Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An Intrinsic Control Elemen..
An Intrinsic Control Elemen..
Uploaded by
b12071973Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Memorial City Mall MapDocument1 pageMemorial City Mall Maptruechris89No ratings yet
- JSA Template 2017-05-30 Powder Actuated ToolsDocument19 pagesJSA Template 2017-05-30 Powder Actuated ToolsJayvee Baradas Valdez100% (2)
- FC AntybodyDocument8 pagesFC AntybodyahmaszitimNo ratings yet
- IFN yDocument1 pageIFN ytuuuiiitNo ratings yet
- Cellular Cofactors For HIV-1 Transcription: IntegrationDocument7 pagesCellular Cofactors For HIV-1 Transcription: IntegrationDevi OktafianiNo ratings yet
- Bromodomain Protein brd4 Is Required For Estrogen Receptor Dependent Enhancer Activation and Gene TranscriptionDocument10 pagesBromodomain Protein brd4 Is Required For Estrogen Receptor Dependent Enhancer Activation and Gene TranscriptionParvinder McCartneyNo ratings yet
- Retrovirus Translation Initiation: Issues and Hypotheses Derived From Study of HIV-1Document9 pagesRetrovirus Translation Initiation: Issues and Hypotheses Derived From Study of HIV-1ThorieForestNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Journal of Biological ChemistryDocument33 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Journal of Biological Chemistryro111111No ratings yet
- 2019 Identifying Novel Targets of Oncogenic EGF Receptor Signaling in Lung Cancer Through Global PhosphoproteomicsDocument16 pages2019 Identifying Novel Targets of Oncogenic EGF Receptor Signaling in Lung Cancer Through Global Phosphoproteomicsmorteza hosseiniNo ratings yet
- Structural Aspects of Drug Resistance and Inhibition of HIV-1 Reverse TranscriptaseDocument34 pagesStructural Aspects of Drug Resistance and Inhibition of HIV-1 Reverse TranscriptaseNam KitNo ratings yet
- tmpBEE5 TMPDocument9 pagestmpBEE5 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Salicylic Acid-Mediated Innate Immunity in Arabidopsis Is Regulated by SIZ1 SUMO E3 LigaseDocument12 pagesSalicylic Acid-Mediated Innate Immunity in Arabidopsis Is Regulated by SIZ1 SUMO E3 LigaseZain BaderNo ratings yet
- Wang 2014Document24 pagesWang 2014Carlos Manuel OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Intracellular Expression of IRF9 Stat Fusion Protein Overcomes The Defective Jak-Stat Signaling and Inhibits HCV RNA ReplicationDocument12 pages2010 - Intracellular Expression of IRF9 Stat Fusion Protein Overcomes The Defective Jak-Stat Signaling and Inhibits HCV RNA ReplicationFernando Fernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 31Document12 pages31Yovan BlancoNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-1993-Wu-9980-5Document6 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-1993-Wu-9980-5Made YudanaNo ratings yet
- Structural Insights Into The Interaction of A Monoclonal Antibody and Nodal Peptides by STD-NMR SpectrosDocument8 pagesStructural Insights Into The Interaction of A Monoclonal Antibody and Nodal Peptides by STD-NMR Spectros6gtnsvdw72No ratings yet
- Journal of Molecular Graphics and ModellingDocument13 pagesJournal of Molecular Graphics and ModellingPencari IlmuNo ratings yet
- Paper Gag TedburyDocument31 pagesPaper Gag TedburyfaisalnadeemNo ratings yet
- Structural Plasticity of Green Fluorescent Protein To Amino Acid Deletions and Fluorescence Rescue by Folding-Enhancing MutationsDocument11 pagesStructural Plasticity of Green Fluorescent Protein To Amino Acid Deletions and Fluorescence Rescue by Folding-Enhancing MutationsIsmael Cervantes ChavezNo ratings yet
- Traduccuón en ProcariotasDocument21 pagesTraduccuón en Procariotasmaria fernanda jarquin marquezNo ratings yet
- Application of Recombinant DNATechnologies On Sub-Cloning of Transcriptional Co-FactorDocument6 pagesApplication of Recombinant DNATechnologies On Sub-Cloning of Transcriptional Co-FactorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0968089606009898 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0968089606009898 Mainjipir64332No ratings yet
- 2_5262827640598841838Document18 pages2_5262827640598841838am55eer55No ratings yet
- Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of IRF3 in Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus)Document8 pagesMolecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of IRF3 in Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus)Rizka Rahmana PutriNo ratings yet
- 1,4-BENZOQUINONE (para-QUINONE) : 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataDocument6 pages1,4-BENZOQUINONE (para-QUINONE) : 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- J. Virol. 1988 Bienkowska Szewczyk 3068 72Document5 pagesJ. Virol. 1988 Bienkowska Szewczyk 3068 72zeeshan aliNo ratings yet
- The Mechanistic Basis For Noncompetitive Ibogaine - Inhibition of Serotonin and Dopamine TransportersDocument11 pagesThe Mechanistic Basis For Noncompetitive Ibogaine - Inhibition of Serotonin and Dopamine TransportersternyNo ratings yet
- 2017 Article 141 Part1Document5 pages2017 Article 141 Part1Karina MonasaNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry: A B A C D C A C D A e A C ADocument13 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry: A B A C D C A C D A e A C AArturo T. Sánchez-MoraNo ratings yet
- A Novel Mechanism of Eukaryotic TranslationDocument10 pagesA Novel Mechanism of Eukaryotic Translationchar462No ratings yet
- TMP 662Document11 pagesTMP 662FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Toxicology LettersDocument32 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Toxicology LettersOmnia FayedNo ratings yet
- tmpC9BA TMPDocument8 pagestmpC9BA TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Codon SelectionDocument9 pagesCodon SelectionKamal JamesNo ratings yet
- Wu2018 VteDocument11 pagesWu2018 VteSofia UribeNo ratings yet
- Cytokine Expression Profile in The Bone-Anchored Hearing System: 12-Week Results From A Prospective Randomized, Controlled StudyDocument11 pagesCytokine Expression Profile in The Bone-Anchored Hearing System: 12-Week Results From A Prospective Randomized, Controlled StudyBagis Emre GulNo ratings yet
- Plant Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homologs Impinge oDocument14 pagesPlant Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homologs Impinge oMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- BJP7 v. 170Document30 pagesBJP7 v. 170LourdesNo ratings yet
- Neurobiology of Pain: June Bryan de La Peña, Zachary T. Campbell TDocument6 pagesNeurobiology of Pain: June Bryan de La Peña, Zachary T. Campbell TPavithra MohanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Papers Merged 40 57Document18 pages2022 Papers Merged 40 57Yeannie YapNo ratings yet
- Linder 1999Document8 pagesLinder 1999EvanEftNo ratings yet
- Resistance Response of Indonesian Native Orchids To Odontoglossum Ringspot VirusDocument7 pagesResistance Response of Indonesian Native Orchids To Odontoglossum Ringspot VirusRafiq FananiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Plant Physiology: Yee-Min Kwan, Sariah Meon, Chai-Ling Ho, Mui-Yun WongDocument6 pagesJournal of Plant Physiology: Yee-Min Kwan, Sariah Meon, Chai-Ling Ho, Mui-Yun WongroseNo ratings yet
- EIF4E Knoclout MiceDocument28 pagesEIF4E Knoclout MiceLaura GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mutations in The Arabidopsis ROL17/isopropylmalate Network, and Suppress The Root Hair Cell Development MutantDocument11 pagesMutations in The Arabidopsis ROL17/isopropylmalate Network, and Suppress The Root Hair Cell Development MutantTheo KhouryNo ratings yet
- Ayissiowona2013 JQ1Document7 pagesAyissiowona2013 JQ1iforaNo ratings yet
- 2016 - The Unique Role of STAT2 in Constitutive and IFN-Induced Transcription and Antiviral ResponsesDocument11 pages2016 - The Unique Role of STAT2 in Constitutive and IFN-Induced Transcription and Antiviral ResponsesFernando Fernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Interaction of The Epigenetic Integrator UHRF1 With The MYST Domain of TIP60 Inside The CellDocument14 pagesInteraction of The Epigenetic Integrator UHRF1 With The MYST Domain of TIP60 Inside The CellWaseemNo ratings yet
- 016 Scas Abstracts Listed Alphabetically by Abstractspdf 19 2016 Scas AbstractsDocument25 pages016 Scas Abstracts Listed Alphabetically by Abstractspdf 19 2016 Scas AbstractsdssagNo ratings yet
- Nao PerderDocument5 pagesNao PerderSara SantosNo ratings yet
- tmpE31A TMPDocument14 pagestmpE31A TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- 5. Antagonist peptides of human interferon-α2b isolated from phage 2006Document7 pages5. Antagonist peptides of human interferon-α2b isolated from phage 2006Leo SirsNo ratings yet
- The Therapeutic Age of The Neonatal FC Receptor: ImmunologyDocument18 pagesThe Therapeutic Age of The Neonatal FC Receptor: ImmunologyonlydarkheartNo ratings yet
- IGF-I Inhibition of Apoptosis Is Associated With Decreased Expression of Prostate Apoptosis Response-4Document9 pagesIGF-I Inhibition of Apoptosis Is Associated With Decreased Expression of Prostate Apoptosis Response-4sonjeonggyu87No ratings yet
- PI3K/Akt Signaling Transduction Pathway, Erythropoiesis and Glycolysis in Hypoxia (Review)Document9 pagesPI3K/Akt Signaling Transduction Pathway, Erythropoiesis and Glycolysis in Hypoxia (Review)pasifikaNo ratings yet
- Publication Tlyp-1Document17 pagesPublication Tlyp-1Samir AcherarNo ratings yet
- Paper para Critica LlamasDocument15 pagesPaper para Critica LlamasGómez PattyNo ratings yet
- Andrew Hu, 2018Document17 pagesAndrew Hu, 2018franciscaNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0021925818816519Document7 pagesPi Is 0021925818816519Claudio IngrossoNo ratings yet
- Research Article Pleurotus Eryngii Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-InducedDocument7 pagesResearch Article Pleurotus Eryngii Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-InducedkierkegardNo ratings yet
- SN Location Machine/Equipment Make Frequency Paln/Actual: Yearly Maintenance Plan - 2021Document2 pagesSN Location Machine/Equipment Make Frequency Paln/Actual: Yearly Maintenance Plan - 2021RiyaZ55No ratings yet
- National Institute of Textile Engineering and Research (NITER)Document6 pagesNational Institute of Textile Engineering and Research (NITER)shahadat hossainNo ratings yet
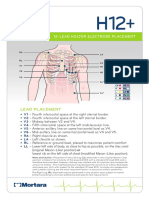
- ECG Holter H12+Document2 pagesECG Holter H12+Dhilah 9246No ratings yet
- ELC270 Proposal WritingDocument15 pagesELC270 Proposal WritingAqil FarisNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Platinum and Palladium From Scrap Automotive Catalytic ConvertersDocument11 pagesRecovery of Platinum and Palladium From Scrap Automotive Catalytic ConvertersMr RhodiumNo ratings yet
- Engineering Manual: Variable Refrigerant Flow Outdoor Units 6.0 To 42.0 TonsDocument156 pagesEngineering Manual: Variable Refrigerant Flow Outdoor Units 6.0 To 42.0 TonsNey Raul Benji JoaquinNo ratings yet
- The Dark Side of ConscientiousnessDocument15 pagesThe Dark Side of ConscientiousnessMerlin PitNo ratings yet
- NK-O3 Manuals - Rev 2.6Document106 pagesNK-O3 Manuals - Rev 2.6greatenick.nbNo ratings yet
- Komiyama Et Al., (2008) Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests A ReviewDocument11 pagesKomiyama Et Al., (2008) Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests A ReviewVandhi Amali100% (1)
- IOCLDocument94 pagesIOCLDebabrat SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 RecruitmentDocument14 pagesModule 6 RecruitmentJoyce Ann Aj TomaleNo ratings yet
- The Glymphatic Pathway in Neurological DisordersDocument20 pagesThe Glymphatic Pathway in Neurological DisordersTeresa BeckNo ratings yet
- Men's Fitness - April 2017 ZADocument116 pagesMen's Fitness - April 2017 ZAjustin VerhoogNo ratings yet
- Fish Processing: By: Laureno, Divina Villaver Dela Cruz, Cedrick P. Estor, Vanessa RDocument24 pagesFish Processing: By: Laureno, Divina Villaver Dela Cruz, Cedrick P. Estor, Vanessa REstor, Vanessa R.No ratings yet
- Orbino, Frances Anne N. 4th Rot FdarDocument2 pagesOrbino, Frances Anne N. 4th Rot FdarFrances OrbinoNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesDocument11 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- CSEC Building and Furniture Technology Study GuideDocument131 pagesCSEC Building and Furniture Technology Study Guidealphonsoashanti473No ratings yet
- Land Reforms in IndiaDocument22 pagesLand Reforms in IndiaiRagpickerNo ratings yet
- Woodsynergy Inc.: Integrating IT Into Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesWoodsynergy Inc.: Integrating IT Into Supply Chain ManagementAarushi BhargavaNo ratings yet
- PX MicDocument6 pagesPX MicSoraire LucasNo ratings yet
- Energy ConservationDocument3 pagesEnergy ConservationakifliaqatNo ratings yet
- Roastilino Manual v2 1 21 6 13Document9 pagesRoastilino Manual v2 1 21 6 13Bigman74066No ratings yet
- Retrofit Guidelines For Dupont Isceon 9 Series RefrigerantsDocument20 pagesRetrofit Guidelines For Dupont Isceon 9 Series RefrigerantsaNo ratings yet
- Y2 Series: Three Phase Cast Iron MotorDocument4 pagesY2 Series: Three Phase Cast Iron MotorMark Christian TorresNo ratings yet
- All at Sea Caribbean 0917Document112 pagesAll at Sea Caribbean 0917Scott NeumanNo ratings yet
- At Home Training Guide: Workout BuilderDocument22 pagesAt Home Training Guide: Workout BuilderAnonymous NO0urGNo ratings yet
- Textile Testing International Total Testing Solutions Inc.: Vendor InformationDocument4 pagesTextile Testing International Total Testing Solutions Inc.: Vendor InformationJawad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Feb28.2015 B.docmandatory Employment of Lifeguards in Public Pools SoughtDocument2 pagesFeb28.2015 B.docmandatory Employment of Lifeguards in Public Pools Soughtpribhor2No ratings yet
An Intrinsic Control Elemen..
An Intrinsic Control Elemen..
Uploaded by
b12071973Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
An Intrinsic Control Elemen..
An Intrinsic Control Elemen..
Uploaded by
b12071973Copyright:
Available Formats
An intrinsic control element for translational ini... [Mol Microbiol. 2002] ... http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.
gov/pubmed/11967073
PubMed
U.S. National Library of Medicine
National Institutes of Health
Display Settings: Abstract
Mol Microbiol. 2002 Apr;44(1):119-30.
An intrinsic control element for translational initiation in class 1
integrons.
Hanau-Berçot B, Podglajen I, Casin I, Collatz E.
INSERM EMI 0004 - LRMA, Université Paris VI, 15, rue de l'Ecole de Médecine, 75270 Paris Cedex 06, France.
Abstract
Integrons are genetic elements able to capture anti-biotic resistance and other genes and to promote their transcription.
