Document30 pagesEee - 7TanvirNo ratings yet
- The Construction of A DC Generator Includes Several Key ComponentsDocument11 pagesThe Construction of A DC Generator Includes Several Key ComponentsMD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet
- Extra Notes DCmotorsDocument19 pagesExtra Notes DCmotorsashikinNo ratings yet
- DC Machine L04Document34 pagesDC Machine L04luckyNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument16 pagesDC GeneratorSK MD WALI ULLAH BULONNo ratings yet
- DC Motors Lecture NotesDocument71 pagesDC Motors Lecture Notesm.investment.kNo ratings yet
- TASK:2: 1.generators and Motors 2.trasnformersDocument24 pagesTASK:2: 1.generators and Motors 2.trasnformersFaiza Tabassam 546-FET/BSEE/F19No ratings yet
- AC GeneratorDocument7 pagesAC Generatoraswardi8756No ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument25 pagesDC MotorsBruceNo ratings yet
- Rotor and Stator Magnetic FieldsDocument4 pagesRotor and Stator Magnetic FieldsJOAO ESTEVAONo ratings yet
- Electric GeneratorDocument7 pagesElectric GeneratorRahul Shivu100% (1)
- DC Generators Jkuat 2024Document10 pagesDC Generators Jkuat 2024sikolia.wanjalaNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument25 pagesDC MachinesAbdallah EssamNo ratings yet
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet