Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hyperbolic Functions: X X - LX X 0 L
Hyperbolic Functions: X X - LX X 0 L
Uploaded by
apocalyptOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hyperbolic Functions: X X - LX X 0 L
Hyperbolic Functions: X X - LX X 0 L
Uploaded by
apocalyptCopyright:
Available Formats
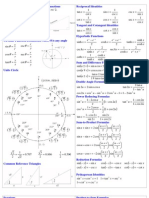
hyperbolic functions
e x - e -x e x + e -x
definition sinhx = coshx =
2 2
4
derivative sinh¢ x = coshx cosh¢ x = sinhx 3
† †
coshx
2
integration † Ú sinhxdx = coshx † Ú coshxdx = sinhx 1
0
symmetry sinh(-x) = -sinhx cosh(-x) = coshx
† †
-1
value at 0 sinh0 = 0 cosh0 = 1 -2 sinhx
† †
-3
x3 x5 x2 x4
series expansion † sinhx = x + + + ... † coshx = 1+ + + ...
3! 5! 2! 4! -4
-2 -1 0 1 2
identities cosh 2 x - sinh 2 x = 1 coshx ± sinhx = e ± x
† †
† †
special equation
X ¢¢(x ) - lX(x ) = 0 l= constant
auxilary equation m2 = l roots m=± l
general solution †
derivative of general solution †
Ï l>0 Ï c 1 le l x - c 2 le - lx l>0
c 1e lx + c 2e - l x Ô
Ô
X(x) = Ì c 1 + c 2x l=0 X¢(x) = Ì c2 l=0
Ôc cos -lx + c sin -lx l<0 Ô-c -l sin -lx + c -l cos -lx l<0
Ó 1 2 Ó 1 2
† †
† †
Ïc cosh lx + c sinh lx Ï c l sinh lx + c l cosh lx l>0
Ô 1 2 l>0 Ô 1 2
X(x) = Ì c 1 + c 2x l=0 X¢(x) = Ì c2 l=0
Ôc cos -lx + c sin -lx Ô-c -l sin -lx + c -l cos -lx l<0
Ó 1 2 l<0 Ó 1 2
† †
† †
Ïc cosh l x - x + c sinh l x - x Ï c l sinh l x - x + c l cosh l x - x l>0
Ô 1 ( 0) 2 ( 0) l>0 Ô 1 ( 0) 2 ( 0)
X(x) = Ì c 1 + c 2 (x - x 0 ) l=0 X¢(x) = Ì c2 l=0
Ô Ô-c -l sin -l x - x + c -l cos -l x - x l<0
Óc 1 cos -l (x - x 0 ) + c 2 sin -l (x - x 0 ) l<0 Ó 1 ( 0) 2 ( 0)
† †
† †
You might also like
- Restaurant-Feasibility-Report-in-Pakistan ZaheerDocument12 pagesRestaurant-Feasibility-Report-in-Pakistan ZaheerzaheerNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument11 pagesHyperbolic Functionslukebyers.masonNo ratings yet
- 2tan 1+tan 1 Tan 1+tan 2t 1 T Sinx Cosx X 2 1 1+t A+b 2 A B 2 A+b 2 A B 2 A+b 2 A B 2 A+b 2 A B 2 Sin (A B) Cosa Cosb Sin (B A) Sina SinbDocument2 pages2tan 1+tan 1 Tan 1+tan 2t 1 T Sinx Cosx X 2 1 1+t A+b 2 A B 2 A+b 2 A B 2 A+b 2 A B 2 A+b 2 A B 2 Sin (A B) Cosa Cosb Sin (B A) Sina SinbJesko ShmittNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb cp2 Ex3bDocument6 pagesAlevelsb cp2 Ex3bkorexi3778No ratings yet
- Test 1 Ssce1693 2122 01 Utmspace-11.12.2021Document4 pagesTest 1 Ssce1693 2122 01 Utmspace-11.12.2021Wan Abdul HadiNo ratings yet
- HW-1 5-1 67Document2 pagesHW-1 5-1 67REYNIEL JOSHUA MERCADONo ratings yet
- Formula 1Document1 pageFormula 1randhawa03023No ratings yet
- 5.0 Formulas MatematicasDocument3 pages5.0 Formulas MatematicasANo ratings yet
- Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument5 pagesInverse Hyperbolic FunctionsFaizal RomadhiNo ratings yet
- EquationzDocument17 pagesEquationzDevin StokerNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument3 pagesHyperbolic FunctionsCP Pikachu Crystal PalaceNo ratings yet
- CheatSheet BBEDocument2 pagesCheatSheet BBEHồng Phúc BùiNo ratings yet
- Limit Yusiva SM SidabutarDocument8 pagesLimit Yusiva SM SidabutarAnggara MirzaNo ratings yet
- Table of Formula ODEDocument3 pagesTable of Formula ODEalif ismaNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument1 pageFormulaejayekochanNo ratings yet
- Typologio 2018Document2 pagesTypologio 2018pkalNo ratings yet
- Default FolderDocument6 pagesDefault FolderUMESHA RANGADHAMAIAHNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Physics Useful Formulae PDFDocument29 pagesMathematical Physics Useful Formulae PDFKunal RanaNo ratings yet
- Funcţia Derivata: C (Constantă) 0 X 1 X XDocument3 pagesFuncţia Derivata: C (Constantă) 0 X 1 X XNatashaScutelinicNo ratings yet
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 102 PDFDocument10 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 102 PDFMrmouzinhoNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument2 pagesMathssatyasravanthNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 (Sol)Document3 pagesProblem Sheet 3 (Sol)Bu Lang NiNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 8 Kalkulus 2Document5 pagesPertemuan Ke 8 Kalkulus 2karolinapuja19No ratings yet
- 0 Math Notes - 1Document8 pages0 Math Notes - 1bdizzle329No ratings yet
- x+4 X x+4 X x+4 X X+ X X X: Repaso para Examen Ejercicios 1.3 Limites Analiticos 60)Document2 pagesx+4 X x+4 X x+4 X X+ X X X: Repaso para Examen Ejercicios 1.3 Limites Analiticos 60)victor floresNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions (Slides)Document20 pagesHyperbolic and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions (Slides)SideTrip SideKickNo ratings yet
- Formulário Lista 2: Interpolação PolinomialDocument1 pageFormulário Lista 2: Interpolação PolinomialRicardoNo ratings yet
- 3 5doneDocument1 page3 5doneeperlaNo ratings yet
- Integration Varsity Practice SheetDocument17 pagesIntegration Varsity Practice Sheetshahjahanarmy30No ratings yet
- Limit 05 Mirza AnggaraDocument8 pagesLimit 05 Mirza AnggaraAnggara MirzaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical FormulasDocument12 pagesMathematical FormulasjoshuariensonNo ratings yet
- 58 HyperbolicDocument22 pages58 Hyperbolicapi-3738981No ratings yet
- FToM Formulary SS2020Document14 pagesFToM Formulary SS2020Shristi SinghNo ratings yet
- Recall That Real Hyperbolic Sine and Hyperbolic Cosine Functions Are Defined AsDocument6 pagesRecall That Real Hyperbolic Sine and Hyperbolic Cosine Functions Are Defined Asmy pcNo ratings yet
- LimxDocument1 pageLimxJames Querimit De LunaNo ratings yet
- Stewart Calcch 3 S 311 e 13Document1 pageStewart Calcch 3 S 311 e 13SB CRTNo ratings yet
- 3.6 The Hyperbolic Identities: X X X XDocument1 page3.6 The Hyperbolic Identities: X X X XKyle PerezNo ratings yet
- Calc-I Formulario 2019-2020Document2 pagesCalc-I Formulario 2019-2020Guilherme RiscadoNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument2 pagesFormulasayasukaNo ratings yet
- HyperbolicFunctionsFormulaEquationofHyperbola, Functions, Example 1710827134265Document6 pagesHyperbolicFunctionsFormulaEquationofHyperbola, Functions, Example 1710827134265pearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- First Factor: Problem 1: X +x+12 0 Problem 3Document1 pageFirst Factor: Problem 1: X +x+12 0 Problem 3patricia masilNo ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaGeramagliquiangNo ratings yet
- CoshDocument4 pagesCoshDaudi Erasto MlangiNo ratings yet
- MA3264Tutorial2 Solutions by LinDocument8 pagesMA3264Tutorial2 Solutions by LinTim CookNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4. Integrals of Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument14 pagesMODULE 4. Integrals of Hyperbolic FunctionsJack NapierNo ratings yet
- Homework #2 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesHomework #2 - SolutionsSayan SamantaNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesHyperbolic Formulas PDFKrishna Gupta100% (1)
- FormularioDocument1 pageFormularioRita MeloNo ratings yet
- Kurnia Andini - Operator Koorinat BolaDocument12 pagesKurnia Andini - Operator Koorinat BolaMutiara DierNo ratings yet
- Primera Parte Trabajo ColaborativoDocument4 pagesPrimera Parte Trabajo Colaborativojose trujilloNo ratings yet
- Reliabilty of StructuresDocument4 pagesReliabilty of StructuresAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16. Trigonometric and Hyperbolic Trigonometric FunctionsDocument5 pagesLesson 16. Trigonometric and Hyperbolic Trigonometric FunctionsAneek M. NoorNo ratings yet
- asdadasdasdasdasdasdsadda: ϕ f (x) f f (x) f x ax x x xlna − sin x x − x x √ − x √ √ √ x − 1 − e e a aDocument2 pagesasdadasdasdasdasdasdsadda: ϕ f (x) f f (x) f x ax x x xlna − sin x x − x x √ − x √ √ √ x − 1 − e e a astankon15No ratings yet
- Talbicee PDFDocument2 pagesTalbicee PDFstankon15No ratings yet
