Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Embryology
Embryology
Uploaded by
Maaz Nasim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pages1. The document discusses the embryological development of various organs systems from the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm).
2. It describes the development of the digestive system including the derivatives of the foregut, midgut, and hindgut as well as changes in the midgut during development.
3. Fetal circulation changes after birth are discussed including the closure of vessels and formation of ligaments from previously patent structures. Common congenital anomalies are also summarized.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses the embryological development of various organs systems from the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm).
2. It describes the development of the digestive system including the derivatives of the foregut, midgut, and hindgut as well as changes in the midgut during development.
3. Fetal circulation changes after birth are discussed including the closure of vessels and formation of ligaments from previously patent structures. Common congenital anomalies are also summarized.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesEmbryology
Embryology
Uploaded by
Maaz Nasim1. The document discusses the embryological development of various organs systems from the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm).
2. It describes the development of the digestive system including the derivatives of the foregut, midgut, and hindgut as well as changes in the midgut during development.
3. Fetal circulation changes after birth are discussed including the closure of vessels and formation of ligaments from previously patent structures. Common congenital anomalies are also summarized.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Embryology
1st term
Derivatives of :
1- Ectoderm.
2- Mesoderm
3- Endoderm
The 2nd term
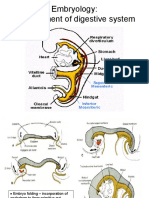
1- derivatives of the forgut:
a- esophagus
b- stomach
c- upper 1½ parts of duodenum
d- pancereas
e- liver
f- spleen
2-derivatives of midgut:
a-lower 2 ½ parts of duodenum
b- jejunum – ileum
c- caecum-appendix
d- ascending colon – right colic flexture
e- right 2/3 of transverse colon
3-derivatives of hindgut:
a- left colic flexture
b- left 1/3 of the transverse colon
c- descending colon – sigmoid colon
d- rectum – upper part of the anal canal
4- derivatives of cloaca ( lower end of hindgut)
a- rectum
b- upper part of anal canal
c- urinary bladder except trigone
d- prostatic urethra in male
e- all female urethra
Development of pancereas : from foregut by 2 buds: urethral pancereas
,dorsal pancereas
Development of the liver: from foregut by 1 bud (liver bud=pars
hepatica)
Changes during development of midgut (4 stages )
1- pre-hernation stage
2- hernation stage
3- post hernation stage
4- rotation(anticlock wise rotates 270 degree
Development of anal canal
1- upper part: from endoderm of hindgut (posterior part of cloaca)
2- lower part: from ectoderm (proctodeum)
development of interarterial septum: from
1- septum premium
2- septum secondum foramen ovals between 2 atria
at birth
closure of foramen ovals- fossa ovalis
septum perimum- margins of fossa ovalis
septum secondum floor of fossa ovalis
Changes in fetal circulation after birth:
1- closure of umbilical vein ligamentum teres
2- closure of ductus venosus ligamentum venosum
3- closure of ductus anteriosus ligamentum anteriosus
4- closure of foramen ovalis fossa ovalis
Congenital anomalies of the kidney
1- pelvic kidney 2- poly cyctic kidney 3- hourse shoe kidney 4- bifid
ureter
5- cake like kidney 6- absence of 1 kidney 7- abeerant renal artery
Development of respiratiory system
By bus from front of upper part of foregut (endoderm)
Bud elongates(trachea) and divides into 2 lung buds (left-right)
Each divides several times (18 generations)
Giving bronchi and alveoli
Development of vertebral column
From mesoderm (somites)
From medial parts ( sclerotomes)
* Each vertebra is formed by the fusion of the adjacent parts of somites
* intervertebral disc: nucleus pulposus develops from notochord
reminants
Congenetal abnormalities of vertebral column(types of spina bifidus)
1- spina bifida occulta
2- spina bifida with meningocele
