Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lithium Presentation
Lithium Presentation
Uploaded by
Ethan Naylor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageLithium is a soft, silver-white metal that is highly reactive. It was discovered in 1817 from petalite ore. Lithium has an atomic number of 3 and is part of the alkali metal group. It exists relatively abundantly in the ocean and is obtained from clays and brines for industrial use. Lithium has many technological uses including in batteries, ceramics, mood stabilizing drugs, and nuclear fusion.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lithium Presentation (2)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLithium is a soft, silver-white metal that is highly reactive. It was discovered in 1817 from petalite ore. Lithium has an atomic number of 3 and is part of the alkali metal group. It exists relatively abundantly in the ocean and is obtained from clays and brines for industrial use. Lithium has many technological uses including in batteries, ceramics, mood stabilizing drugs, and nuclear fusion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageLithium Presentation
Lithium Presentation
Uploaded by
Ethan NaylorLithium is a soft, silver-white metal that is highly reactive. It was discovered in 1817 from petalite ore. Lithium has an atomic number of 3 and is part of the alkali metal group. It exists relatively abundantly in the ocean and is obtained from clays and brines for industrial use. Lithium has many technological uses including in batteries, ceramics, mood stabilizing drugs, and nuclear fusion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
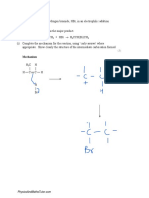
Atomic Symbol:
•Li
History:
•1817, petalite ore, Berzelius, “lithos”, similar
to Na and K but less soluble
Basic Facts: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4
•Alkali metal group, atomic number is 3 /4d/Battery-lithium-cr2032.jpg
• Highly reactive so often stored in mineral oil Sources:
or petroleum jelly •Appears only in compounds due to its high
•Serves no apparent vital function in humans reactivity
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/
•Transmutation of tritium from lithium was b/b6/Lithium.svg/424px-Lithium.svg.png •Mostly obtained from clays and brines
the first man-made nuclear fusion reaction •Industrially refined using electrolysis
•Exists relatively abundantly in the ocean
•25th most abundant element on Earth Uses:
•Mood stabilizing drugs
Chemical Properties: •Ceramics
•Crimson color given when heated •Batteries
•Ignites when exposed to water or water •Coolants and heat transfer processes due
vapor to high specific heat capacity
•Highest specific heat capacity of all solids •Isotopes are used for nuclear fusion
•Electronegativity: 0.98 •Pyrotechnics
Physical Properties: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/81/Electron_shell_003_lithium.png
•Soft After Oxidation
•Silver-white metal, has luster when cut but is Before Oxidation
corroded quickly by moisture in air turning it
gray and eventually black with
corrosion(oxidation)
•Single valence electron
• Good heat and electricity conductor
•Melting point: 180.54 (C)
•Boiling point: 1342 (C)
• Atomic radius: 152 pm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lithium http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lithium_paraffin.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Limetal.JPG
You might also like
- Grade 7 Entrance ExamDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Entrance Examlyniel john solitario100% (1)
- Li Ion BatteriesDocument25 pagesLi Ion BatteriesSreed Sharma K0% (1)
- Igcse V GcseDocument26 pagesIgcse V GcsemillergraNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Physiological Reactions Part 2 BiochemistryDocument7 pagesChemical and Physiological Reactions Part 2 BiochemistryDan Paulene AceboNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion Battery YEMNA PRESENTATIONDocument28 pagesLithium Ion Battery YEMNA PRESENTATIONYemna Badar100% (1)
- WINSEM2021-22 CHY1701 ETH VL2021220503815 Reference Material II 10-03-2022 Module 5 Last PartDocument42 pagesWINSEM2021-22 CHY1701 ETH VL2021220503815 Reference Material II 10-03-2022 Module 5 Last PartKillari RohithNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document94 pagesUnit 1akshair03No ratings yet
- AEES Note-2Document39 pagesAEES Note-2joslanginNo ratings yet
- Chap 5. BatteriesDocument41 pagesChap 5. Batteries맛있는감자No ratings yet
- Sdoc 11 06 SiDocument12 pagesSdoc 11 06 SimahahajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Structures + Bonding: AnswersDocument2 pagesChemistry Structures + Bonding: Answersapi-25909541No ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements: The Elements in Which Last Electron Enters The S-Subshell Are Called As S-Block ElementsDocument36 pagesThe S-Block Elements: The Elements in Which Last Electron Enters The S-Subshell Are Called As S-Block ElementstheDarknight2050 (Karthik Sunil)No ratings yet
- Modern Lithium BatteryDocument16 pagesModern Lithium BatteryHoang ChauAnhNo ratings yet
- Types of BatteriesDocument37 pagesTypes of BatteriesvendralokeshNo ratings yet
- Bonding & Molecular Structure: Topic Outline: Directions For BLOOMS - Lower Order - UnderstandingDocument4 pagesBonding & Molecular Structure: Topic Outline: Directions For BLOOMS - Lower Order - Understandingapi-320784618No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 CHY1701 ETH VL2019201006698 Reference Material I 06-Sep-2019 Module-5-EC-2018-Fall UpdatedDocument54 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 CHY1701 ETH VL2019201006698 Reference Material I 06-Sep-2019 Module-5-EC-2018-Fall UpdatedSandhya SundarNo ratings yet
- 35f23f - Batteries and Electrochemical ProcessesDocument14 pages35f23f - Batteries and Electrochemical ProcessesZainNo ratings yet
- Chapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01Document65 pagesChapter2carboncompoundsasing 150401093408 Conversion Gate01VinnySha SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- 2021B8018137003-ADEOTI Monrenike Houlifath-Final PresentationDocument21 pages2021B8018137003-ADEOTI Monrenike Houlifath-Final PresentationHoulifathNo ratings yet
- ElectrolplatingDocument17 pagesElectrolplatingMaham khanNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 4 - Classifications of Materials - PPTDocument15 pagesKelompok 4 - Classifications of Materials - PPTAnnas HanifNo ratings yet
- Leach in GGGGDocument1 pageLeach in GGGGAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Alkali Metals: BS Chemistry 1ADocument50 pagesHydrogen and Alkali Metals: BS Chemistry 1AReenaNo ratings yet
- Unit A - Chemistry NotesDocument54 pagesUnit A - Chemistry NotesfgdfgdfgfgdfggNo ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument41 pagesThe S-Block ElementsRavinder singh100% (2)
- Metal FinishingDocument29 pagesMetal FinishingEeraúNo ratings yet
- Manufactured Substances in Industry: Name: Irdina BT Azhar CLASS: 401 Teacher'S Name: Pn. NorlizaDocument10 pagesManufactured Substances in Industry: Name: Irdina BT Azhar CLASS: 401 Teacher'S Name: Pn. NorlizaKHAYRA AZHARNo ratings yet
- SCI405-Lecture 2aDocument37 pagesSCI405-Lecture 2aandreipelaez17No ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument8 pagesChem ReviewerJULLIANA KEI PINONo ratings yet
- Larry Brown Tom Holme: Jacqueline Bennett - SUNY OneontaDocument8 pagesLarry Brown Tom Holme: Jacqueline Bennett - SUNY OneontaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Battery Technology: Lithium Ion BatteriesDocument14 pagesBattery Technology: Lithium Ion BatteriesdepakNo ratings yet
- Conductors, Insulator, Semiconductor, and SuperconductorDocument12 pagesConductors, Insulator, Semiconductor, and SuperconductorAngelinee C.No ratings yet
- 3 OresDocument22 pages3 OresmohammedsharmaarkeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic Concepts of CorrosionDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Concepts of CorrosionAmalina JamilNo ratings yet
- 3208 03 07 Metalloids GN SEDocument9 pages3208 03 07 Metalloids GN SELILA LEWISNo ratings yet
- Battery Technology: Lithium Flow BatteriesDocument14 pagesBattery Technology: Lithium Flow BatteriesdepakNo ratings yet
- CHM 222, Organic Chemistry II Chapter 15 Organometallic Compunds PDFDocument34 pagesCHM 222, Organic Chemistry II Chapter 15 Organometallic Compunds PDFMelissa ChehwaneNo ratings yet
- Lithium: Choosing The Right Analysis MethodDocument2 pagesLithium: Choosing The Right Analysis MethodDavid Bolívar FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Presented By-1) Harpreet Khanna. 2) Prince Goel 3) Roopashree Panda (18) (32) (33) 4) - Shiv Verdhan SinghDocument23 pagesPresented By-1) Harpreet Khanna. 2) Prince Goel 3) Roopashree Panda (18) (32) (33) 4) - Shiv Verdhan Singhbat champNo ratings yet
- 1.2 CHAP 1 and CHAP2 Lecture 1Document28 pages1.2 CHAP 1 and CHAP2 Lecture 1Business MatterNo ratings yet
- Battery - Fast Ion and Solid StateDocument35 pagesBattery - Fast Ion and Solid StateElfhyElfridaPasaribuNo ratings yet
- Reu Poster IDocument1 pageReu Poster Iapi-355836337No ratings yet
- 1 - Chapter 1Document39 pages1 - Chapter 1jenichoppalaNo ratings yet
- 4 RecyclingDocument20 pages4 RecyclingmohammedsharmaarkeNo ratings yet
- Lithium Ion BatteriesDocument1 pageLithium Ion BatteriesDimas Candra AtmajaNo ratings yet
- SSS ReviewerDocument6 pagesSSS ReviewerDanica LimNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals Fuction and PurposesDocument2 pagesAlkali Metals Fuction and Purposesdamiarizuan31No ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Materials Science and Engineering PDFDocument2 pagesUnit 4 - Materials Science and Engineering PDFDanielle AdelanteNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Unit 2 As ChemistryDocument24 pagesEdexcel Unit 2 As ChemistrymukeshNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Fuel CellDocument19 pagesAlkaline Fuel CellMadan KaushishNo ratings yet
- Matter and SubstancesDocument32 pagesMatter and SubstancesnorazlanwahabNo ratings yet
- Electric_vehicles_U3Document31 pagesElectric_vehicles_U3Sonal SinghNo ratings yet
- Clay Chemistry StateDocument62 pagesClay Chemistry Statebanke bihariNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Energy-Opportunities and Challenges: Aneesh C. GangalDocument28 pagesHydrogen Energy-Opportunities and Challenges: Aneesh C. GangalAneesh GangalNo ratings yet
- Lithium Technical NoteDocument2 pagesLithium Technical NoteJGGNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction HazardsDocument25 pagesChemical Reaction HazardsVadapalli TarunNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument14 pagesBatteryAliya BeegomNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 CarboncompoundsDocument71 pagesChapter2 CarboncompoundsJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 4 in Eng - 1Document7 pagesChem Unit 4 in Eng - 1harriharan2003No ratings yet
- Primary Lithium Battery Guide (TM SAFT Li 200802 En)Document93 pagesPrimary Lithium Battery Guide (TM SAFT Li 200802 En)MedSparkNo ratings yet
- Application Note: Moisture, Volatile Matter, Ash, and Fixed Carbon Determination in CokeDocument2 pagesApplication Note: Moisture, Volatile Matter, Ash, and Fixed Carbon Determination in CokeLab kimia bahan bakarNo ratings yet
- Furstenberg-Hagg Et Al. 2013. Plant Defense Against Insect Herbivores.Document56 pagesFurstenberg-Hagg Et Al. 2013. Plant Defense Against Insect Herbivores.J Alberto LucasNo ratings yet
- ALCOADocument8 pagesALCOAsuryaNo ratings yet
- Geopolymer SynthesisDocument6 pagesGeopolymer SynthesisAhmad UllahNo ratings yet
- Impact of Coal Based Thermal Power Plant On Environment and Its Mitigation MeasureDocument6 pagesImpact of Coal Based Thermal Power Plant On Environment and Its Mitigation MeasureAnirudh KalliNo ratings yet
- Vinegar Planning and Design LabDocument3 pagesVinegar Planning and Design LabKim ThaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EvapotranspirationDocument20 pagesChapter 3 EvapotranspirationnimcanNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Fabrication of B C and Aloe Vera Reinforced Aluminium-Matrix-CompositeDocument13 pagesOptimization and Fabrication of B C and Aloe Vera Reinforced Aluminium-Matrix-CompositeHaider SyedNo ratings yet
- 4 - Best Practices For Sodium Hypochlorite Storage and Metering SystemsDocument48 pages4 - Best Practices For Sodium Hypochlorite Storage and Metering SystemsZain Ali100% (1)
- Alkenes 2 QP AnsDocument11 pagesAlkenes 2 QP AnshhheeeNo ratings yet
- Sound Velocity Chart PDFDocument1 pageSound Velocity Chart PDFJamesNo ratings yet
- Venturi ScrubberDocument3 pagesVenturi ScrubberRoger FernandezNo ratings yet
- Aqa Bly2h W Ms Jan12Document13 pagesAqa Bly2h W Ms Jan12ApplemeisterNo ratings yet
- Paper 3Document10 pagesPaper 3zulhariszan abd mananNo ratings yet
- Sikadur - 52: Low Viscosity Injection ResinDocument3 pagesSikadur - 52: Low Viscosity Injection ResinSunny RohillaNo ratings yet
- SandCasting by Yaser ElkelawyDocument12 pagesSandCasting by Yaser ElkelawyYaserElkelawyNo ratings yet
- Thermol-D DescriptionDocument4 pagesThermol-D Descriptionajeeit8No ratings yet
- Chicken EggshellsDocument27 pagesChicken EggshellsBenmar L. OrterasNo ratings yet
- Introduction Marketing DepartmentDocument6 pagesIntroduction Marketing Departmentghulam murtazaNo ratings yet
- Contaminated SoilDocument873 pagesContaminated SoilMohamed EL BAGHDADINo ratings yet
- TB072A Evaluation of A.C. in Liquid Phase Appl. (Preparation of Isotherms)Document7 pagesTB072A Evaluation of A.C. in Liquid Phase Appl. (Preparation of Isotherms)mhuurNo ratings yet
- Platinum-Group Elements PDFDocument6 pagesPlatinum-Group Elements PDFcristianNo ratings yet
- Sintering Mechanisms of Porcelain Stoneware Tiles: Castell6N (Spain)Document13 pagesSintering Mechanisms of Porcelain Stoneware Tiles: Castell6N (Spain)volkanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Periodicity of Properties: Major ConceptsDocument14 pagesPeriodic Table and Periodicity of Properties: Major ConceptsAbdullah AdeelNo ratings yet
- Screw DesignDocument13 pagesScrew DesignDiptendu Basu100% (2)
- 17ME64 DME II Module 5Document13 pages17ME64 DME II Module 5Shridhar ChinuuNo ratings yet
- Msci406 Sols05 PDFDocument3 pagesMsci406 Sols05 PDFEryWiyadi100% (1)
- Nabu Study Ammonia Marine FuelDocument60 pagesNabu Study Ammonia Marine FuelSalimNo ratings yet
- PC Cell 64004Document1 pagePC Cell 64004SutarnoNo ratings yet