Here, we have investigated integron-dependent translation of an aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase gene (aac(6')-Ib7)
inserted at the attI1 site. N-terminal sequencing revealed that translation of this gene was initiated at a GTG codon, which
is not part of a plausible translation initiation region (TIR). A short open reading frame (called ORF-11) overlapping the
attI1 site was probed by site-directed mutagenesis for its contribution to aac(6')-Ib7 translation. When ORF-11 and its TIR
were deleted en bloc, translational efficiency dropped by over 80%, as determined with an acetyltransferase- luciferase
fusion product. Invalidation of the ATG start codon of ORF-11 or its putative Shine-Dalgarno sequence resulted in a
decrease of over 60%, whereas the decrease was much less pronounced when the amino acid sequence of the putative
ORF-11-encoded peptide was altered or when the distance between ORF-11 and aac(6')-Ib7 was doubled. This
demonstrates that aac(6')-Ib7 translation is dependent upon the translation of ORF-11, but almost certainly not upon the
corresponding peptide. These results lead us to conclude that an intrinsic short ORF present in the 5'-conserved segment
of many class 1 integrons may substantially enhance expression at the translational level of captured TIR-deficient
anti-biotic resistance genes.
PMID: 11967073 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Publication Types, MeSH Terms, Substances
LinkOut - more resources
1 of 1 05/11/2010 05:45 p.m.
You might also like
- Memorial City Mall MapDocument1 pageMemorial City Mall Maptruechris89No ratings yet
- JSA Template 2017-05-30 Powder Actuated ToolsDocument19 pagesJSA Template 2017-05-30 Powder Actuated ToolsJayvee Baradas Valdez100% (2)
- FC AntybodyDocument8 pagesFC AntybodyahmaszitimNo ratings yet
- IFN yDocument1 pageIFN ytuuuiiitNo ratings yet
- Cellular Cofactors For HIV-1 Transcription: IntegrationDocument7 pagesCellular Cofactors For HIV-1 Transcription: IntegrationDevi OktafianiNo ratings yet
- Bromodomain Protein brd4 Is Required For Estrogen Receptor Dependent Enhancer Activation and Gene TranscriptionDocument10 pagesBromodomain Protein brd4 Is Required For Estrogen Receptor Dependent Enhancer Activation and Gene TranscriptionParvinder McCartneyNo ratings yet
- Retrovirus Translation Initiation: Issues and Hypotheses Derived From Study of HIV-1Document9 pagesRetrovirus Translation Initiation: Issues and Hypotheses Derived From Study of HIV-1ThorieForestNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Journal of Biological ChemistryDocument33 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Journal of Biological Chemistryro111111No ratings yet
- 2019 Identifying Novel Targets of Oncogenic EGF Receptor Signaling in Lung Cancer Through Global PhosphoproteomicsDocument16 pages2019 Identifying Novel Targets of Oncogenic EGF Receptor Signaling in Lung Cancer Through Global Phosphoproteomicsmorteza hosseiniNo ratings yet
- Structural Aspects of Drug Resistance and Inhibition of HIV-1 Reverse TranscriptaseDocument34 pagesStructural Aspects of Drug Resistance and Inhibition of HIV-1 Reverse TranscriptaseNam KitNo ratings yet
- tmpBEE5 TMPDocument9 pagestmpBEE5 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Salicylic Acid-Mediated Innate Immunity in Arabidopsis Is Regulated by SIZ1 SUMO E3 LigaseDocument12 pagesSalicylic Acid-Mediated Innate Immunity in Arabidopsis Is Regulated by SIZ1 SUMO E3 LigaseZain BaderNo ratings yet
- Wang 2014Document24 pagesWang 2014Carlos Manuel OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Intracellular Expression of IRF9 Stat Fusion Protein Overcomes The Defective Jak-Stat Signaling and Inhibits HCV RNA ReplicationDocument12 pages2010 - Intracellular Expression of IRF9 Stat Fusion Protein Overcomes The Defective Jak-Stat Signaling and Inhibits HCV RNA ReplicationFernando Fernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 31Document12 pages31Yovan BlancoNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-1993-Wu-9980-5Document6 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-1993-Wu-9980-5Made YudanaNo ratings yet
- Structural Insights Into The Interaction of A Monoclonal Antibody and Nodal Peptides by STD-NMR SpectrosDocument8 pagesStructural Insights Into The Interaction of A Monoclonal Antibody and Nodal Peptides by STD-NMR Spectros6gtnsvdw72No ratings yet
- Journal of Molecular Graphics and ModellingDocument13 pagesJournal of Molecular Graphics and ModellingPencari IlmuNo ratings yet
- Paper Gag TedburyDocument31 pagesPaper Gag TedburyfaisalnadeemNo ratings yet
- Structural Plasticity of Green Fluorescent Protein To Amino Acid Deletions and Fluorescence Rescue by Folding-Enhancing MutationsDocument11 pagesStructural Plasticity of Green Fluorescent Protein To Amino Acid Deletions and Fluorescence Rescue by Folding-Enhancing MutationsIsmael Cervantes ChavezNo ratings yet
- Traduccuón en ProcariotasDocument21 pagesTraduccuón en Procariotasmaria fernanda jarquin marquezNo ratings yet
- Application of Recombinant DNATechnologies On Sub-Cloning of Transcriptional Co-FactorDocument6 pagesApplication of Recombinant DNATechnologies On Sub-Cloning of Transcriptional Co-FactorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0968089606009898 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0968089606009898 Mainjipir64332No ratings yet
- 2_5262827640598841838Document18 pages2_5262827640598841838am55eer55No ratings yet
- Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of IRF3 in Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus)Document8 pagesMolecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of IRF3 in Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus)Rizka Rahmana PutriNo ratings yet
- 1,4-BENZOQUINONE (para-QUINONE) : 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataDocument6 pages1,4-BENZOQUINONE (para-QUINONE) : 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- J. Virol. 1988 Bienkowska Szewczyk 3068 72Document5 pagesJ. Virol. 1988 Bienkowska Szewczyk 3068 72zeeshan aliNo ratings yet
- The Mechanistic Basis For Noncompetitive Ibogaine - Inhibition of Serotonin and Dopamine TransportersDocument11 pagesThe Mechanistic Basis For Noncompetitive Ibogaine - Inhibition of Serotonin and Dopamine TransportersternyNo ratings yet
- 2017 Article 141 Part1Document5 pages2017 Article 141 Part1Karina MonasaNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry: A B A C D C A C D A e A C ADocument13 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry: A B A C D C A C D A e A C AArturo T. Sánchez-MoraNo ratings yet
- A Novel Mechanism of Eukaryotic TranslationDocument10 pagesA Novel Mechanism of Eukaryotic Translationchar462No ratings yet
- TMP 662Document11 pagesTMP 662FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Toxicology LettersDocument32 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Toxicology LettersOmnia FayedNo ratings yet
- tmpC9BA TMPDocument8 pagestmpC9BA TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Codon SelectionDocument9 pagesCodon SelectionKamal JamesNo ratings yet
- Wu2018 VteDocument11 pagesWu2018 VteSofia UribeNo ratings yet
- Cytokine Expression Profile in The Bone-Anchored Hearing System: 12-Week Results From A Prospective Randomized, Controlled StudyDocument11 pagesCytokine Expression Profile in The Bone-Anchored Hearing System: 12-Week Results From A Prospective Randomized, Controlled StudyBagis Emre GulNo ratings yet
- Plant Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homologs Impinge oDocument14 pagesPlant Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homologs Impinge oMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- BJP7 v. 170Document30 pagesBJP7 v. 170LourdesNo ratings yet
- Neurobiology of Pain: June Bryan de La Peña, Zachary T. Campbell TDocument6 pagesNeurobiology of Pain: June Bryan de La Peña, Zachary T. Campbell TPavithra MohanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Papers Merged 40 57Document18 pages2022 Papers Merged 40 57Yeannie YapNo ratings yet
- Linder 1999Document8 pagesLinder 1999EvanEftNo ratings yet
- Resistance Response of Indonesian Native Orchids To Odontoglossum Ringspot VirusDocument7 pagesResistance Response of Indonesian Native Orchids To Odontoglossum Ringspot VirusRafiq FananiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Plant Physiology: Yee-Min Kwan, Sariah Meon, Chai-Ling Ho, Mui-Yun WongDocument6 pagesJournal of Plant Physiology: Yee-Min Kwan, Sariah Meon, Chai-Ling Ho, Mui-Yun WongroseNo ratings yet
- EIF4E Knoclout MiceDocument28 pagesEIF4E Knoclout MiceLaura GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mutations in The Arabidopsis ROL17/isopropylmalate Network, and Suppress The Root Hair Cell Development MutantDocument11 pagesMutations in The Arabidopsis ROL17/isopropylmalate Network, and Suppress The Root Hair Cell Development MutantTheo KhouryNo ratings yet
- Ayissiowona2013 JQ1Document7 pagesAyissiowona2013 JQ1iforaNo ratings yet
- 2016 - The Unique Role of STAT2 in Constitutive and IFN-Induced Transcription and Antiviral ResponsesDocument11 pages2016 - The Unique Role of STAT2 in Constitutive and IFN-Induced Transcription and Antiviral ResponsesFernando Fernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Interaction of The Epigenetic Integrator UHRF1 With The MYST Domain of TIP60 Inside The CellDocument14 pagesInteraction of The Epigenetic Integrator UHRF1 With The MYST Domain of TIP60 Inside The CellWaseemNo ratings yet
- 016 Scas Abstracts Listed Alphabetically by Abstractspdf 19 2016 Scas AbstractsDocument25 pages016 Scas Abstracts Listed Alphabetically by Abstractspdf 19 2016 Scas AbstractsdssagNo ratings yet
- Nao PerderDocument5 pagesNao PerderSara SantosNo ratings yet
- tmpE31A TMPDocument14 pagestmpE31A TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- 5. Antagonist peptides of human interferon-α2b isolated from phage 2006Document7 pages5. Antagonist peptides of human interferon-α2b isolated from phage 2006Leo SirsNo ratings yet
- The Therapeutic Age of The Neonatal FC Receptor: ImmunologyDocument18 pagesThe Therapeutic Age of The Neonatal FC Receptor: ImmunologyonlydarkheartNo ratings yet
- IGF-I Inhibition of Apoptosis Is Associated With Decreased Expression of Prostate Apoptosis Response-4Document9 pagesIGF-I Inhibition of Apoptosis Is Associated With Decreased Expression of Prostate Apoptosis Response-4sonjeonggyu87No ratings yet
- PI3K/Akt Signaling Transduction Pathway, Erythropoiesis and Glycolysis in Hypoxia (Review)Document9 pagesPI3K/Akt Signaling Transduction Pathway, Erythropoiesis and Glycolysis in Hypoxia (Review)pasifikaNo ratings yet
- Publication Tlyp-1Document17 pagesPublication Tlyp-1Samir AcherarNo ratings yet
- Paper para Critica LlamasDocument15 pagesPaper para Critica LlamasGómez PattyNo ratings yet
- Andrew Hu, 2018Document17 pagesAndrew Hu, 2018franciscaNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0021925818816519Document7 pagesPi Is 0021925818816519Claudio IngrossoNo ratings yet
- Research Article Pleurotus Eryngii Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-InducedDocument7 pagesResearch Article Pleurotus Eryngii Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-InducedkierkegardNo ratings yet
- SN Location Machine/Equipment Make Frequency Paln/Actual: Yearly Maintenance Plan - 2021Document2 pagesSN Location Machine/Equipment Make Frequency Paln/Actual: Yearly Maintenance Plan - 2021RiyaZ55No ratings yet
- National Institute of Textile Engineering and Research (NITER)Document6 pagesNational Institute of Textile Engineering and Research (NITER)shahadat hossainNo ratings yet
- ECG Holter H12+Document2 pagesECG Holter H12+Dhilah 9246No ratings yet
- ELC270 Proposal WritingDocument15 pagesELC270 Proposal WritingAqil FarisNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Platinum and Palladium From Scrap Automotive Catalytic ConvertersDocument11 pagesRecovery of Platinum and Palladium From Scrap Automotive Catalytic ConvertersMr RhodiumNo ratings yet
- Engineering Manual: Variable Refrigerant Flow Outdoor Units 6.0 To 42.0 TonsDocument156 pagesEngineering Manual: Variable Refrigerant Flow Outdoor Units 6.0 To 42.0 TonsNey Raul Benji JoaquinNo ratings yet
- The Dark Side of ConscientiousnessDocument15 pagesThe Dark Side of ConscientiousnessMerlin PitNo ratings yet
- NK-O3 Manuals - Rev 2.6Document106 pagesNK-O3 Manuals - Rev 2.6greatenick.nbNo ratings yet
- Komiyama Et Al., (2008) Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests A ReviewDocument11 pagesKomiyama Et Al., (2008) Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests A ReviewVandhi Amali100% (1)
- IOCLDocument94 pagesIOCLDebabrat SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 RecruitmentDocument14 pagesModule 6 RecruitmentJoyce Ann Aj TomaleNo ratings yet
- The Glymphatic Pathway in Neurological DisordersDocument20 pagesThe Glymphatic Pathway in Neurological DisordersTeresa BeckNo ratings yet
- Men's Fitness - April 2017 ZADocument116 pagesMen's Fitness - April 2017 ZAjustin VerhoogNo ratings yet
- Fish Processing: By: Laureno, Divina Villaver Dela Cruz, Cedrick P. Estor, Vanessa RDocument24 pagesFish Processing: By: Laureno, Divina Villaver Dela Cruz, Cedrick P. Estor, Vanessa REstor, Vanessa R.No ratings yet
- Orbino, Frances Anne N. 4th Rot FdarDocument2 pagesOrbino, Frances Anne N. 4th Rot FdarFrances OrbinoNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesDocument11 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- CSEC Building and Furniture Technology Study GuideDocument131 pagesCSEC Building and Furniture Technology Study Guidealphonsoashanti473No ratings yet
- Land Reforms in IndiaDocument22 pagesLand Reforms in IndiaiRagpickerNo ratings yet
- Woodsynergy Inc.: Integrating IT Into Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesWoodsynergy Inc.: Integrating IT Into Supply Chain ManagementAarushi BhargavaNo ratings yet
- PX MicDocument6 pagesPX MicSoraire LucasNo ratings yet
- Energy ConservationDocument3 pagesEnergy ConservationakifliaqatNo ratings yet
- Roastilino Manual v2 1 21 6 13Document9 pagesRoastilino Manual v2 1 21 6 13Bigman74066No ratings yet
- Retrofit Guidelines For Dupont Isceon 9 Series RefrigerantsDocument20 pagesRetrofit Guidelines For Dupont Isceon 9 Series RefrigerantsaNo ratings yet
- Y2 Series: Three Phase Cast Iron MotorDocument4 pagesY2 Series: Three Phase Cast Iron MotorMark Christian TorresNo ratings yet
- All at Sea Caribbean 0917Document112 pagesAll at Sea Caribbean 0917Scott NeumanNo ratings yet
- At Home Training Guide: Workout BuilderDocument22 pagesAt Home Training Guide: Workout BuilderAnonymous NO0urGNo ratings yet
- Textile Testing International Total Testing Solutions Inc.: Vendor InformationDocument4 pagesTextile Testing International Total Testing Solutions Inc.: Vendor InformationJawad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Feb28.2015 B.docmandatory Employment of Lifeguards in Public Pools SoughtDocument2 pagesFeb28.2015 B.docmandatory Employment of Lifeguards in Public Pools Soughtpribhor2No ratings yet