Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan For Patiients With Meningitis
Nursing Care Plan For Patiients With Meningitis
Uploaded by
ixa_morales67%(6)67% found this document useful (6 votes)
21K views35 pages1) The patient has meningitis with symptoms including altered respiratory rate, decreased oxygen saturation, pale and weak appearance, and use of accessory muscles.
2) The nursing care plan involves assessing the patient, providing oxygen therapy, monitoring conditions and notifying the physician if the condition deteriorates.
3) Additional interventions include ensuring family and visitors practice proper hand hygiene and use protective equipment to prevent spread of infection from the patient.
Original Description:
Original Title
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR PATIIENTS WITH MENINGITIS
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The patient has meningitis with symptoms including altered respiratory rate, decreased oxygen saturation, pale and weak appearance, and use of accessory muscles.
2) The nursing care plan involves assessing the patient, providing oxygen therapy, monitoring conditions and notifying the physician if the condition deteriorates.
3) Additional interventions include ensuring family and visitors practice proper hand hygiene and use protective equipment to prevent spread of infection from the patient.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
67%(6)67% found this document useful (6 votes)
21K views35 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patiients With Meningitis
Nursing Care Plan For Patiients With Meningitis
Uploaded by
ixa_morales1) The patient has meningitis with symptoms including altered respiratory rate, decreased oxygen saturation, pale and weak appearance, and use of accessory muscles.
2) The nursing care plan involves assessing the patient, providing oxygen therapy, monitoring conditions and notifying the physician if the condition deteriorates.
3) Additional interventions include ensuring family and visitors practice proper hand hygiene and use protective equipment to prevent spread of infection from the patient.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 35
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR
PATIIENTS WITH
MENINGITIS
By Diane Kathryn S. Nierva, RN.
GOOD AFTERNOON!!!!!!! GUYS!!
• ARE YOU STILL THERE???
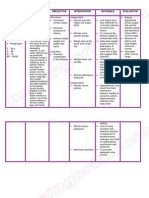
Objective:
• RR: 50
• O2 saturation: 89%
• GCS= 11
• Pale and weak in
appearance
• Use of accessory muscles
• With nasal flaring
• With chest retractions
INEFFECTIVE BREATHING
PATTERN RELATED TO
DECREASED LEVEL OF
CONSCIOUSNESS AND
RESPIRATORY FATIGUE AS
EVIDENCED BY ALTERED
RESPIRATORY RATE
Plan of Action
• At the end of nursing intervention the
patients respiration will be reestablished
and it’s rate return to normal range.
Nursing Interventions:
• Assess the condition of patient. Check for the
level of consciousness.
• Identify if there is an impending respiratory
failure by monitoring respiration changes. Note
respiratory rate, depth, rhythm, symmetry of
chest movement and use of accessory muscles.
• Assess Arterial blood gas level and oxygen
saturation.
• Provide oxygen therapy .
• Notify the attending physician of the patient’s
current condition.
• Assist with the implementation of ventilatory
support as indicated. Check ventilator alarms
if functioning. Look if oxygen line is connected
to the proper outlet.
• Administer medications as ordered. Check
patients response to the medication.
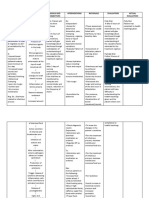
• SUBJECTIVE: • Objective:
• “ Masakit ang ulo ko” as • Pain scale: 9/10
verbalized by patient • With facial grimace
• Irritable
• Restless
• With high pitched cry
• BP: 120/70 mmHg
ALTERATION IN COMFORT,
PAIN RELATED TO
MENINGEAL IRRITATION
SECONDARY TO DISEASE
CONDITION.
Plan of action
• At the end of nursing intervention, pain
level experienced will be decreased or
alleviated.
Nursing Interventions
• Assess patients pain scale.
• Place child on a comfortable position. Be
careful not to flex the childs neck when
turning or positioning her. Allow the child to
assume a comfortable position. (mostly
opisthotonic position wherein the neck and
head is hyperextended to relieve discomfort.)
• Provide rest periods to facilitate comfort,
sleep, and relaxation.
• Keep the lights dim and maintain quiet
environment.
• Provide pain medication as ordered and
check effectiveness of medication given.
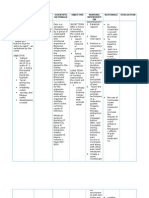
• OBJECTIVE:
• Restlessness
• Irritable
• GCS= 12
• High pitched cry
• Tensed bulging anterior fontanelle upon palpation
• Pulse rate 70 bpm
• RR= 18
• With unequal pupil size L= 4, R= 2
ALTERED CEREBRAL TISSUE
PERFUSION RELATED
DECREASED BLOOD FLOW TO
THE BRAIN DUE TO
CEREBRAL EDEMA/
INCREASED ICP SECONDARY
TO DISEASE CONDITION.
Plan of Action
• At the end of nursing intervention,
optimal tissue perfusion will be
improved in the brain as evidenced
by increase in the level of
consciousness.
Nursing Interventions:
• Assess patients condition. Check for signs of increased ICP like
restlessness and irritability, high pitched cry, vomiting, and
headache.
• Check for the Level of consciousness.
• Monitor vital signs. Get the temperature, Respiratory rate,
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure. Note: Increased Blood
pressure, bradycardia and Wide pulse pressure are indicators
of increased ICP.
• Measure child’s head circumference.
• Weigh him or her daily.
• Give oxygen inhalation via nasal cannula.
• Place child head positioned on midline to encourage
jugular venous drainage and the head of the bed is
elevated to 15[degrees] to 30[degrees]. The child's
head should be maintained midline to prevent
impairment in drainage from the external jugular
veins and the head of bed should be maintained at
30[degrees] with alterations based on the child's
response. The child must be euvolemic prior to
placing in this position to avoid orthostatic
hypotension.
• Regulate IV fluids properly at the rate ordered.
• Provide medication as prescribed like mannitol.
Subjective Objective:
• “Parang mainit ang katawan • With flushed face
nya” as verbalized by • Skin warm to touch
mother • Pale and weak in
appearance
• temperature= 39 C
• RR= 46 breaths/min
• HR= 96
Alteration in Body temperature;
hyperthermia; related to presence
of pyogenic microorganisms in the
thermoregulating center of the
brain.
Plan of Action
• At the end of nursing intervention,
temperature will decrease or return
to normal range.
Nursing Interventions:
• Assess for the possible contributing factors.
• Monitor vital signs
• Render continuous tepid spongebath and teach
significant others on proper provision.
• Provide adequate ventilation. Remove overly
constricting or thick clothing.
• Maintain a quiet and restful environment.
• Regulate IV fluids properly.
• Administer antipyretics as ordered.
• Subjective: • Objective:
• “Nurse nanginginig • With Upward rolling of
yung anak ko at the eye
tumatarak ang mata”
• With tonic clonic
seizure of 2 minutes
duration
• Pale in appearance
• With drooling noted
• with cyanotic lips noted
• With cyanotic nailbeds
Risk for injury related to
seizure episodes
secondary to disease
condition
Plan of Action
• At the end of nursing
intervention, significant others
will understand and
demonstrate ways on how to
manage patient when seizure
occurs
Nursing Interventions:
• Monitor Childs vital signs.
• Remove unnecessary articles on patients’ bed.
• Provide oxygen to patient.
• Place child on side lying position to avoid aspiration.
• Do not put anything on child's mouth when there is a
seizure attack. Do not restrain child.
• Provide a quiet non stimulating environment and dim
the lights.
• Teach parents on management of patient with seizure.
Subjective objective
“Nasasamid siya pag • GCS= 11
pinapadede ko, hidi • With poor sucking
sya masyadong and swallowing
makalunok” as reflex noted
verbalized by • With increased
mother. accumulation of
saliva in the mouth.
RISK FOR ASPIRATION
RELATED TO DECREASE
LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS
AND POOR SECRETION
CONTROL.
Plan of Action
• At the end of nursing
intervention, the risk for
aspiration will be
minimized as exhibited by
proper feeding of mother.
Nursing Interventions:
• Assess patient’s level of consciousness. Assess
patient’s ability to swallow and strength of gag and
cough reflex.
• Instruct significant other not to feed patient on lying
position.
• Maintain operational suction equipment at bedside.
• Suction oral cavity and nose as needed.
• Place patient’s head of bed at 30 degrees elevation.
• Teach significant others on proper feeding
with head slightly elevated and propped on
right side after feeding.
• Provide oral care after meals.
• Notify the physician or other health care
provider immediately of noted decrease in
cough and/or gag reflexes or difficulty in
swallowing
• When feeding per orem is not possible:
• Assist in insertion of nasogastric tube as ordered.
Prepare the necessary materials needed.
• Check for patency of NGT prior to tube feeding.
• Check for any residual in the tube
• Flush NGT with 20-30 cc of water
• Feed patient with head part of bed elevated.
For Family and Other Persons
safety
Risk for Infection related to
presence of pathogenic
microorganism in the cerebrospinal
fluid as evidenced by lab result.
Plan of Action
• At the end of Nursing Intervention,
Significant others will demonstrate
ways and means to prevent spread
of infection.
Nursing Interventions:
• Assess family’s level of understanding of child’s
current condition.
• Demonstrate proper hand washing technique to
relatives and stress out its importance.
• Instruct significant others to wear protective gears
such as face mask.
• Isolate patient as quickly as possible.
• Minimize room visits as much as possible.
• Discard any articles or body secretions from the
patient in the proper waste disposal bin.
• Acquire prophylaxis by taking prescribed medications
or vaccination.
You might also like
- Central Nervous System Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous System Nursing Care PlanUday Kumar100% (1)
- Peds Presentation MeningitisDocument20 pagesPeds Presentation Meningitisapi-533578725No ratings yet
- SHADOW WORK - Noticing, Naming & Embracing The Shadow - J Abrams: Connie Zweig PDFDocument5 pagesSHADOW WORK - Noticing, Naming & Embracing The Shadow - J Abrams: Connie Zweig PDFdorje@blueyonder.co.uk100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Different Age GroupsDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Different Age GroupsBrenden Justin NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Diabetic KetoacidosisJordz Placi100% (2)
- 00.00 Reference Care Plan Tonsillectomy and Adnoidectomy Post OpDocument5 pages00.00 Reference Care Plan Tonsillectomy and Adnoidectomy Post OpMarya KemmieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For TonsillitisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For TonsillitisEden Cruz50% (6)
- Nursing Diagnosis DKA Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis DKA Care Planعبدالله خليل العسل100% (1)
- Schizophreniform DisorderDocument16 pagesSchizophreniform Disorderfeva55No ratings yet
- Piston Damage Recognising and Rectifying - 51730 PDFDocument92 pagesPiston Damage Recognising and Rectifying - 51730 PDFnaveentaak100% (1)
- Mitsubishi Lancer Owners HandbookDocument194 pagesMitsubishi Lancer Owners Handbookahmadkeshta100% (1)
- NCP MeningitisDocument6 pagesNCP MeningitisSkyerex67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis For Pediatrics Gastroenteritis 1Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis For Pediatrics Gastroenteritis 1densu4u100% (4)
- NCP FVDDocument2 pagesNCP FVDMarlon AnryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJamie Haravata0% (1)
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Etiology of TonsillitisDocument15 pagesEtiology of TonsillitisRendy Candra100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan TB MeningitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan TB Meningitisderic74% (19)
- To Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and ConductionDocument11 pagesTo Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and Conductioniaekawa100% (6)
- Bronchitis N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageBronchitis N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Problem Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objective of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Problem Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objective of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationplug06100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Pedia TB MeningitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pedia TB Meningitisderic100% (10)
- NCP HydrocephalusDocument6 pagesNCP HydrocephalusgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Chloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Document3 pagesChloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- RHD DIScharge PlanDocument2 pagesRHD DIScharge PlanPearl Anne SanfordNo ratings yet
- Revised Case Study Umbilical HerniaDocument14 pagesRevised Case Study Umbilical HerniaLance Angelo Bernandino100% (1)
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 pagesFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities of Hematinic DrugsDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities of Hematinic DrugsStudent Nurse0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- 2 Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument6 pages2 Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsHikaru TakishimaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Hydrocephalusstar7707100% (1)
- CholecystitisDocument1 pageCholecystitisDianne ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesAcute PancreatitisAkocmeme Sanchez100% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument28 pagesNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- Standing Order-Diarrhea DraftDocument1 pageStanding Order-Diarrhea DraftKatelyn Brissey50% (2)
- Case Study On Wilson's DiseaseDocument49 pagesCase Study On Wilson's Diseaseamit100% (2)
- ClubfootDocument1 pageClubfootBheru LalNo ratings yet
- CcroupDocument53 pagesCcroupOlivia BernadiNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Care of Child With Head InjuryDocument34 pagesCare of Child With Head InjurySHAFIQNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisVaneca Go67% (9)
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPJayr DiazNo ratings yet
- F. NCP ProperDocument4 pagesF. NCP ProperAle SandraNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- NCP TyphoidDocument4 pagesNCP TyphoidFate ZephyrNo ratings yet
- Fever NCPDocument3 pagesFever NCPBruno MercuryNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionDocument24 pagesManagement of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionYahya AL-HelihNo ratings yet
- NCP Post CSDocument5 pagesNCP Post CSPeachy Marie AncaNo ratings yet
- PT Oranization of Neonatal Care ServicesDocument10 pagesPT Oranization of Neonatal Care ServicesPragati BholeNo ratings yet
- 19 Nursing Care of A Child With Life Threatening ConditionsDocument31 pages19 Nursing Care of A Child With Life Threatening ConditionsBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- NRPDocument15 pagesNRPmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of The Unconscious PatientDocument34 pagesNursing Management of The Unconscious Patientcamaralamin209_54266100% (2)
- High Risk Newborn2Document15 pagesHigh Risk Newborn2Catherine Villanueva Sta Monica100% (1)
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument51 pagesNeonatal ResuscitationAbdulkadir HasanNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objective Nursing Interventi ON Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objective Nursing Interventi ON Rationale EvaluationTamil VillardoNo ratings yet
- Smart MaterialDocument3 pagesSmart MaterialyokaNo ratings yet
- Minnesota Urolith Center University of Minnesota: PreventionDocument3 pagesMinnesota Urolith Center University of Minnesota: PreventionvalisianoNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For Gender TrainersDocument43 pagesTraining Manual For Gender TrainersMiqz ZenNo ratings yet
- AttendancepolicyDocument6 pagesAttendancepolicyapi-262412035No ratings yet
- Ultra High Temperature 100HTL Adhesive Transfer Tapes: Technical Data November, 2006Document4 pagesUltra High Temperature 100HTL Adhesive Transfer Tapes: Technical Data November, 2006Iris SoonNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Semester 2 Bing 7Document5 pagesSoal Pat Semester 2 Bing 7SAIFULNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire PresentationDocument14 pagesSurvey Questionnaire PresentationFaith PaladoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Mathematical Applications For The Management Life and Social Sciences 12th Edition Ronald J Harshbarger James J ReynoldsDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Mathematical Applications For The Management Life and Social Sciences 12th Edition Ronald J Harshbarger James J Reynoldsdiclinicauroravsl9100% (53)
- Quote Vendor File ExcelDocument254 pagesQuote Vendor File ExcelsefiplanNo ratings yet
- 4-Spare Parts Management 1Document76 pages4-Spare Parts Management 1Mohd Kamil100% (4)
- Quick PharmaDocument4 pagesQuick Pharmahva.terrenceavillaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Siswa Analytical Exposition 25 SoalDocument7 pagesTugas Siswa Analytical Exposition 25 SoalSid Nade DwNo ratings yet
- Cable CatalogDocument44 pagesCable CatalogRahmat Izaizi100% (3)
- Rhenogran Short Fiber Reinforcement For Rubber A4!04!2017Document6 pagesRhenogran Short Fiber Reinforcement For Rubber A4!04!2017vlabat2017No ratings yet
- Causes of Migraine PDFDocument7 pagesCauses of Migraine PDFJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Manual Lab Anatomy of Breast - LA RPS2 W3Document6 pagesManual Lab Anatomy of Breast - LA RPS2 W3Maharani KartikaNo ratings yet
- TB1 Chapter 6 - Multiple ChoiceDocument62 pagesTB1 Chapter 6 - Multiple ChoiceMonica100% (1)
- Basic Subsurface Flow (Steady State Condition) : Group 5Document63 pagesBasic Subsurface Flow (Steady State Condition) : Group 5jek vinNo ratings yet
- ITT American Electric Ultra Flood Series 277 & 278 Spec Sheet 2-80Document6 pagesITT American Electric Ultra Flood Series 277 & 278 Spec Sheet 2-80Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Hayagreeva - Pudding Prepared Using Split Chik PeasDocument8 pagesHayagreeva - Pudding Prepared Using Split Chik PeasSampathKumarGodavarthiNo ratings yet
- F 27414 3Document216 pagesF 27414 3VinothKumarDhananjayanNo ratings yet
- Trans-Savi-Med2-Lec 28-Introduction-to-Infectious-Diseases-1st-SemesterDocument7 pagesTrans-Savi-Med2-Lec 28-Introduction-to-Infectious-Diseases-1st-SemesterAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Price List: Heavy Duty Foodwaste Disposers and Electrical ControlsDocument39 pagesPrice List: Heavy Duty Foodwaste Disposers and Electrical Controlsedgar ricoNo ratings yet
- 01 Health Safety & Environmental MGMTDocument134 pages01 Health Safety & Environmental MGMTLau Siong Kwong67% (3)
- Godrej Case Study For Business Intelligence and Reporting ServicesDocument4 pagesGodrej Case Study For Business Intelligence and Reporting ServicesSonu LovesforuNo ratings yet
- Steve F. Carlisle,: Professional SummaryDocument5 pagesSteve F. Carlisle,: Professional SummaryRickey StokesNo ratings yet