- Talbsicee PDFDocument2 pagesTalbsicee PDFstankon15No ratings yet
- CoshxDocument4 pagesCoshxMirellea AndurayNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument3 pagesExampleNguyễn Phi Anh KhôiNo ratings yet
- 1 Solutions in Cylindrical Coordinates: Bessel FunctionsDocument16 pages1 Solutions in Cylindrical Coordinates: Bessel FunctionsPopescu Viorel-MihaiNo ratings yet
- Section 6.9, The Hyperbolic Functions and Their InversesDocument3 pagesSection 6.9, The Hyperbolic Functions and Their InversesDiegoNo ratings yet
- Hate Speech - FinalDocument205 pagesHate Speech - FinalThavamNo ratings yet
- Words, Sentence and Dictionaries. MorphologyDocument5 pagesWords, Sentence and Dictionaries. MorphologyNur Al-AsimaNo ratings yet
- RUSLEDocument16 pagesRUSLEVivek KasarNo ratings yet
- Task 1-Critical AnalysisDocument5 pagesTask 1-Critical AnalysisShashni RaiNo ratings yet
- Thirumurai 2Document188 pagesThirumurai 2thegodkannanNo ratings yet
- PROJECT REPORT ON AViva LIFE INSURANCEDocument62 pagesPROJECT REPORT ON AViva LIFE INSURANCEMayank100% (12)
- Elecciones Injustas, Una Cronología de Incidentes No Democráticos Desde 1999. Por Vladimir Chelminski (No Publicado)Document124 pagesElecciones Injustas, Una Cronología de Incidentes No Democráticos Desde 1999. Por Vladimir Chelminski (No Publicado)AgusGulman100% (1)
- 8 Physio OB - Physiology of Labor I - IIDocument14 pages8 Physio OB - Physiology of Labor I - IIArnoldBorromeoNo ratings yet
- Proy. Final p2Document2 pagesProy. Final p2Antuan ButabiNo ratings yet
- The Syntactic Position of Negative Markers in IdomDocument22 pagesThe Syntactic Position of Negative Markers in IdomFABIAN AGOLONo ratings yet
- Resume For Teachers in KeralaDocument6 pagesResume For Teachers in Keralaitvgpljbf100% (2)
- Angelo de DonatisDocument6 pagesAngelo de DonatisNandu RaviNo ratings yet
- 6826 Gruhn SafetyDocument28 pages6826 Gruhn SafetyvishadkapadiaNo ratings yet
- Active Lessons ELT The Movable Class Kevin - MccaugheyDocument12 pagesActive Lessons ELT The Movable Class Kevin - MccaugheyThuy T TranNo ratings yet
- Pre EssayDocument2 pagesPre EssayalejandroleonarocaNo ratings yet
- Walking With Miss Millie Readers TheaterDocument6 pagesWalking With Miss Millie Readers Theaterapi-547921371No ratings yet
- MSC 1-Circ 1164-Rev 26Document6 pagesMSC 1-Circ 1164-Rev 26armanNo ratings yet
- FT USITT07 18x24 PDFDocument1 pageFT USITT07 18x24 PDFHika007No ratings yet
- A Hero Is Someone Who Understands The Responsibility That Comes With His FreedomDocument2 pagesA Hero Is Someone Who Understands The Responsibility That Comes With His FreedomellyabNo ratings yet
- Social Cognitive Theory and Physical ActivityDocument13 pagesSocial Cognitive Theory and Physical ActivityMega AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- The Five Chapters by Jamie AndreasDocument2 pagesThe Five Chapters by Jamie AndreasYuki Arashi100% (2)
- EARTHSCIENCE MODULE8 9 Week9.Document30 pagesEARTHSCIENCE MODULE8 9 Week9.keith tambaNo ratings yet
- Writing The Article: Strategy and Preparations: Lesson SummaryDocument7 pagesWriting The Article: Strategy and Preparations: Lesson SummarySol VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: 3 Quarter Week 1Document7 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: 3 Quarter Week 1Romnick PortillanoNo ratings yet
- Case Study GoogleDocument6 pagesCase Study GoogleDevyana Indah Fajriani100% (1)
- COTDocument19 pagesCOTAF Dowell Mirin0% (1)
- Lwbli20226-Tanu Priya-Indian Cultural HeritageDocument16 pagesLwbli20226-Tanu Priya-Indian Cultural HeritageTANU PRIYANo ratings yet
- Survey Letter July 17Document2 pagesSurvey Letter July 17Michael ScarfoNo ratings yet
- In Re Hill Trustees Preliminary Recommendation On Sanctions For Leslie PUIDA and GMM 17 Nov 2010Document9 pagesIn Re Hill Trustees Preliminary Recommendation On Sanctions For Leslie PUIDA and GMM 17 Nov 2010William A. Roper Jr.No ratings yet