Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP For Pleural Effusion
NCP For Pleural Effusion
Uploaded by
Lilian LinogaoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN87% (62)
- Pleural Effusion - Case StudyDocument25 pagesPleural Effusion - Case StudyLilian Linogao95% (19)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument7 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEjie Boy Isaga100% (2)
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocument1 pageDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)deric94% (17)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- POC Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pagePOC Ineffective Breathing Patterncuicuita100% (1)
- NCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaDocument11 pagesNCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaChristy Rose AgrisNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Acute Lymphocytic/Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument22 pagesCase Study On Acute Lymphocytic/Lymphoblastic LeukemiaLilian Linogao86% (21)
- Charles Stevenson - On What Is PoemDocument35 pagesCharles Stevenson - On What Is PoemFilip Nikolić100% (1)
- Discerning of Spirits - Francis FrangipaneDocument32 pagesDiscerning of Spirits - Francis FrangipaneOgoo Honysco100% (7)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEli Xma100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- NCP For TBDocument3 pagesNCP For TBNelle Agni100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternChristianmel JavierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNo ratings yet
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP HemoDocument2 pagesNCP HemoJigs HechNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Ncp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONDocument4 pagesNcp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONHania Polangi100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocument8 pagesNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (2)
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeNo ratings yet
- Disturbed SleepDocument1 pageDisturbed Sleepmawel100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument6 pagesNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanNo ratings yet
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- Pulmo Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesPulmo Nursing Care PlanVincent RoyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKen RegalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute BronchitisDocument9 pagesNCP Acute BronchitisCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Performance Task # 9Document6 pagesPerformance Task # 9Aileen Reign MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Capitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityDocument2 pagesCapitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityChaine Agolito100% (1)
- NCP PTBDocument4 pagesNCP PTBbryan matiasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Manila Doctors College: Pres. Diosdado Macapagal BLVD., Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityDocument3 pagesManila Doctors College: Pres. Diosdado Macapagal BLVD., Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityNichole CastleNo ratings yet
- NCP Anaphylactic ShockDocument6 pagesNCP Anaphylactic ShockKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Machate - Kia - Belle A. BSN 4a LP1 NCM 118Document9 pagesMachate - Kia - Belle A. BSN 4a LP1 NCM 118Arriane AndoyoNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter - SampleDocument1 pageAuthorization Letter - SampleLilian Linogao100% (1)
- NCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument7 pagesNCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaLilian Linogao100% (10)
- Microsoft Office Specialist: Microsoft Excel Expert (Excel and Excel 2019) - Skills MeasuredDocument3 pagesMicrosoft Office Specialist: Microsoft Excel Expert (Excel and Excel 2019) - Skills MeasuredRishabh Gangwar0% (1)
- Lebato-Pr2Document6 pagesLebato-Pr2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- 2 星期二 晚课课本 Saturday-Tuesday Chanting Book - 宁心寺 Santi Forest Monastery PDFDocument47 pages2 星期二 晚课课本 Saturday-Tuesday Chanting Book - 宁心寺 Santi Forest Monastery PDFLois ChuangNo ratings yet
- HomicideDocument15 pagesHomicideCHAW HUI XINNo ratings yet
- Using Flexible Clinical Processes in The Unified Protocol For The Treatment of Emotional Disorders in AdolescenceDocument6 pagesUsing Flexible Clinical Processes in The Unified Protocol For The Treatment of Emotional Disorders in AdolescenceLaura SanabriaNo ratings yet
- 1E Star Trek Customizable Card Game - 4 Introductory Two-Player Rule BookDocument9 pages1E Star Trek Customizable Card Game - 4 Introductory Two-Player Rule Bookmrtibbles100% (1)
- What Is MentoringDocument5 pagesWhat Is MentoringDeepak Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- HUMA1950SU 2023 SyllabusDocument11 pagesHUMA1950SU 2023 SyllabusHumza T kingNo ratings yet
- Laptop vs. Desktop Computer: A Research Based On Computer Preference of Ramon Magsaysay High School StudentsDocument14 pagesLaptop vs. Desktop Computer: A Research Based On Computer Preference of Ramon Magsaysay High School StudentsLhenz PaghunasanNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech 2Document26 pagesDirect Indirect Speech 2bobisetiawan016No ratings yet
- Announcement of Test Date, Time and VenueDocument240 pagesAnnouncement of Test Date, Time and VenueAriful IslamNo ratings yet
- Mahasneh 2010 Emotiveness in Darwish PDFDocument140 pagesMahasneh 2010 Emotiveness in Darwish PDFAlaa SabbahNo ratings yet
- Flamenco FormsDocument3 pagesFlamenco FormsNayvi KirkendallNo ratings yet
- 11 - NCPsDocument6 pages11 - NCPsellian3leiNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2191280 1Document21 pagesSSRN Id2191280 1Andrew TandohNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument119 pagesQuiz Letnagap1914No ratings yet
- Annual Implementation PlanDocument4 pagesAnnual Implementation PlanNeil Atanacio50% (2)
- Spreading of The Ocean Floor: New EvidenceDocument11 pagesSpreading of The Ocean Floor: New EvidenceDonk FarhoudNo ratings yet
- Missouri Quit Claim Deed FormDocument2 pagesMissouri Quit Claim Deed FormHiNo ratings yet
- FS360 - Life Partner SelectionDocument71 pagesFS360 - Life Partner Selectioneliza.dias100% (17)
- NEW-LP-WEEK-1Document3 pagesNEW-LP-WEEK-1Gel VelasquezcauzonNo ratings yet
- Unnecessary Comma in A Complex SentenceDocument2 pagesUnnecessary Comma in A Complex SentenceSellappan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Colegio Elena Ch. de Pinate: Ministry of EducationDocument10 pagesColegio Elena Ch. de Pinate: Ministry of EducationEdna Elida Guittens CamposNo ratings yet
- Report MAN AS EMBODIED SUBJECTIVITYDocument7 pagesReport MAN AS EMBODIED SUBJECTIVITYCute TzyNo ratings yet
- Credit Transactions TranscriptDocument12 pagesCredit Transactions TranscriptFloramae PasculadoNo ratings yet
- Ict PresentationDocument22 pagesIct Presentationadilattique859No ratings yet
- Hygienic Assessment of Working Conditions in Carpet Weaving ProductionDocument4 pagesHygienic Assessment of Working Conditions in Carpet Weaving ProductionCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- 11 Partnership DissolutionDocument10 pages11 Partnership DissolutionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet
NCP For Pleural Effusion
NCP For Pleural Effusion
Uploaded by
Lilian LinogaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP For Pleural Effusion
NCP For Pleural Effusion
Uploaded by
Lilian LinogaoCopyright:
Available Formats
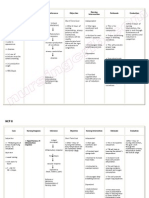
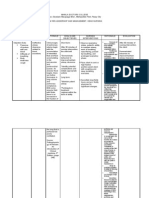
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR PLEURAL EFFUSION
page 18
PATIENT PROBLEM PLANNING & IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION
DATE PATIENT OUTCOME
ACTUAL/POTENTIAL NURSING INTERVENTION DATE COMMENTS
Ineffective breathing pattern Client will be able to restore Assess client respiration 4 hourly e.g., rate, 14.1.2011 Client was able to restore 80% of
related to decreased lung effective lung expansion rhythm, depth and breath sound. Note lung expansion
expansion secondary to manifestation of ineffective breathing. Early
accumulation of fluid in the identification of respirations allow timely and
pleural cavity appropriate initiation of interventions
Client will be comfortable Client was comfortable
Monitoring vital signs 4 hourly. Tachypnea,
tachycardia, elevated blood pressure and
increasing hypoxemia and hypercapnia are signs
of compromised respiratory status.
Client will breath easily Client breathed easily
Assess client during self care activities. This
conserves energy and reduces fatigue.
Provide rest periods between scheduled activites
Client will be comfortable and treatments to prevent fatigue and reduce Client was comfortable
oxygen demands.
Positon client in semi fowlers or high fowlers
with head and arms supported on the cardiac
table to reduces pressure on the diaphragm and
permit optimal lung expansion.
Teach client to do deep breathing technique to
promote lung expansion
Provide oxygen theraphy e.g. 3L/min. nasal
prong or as ordered by physician to increase
oxygen saturation of the blood
Use pulse oximeter to monitor oxygen
saturation and pulse rate to detect oxygenation
level and effectiveness of treatment
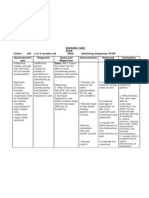
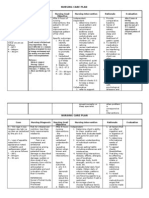
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR PLEURAL EFFUSION
page 19
PATIENT PROBLEM PATIENT PLANNING & IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION
DATE OUTCOME
ACTUAL/POTENTIAL NURSING INTERVENTION DATE COMMENTS
1/16/2011 Knowledge deficit Client will verbalize 14.1.2011 Client verbalized understanding on
regarding health condition, understanding of the Provide knowledge base for understanding the cause of his current condition,
treatment regimen and self cause of problem, dynamics of condition and significance of complications and identified signs
care related to lack of complications and therapeutic interventions to reduce fear of and symptoms requiring medical
exposure to information identify signs and unknown. attention
symptoms requiring
medical attention.
Encourage client to follow strict treatment
regimen to prevent complications like
pneumothorax, emyema, and collapsed lung
will develop if treatment is delayed.
Teach client that maintenance of general
well-being e.g., eat healthy heart food,
exercise, personal hygiene pomotes healing
and may prevent/limit recurrences
Teach client the signs and symptoms of all
his illness especially pleuritic pain, SOB,
dyspnea, hymoptysis, coughing of blood, etc.
that needs immediate medical attention to
prevent further damage and complications.
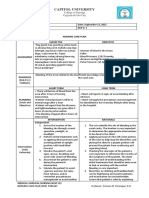
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR PLEURAL EFFUSION
page 20
PATIENT PROBLEM PATIENT PLANNING & IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION
DATE OUTCOME
ACTUAL/POTENTIAL NURSING INTERVENTION DATE COMMENTS
09.1.11 Risk of injury related Client will not get Monitor client pulse, skin color, oxygen 14.1.2011 Client pleural tapping was
to pleural tapping pleural tapping saturation during thoracentesis for indicated successful and no complications
14.1.11 complications of physiologic tolerance of the procedure
Client will feel Apply client dressing over the puncture site Client felt less pain and
comfortable and less and position on the unaffected site for 1 hour comfortable
pain to allows the pleural puncture to heal
Administer client a cough suppressant as
ordered because movement and coughing
during the procedure may cause damage to
the lung or pleural
Position client to upright, learning forward
with arms and head supported on an
anchored overbed or cardiac table to
promote expansion of the rib enlarging
intercostal space for easy needle insertion
Inform client that local anesthesia will be
given to reduce pain/sensation pressure as
needle will be inserted to puncture the
parietal pleural to enter the pleural space
You might also like
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN87% (62)
- Pleural Effusion - Case StudyDocument25 pagesPleural Effusion - Case StudyLilian Linogao95% (19)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument7 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEjie Boy Isaga100% (2)
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocument1 pageDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)deric94% (17)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- POC Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pagePOC Ineffective Breathing Patterncuicuita100% (1)
- NCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaDocument11 pagesNCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaChristy Rose AgrisNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Acute Lymphocytic/Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument22 pagesCase Study On Acute Lymphocytic/Lymphoblastic LeukemiaLilian Linogao86% (21)
- Charles Stevenson - On What Is PoemDocument35 pagesCharles Stevenson - On What Is PoemFilip Nikolić100% (1)
- Discerning of Spirits - Francis FrangipaneDocument32 pagesDiscerning of Spirits - Francis FrangipaneOgoo Honysco100% (7)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEli Xma100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- NCP For TBDocument3 pagesNCP For TBNelle Agni100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternChristianmel JavierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNo ratings yet
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP HemoDocument2 pagesNCP HemoJigs HechNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Ncp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONDocument4 pagesNcp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONHania Polangi100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocument8 pagesNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (2)
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeNo ratings yet
- Disturbed SleepDocument1 pageDisturbed Sleepmawel100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument6 pagesNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanNo ratings yet
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- Pulmo Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesPulmo Nursing Care PlanVincent RoyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKen RegalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute BronchitisDocument9 pagesNCP Acute BronchitisCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Performance Task # 9Document6 pagesPerformance Task # 9Aileen Reign MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Capitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityDocument2 pagesCapitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityChaine Agolito100% (1)
- NCP PTBDocument4 pagesNCP PTBbryan matiasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Manila Doctors College: Pres. Diosdado Macapagal BLVD., Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityDocument3 pagesManila Doctors College: Pres. Diosdado Macapagal BLVD., Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityNichole CastleNo ratings yet
- NCP Anaphylactic ShockDocument6 pagesNCP Anaphylactic ShockKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Machate - Kia - Belle A. BSN 4a LP1 NCM 118Document9 pagesMachate - Kia - Belle A. BSN 4a LP1 NCM 118Arriane AndoyoNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter - SampleDocument1 pageAuthorization Letter - SampleLilian Linogao100% (1)
- NCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument7 pagesNCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaLilian Linogao100% (10)
- Microsoft Office Specialist: Microsoft Excel Expert (Excel and Excel 2019) - Skills MeasuredDocument3 pagesMicrosoft Office Specialist: Microsoft Excel Expert (Excel and Excel 2019) - Skills MeasuredRishabh Gangwar0% (1)
- Lebato-Pr2Document6 pagesLebato-Pr2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- 2 星期二 晚课课本 Saturday-Tuesday Chanting Book - 宁心寺 Santi Forest Monastery PDFDocument47 pages2 星期二 晚课课本 Saturday-Tuesday Chanting Book - 宁心寺 Santi Forest Monastery PDFLois ChuangNo ratings yet
- HomicideDocument15 pagesHomicideCHAW HUI XINNo ratings yet
- Using Flexible Clinical Processes in The Unified Protocol For The Treatment of Emotional Disorders in AdolescenceDocument6 pagesUsing Flexible Clinical Processes in The Unified Protocol For The Treatment of Emotional Disorders in AdolescenceLaura SanabriaNo ratings yet
- 1E Star Trek Customizable Card Game - 4 Introductory Two-Player Rule BookDocument9 pages1E Star Trek Customizable Card Game - 4 Introductory Two-Player Rule Bookmrtibbles100% (1)
- What Is MentoringDocument5 pagesWhat Is MentoringDeepak Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- HUMA1950SU 2023 SyllabusDocument11 pagesHUMA1950SU 2023 SyllabusHumza T kingNo ratings yet
- Laptop vs. Desktop Computer: A Research Based On Computer Preference of Ramon Magsaysay High School StudentsDocument14 pagesLaptop vs. Desktop Computer: A Research Based On Computer Preference of Ramon Magsaysay High School StudentsLhenz PaghunasanNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech 2Document26 pagesDirect Indirect Speech 2bobisetiawan016No ratings yet
- Announcement of Test Date, Time and VenueDocument240 pagesAnnouncement of Test Date, Time and VenueAriful IslamNo ratings yet
- Mahasneh 2010 Emotiveness in Darwish PDFDocument140 pagesMahasneh 2010 Emotiveness in Darwish PDFAlaa SabbahNo ratings yet
- Flamenco FormsDocument3 pagesFlamenco FormsNayvi KirkendallNo ratings yet
- 11 - NCPsDocument6 pages11 - NCPsellian3leiNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2191280 1Document21 pagesSSRN Id2191280 1Andrew TandohNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument119 pagesQuiz Letnagap1914No ratings yet
- Annual Implementation PlanDocument4 pagesAnnual Implementation PlanNeil Atanacio50% (2)
- Spreading of The Ocean Floor: New EvidenceDocument11 pagesSpreading of The Ocean Floor: New EvidenceDonk FarhoudNo ratings yet
- Missouri Quit Claim Deed FormDocument2 pagesMissouri Quit Claim Deed FormHiNo ratings yet
- FS360 - Life Partner SelectionDocument71 pagesFS360 - Life Partner Selectioneliza.dias100% (17)
- NEW-LP-WEEK-1Document3 pagesNEW-LP-WEEK-1Gel VelasquezcauzonNo ratings yet
- Unnecessary Comma in A Complex SentenceDocument2 pagesUnnecessary Comma in A Complex SentenceSellappan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Colegio Elena Ch. de Pinate: Ministry of EducationDocument10 pagesColegio Elena Ch. de Pinate: Ministry of EducationEdna Elida Guittens CamposNo ratings yet
- Report MAN AS EMBODIED SUBJECTIVITYDocument7 pagesReport MAN AS EMBODIED SUBJECTIVITYCute TzyNo ratings yet
- Credit Transactions TranscriptDocument12 pagesCredit Transactions TranscriptFloramae PasculadoNo ratings yet
- Ict PresentationDocument22 pagesIct Presentationadilattique859No ratings yet
- Hygienic Assessment of Working Conditions in Carpet Weaving ProductionDocument4 pagesHygienic Assessment of Working Conditions in Carpet Weaving ProductionCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- 11 Partnership DissolutionDocument10 pages11 Partnership DissolutionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet