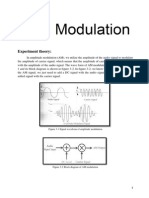
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modulation Index
Modulation Index
Uploaded by
Sid VibhorOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modulation Index
Modulation Index
Uploaded by
Sid VibhorCopyright:
Available Formats
2-13 MODULATION INDEX.
—This ratio of frequency deviation to frequency of the modulating signal is useful because it also describes the ratio of
amplitude to tone for the audio signal. These factors determine the number and spacing of the side frequencies of the
transmitted signal. The modulation index formula is shown below: Views (A) and (B) of figure 2-9 show the
frequency spectrum for various fm signals. In the four examples of view (A), the modulating frequency is constant;
the deviation frequency is changed to show the effects of modulation indexes of 0.5, 1.0, 5.0, and 10.0. In view (B)
the deviation frequency is held constant and the modulating frequency is varied to give the same modulation
indexes. Figure 2-9.—Frequency spectra of fm waves under various conditions. You can determine several facts about fm signals by studying the
frequency spectrum. For example, table 2-1 was developed from the information in figure 2-9. Notice in the top
spectrums of both views (A) and (B) that the modulation index is 0.5. Also notice as you look at the next lower
spectrums that the modulation index is 1.0. Next down is 5.0, and finally, the bottom spectrums have modulation
indexes of
You might also like
- CM 3Document39 pagesCM 3Janica Rheanne JapsayNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 4 Angle Modulation: (PM) (FM)Document11 pagesChapter No. 4 Angle Modulation: (PM) (FM)krishnagdeshpandeNo ratings yet
- 2 Unit 2 Angle ModulationDocument20 pages2 Unit 2 Angle ModulationvipularunpatilNo ratings yet
- AM Modulator: Experiment TheoryDocument14 pagesAM Modulator: Experiment Theorycluj24No ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation (FM) 5.1Document11 pagesFrequency Modulation (FM) 5.1vipularunpatilNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document14 pagesExperiment 3Nguyen Duc MinhNo ratings yet
- ExperimentDocument9 pagesExperimentsamar shaikhNo ratings yet
- Frequency ModulationDocument4 pagesFrequency ModulationHafid AlifiantoNo ratings yet
- Modulation and Delay Line Based Digital Audio EffectsDocument4 pagesModulation and Delay Line Based Digital Audio Effectsavi_weberNo ratings yet
- Analog and DigitalDocument26 pagesAnalog and DigitalMd Raton AliNo ratings yet
- Exp5 (Study of Frequency Modulation (FM) )Document4 pagesExp5 (Study of Frequency Modulation (FM) )TA TiusNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional UniversityDocument14 pagesLovely Professional Universityshailesh singhNo ratings yet
- FM ModulationDocument12 pagesFM ModulationPhyo Pyae Pyae ZawNo ratings yet
- Communication TheoryDocument50 pagesCommunication TheoryKamrun NaharNo ratings yet
- Over ModulationDocument5 pagesOver ModulationAbenk's BembenkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication Notes EE351-Course - Presentation - CH4Document244 pagesIntroduction To Communication Notes EE351-Course - Presentation - CH4FAISAL ALOTAIBINo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 17 Aug 2023 1Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 17 Aug 2023 1Uttam KumarNo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesFrequency Modulation Lecture NotesKaushik Patnaik100% (1)
- John Chowning - The Synthesis of Complex Audio SpectraDocument10 pagesJohn Chowning - The Synthesis of Complex Audio SpectraCharlex LópezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Topics Discussed in This SectionDocument37 pagesChapter Three: Topics Discussed in This SectionSolomon Tadesse AthlawNo ratings yet
- FM - Modulation DemodulationDocument26 pagesFM - Modulation DemodulationKunal MohiteNo ratings yet
- Exp3 (Study of DSB-SC Modulation)Document6 pagesExp3 (Study of DSB-SC Modulation)TA Tius100% (1)
- Reading 34: Frequency Modulation What Is Frequency Modulation?Document15 pagesReading 34: Frequency Modulation What Is Frequency Modulation?Mustafa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 5Document13 pagesExp 3 5JimVeluzPeñaflorida100% (1)
- Module 4 (Frequency Modulation)Document14 pagesModule 4 (Frequency Modulation)Sarah J SinfuegoNo ratings yet
- Amplitude ModulatorDocument4 pagesAmplitude ModulatorAmeet KumarNo ratings yet
- ELX 122 MODULE 4 Radio Frequency TransmittersDocument8 pagesELX 122 MODULE 4 Radio Frequency TransmittersErvert SoteraniaNo ratings yet
- Lab-Report Analogue Communications: Amplitude ModulationDocument11 pagesLab-Report Analogue Communications: Amplitude ModulationmahinNo ratings yet
- FM: Modulation Index: Application NoteDocument2 pagesFM: Modulation Index: Application NoteKarthik ItachiNo ratings yet
- FM Modulators: Experiment 7Document17 pagesFM Modulators: Experiment 7banduat83No ratings yet
- Topic 2 Analog ModulationDocument37 pagesTopic 2 Analog ModulationAfie FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation FMDocument16 pagesFrequency Modulation FMguerrouiNo ratings yet
- Khon Kaen University Department of Electrical Engineering CM - 03: Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Frequency Modulation Preliminary DiscussionDocument23 pagesKhon Kaen University Department of Electrical Engineering CM - 03: Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Frequency Modulation Preliminary DiscussionMichelNo ratings yet
- EE 3206, Exp 01Document7 pagesEE 3206, Exp 01Tahsin Zaman TalhaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Two Marks QuestionsDocument3 pagesUnit Ii Two Marks QuestionsmuthubeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EP301 - Communication System FundamentalsDocument32 pagesChapter 2 EP301 - Communication System FundamentalsPoit X Nincompoops0% (1)
- Ec8395 Ce QBDocument35 pagesEc8395 Ce QBpriyaNo ratings yet
- 078 Experiment#7 CSDocument10 pages078 Experiment#7 CSAsad saeedNo ratings yet
- Lab 07 FM Modulation: EEC3043 Communication SystemsDocument7 pagesLab 07 FM Modulation: EEC3043 Communication SystemsMaitha SaeedNo ratings yet
- AC 4 JntukDocument63 pagesAC 4 JntukKavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11castroDocument13 pagesExperiment 11castroHarry FabrosNo ratings yet
- Signals Using Bessel Function (Hangga Kusumah Yusuf) PDFDocument5 pagesSignals Using Bessel Function (Hangga Kusumah Yusuf) PDFHanggaKusumaYusufNo ratings yet
- PCS - Unit III - ASV - V1Document139 pagesPCS - Unit III - ASV - V1Anup S. Vibhute DITNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Frequency Modulation: Graphical Representation of Frequency Modulated WaveDocument2 pages2.5 Frequency Modulation: Graphical Representation of Frequency Modulated WaveShairryal AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Experiment Topic: AM Modulator: 3.1: Curriculum ObjectivesDocument14 pagesExperiment Topic: AM Modulator: 3.1: Curriculum ObjectivesBENSON MAKWABANo ratings yet
- Analog To AnalogDocument15 pagesAnalog To AnalogHarshit PandeyNo ratings yet
- A Reactance ModulatorDocument17 pagesA Reactance ModulatorAldrin Sagum100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - Amplitude ModulationDocument17 pagesLesson 3 - Amplitude ModulationYousef BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Angle ModulationDocument32 pagesChapter-3 Angle ModulationMd. Mamun Hossan 31No ratings yet
- Frequency ModulationDocument26 pagesFrequency ModulationYunita FtrynNo ratings yet
- Adc Lab Manual STUDENTDocument59 pagesAdc Lab Manual STUDENTramNo ratings yet
- OC Expt05 60002200083Document14 pagesOC Expt05 60002200083Raj mehtaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Using Optical LinkDocument11 pagesFrequency Modulation and Demodulation Using Optical LinkPriyansh RupaniNo ratings yet
- Empirical Formula For Propagation Loss Land Mobile Radio ServicesDocument9 pagesEmpirical Formula For Propagation Loss Land Mobile Radio ServicesAna Letícia AvelinoNo ratings yet
- ADC V NotesDocument110 pagesADC V Noteskrishnakk100No ratings yet
- Exp 7 - Com01lab - LimDocument8 pagesExp 7 - Com01lab - LimLIM Sheryl M.No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet