Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xfmea Pfmea
Xfmea Pfmea
Uploaded by
rkhaireenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Xfmea Pfmea
Xfmea Pfmea
Uploaded by
rkhaireenCopyright:
Available Formats
REPORT SUMMARY
Date: 3/26/2003
Page 1 of 7
In addition to this summary, this report includes the following forms:
1 RATING CRITERIA AND CLASSIFICATIONS
2 PROJECT PROPERTIES AND ANALYSIS PROPERTIES SUMMARY
3 FMEA SPREADSHEET REPORT
4 FAILURE CAUSES
5 RECOMMENDED ACTIONS (Summary Report)
6 CURRENT CONTROLS
Xfmea Report Sample – Process FMEA
This report was generated with ReliaSoft’s Xfmea software in Microsoft Word. Similar reports can also be
generated in Microsoft Excel. You can easily replace the Xfmea logo graphic with your own company logo.
Within Word and Excel, reports can be edited/annotated, if necessary, and generated in PDF and/or HTML
format for easy distribution.
This report includes:
• A summary of the rating criteria (Severity Scale, Occurrence Scale, Detection Scale) and classifications that
were used in the analysis.
• A summary of the project and analysis properties that were defined for the analysis.
• The Process FMEA (PFMEA) spreadsheet report in the AIAG FMEA-3 reporting format.
• A summary list of the potential causes of failure that were identified through the analysis, ranked by Initial
Occurrence rating.
• A summary list of the recommended actions identified during the analysis.
• A summary list of the current controls identified during the analysis.
The report is based on the sample analysis provided in the AIAG FMEA-3 guidelines, on page 36.
Non-proprietary and non-confidential information.
Document Created 3/26/2003 Generated By ReliaSoft’s Xfmea Software http://www.ReliaSoft.com
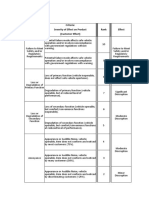
RATING CRITERIA AND CLASSIFICATIONS
Date: 3/26/2003
Page 2 of 7
RPN Calculation Method: Cause RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection Mode RPN = Sum of Cause RPNs Item RPN = Sum of Mode RPNS plus Sub Item RPNs
Severity Rating Scale Occurrence Rating Scale
# Description Criteria # Description Criteria
1 None Slight inconvenience to operation or operator or no effect. 1 Remote: Failure is unlikely <= 0.01 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 1.67.
A portion (less than 100%) of the product may have to be reworked,
2 Very Minor 2 Low: Relatively few failures 0.1 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 1.30.
with no scrap, on-line but in-station.
A portion (less than 100%) of the product may have to be reworked,
3 Minor 3 Low: Relatively few failures 0.5 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 1.20.
with no scrap, on-line but out-of-station.
The product may have to be sorted, with no scrap, an a portion (less
4 Very Low 4 Moderate: Occasional failures 1 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 1.10.
than 100%) reworked
100% of product may have to be reworked, or vehicle/item repaired off-
5 Low 5 Moderate: Occasional failures 2 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 1.00.
line but does not go to repair department.
A portion (less than 100%) of the product may have to be scrapped with
6 Moderate no sorting, or vehicle/item repaired in repair department with repair time 6 Moderate: Occasional failures 5 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 0.94.
less than half an hour.
Product may have to be sorted an a portion (less than 100%) scrapped,
7 High or vehicle/item repaired in repair department with repair time between 7 High: Frequent failures 10 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 0.86.
half an hour and an hour.
100% of product may have to be scrapped, or vehicle/item repaired in
8 Very High 8 High: Frequent failures 20 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 0.78.
repair department with a repair time greater than one hour.
9 Hazardous with warning May endanger operator (machine or assembly) with warning. 9 Very High: Persistent failures 50 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 0.55.
10 Hazardous without warning May endanger operator (machine or assembly) without warning. 10 Very High: Persistent failures => 100 per thousand pieces; Ppk => 0.55.
Detection Rating Scale Classification Options
# Description Criteria Abbreviation Description
Discrepant parts cannot be made because item has been error proofed
1 Very High C Critical
by process/product design.
Error Proofed or Gauging Inspection. Error detection in-station
2 Very High (automatic gauging with automatic stop feature). Cannot pass KI Key Intermediate
discrepant part.
Error Proofed or Gauging Inspection. Error detection in-station, OR in
3 High subsequent operations by multiple layers of acceptance: supply, select, KLd Key Leading
install, verify. Cannot accept discrepant part.
Error Proofed or Gauging Inspection. Error detection in subsequent
4 Moderately High operations, OR gauging performed on setup and first-piece check (for KLg Key Lagging
setup causes only).
Gauging Inspection. Control is based on variable gauging after parts
5 Moderate have left the station, OR Go/No Go gauging performed on 100% of the S Significant
parts after parts have left the station.
Gauging or Manual Inspection. Control is achieved with charting
6 Low
methods, such as SPC (Statistical Process Control)
7 Very Low Manual Inspection. Control is achieved w/ double visual inspection only.
8 Remote Manual Inspection. Control is achieved w/ visual inspection only.
Manual Inspection. Control is achieved w/ indirect or random checks
9 Very Remote
only.
10 Almost Impossible Manual Inspection. Cannot detect or is not checked.
Non-proprietary and non-confidential information.
Document Created 3/26/2003 Generated By ReliaSoft’s Xfmea Software http://www.ReliaSoft.com
PROJECT PROPERTIES AND ANALYSIS PROPERTIES
Date: 3/26/2003
Page 3 of 7
Project Properties
Project Name Based on Profile
Process FMEA AIAG PFMEA
Project Description
This sample project was prepared based on the Process FMEA (PFMEA) on page 70 of the AIAG FMEA-3 guidelines.
Remarks
The information in this project could also be used to prepare a sample PFMEA like the one on page 42 of the SAE J1739 guidelines. To do this, the J1739 PFMEA profile must be applied to
the project.
Analysis Properties
ITEM 3 - Front Door L.H.
FMEA Number Prepared By Key Date FMEA Date (Orig.) FMEA Date (Rev.) Primary Approval Approval Date
1450 J. Ford - X6521 - Assy Ops 3/31/2003 3/10/2003 3/21/2003
Product Model Year(s)/Vehicle(s) Mission
199X/Lion 4dr/Wagon
Process Responsibility Release Date Core Team Others Affected
Body Engineering A. Tate Body Engrg, J. Smith - OC, R. James - Production,
J. Jones - Maintenance
Non-proprietary and non-confidential information.
Document Created 3/26/2003 Generated By ReliaSoft’s Xfmea Software http://www.ReliaSoft.com
POTENTIAL
System 1 - Automobile FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS FMEA Number 1450
Subsystem 2 - Closures Front Door L.H. Page 4 of 7
X Component 3 - Front Door L.H. Process Responsibility Body Engineering Prepared By J. Ford - X6521 - Assy Ops
Model Year(s)/Vehicle(s) 199X/Lion 4dr/Wagon Key Date 3/31/2003 FMEA Date (Orig.) 3/10/2003 (Rev) 3/21/2003
Core Team A. Tate Body Engrg, J. Smith - OC, R. James - Production, J. Jones - Maintenance
Action Results
Item
Potential Current Process Current Process
Occur
Detec
Class
Potential Effect(s) of Responsibility &
RPN
Sev
Potential Failure Mode Cause(s)/Mechanism(s) Controls Controls Recommended Action(s)
Failure Target Completion Date
RPN
Occ
of Failure Prevention Detection
Sev
Det
Actions Taken
Process
Function/Requirements
3 - Front Door L.H.
Manual application of wax Insufficient wax Deteriorated life of door 7 Manually inserted spray 8 Visual check each 5 280 Add positive depth stop to Mfg Engrg Stop added, sprayer 7 2 5 70
inside door. coverage over specified leading to: head not inserted far hour - 1/shift for sprayer. - 3/10/2003 checked on line.
surface. - Unsatisfactory enough. film thickness
To cover inner door, lower appearance due to rust (depth meter) and Automate spraying. Mfg Engrg Rejected due to
surfaces at minimum wax through paint over time. coverage. - 3/10/2003 complexity of different
thickness to retard - Impaired function of doors on same line.
corrosion. interior door hardware.
Spray head clogged 5 Test spray pattern Visual check each 3 105 Use Design of Mfg Engrg Temp and press limits 7 1 3 21
- Viscosity too high at start-up and after hour - 1/shift for Experiments (DOE) on - 3/10/2003 were determined and
- Temperature too low idle periods, and film thickness viscosity vs. temperature limit controls have been
- Pressure too low. preventive (depth meter) and vs. pressure. installed - control
maintenance coverage. charts show process is
program to clean in control Cpk = 1.85.
heads.
Spray head deformed due 2 Preventive Visual check each 2 28 7 2 2 28
to impact. maintenance hour - 1/shift for
program to film thickness
maintain heads. (depth meter) and
coverage.
Spray time insufficient. 8 Operator 7 392 Install spray timer. Maintenance Automatic spray timer 7 1 7 49
instructions and lot - 3/10/2003 installed - operator
sampling (10 starts spray, timer
doors/shift) to controls shut-off -
check for coverage control charts show
of critical areas. process is in control
Cpk = 2.05.
Non-proprietary and non-confidential information.
Document Created 3/26/2003 Generated By ReliaSoft’s Xfmea Software http://www.ReliaSoft.com
FAILURE CAUSES
Date: 3/26/2003
Page 5 of 7
Cause Cause
% Reduction Potential Cause(s)/Mechanism(s) Occ Occ Det Det Process Potential Effect(s) of
RPN RPN Class Item Potential Failure Mode
in RPN of Failure (Init) (Rev) (Init) (Rev) Function/Requirements Failure
(Init) (Rev)
280 70 75 Manually inserted spray head not 8 2 5 5 Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax Insufficient wax coverage Deteriorated life of door
inserted far enough. inside door. over specified surface. leading to:
- Unsatisfactory appearance
To cover inner door, lower due to rust through paint over
surfaces at minimum wax time.
thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior
corrosion. door hardware.
392 49 87.5 Spray time insufficient. 8 1 7 7 Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax Insufficient wax coverage Deteriorated life of door
inside door. over specified surface. leading to:
- Unsatisfactory appearance
To cover inner door, lower due to rust through paint over
surfaces at minimum wax time.
thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior
corrosion. door hardware.
105 21 80 Spray head clogged 5 1 3 3 Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax Insufficient wax coverage Deteriorated life of door
- Viscosity too high inside door. over specified surface. leading to:
- Temperature too low - Unsatisfactory appearance
- Pressure too low. To cover inner door, lower due to rust through paint over
surfaces at minimum wax time.
thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior
corrosion. door hardware.
28 28 0 Spray head deformed due to impact. 2 2 2 2 Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax Insufficient wax coverage Deteriorated life of door
inside door. over specified surface. leading to:
- Unsatisfactory appearance
To cover inner door, lower due to rust through paint over
surfaces at minimum wax time.
thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior
corrosion. door hardware.
Non-proprietary and non-confidential information.
Document Created 3/26/2003 Generated By ReliaSoft’s Xfmea Software http://www.ReliaSoft.com
RECOMMENDED ACTIONS
(Summary Report)
Date: 3/26/2003
Page 6 of 7
Potential
Target
# Recommended Action(s) Responsibility Actions Taken Item Cause(s)/Mechanism(s) of Priority
Completion Date
Failure
1 Add positive depth stop to sprayer. 3/10/2003 Mfg Engrg Stop added, sprayer checked on line. Front Door L.H. Manually inserted spray head not
inserted far enough.
2 Automate spraying. 3/10/2003 Mfg Engrg Rejected due to complexity of different Front Door L.H. Manually inserted spray head not
doors on same line. inserted far enough.
3 Use Design of Experiments (DOE) on viscosity vs. 3/10/2003 Mfg Engrg Temp and press limits were determined Front Door L.H. Spray head clogged
temperature vs. pressure. and limit controls have been installed - - Viscosity too high
control charts show process is in control - Temperature too low
Cpk = 1.85. - Pressure too low.
4 Install spray timer. 3/10/2003 Maintenance Automatic spray timer installed - operator Front Door L.H. Spray time insufficient.
starts spray, timer controls shut-off - control
charts show process is in control Cpk =
2.05.
Non-proprietary and non-confidential information.
Document Created 3/26/2003 Generated By ReliaSoft’s Xfmea Software http://www.ReliaSoft.com
CURRENT CONTROLS
Date: 3/26/2003
Page 7 of 7
Potential Cause(s)/Mechanism(s) of
# Current Process Controls Control Type Item Process Function/Requirements Potential Failure Mode Potential Effect(s) of Failure
Failure
1 Visual check each hour - 1/shift for film Detection Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax inside door. Insufficient wax coverage over Deteriorated life of door leading to: Manually inserted spray head not
thickness (depth meter) and coverage. specified surface. - Unsatisfactory appearance due inserted far enough.
To cover inner door, lower surfaces at to rust through paint over time.
minimum wax thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior door
corrosion. hardware.
2 Test spray pattern at start-up and after idle Prevention Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax inside door. Insufficient wax coverage over Deteriorated life of door leading to: Spray head clogged
periods, and preventive maintenance specified surface. - Unsatisfactory appearance due - Viscosity too high
program to clean heads. To cover inner door, lower surfaces at to rust through paint over time. - Temperature too low
minimum wax thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior door - Pressure too low.
corrosion. hardware.
3 Preventive maintenance program to Prevention Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax inside door. Insufficient wax coverage over Deteriorated life of door leading to: Spray head deformed due to impact.
maintain heads. specified surface. - Unsatisfactory appearance due
To cover inner door, lower surfaces at to rust through paint over time.
minimum wax thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior door
corrosion. hardware.
4 Operator instructions and lot sampling (10 Detection Front Door L.H. Manual application of wax inside door. Insufficient wax coverage over Deteriorated life of door leading to: Spray time insufficient.
doors/shift) to check for coverage of critical specified surface. - Unsatisfactory appearance due
areas. To cover inner door, lower surfaces at to rust through paint over time.
minimum wax thickness to retard - Impaired function of interior door
corrosion. hardware.
Non-proprietary and non-confidential information.
Document Created 3/26/2003 Generated By ReliaSoft’s Xfmea Software http://www.ReliaSoft.com
You might also like
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- PFMEA Reference CardDocument2 pagesPFMEA Reference Cardkeyoor_pat100% (2)
- TQM PolaroidDocument36 pagesTQM Polaroiduttam.nift100% (1)
- Ultrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentFrom EverandUltrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Process Fmea: Table 6 Suggested Pfmea Severity Evaluation CriteriaDocument4 pagesProcess Fmea: Table 6 Suggested Pfmea Severity Evaluation CriteriaSelvakumaran Dhandapani100% (1)
- Xfmea Pfmea PDFDocument8 pagesXfmea Pfmea PDFvinidesoNo ratings yet
- FEMEA Ranking TablesDocument3 pagesFEMEA Ranking TablesAhmed KsibiNo ratings yet
- Xfmea Report Sample - Process FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following FormsDocument8 pagesXfmea Report Sample - Process FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following Formssenzo scholar100% (1)
- "Fmea & Case Study": Kelompok: Rohmat Setiawan Titin NuryawatiDocument41 pages"Fmea & Case Study": Kelompok: Rohmat Setiawan Titin Nuryawatirohmat_setiawan77No ratings yet
- Design and Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (Dfmea & Pfmea)Document19 pagesDesign and Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (Dfmea & Pfmea)Mohammed KassemNo ratings yet
- Xfmea PfmeaDocument10 pagesXfmea PfmeaNavnath TamhaneNo ratings yet
- SOD Machinery FMEADocument3 pagesSOD Machinery FMEAUmashankar Gautam100% (1)
- Copia de FORMATO AmefDocument2 pagesCopia de FORMATO AmefDavid SaucedoNo ratings yet
- BTH 780 Reliability Engineering: Topic: Maintenance, Maintainability & AvailabilityDocument38 pagesBTH 780 Reliability Engineering: Topic: Maintenance, Maintainability & AvailabilityNeuky ElsNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - 1 PDFDocument43 pagesUnit IV - 1 PDFsudarsan kingNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument25 pagesFailure Mode and Effect AnalysislokelooksNo ratings yet
- Fmea Notes-1Document6 pagesFmea Notes-1sagarvadhel78No ratings yet
- Effect Criteria Rank: Typical Rankings of Severity Indices (Ford Motor Company, 2001)Document4 pagesEffect Criteria Rank: Typical Rankings of Severity Indices (Ford Motor Company, 2001)ain liyanaNo ratings yet
- FMEA StandardDocument4 pagesFMEA Standardjawahar ramNo ratings yet
- Control Charts For Variables Contd ..: Department of Industrial Engineering UET PeshawarDocument19 pagesControl Charts For Variables Contd ..: Department of Industrial Engineering UET PeshawarZara SaharNo ratings yet
- +PFMEA Rating Scale GuidelinesDocument2 pages+PFMEA Rating Scale GuidelinesBalaji SNo ratings yet
- FMEA Scoring GuidelinesDocument3 pagesFMEA Scoring Guidelineskalpesh prajapatiNo ratings yet
- GM PFMEA RankingsDocument1 pageGM PFMEA RankingssathyabalaramanNo ratings yet
- SeverityDocument10 pagesSeverityVijayamalar AmruthalingamNo ratings yet
- FMEA Rating ScaleDocument2 pagesFMEA Rating ScaleSridharan VenkatNo ratings yet
- MeasureDocument51 pagesMeasureAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- Module III Lec3Document10 pagesModule III Lec3Surajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Unit 05 Statistical Quality Control: Prof N D Sadaphal Mechanical Engg. DepartmentDocument42 pagesUnit 05 Statistical Quality Control: Prof N D Sadaphal Mechanical Engg. DepartmentAbhijeet RandhirNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad SabriDocument42 pagesFailure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad Sabricalvin100% (1)
- Xfmea Report Sample - Machinery FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following FormsDocument6 pagesXfmea Report Sample - Machinery FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following FormsRoland JoldisNo ratings yet
- Severity, Occurrence, and Detection Criteria For Design FMEADocument2 pagesSeverity, Occurrence, and Detection Criteria For Design FMEAtejashraj93No ratings yet
- Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis of Blanking, Forming and Piercing of Hinge L NovaDocument6 pagesCost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis of Blanking, Forming and Piercing of Hinge L NovaRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Fmea TableDocument4 pagesFmea TableAfzal RNo ratings yet
- AIAG FMEA TemplateDocument25 pagesAIAG FMEA TemplateIqbal Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Plant Wellness Way Book Process3-Numerate Your Options PDFDocument30 pagesPlant Wellness Way Book Process3-Numerate Your Options PDFrbdubey2020No ratings yet
- Fmea RatingDocument6 pagesFmea RatingjanaprathapNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis With Pareto Chart For Various Critical Equipment Used in Ceramic IndustryDocument6 pagesFailure Mode Effect Analysis With Pareto Chart For Various Critical Equipment Used in Ceramic IndustrynsrinNo ratings yet
- Suggested Pfmea Evaluation CriteriaDocument2 pagesSuggested Pfmea Evaluation Criteriatrfcprop100% (1)
- PFMEA Ranking Table Rating Criteria Action GuidelineDocument10 pagesPFMEA Ranking Table Rating Criteria Action GuidelineEnrico Miguel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Xfmea Report Sample - Machinery FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following FormsDocument5 pagesXfmea Report Sample - Machinery FMEA: in Addition To This Summary, This Report Includes The Following FormsMalkeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Statistical Process Control: by H.S.PundleDocument31 pagesStatistical Process Control: by H.S.PundlePALLAVI BHISENo ratings yet
- Question Paper SPC - MSTCDocument11 pagesQuestion Paper SPC - MSTCRajesh SahasrabuddheNo ratings yet
- Sevrity Reating Table Old & NewDocument26 pagesSevrity Reating Table Old & NewSibaram DasNo ratings yet
- OM - Session 24 Quality Control Lean MFGDocument70 pagesOM - Session 24 Quality Control Lean MFGSiddhant Singh100% (1)
- Anirudh Acharya FA Exp 1Document5 pagesAnirudh Acharya FA Exp 1Anirudh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis of Hotwell System Motor Operated Butterfly ValveDocument19 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis of Hotwell System Motor Operated Butterfly ValveBalan SelvanNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: HD-F731 Chair Swivel TesterDocument11 pagesOperation Manual: HD-F731 Chair Swivel TesterAval SaxenaNo ratings yet
- PR Series Electrolytes Analyzer Service Manual: Meizhou Cornley© Hi-Tech Co., LTDDocument25 pagesPR Series Electrolytes Analyzer Service Manual: Meizhou Cornley© Hi-Tech Co., LTDTulu TvNo ratings yet
- Radiometer - Blood Gas Analyzer - Abl80 Flex Operator Manual-3 (287-344)Document58 pagesRadiometer - Blood Gas Analyzer - Abl80 Flex Operator Manual-3 (287-344)Miguel FigueroaNo ratings yet
- K-Litte5 Service ManualDocument25 pagesK-Litte5 Service ManualJackson Njaramba100% (1)
- Pfmea TableDocument1 pagePfmea TableAlberto CastelanNo ratings yet
- DfmeaDocument13 pagesDfmeaAshisNo ratings yet
- Updates Dec09 AIAG FMEA-Ranking-TablesDocument3 pagesUpdates Dec09 AIAG FMEA-Ranking-TablesSuresh Velu100% (1)
- Fmeca ProcedureDocument11 pagesFmeca Procedurewarigiyatno100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Rotating Machinery: Including Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, Reciprocating Pumps and Compressors, Fans, Steam Turbines, Electric Motors, and MoreFrom EverandTroubleshooting Rotating Machinery: Including Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, Reciprocating Pumps and Compressors, Fans, Steam Turbines, Electric Motors, and MoreNo ratings yet
- Automated X-Ray Inspection Robot: Enhancing Quality Control Through Computer VisionFrom EverandAutomated X-Ray Inspection Robot: Enhancing Quality Control Through Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Creating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowFrom EverandCreating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)