Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views3rd Nerve Localization
3rd Nerve Localization
Uploaded by
Mohamed HegazyThis document describes the localization of lesions along the oculomotor nerve (CN III) based on the clinical manifestations. It outlines locations including the oculomotor nucleus, subnuclei, fasciculus, subarachnoid space, cavernous sinus, superior orbital fissure, and orbit. Specific lesions are associated with isolated palsies of individual muscles or combinations of palsies along with involvement of other cranial nerves or neurological findings depending on the location along the nerve course.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- CN FanyDocument24 pagesCN FanymiaNo ratings yet
- 3RD CN - SeminarDocument49 pages3RD CN - Seminarabhishek tNo ratings yet
- Neurology ReviewDocument42 pagesNeurology ReviewShahnaaz Shah50% (2)
- Cranial NervesDocument30 pagesCranial NervesNia RwNo ratings yet
- BCSC 2014-2015Document2 pagesBCSC 2014-2015Rianda PutraNo ratings yet
- Draw It To Know It NotesDocument13 pagesDraw It To Know It Noteskat9210100% (1)
- 2 OverviewIII Iaat12i5p621Document4 pages2 OverviewIII Iaat12i5p621FadhilAfifNo ratings yet
- Articulo PDFDocument6 pagesArticulo PDFLuisa Vanessa CueroNo ratings yet
- Neuro LO W4Document55 pagesNeuro LO W4nilaahanifahNo ratings yet
- Leavitt 2005Document16 pagesLeavitt 2005qr7bht566gNo ratings yet
- OculoparesiasDocument31 pagesOculoparesiasCarmen Mansilla De LatorreNo ratings yet
- Kirsch 2017Document13 pagesKirsch 2017RalucaNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem SyndromDocument27 pagesBrain Stem SyndromSafitri MuhlisaNo ratings yet
- Divided Into Upper Part & Lower PartDocument20 pagesDivided Into Upper Part & Lower PartMohan KrishabiNo ratings yet
- (MicroB) Brainstem Lesions - Dr. Bravo (Nico Castillo)Document4 pages(MicroB) Brainstem Lesions - Dr. Bravo (Nico Castillo)miguel cuevas100% (1)
- Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDocument6 pagesCavernous Sinus ThrombosismcwnotesNo ratings yet
- Cranial NeuropathiesDocument74 pagesCranial NeuropathiesKevin Woodard100% (1)
- Cranial NervesDocument118 pagesCranial NervesGan'sNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Introduction To Neuro-OphthalmologyDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - Introduction To Neuro-Ophthalmology1330658No ratings yet
- Neurologic Examination: Cranial NervesDocument68 pagesNeurologic Examination: Cranial Nerves2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation of Acute Spinal Cord InjuryDocument6 pagesClinical Manifestation of Acute Spinal Cord InjurycpradheepNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesBrainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Brainstem LesionsDocument10 pagesClinical Approach To Brainstem LesionsJosé SánchezNo ratings yet
- Brainstem II: Eye Movements and Pupillary ControlDocument34 pagesBrainstem II: Eye Movements and Pupillary ControlhemendreNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Tomandl FinalDocument6 pagesCranial Nerves Tomandl FinalGaltieri OtavioNo ratings yet
- 1 Anterior Spinal Artery OcclusionDocument7 pages1 Anterior Spinal Artery OcclusionPrakashNo ratings yet
- Isolated Third Nerve PalsyDocument4 pagesIsolated Third Nerve PalsySora KerovaNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Handout 2006Document12 pagesNeuromuscular Handout 2006Windy MentariiNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Ischemia in Vertebral-Basilar T TerritoryDocument7 pagesModule 5. Ischemia in Vertebral-Basilar T Territorytarun956519No ratings yet
- Neurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Document158 pagesNeurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Muhammad Haneef100% (2)
- Spinal CordDocument15 pagesSpinal Cordsimi y100% (1)
- Referral of Diagnosis and Management of Erb-Duchenne PalsyDocument22 pagesReferral of Diagnosis and Management of Erb-Duchenne PalsyAshielaNo ratings yet
- False Localising Signs PDFDocument7 pagesFalse Localising Signs PDFSubhita FeninNo ratings yet
- Neuro LesionsDocument7 pagesNeuro Lesionskep1313100% (5)
- Gangguan Saraf KranialDocument30 pagesGangguan Saraf KranialWisnu Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Paraplegia Types Causes and DiagnosisDocument15 pagesParaplegia Types Causes and Diagnosismudzung100% (1)
- CBL-I Mod-IIDocument14 pagesCBL-I Mod-IIHammad AkramNo ratings yet
- Early Resolution of Third Nerve Palsy Following Endovascular Treatment of A Posterior Communicating Artery AneurysmDocument3 pagesEarly Resolution of Third Nerve Palsy Following Endovascular Treatment of A Posterior Communicating Artery AneurysmZakiyul FuadNo ratings yet
- HemiplegiaDocument30 pagesHemiplegiasarguss14100% (1)
- Brief Review Ulnar Nerve Palsy at The Elbow After General AnaesthesiaDocument5 pagesBrief Review Ulnar Nerve Palsy at The Elbow After General AnaesthesiaAnonymous ZAmlriyhNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus InjuryDocument8 pagesBrachial Plexus InjurylewienNo ratings yet
- Clincal Cases FinalDocument13 pagesClincal Cases FinalSharifa AbdulghaffarNo ratings yet
- Neuro Usmle EndpointDocument197 pagesNeuro Usmle EndpointIris BakerNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Review in Clinical (0753-1506)Document754 pagesComprehensive Review in Clinical (0753-1506)Abdurrahman HasanuddinNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Ophthalmology - Third Year Student - 2018Document126 pagesNeuro-Ophthalmology - Third Year Student - 2018Surat TanprawateNo ratings yet
- ParaplegiaDocument56 pagesParaplegiarashid38No ratings yet
- Responsi Saraf MyelopathyDocument85 pagesResponsi Saraf MyelopathykeratonNo ratings yet
- REMS Ophthalmology July 2022Document10 pagesREMS Ophthalmology July 2022vanisaezukuseNo ratings yet
- Ghostdogg Productions Presents - Dysfunction of The Cranial Nerves and Paralytic Strabismus - OnlinevrsnDocument56 pagesGhostdogg Productions Presents - Dysfunction of The Cranial Nerves and Paralytic Strabismus - OnlinevrsnAlistair HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Neorology Stroke ParalysisDocument1 pageNeorology Stroke ParalysisSher AliNo ratings yet
- CN DisordersDocument15 pagesCN DisordersMogtaba M HilalNo ratings yet
- BMS2 K10 Spinal Cord DiseaseDocument26 pagesBMS2 K10 Spinal Cord Disease103Juffry PrayogaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ophthalmology For Med Student - 2016Document120 pagesNeuro Ophthalmology For Med Student - 2016Surat Tanprawate100% (3)
- 19 Spinal CordDocument8 pages19 Spinal Cordkarar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Posterior Circulation Stroke: By: DR - Pardeep MandhanDocument68 pagesPosterior Circulation Stroke: By: DR - Pardeep MandhanSana ShafeeqNo ratings yet
- Eye Movements - AfradDocument9 pagesEye Movements - AfradAfradhRasheedNo ratings yet
3rd Nerve Localization
3rd Nerve Localization
Uploaded by
Mohamed Hegazy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesThis document describes the localization of lesions along the oculomotor nerve (CN III) based on the clinical manifestations. It outlines locations including the oculomotor nucleus, subnuclei, fasciculus, subarachnoid space, cavernous sinus, superior orbital fissure, and orbit. Specific lesions are associated with isolated palsies of individual muscles or combinations of palsies along with involvement of other cranial nerves or neurological findings depending on the location along the nerve course.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the localization of lesions along the oculomotor nerve (CN III) based on the clinical manifestations. It outlines locations including the oculomotor nucleus, subnuclei, fasciculus, subarachnoid space, cavernous sinus, superior orbital fissure, and orbit. Specific lesions are associated with isolated palsies of individual muscles or combinations of palsies along with involvement of other cranial nerves or neurological findings depending on the location along the nerve course.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pages3rd Nerve Localization
3rd Nerve Localization
Uploaded by
Mohamed HegazyThis document describes the localization of lesions along the oculomotor nerve (CN III) based on the clinical manifestations. It outlines locations including the oculomotor nucleus, subnuclei, fasciculus, subarachnoid space, cavernous sinus, superior orbital fissure, and orbit. Specific lesions are associated with isolated palsies of individual muscles or combinations of palsies along with involvement of other cranial nerves or neurological findings depending on the location along the nerve course.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
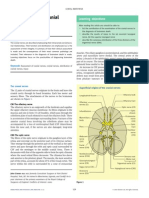
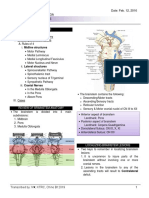
TABLE 8-2 The Localization of Oculomotor Nerve Lesions
Structure Involved Clinical Manifestation
Lesions affecting the third nerve nucleus
Oculomotor nucleus Ipsilateral complete CN III palsy; contralateral ptosis and superior
rectus paresis
Oculomotor subnucleus Isolated muscle palsy (e.g., inferior rectus)
Isolated levator subnucleus Isolated bilateral ptosis
Lesions affecting the third nerve fasciculus
Isolated fascicle Partial or complete isolated CN III palsy with or without pupil
involvement
Paramedian mesencephalon Plus-minus syndrome (ipsilateral ptosis and contralateral eyelid
retraction)
Fascicle, red nucleus, Ipsilateral CN III palsy with contralateral ataxia and tremor
superior cerebellar peduncle (Claude)
Fascicle and cerebral Ipsilateral CN III palsy with contralateral hemiparesis (Weber's)
peduncle
Fascicle and red Ipsilateral CN III palsy with contralateral choreiform movements
nucleus/substantia nigra (Benedikt)
Lesions affecting the third nerve in the subarachnoid space
Oculomotor nerve Complete CN III palsy with or without other CN involvement;
superior or inferior division palsy
Lesions affecting the third nerve in the cavernous sinus
Cavernous sinus lesion Painful or painless CN III palsy; with or without palsies of CN IV,
VI, and V1; CN III palsy with small pupil (Horner syndrome);
primary aberrant CN III regeneration
Lesions affecting the third nerve in the superior orbital fissure
Superior orbital fissure CN III palsy with or without palsies of CN IV, VI, V1; often with
lesion proptosis
Lesion affecting the third nerve in the orbit
Oculomotor nerve; superior CN III palsy; superior or inferior CN III branch palsy
or branch lesion
Optic nerve; orbital Visual loss; proptosis; swelling of lids; chemosis
structures
CN = cranial nerve.
You might also like
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- CN FanyDocument24 pagesCN FanymiaNo ratings yet
- 3RD CN - SeminarDocument49 pages3RD CN - Seminarabhishek tNo ratings yet
- Neurology ReviewDocument42 pagesNeurology ReviewShahnaaz Shah50% (2)
- Cranial NervesDocument30 pagesCranial NervesNia RwNo ratings yet
- BCSC 2014-2015Document2 pagesBCSC 2014-2015Rianda PutraNo ratings yet
- Draw It To Know It NotesDocument13 pagesDraw It To Know It Noteskat9210100% (1)
- 2 OverviewIII Iaat12i5p621Document4 pages2 OverviewIII Iaat12i5p621FadhilAfifNo ratings yet
- Articulo PDFDocument6 pagesArticulo PDFLuisa Vanessa CueroNo ratings yet
- Neuro LO W4Document55 pagesNeuro LO W4nilaahanifahNo ratings yet
- Leavitt 2005Document16 pagesLeavitt 2005qr7bht566gNo ratings yet
- OculoparesiasDocument31 pagesOculoparesiasCarmen Mansilla De LatorreNo ratings yet
- Kirsch 2017Document13 pagesKirsch 2017RalucaNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem SyndromDocument27 pagesBrain Stem SyndromSafitri MuhlisaNo ratings yet
- Divided Into Upper Part & Lower PartDocument20 pagesDivided Into Upper Part & Lower PartMohan KrishabiNo ratings yet
- (MicroB) Brainstem Lesions - Dr. Bravo (Nico Castillo)Document4 pages(MicroB) Brainstem Lesions - Dr. Bravo (Nico Castillo)miguel cuevas100% (1)
- Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDocument6 pagesCavernous Sinus ThrombosismcwnotesNo ratings yet
- Cranial NeuropathiesDocument74 pagesCranial NeuropathiesKevin Woodard100% (1)
- Cranial NervesDocument118 pagesCranial NervesGan'sNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Introduction To Neuro-OphthalmologyDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - Introduction To Neuro-Ophthalmology1330658No ratings yet
- Neurologic Examination: Cranial NervesDocument68 pagesNeurologic Examination: Cranial Nerves2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation of Acute Spinal Cord InjuryDocument6 pagesClinical Manifestation of Acute Spinal Cord InjurycpradheepNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesBrainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Brainstem LesionsDocument10 pagesClinical Approach To Brainstem LesionsJosé SánchezNo ratings yet
- Brainstem II: Eye Movements and Pupillary ControlDocument34 pagesBrainstem II: Eye Movements and Pupillary ControlhemendreNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Tomandl FinalDocument6 pagesCranial Nerves Tomandl FinalGaltieri OtavioNo ratings yet
- 1 Anterior Spinal Artery OcclusionDocument7 pages1 Anterior Spinal Artery OcclusionPrakashNo ratings yet
- Isolated Third Nerve PalsyDocument4 pagesIsolated Third Nerve PalsySora KerovaNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Handout 2006Document12 pagesNeuromuscular Handout 2006Windy MentariiNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Ischemia in Vertebral-Basilar T TerritoryDocument7 pagesModule 5. Ischemia in Vertebral-Basilar T Territorytarun956519No ratings yet
- Neurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Document158 pagesNeurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Muhammad Haneef100% (2)
- Spinal CordDocument15 pagesSpinal Cordsimi y100% (1)
- Referral of Diagnosis and Management of Erb-Duchenne PalsyDocument22 pagesReferral of Diagnosis and Management of Erb-Duchenne PalsyAshielaNo ratings yet
- False Localising Signs PDFDocument7 pagesFalse Localising Signs PDFSubhita FeninNo ratings yet
- Neuro LesionsDocument7 pagesNeuro Lesionskep1313100% (5)
- Gangguan Saraf KranialDocument30 pagesGangguan Saraf KranialWisnu Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Paraplegia Types Causes and DiagnosisDocument15 pagesParaplegia Types Causes and Diagnosismudzung100% (1)
- CBL-I Mod-IIDocument14 pagesCBL-I Mod-IIHammad AkramNo ratings yet
- Early Resolution of Third Nerve Palsy Following Endovascular Treatment of A Posterior Communicating Artery AneurysmDocument3 pagesEarly Resolution of Third Nerve Palsy Following Endovascular Treatment of A Posterior Communicating Artery AneurysmZakiyul FuadNo ratings yet
- HemiplegiaDocument30 pagesHemiplegiasarguss14100% (1)
- Brief Review Ulnar Nerve Palsy at The Elbow After General AnaesthesiaDocument5 pagesBrief Review Ulnar Nerve Palsy at The Elbow After General AnaesthesiaAnonymous ZAmlriyhNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus InjuryDocument8 pagesBrachial Plexus InjurylewienNo ratings yet
- Clincal Cases FinalDocument13 pagesClincal Cases FinalSharifa AbdulghaffarNo ratings yet
- Neuro Usmle EndpointDocument197 pagesNeuro Usmle EndpointIris BakerNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Review in Clinical (0753-1506)Document754 pagesComprehensive Review in Clinical (0753-1506)Abdurrahman HasanuddinNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Ophthalmology - Third Year Student - 2018Document126 pagesNeuro-Ophthalmology - Third Year Student - 2018Surat TanprawateNo ratings yet
- ParaplegiaDocument56 pagesParaplegiarashid38No ratings yet
- Responsi Saraf MyelopathyDocument85 pagesResponsi Saraf MyelopathykeratonNo ratings yet
- REMS Ophthalmology July 2022Document10 pagesREMS Ophthalmology July 2022vanisaezukuseNo ratings yet
- Ghostdogg Productions Presents - Dysfunction of The Cranial Nerves and Paralytic Strabismus - OnlinevrsnDocument56 pagesGhostdogg Productions Presents - Dysfunction of The Cranial Nerves and Paralytic Strabismus - OnlinevrsnAlistair HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Neorology Stroke ParalysisDocument1 pageNeorology Stroke ParalysisSher AliNo ratings yet
- CN DisordersDocument15 pagesCN DisordersMogtaba M HilalNo ratings yet
- BMS2 K10 Spinal Cord DiseaseDocument26 pagesBMS2 K10 Spinal Cord Disease103Juffry PrayogaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ophthalmology For Med Student - 2016Document120 pagesNeuro Ophthalmology For Med Student - 2016Surat Tanprawate100% (3)
- 19 Spinal CordDocument8 pages19 Spinal Cordkarar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Posterior Circulation Stroke: By: DR - Pardeep MandhanDocument68 pagesPosterior Circulation Stroke: By: DR - Pardeep MandhanSana ShafeeqNo ratings yet
- Eye Movements - AfradDocument9 pagesEye Movements - AfradAfradhRasheedNo ratings yet