3- spina bifida with meningomyelocele
Development of the uterus
From mesoderm by paramesonephric ducts (mullerian ducts)
Fusion to form
Uterovaginal vanal
Which gives
1- uterine tubes
2- uterus
3- upper vagina
Congenital anomalities of the uterus
1- abnormal position (retro verted – retro flexed )
2- double uterus
3- septum in the uterus
4- atresia
Development of the testis
From mesoderm of intermediate cell mass seminiferous tubules
Spermatogonia develops from yolk sac
Desecent of testis from abdomin into scrotum :
1- contraction of gubernaculums
2- increase intra abdominal pressure
3- hormones
4- presence of processus vaginalis
Anomalies in the development of the testis
1- undescended testis in the abdomin or in the inguinal canal
2- ectopic testis (an abnormal site)
a- in the thigh
b- abdominal wall
c- perineum
You might also like
- DHA 300 Questions For PharmacistDocument44 pagesDHA 300 Questions For PharmacistZahra83% (40)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer-CompleteDocument66 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer-Completeposh003892% (39)
- Ain Shams MCQDocument84 pagesAin Shams MCQAhmed M. Haroun67% (6)
- Ma. Elizabeth F. FontanillaDocument48 pagesMa. Elizabeth F. Fontanillatam mei100% (1)
- 600 MCQ With Answers 2Document72 pages600 MCQ With Answers 2Maaz Nasim73% (11)
- Development of GITDocument61 pagesDevelopment of GITEsther MathengeNo ratings yet
- JSMU Semester 3 Embrology McqsDocument12 pagesJSMU Semester 3 Embrology McqsNazia WasimNo ratings yet
- 3.abdomen and Thorax - OSPEDocument16 pages3.abdomen and Thorax - OSPEArjun KumarNo ratings yet
- Pancreas A PDFDocument36 pagesPancreas A PDFtjqch6r2x8No ratings yet
- Embriologi PDFDocument97 pagesEmbriologi PDFbarbiemeNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive OrgansDocument32 pagesFemale Reproductive Organsapi-19916399100% (1)
- 5 6231171839033344469 PDFDocument194 pages5 6231171839033344469 PDFxxxxNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument40 pagesPancreasMuthannah MarawanNo ratings yet
- Repro FinalDocument60 pagesRepro FinalSamdisha DebraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraHemanta PunNo ratings yet
- Development of Gut Tube Fore GutDocument52 pagesDevelopment of Gut Tube Fore GutSusan SarkerNo ratings yet
- OBGYN Self ReviewDocument91 pagesOBGYN Self ReviewjyothiNo ratings yet
- Breech PresentationDocument40 pagesBreech PresentationShuhada Wahab100% (3)
- POP June 10,2021 1Document48 pagesPOP June 10,2021 1Kerod AbebeNo ratings yet
- 28-29 - BMS305 - Anatomy - Development of Urinary system-Lect-7-8-Spring 2024Document28 pages28-29 - BMS305 - Anatomy - Development of Urinary system-Lect-7-8-Spring 2024kareemosama9916No ratings yet
- Urogenital and Reproductive Female. Carangian and SiribanDocument14 pagesUrogenital and Reproductive Female. Carangian and SiribanKariza AbuNo ratings yet
- Embryology: The Anatomic Basis of Fetal MedicineDocument55 pagesEmbryology: The Anatomic Basis of Fetal Medicinejidat lawak100% (1)
- Genital Prolapse: Unit - V 2K15Document58 pagesGenital Prolapse: Unit - V 2K15sushma nakkinaNo ratings yet
- 41-42-BMS305 - Anatomy - Embryology of Genital System - Lect 9-10-Spring 2024Document29 pages41-42-BMS305 - Anatomy - Embryology of Genital System - Lect 9-10-Spring 2024kareemosama9916No ratings yet
- 7th Lecture The Third Week of DevelopmentDocument17 pages7th Lecture The Third Week of DevelopmentHussein Al SaediNo ratings yet
- Dev of Reproductive SystemDocument75 pagesDev of Reproductive SystemAravindkumar ManivannanNo ratings yet
- Abdomen CAP Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesAbdomen CAP Questions and AnswersRathnaNo ratings yet
- UvpDocument43 pagesUvpgaasheNo ratings yet
- Scrotum: DR / Kamel Male Genital System / General Surgery Page1Document52 pagesScrotum: DR / Kamel Male Genital System / General Surgery Page1Mahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Development of Digestive and Respiratory SystemDocument48 pagesDevelopment of Digestive and Respiratory SystemFitria PuspariniNo ratings yet
- 22 - Development of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocument14 pages22 - Development of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 303 Development of Genital SystemDocument112 pages303 Development of Genital SystemHarini ThiruNo ratings yet
- Syncytiotrophoblast & The Decidua. This Is The Cytotrophoblastic ShellDocument6 pagesSyncytiotrophoblast & The Decidua. This Is The Cytotrophoblastic Shellanimebests9No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Embryology of The Female Genital SystemDocument86 pagesAnatomy & Embryology of The Female Genital SystemyazNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive Tract: by Ekaterina Tchmoutina R1 3/11/2015Document27 pagesCongenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive Tract: by Ekaterina Tchmoutina R1 3/11/2015zahalina90No ratings yet
- Embryology Urogenital System: DiagramsDocument36 pagesEmbryology Urogenital System: DiagramsBhavya KansalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ahlam Al-Kharabsheh: Assistant Professor, OBS & GYN Department Mu'tah UniversityDocument36 pagesDr. Ahlam Al-Kharabsheh: Assistant Professor, OBS & GYN Department Mu'tah Universityraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Modul of Reproductive SystemDocument66 pagesModul of Reproductive SystemagungNo ratings yet
- OB - TransesDocument112 pagesOB - TransesAldwin BagtasNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Organ ProlapseDocument5 pagesPelvic Organ Prolapsecgao30No ratings yet
- Embryology and Anatomy of The Gastrointestinal Tract NASPGHANDocument14 pagesEmbryology and Anatomy of The Gastrointestinal Tract NASPGHANOana OanapNo ratings yet
- Gyna UNIT IDocument141 pagesGyna UNIT ISúñîl BîrãdãräNo ratings yet
- 17 Urogenital PDFDocument15 pages17 Urogenital PDFArnytha VebrianiNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument40 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- SHRIYADocument27 pagesSHRIYAsakshi.garg320No ratings yet
- Urogenital System DevelopmentDocument107 pagesUrogenital System DevelopmentTadesse MuhammedNo ratings yet
- I 1.dystociaDocument3 pagesI 1.dystociaAllan NacinoNo ratings yet
- Kub Gyne Anemia PDFDocument117 pagesKub Gyne Anemia PDFWaterfall ShapelessNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology UterusDocument65 pagesAnatomy and Embryology UterusashwiniNo ratings yet
- NEET PG 2016 Question Paper With SolutionsDocument1,914 pagesNEET PG 2016 Question Paper With SolutionsmedpoxNo ratings yet
- Exam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersDocument118 pagesExam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersIsmail Ahmed0% (1)
- Endodermal Derivatives, Formation of The Gut and Its Subsequent RotationDocument14 pagesEndodermal Derivatives, Formation of The Gut and Its Subsequent RotationmikeNo ratings yet
- Embryology and Anatomy of The Gastrointestinal TractDocument58 pagesEmbryology and Anatomy of The Gastrointestinal TractYitancloud100% (1)
- Urinary System: J.-H. LueDocument42 pagesUrinary System: J.-H. LueTom WuNo ratings yet
- Development of Gastrointestinal TractDocument28 pagesDevelopment of Gastrointestinal TractSaif100% (1)
- Embryology: Lecture 2: Development and Anomalies of Urinary TractDocument35 pagesEmbryology: Lecture 2: Development and Anomalies of Urinary TractMohamed AlmetwaliNo ratings yet
- Development of Digestive TractDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Digestive TractSulochan Ssplendid Splinterr LohaniNo ratings yet
- Nephrologi: - PWM Olly Indrajani - 18-3-2015Document128 pagesNephrologi: - PWM Olly Indrajani - 18-3-2015NandatholoeNo ratings yet
- MCN Jane Lou GargaritanoDocument918 pagesMCN Jane Lou GargaritanoJanelle Estrabela GargaritanoNo ratings yet
- Abdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyDocument29 pagesAbdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyRathnaNo ratings yet
- Coupling of Monoclonal Antibodies With Fluorophores: Rosaria P. HauglandDocument17 pagesCoupling of Monoclonal Antibodies With Fluorophores: Rosaria P. HauglandMaaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Microarrays: Label and Label-Free Detection Techniques For Protein MicroarraysDocument17 pagesMicroarrays: Label and Label-Free Detection Techniques For Protein MicroarraysMaaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Serum Free Cell CultureDocument10 pagesSerum Free Cell CultureMaaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Dinesh - SopDocument2 pagesDinesh - SopMaaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Litdoclsn6-7 20110830221427Document4 pagesLitdoclsn6-7 20110830221427Maaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Countable Uncountable gr8AmbitionZ PDFDocument4 pagesAdjectives Countable Uncountable gr8AmbitionZ PDFSelvaraj VillyNo ratings yet
- 1 General Pharmacology MCQSDocument7 pages1 General Pharmacology MCQSMaaz Nasim83% (6)
- Dha Exam 10-11-2013Document2 pagesDha Exam 10-11-2013Shan Shani78% (18)
- PomgraniteDocument6 pagesPomgraniteMaaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 3Document295 pagesMathematics 3Maaz Nasim100% (1)
- Gen Kiyani and AmericaDocument4 pagesGen Kiyani and AmericaMaaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Q: Why Aminoglycosides Are Bactericidal While All Other Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Are Bacteriostatic?Document1 pageQ: Why Aminoglycosides Are Bactericidal While All Other Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Are Bacteriostatic?Maaz NasimNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesHuman Digestive Systemfatimah17No ratings yet
- CIE-10 RIPS - Xls - 1Document547 pagesCIE-10 RIPS - Xls - 1john_trianaNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesAnaPhy Digestive SystemKiara Catelyn RetretaNo ratings yet
- Joint Clinico-Pathologic Conference: October 3, 2008Document50 pagesJoint Clinico-Pathologic Conference: October 3, 2008ianjohn724No ratings yet
- GI and Hemagology & Oncology QuizDocument41 pagesGI and Hemagology & Oncology Quizwalt65No ratings yet
- Muscular Tube Lined With Mucous Membrane That Is Continuous With The External Skin at The Mouth and at The AnusDocument90 pagesMuscular Tube Lined With Mucous Membrane That Is Continuous With The External Skin at The Mouth and at The AnusRamaNo ratings yet
- Las Science 8 m1Document9 pagesLas Science 8 m1Diamond CrsktNo ratings yet
- Ileus Obstruksi PDFDocument20 pagesIleus Obstruksi PDFherfikaNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability of Raw and Cooked EggsDocument7 pagesBioavailability of Raw and Cooked EggsVirtuosoXNo ratings yet
- Test Questions: A. Cardiovascular System and LymphaticsDocument24 pagesTest Questions: A. Cardiovascular System and LymphaticsLunna Cruz100% (1)
- Female RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFDocument129 pagesFemale RTOG Normal Pelvis Atlas PDFsusdoctor100% (1)
- Enema ModuleDocument78 pagesEnema ModuleRomelyn Duque DellomesNo ratings yet
- Examination of AbdomenDocument67 pagesExamination of Abdomenvikram kumarNo ratings yet
- Degestive and Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesDegestive and Skeletal SystemAsad MehmoodNo ratings yet
- June 19 - QPDocument36 pagesJune 19 - QPDiva NoorzaiNo ratings yet
- Different Types of EnemaDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of EnemaIlu AbrahimNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Norman V.Valera, MD, DpsaDocument81 pagesDigestive System: Norman V.Valera, MD, DpsaKarl PunzalNo ratings yet
- Gupta Divye Module3 Appendix Block5 Subgrp1Document50 pagesGupta Divye Module3 Appendix Block5 Subgrp1Shashi Royal TNNo ratings yet
- Urologic Principles and Practice 2nd EditionDocument692 pagesUrologic Principles and Practice 2nd EditionRonuve RonuveNo ratings yet
- Colonoscopy GESA3Document3 pagesColonoscopy GESA3Tero NuppiNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDocument65 pagesCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Barium EnemaDocument13 pagesBarium Eneman100% (2)
- Q2 ScienceDocument6 pagesQ2 ScienceRosa MariaNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Digestive SystemDocument70 pagesHistology of The Digestive Systemiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- سكيمة ممكن تفكرك ب 70 % من MCQ المنهج كله وتتقرى ف 10 دقايق بسDocument8 pagesسكيمة ممكن تفكرك ب 70 % من MCQ المنهج كله وتتقرى ف 10 دقايق بسNoona JamalNo ratings yet
- Gastro 2014 Handout Wo Images PDFDocument188 pagesGastro 2014 Handout Wo Images PDFmike huntNo ratings yet
- Mini Medical DictionaryDocument106 pagesMini Medical DictionarySabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Vegan DogsDocument64 pagesVegan DogsOuerGentorix50% (2)
- Chronotherapeutic Drug Delivery System of FlurbiprofenDocument99 pagesChronotherapeutic Drug Delivery System of FlurbiprofenVenkatesh GaviniNo ratings yet
- Manas Yog Sadhna Magzine EngDocument24 pagesManas Yog Sadhna Magzine EngKamal RajharshaNo ratings yet