Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Initial Velocity
Initial Velocity
Uploaded by
Wakee Bautista MangawerzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Commercial Catalogue Kompanija Sloboda AdDocument79 pagesCommercial Catalogue Kompanija Sloboda AdИван МилутиновићNo ratings yet
- Physics Projectile Problem SolvingDocument21 pagesPhysics Projectile Problem SolvingNathaniel Cruz100% (1)
- Type of Force Description of ForceDocument2 pagesType of Force Description of Forcezaiayra71No ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument22 pagesProjectile MotionHarshVasoya100% (1)
- Projectile LaunchDocument7 pagesProjectile LaunchScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- What Is A Projectile?: Defining ProjectilesDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Projectile?: Defining ProjectilesJeje NutNo ratings yet
- Weightlessness Is A Phenomenon Experienced by People During FreeDocument6 pagesWeightlessness Is A Phenomenon Experienced by People During FreeNithin MadhuNo ratings yet
- Force Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaDocument18 pagesForce Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaHazel LiporadaNo ratings yet
- Free Fall: Mass WeightDocument5 pagesFree Fall: Mass WeightChuchuLoloNo ratings yet
- What Is A Projectile?: Unit 1 Unit 2Document4 pagesWhat Is A Projectile?: Unit 1 Unit 2Josh Achaso LabragueNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument22 pagesProjectile MotionChris PuelasNo ratings yet
- Ang Uri NG Pang Abay at Mga Halimbawa NitoDocument3 pagesAng Uri NG Pang Abay at Mga Halimbawa NitoJailian Rhainne Delloso BretañaNo ratings yet
- S Summarized Symbolically As: Using Newton's Gravitation Equation To Solve ProblemsDocument5 pagesS Summarized Symbolically As: Using Newton's Gravitation Equation To Solve ProblemsJustine Matthan DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Free Fall - Common Term For Any Motion That, in Theory, IsDocument1 pageFree Fall - Common Term For Any Motion That, in Theory, IsJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- What Is A ProjectileDocument11 pagesWhat Is A ProjectileLorieAnnBringasNo ratings yet
- Genphysics1 Lesson 2Document19 pagesGenphysics1 Lesson 2Ariane AngelesNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 2Document43 pagesProjectile Motion 2Anonymous VLzpakNbNo ratings yet
- PROJECTILE MOTIONDocument4 pagesPROJECTILE MOTIONMohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Fuerza - 1 UamDocument23 pagesFuerza - 1 UamJOSE ANDRES MAMANI CALDASNo ratings yet
- What Are Forces in PhysicsDocument3 pagesWhat Are Forces in PhysicsJessNo ratings yet
- GSE Slide 1-4Document8 pagesGSE Slide 1-4Abrar RatulNo ratings yet
- Kinds of ForcesDocument5 pagesKinds of ForcesDhenzhel CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Force Flash CardsDocument2 pagesForce Flash CardsMaki ShurikenNo ratings yet
- GravityDocument1 pageGravityEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Q4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesQ4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile Motionluispacifico.pagkalinawanNo ratings yet
- Sports Bio-Mechanics: Assignment OnDocument4 pagesSports Bio-Mechanics: Assignment Onjohnjoseph4069No ratings yet
- Application of Circular MotionDocument13 pagesApplication of Circular MotionChi KoyNo ratings yet
- Esc 17 1Document21 pagesEsc 17 1elaco56No ratings yet
- ProjectDocument10 pagesProjectChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Free-Body DiagramDocument8 pagesLecture 3 - Free-Body DiagramMarjorie Jean AnogNo ratings yet
- ProjectileDocument1 pageProjectileJaspreet Singh ChopraNo ratings yet
- Gravitational ForceDocument4 pagesGravitational ForcemainlyiiiNo ratings yet
- قوانين نيوتنDocument6 pagesقوانين نيوتنhaedraldrage1No ratings yet
- Types of ForcesDocument7 pagesTypes of ForcesimanuelsukarnoNo ratings yet
- Asm1 8776Document4 pagesAsm1 8776vishwajitmisal0No ratings yet
- Phys 11 Mechanics Part 2Document67 pagesPhys 11 Mechanics Part 2Alex EquiasNo ratings yet
- Force of GravityDocument22 pagesForce of GravityBiplobNo ratings yet
- CP Project Report 045Document3 pagesCP Project Report 045Shahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- What Are ForcesDocument2 pagesWhat Are ForcesChi EdzaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Types of ForcesDocument3 pagesTypes of Forcesaleakim13XDNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument2 pagesGravitationprateeksinghmbd01No ratings yet
- Nowy Dokument TekstowyDocument2 pagesNowy Dokument TekstowyCuCumber CCNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Project Prakhar Sharma 11-CDocument16 pagesProjectile Motion Project Prakhar Sharma 11-Cboiy3499No ratings yet
- HW - Types of Forces and FBD NotesDocument4 pagesHW - Types of Forces and FBD NotesAstro AarivuNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 11thDocument11 pagesGravitation 11thpiyushdua01No ratings yet
- p6 Exam 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesp6 Exam 4th QuarterproductivejuswaNo ratings yet
- 02.1 - Forces Acting On A Ship PDFDocument33 pages02.1 - Forces Acting On A Ship PDFClarence PieterszNo ratings yet
- Trying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P oDocument4 pagesTrying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P odjbhetaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Lo.1Document40 pagesPhysics 2 Lo.1Mohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesForce and Pressure Notesmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramDocument4 pagesFree Body DiagramMaika Pilley DaduboNo ratings yet
- Forceandmotion 181112055529Document36 pagesForceandmotion 181112055529FernandoNo ratings yet
- Stability - ForceDocument17 pagesStability - Forcelife & logicNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument6 pagesForce and Motionohnmarhtet09No ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - WorksheetDocument15 pagesProjectile Motion - WorksheetRaniya LittlejohnNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Claire FabellarNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument16 pagesForceLIZETTE GARCIANo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsArun RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer ScienceKeizer FiscoNo ratings yet
- DAAAM04 Zecevic-DesignDocument3 pagesDAAAM04 Zecevic-DesignMol MolNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4, Wk2 - Module 2Document31 pagesScience: Quarter 4, Wk2 - Module 2Arthur Capawing45% (11)
- Matag-Ob National High SchoolDocument4 pagesMatag-Ob National High SchoolTEREMIE JOSEPH OBADONo ratings yet
- Test 1 Unit 1 Physics Sem 1 2017Document10 pagesTest 1 Unit 1 Physics Sem 1 2017SongNo ratings yet
- PROJECTILE MOTION (Example Lab Report) : Total Mechanical EnergyDocument7 pagesPROJECTILE MOTION (Example Lab Report) : Total Mechanical EnergyEmily Watts100% (3)
- All 923, 023, 2123 Lot-Main - CPT-1 - RT-1 - VD - SD - BDocument19 pagesAll 923, 023, 2123 Lot-Main - CPT-1 - RT-1 - VD - SD - BSamarth Aggarwal100% (1)
- ADMModule - GP12KIN Ic 22 PDFDocument25 pagesADMModule - GP12KIN Ic 22 PDFJake Eulogio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 1-Projectile Motion (Part 1)Document33 pagesQ4-WEEK 1-Projectile Motion (Part 1)Adonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNo ratings yet
- MainDocument45 pagesMainapi-534925017No ratings yet
- Answer Key For WK3-4Document9 pagesAnswer Key For WK3-4April Joy LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Simulator WorksheetDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Simulator WorksheetJose MasarateNo ratings yet
- Ballistic Fabric Moultrie MurphyDocument2 pagesBallistic Fabric Moultrie MurphyTamer Farouk KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Essential Physics Student Lab ManualDocument143 pagesEssential Physics Student Lab ManualSteven BTCNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion WebquestDocument4 pagesProjectile Motion Webquestsara motleyNo ratings yet
- Forensic 6 Week-1Document3 pagesForensic 6 Week-1Ella BanlasanNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion QuiZDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion QuiZyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Projectiles P2Document13 pagesProjectiles P2MEXI EVYNo ratings yet
- FSMA Galileo's Projectile Model StudentDocument5 pagesFSMA Galileo's Projectile Model StudentLea Mae MimayNo ratings yet
- Gunshot Wounds - Rifled Weapons - WWW - Forensicmed.coDocument22 pagesGunshot Wounds - Rifled Weapons - WWW - Forensicmed.coBindashboy0No ratings yet
- General Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Title: Components of Projectile MotionDocument25 pagesGeneral Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Title: Components of Projectile MotionFaith AsdfNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesProjectile MotionAbiegail Asas PelenioNo ratings yet
- AP Physics: - Work and EnergyDocument34 pagesAP Physics: - Work and Energynicolae cuneNo ratings yet
- Ap Lab#2Document12 pagesAp Lab#2Talharashid RamzanNo ratings yet
- Ap Phys1 - Kinematics 2d Multiple Choice - 2023 10 07Document14 pagesAp Phys1 - Kinematics 2d Multiple Choice - 2023 10 07Abdullah MalikNo ratings yet
- T2 B7 Corken Memo FDR - 3-30-00 Legal Memorandum by Attorney Robert A de La Cruz - Aerial Intercepts and Shoot Downs 655Document34 pagesT2 B7 Corken Memo FDR - 3-30-00 Legal Memorandum by Attorney Robert A de La Cruz - Aerial Intercepts and Shoot Downs 6559/11 Document ArchiveNo ratings yet
- Trebuchet DynamicsDocument8 pagesTrebuchet DynamicsLeo KutsNo ratings yet
- National University: Name/Section Rating Date Performed Date SubmittedDocument4 pagesNational University: Name/Section Rating Date Performed Date SubmittedGail Domingo0% (1)
Initial Velocity
Initial Velocity
Uploaded by
Wakee Bautista MangawerzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Initial Velocity
Initial Velocity
Uploaded by
Wakee Bautista MangawerzCopyright:
Available Formats
Initial velocity, the velocity of a moving body at
starting; especially, the velocity of a projectile as it
leaves the mouth of a firearm from which it is discharged.
In physics, velocity is the measurement of the rate and direction of change in position of an object. It is a
vector physical quantity; both magnitude and direction are required to define it.
gravitational force - (physics) the force of attraction between all masses in the universe; especially the
attraction of the earth's mass for bodies near its surface; "the more remote the body the less the
gravity"; "the gravitation between two bodies is proportional to the product of their masses and
inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them"; "gravitation cannot be held
responsible for people falling in love"--Albert Einstein
A projectile is an object upon which the only force acting is gravity. There are a variety of examples of
projectiles. An object dropped from rest is a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is
negligible). An object that is thrown vertically upward is also a projectile (provided that the influence of
air resistance is negligible). And an object which is thrown upward at an angle to the horizontal is also a
projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). A projectile is any object that once
projected or dropped continues in motion by its own inertia and is influenced only by the downward
force of gravity.
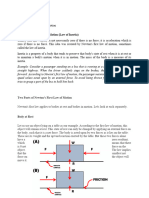
By definition, a projectile has a single force that acts upon it - the force of gravity. If there were any
other force acting upon an object, then that object would not be a projectile. Thus, the free-body
diagram of a projectile would show a single force acting downwards and labeled force of gravity (or
simply Fgrav). Regardless of whether a projectile is moving downwards, upwards, upwards and
rightwards, or downwards and leftwards, the free-body diagram of the projectile is still as depicted in
the diagram at the right. By definition, a projectile is any object upon which the only force is gravity.
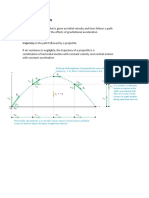
A trajectory is the path a moving object follows through space as a function of time. The object might be
a projectile or a satellite, for example. It thus includes the meaning of orbit—the path of a planet, an
asteroid or a comet as it travels around a central mass. A trajectory can be described mathematically
either by the geometry of the path, or as the position of the object over time.
You might also like
- Commercial Catalogue Kompanija Sloboda AdDocument79 pagesCommercial Catalogue Kompanija Sloboda AdИван МилутиновићNo ratings yet
- Physics Projectile Problem SolvingDocument21 pagesPhysics Projectile Problem SolvingNathaniel Cruz100% (1)
- Type of Force Description of ForceDocument2 pagesType of Force Description of Forcezaiayra71No ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument22 pagesProjectile MotionHarshVasoya100% (1)
- Projectile LaunchDocument7 pagesProjectile LaunchScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- What Is A Projectile?: Defining ProjectilesDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Projectile?: Defining ProjectilesJeje NutNo ratings yet
- Weightlessness Is A Phenomenon Experienced by People During FreeDocument6 pagesWeightlessness Is A Phenomenon Experienced by People During FreeNithin MadhuNo ratings yet
- Force Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaDocument18 pagesForce Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaHazel LiporadaNo ratings yet
- Free Fall: Mass WeightDocument5 pagesFree Fall: Mass WeightChuchuLoloNo ratings yet
- What Is A Projectile?: Unit 1 Unit 2Document4 pagesWhat Is A Projectile?: Unit 1 Unit 2Josh Achaso LabragueNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument22 pagesProjectile MotionChris PuelasNo ratings yet
- Ang Uri NG Pang Abay at Mga Halimbawa NitoDocument3 pagesAng Uri NG Pang Abay at Mga Halimbawa NitoJailian Rhainne Delloso BretañaNo ratings yet
- S Summarized Symbolically As: Using Newton's Gravitation Equation To Solve ProblemsDocument5 pagesS Summarized Symbolically As: Using Newton's Gravitation Equation To Solve ProblemsJustine Matthan DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Free Fall - Common Term For Any Motion That, in Theory, IsDocument1 pageFree Fall - Common Term For Any Motion That, in Theory, IsJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- What Is A ProjectileDocument11 pagesWhat Is A ProjectileLorieAnnBringasNo ratings yet
- Genphysics1 Lesson 2Document19 pagesGenphysics1 Lesson 2Ariane AngelesNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 2Document43 pagesProjectile Motion 2Anonymous VLzpakNbNo ratings yet
- PROJECTILE MOTIONDocument4 pagesPROJECTILE MOTIONMohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Fuerza - 1 UamDocument23 pagesFuerza - 1 UamJOSE ANDRES MAMANI CALDASNo ratings yet
- What Are Forces in PhysicsDocument3 pagesWhat Are Forces in PhysicsJessNo ratings yet
- GSE Slide 1-4Document8 pagesGSE Slide 1-4Abrar RatulNo ratings yet
- Kinds of ForcesDocument5 pagesKinds of ForcesDhenzhel CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Force Flash CardsDocument2 pagesForce Flash CardsMaki ShurikenNo ratings yet
- GravityDocument1 pageGravityEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Q4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesQ4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile Motionluispacifico.pagkalinawanNo ratings yet
- Sports Bio-Mechanics: Assignment OnDocument4 pagesSports Bio-Mechanics: Assignment Onjohnjoseph4069No ratings yet
- Application of Circular MotionDocument13 pagesApplication of Circular MotionChi KoyNo ratings yet
- Esc 17 1Document21 pagesEsc 17 1elaco56No ratings yet
- ProjectDocument10 pagesProjectChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Free-Body DiagramDocument8 pagesLecture 3 - Free-Body DiagramMarjorie Jean AnogNo ratings yet
- ProjectileDocument1 pageProjectileJaspreet Singh ChopraNo ratings yet
- Gravitational ForceDocument4 pagesGravitational ForcemainlyiiiNo ratings yet
- قوانين نيوتنDocument6 pagesقوانين نيوتنhaedraldrage1No ratings yet
- Types of ForcesDocument7 pagesTypes of ForcesimanuelsukarnoNo ratings yet
- Asm1 8776Document4 pagesAsm1 8776vishwajitmisal0No ratings yet
- Phys 11 Mechanics Part 2Document67 pagesPhys 11 Mechanics Part 2Alex EquiasNo ratings yet
- Force of GravityDocument22 pagesForce of GravityBiplobNo ratings yet
- CP Project Report 045Document3 pagesCP Project Report 045Shahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- What Are ForcesDocument2 pagesWhat Are ForcesChi EdzaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Types of ForcesDocument3 pagesTypes of Forcesaleakim13XDNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument2 pagesGravitationprateeksinghmbd01No ratings yet
- Nowy Dokument TekstowyDocument2 pagesNowy Dokument TekstowyCuCumber CCNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Project Prakhar Sharma 11-CDocument16 pagesProjectile Motion Project Prakhar Sharma 11-Cboiy3499No ratings yet
- HW - Types of Forces and FBD NotesDocument4 pagesHW - Types of Forces and FBD NotesAstro AarivuNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 11thDocument11 pagesGravitation 11thpiyushdua01No ratings yet
- p6 Exam 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesp6 Exam 4th QuarterproductivejuswaNo ratings yet
- 02.1 - Forces Acting On A Ship PDFDocument33 pages02.1 - Forces Acting On A Ship PDFClarence PieterszNo ratings yet
- Trying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P oDocument4 pagesTrying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P odjbhetaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Lo.1Document40 pagesPhysics 2 Lo.1Mohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesForce and Pressure Notesmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramDocument4 pagesFree Body DiagramMaika Pilley DaduboNo ratings yet
- Forceandmotion 181112055529Document36 pagesForceandmotion 181112055529FernandoNo ratings yet
- Stability - ForceDocument17 pagesStability - Forcelife & logicNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument6 pagesForce and Motionohnmarhtet09No ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - WorksheetDocument15 pagesProjectile Motion - WorksheetRaniya LittlejohnNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - Fundamental Physics (Forces)Claire FabellarNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument16 pagesForceLIZETTE GARCIANo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsArun RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer ScienceKeizer FiscoNo ratings yet
- DAAAM04 Zecevic-DesignDocument3 pagesDAAAM04 Zecevic-DesignMol MolNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4, Wk2 - Module 2Document31 pagesScience: Quarter 4, Wk2 - Module 2Arthur Capawing45% (11)
- Matag-Ob National High SchoolDocument4 pagesMatag-Ob National High SchoolTEREMIE JOSEPH OBADONo ratings yet
- Test 1 Unit 1 Physics Sem 1 2017Document10 pagesTest 1 Unit 1 Physics Sem 1 2017SongNo ratings yet
- PROJECTILE MOTION (Example Lab Report) : Total Mechanical EnergyDocument7 pagesPROJECTILE MOTION (Example Lab Report) : Total Mechanical EnergyEmily Watts100% (3)
- All 923, 023, 2123 Lot-Main - CPT-1 - RT-1 - VD - SD - BDocument19 pagesAll 923, 023, 2123 Lot-Main - CPT-1 - RT-1 - VD - SD - BSamarth Aggarwal100% (1)
- ADMModule - GP12KIN Ic 22 PDFDocument25 pagesADMModule - GP12KIN Ic 22 PDFJake Eulogio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 1-Projectile Motion (Part 1)Document33 pagesQ4-WEEK 1-Projectile Motion (Part 1)Adonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNo ratings yet
- MainDocument45 pagesMainapi-534925017No ratings yet
- Answer Key For WK3-4Document9 pagesAnswer Key For WK3-4April Joy LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Simulator WorksheetDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Simulator WorksheetJose MasarateNo ratings yet
- Ballistic Fabric Moultrie MurphyDocument2 pagesBallistic Fabric Moultrie MurphyTamer Farouk KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Essential Physics Student Lab ManualDocument143 pagesEssential Physics Student Lab ManualSteven BTCNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion WebquestDocument4 pagesProjectile Motion Webquestsara motleyNo ratings yet
- Forensic 6 Week-1Document3 pagesForensic 6 Week-1Ella BanlasanNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion QuiZDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion QuiZyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Projectiles P2Document13 pagesProjectiles P2MEXI EVYNo ratings yet
- FSMA Galileo's Projectile Model StudentDocument5 pagesFSMA Galileo's Projectile Model StudentLea Mae MimayNo ratings yet
- Gunshot Wounds - Rifled Weapons - WWW - Forensicmed.coDocument22 pagesGunshot Wounds - Rifled Weapons - WWW - Forensicmed.coBindashboy0No ratings yet
- General Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Title: Components of Projectile MotionDocument25 pagesGeneral Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Title: Components of Projectile MotionFaith AsdfNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesProjectile MotionAbiegail Asas PelenioNo ratings yet
- AP Physics: - Work and EnergyDocument34 pagesAP Physics: - Work and Energynicolae cuneNo ratings yet
- Ap Lab#2Document12 pagesAp Lab#2Talharashid RamzanNo ratings yet
- Ap Phys1 - Kinematics 2d Multiple Choice - 2023 10 07Document14 pagesAp Phys1 - Kinematics 2d Multiple Choice - 2023 10 07Abdullah MalikNo ratings yet
- T2 B7 Corken Memo FDR - 3-30-00 Legal Memorandum by Attorney Robert A de La Cruz - Aerial Intercepts and Shoot Downs 655Document34 pagesT2 B7 Corken Memo FDR - 3-30-00 Legal Memorandum by Attorney Robert A de La Cruz - Aerial Intercepts and Shoot Downs 6559/11 Document ArchiveNo ratings yet
- Trebuchet DynamicsDocument8 pagesTrebuchet DynamicsLeo KutsNo ratings yet
- National University: Name/Section Rating Date Performed Date SubmittedDocument4 pagesNational University: Name/Section Rating Date Performed Date SubmittedGail Domingo0% (1)