Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Mechanism of Primary Alcohol Oxidation by Acidified Potassium Manganate
The Mechanism of Primary Alcohol Oxidation by Acidified Potassium Manganate
Uploaded by
Wee Ee Ee100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views1 pagePrimary alcohols are readily oxidized by acidified potassium manganate (VII) to form carboxylic acids without isolating the intermediate aldehyde. Potassium manganate (VII) is a strong oxidizing agent that oxidizes the alcohol to an unstable aldehyde intermediate which then further oxidizes to the carboxylic acid product, evidenced by the solution changing color from purple to colorless and brown manganese dioxide precipitating out.
Original Description:
Original Title
The mechanism of primary alcohol oxidation by acidified potassium manganate
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPrimary alcohols are readily oxidized by acidified potassium manganate (VII) to form carboxylic acids without isolating the intermediate aldehyde. Potassium manganate (VII) is a strong oxidizing agent that oxidizes the alcohol to an unstable aldehyde intermediate which then further oxidizes to the carboxylic acid product, evidenced by the solution changing color from purple to colorless and brown manganese dioxide precipitating out.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views1 pageThe Mechanism of Primary Alcohol Oxidation by Acidified Potassium Manganate
The Mechanism of Primary Alcohol Oxidation by Acidified Potassium Manganate
Uploaded by
Wee Ee EePrimary alcohols are readily oxidized by acidified potassium manganate (VII) to form carboxylic acids without isolating the intermediate aldehyde. Potassium manganate (VII) is a strong oxidizing agent that oxidizes the alcohol to an unstable aldehyde intermediate which then further oxidizes to the carboxylic acid product, evidenced by the solution changing color from purple to colorless and brown manganese dioxide precipitating out.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
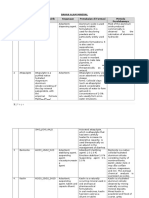
The mechanism of primary alcohol oxidation by acidified
potassium manganate (VII)
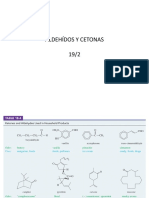
Primary alcohols are easily oxidized. Potassium manganate (VII) is a
strong oxidizing agent as compared to potassium dichromate (VI).
For potassium manganate (VII), it is impossible to extract the
aldehyde formed. The only product is the carboxylic acid.
The mechanism of primary alcohol by acidified potassium
manganate (VII) is as shown below:
The aldehyde is formed as an intermediate, but it is unstable under
the reaction conditions and cannot be isolated. There is a colour
change that accompanies the reaction - the purple solution of
KMnO4 turns colourless and brown precipitate of MnO2 is formed.
You might also like
- Chemi Full ReportDocument2 pagesChemi Full ReportLim Kai Xuan100% (1)
- AISI 4140 Alloy Steel (UNS G41400) : Topics CoveredDocument3 pagesAISI 4140 Alloy Steel (UNS G41400) : Topics Covereda.mohamedlathifNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of AlcoholsDocument7 pagesOxidation of AlcoholsCrisa ChinaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Potassium Manganate ViiDocument2 pagesAlkenes and Potassium Manganate ViiShirmara Pile-fordeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Research AssignmentDocument3 pagesChemistry Research AssignmentDavid AddisonNo ratings yet
- 19 - Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives PDFDocument16 pages19 - Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives PDFAzhar GoolfeeNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1WHITTINHGAM RAYANNANo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 7: Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 7: Chemical Reactionsdomenico123No ratings yet
- Redox Revision Test:) A B C DDocument9 pagesRedox Revision Test:) A B C DHamza KhalidNo ratings yet
- Catalog ChemfineDocument11 pagesCatalog Chemfinechemfine1No ratings yet
- Oxidising and Reducing AgentDocument1 pageOxidising and Reducing AgentjahangirNo ratings yet
- Identification of Unknown Organic CompoundsDocument8 pagesIdentification of Unknown Organic CompoundsMomer100% (7)
- Abnormal Behaviour of Formic (Methanoic) AcidDocument6 pagesAbnormal Behaviour of Formic (Methanoic) AcidFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Notes (Updated)Document8 pagesQualitative Analysis Notes (Updated)Abdullah HaroonNo ratings yet
- 8.4. Identification of Ions and GasesDocument4 pages8.4. Identification of Ions and GasesNatasa NikolicNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Exercise 5 - Ionic EquationsDocument1 pageTopic 2 Exercise 5 - Ionic EquationsRoshae SinclairNo ratings yet
- Alcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic CompoundsDocument31 pagesAlcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic CompoundslongchinNo ratings yet
- Alkohol Dari Senyawa KarbonilDocument31 pagesAlkohol Dari Senyawa KarbonilAshfie MarwaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Preparation of Manganese (II) ChlorideDocument2 pagesExperiment 5: Preparation of Manganese (II) ChlorideFatin NurhudaNo ratings yet
- Kmno4 Why Must Be Acidified: Guide To Potassium Manganate (VII) TitrationDocument1 pageKmno4 Why Must Be Acidified: Guide To Potassium Manganate (VII) TitrationAnn JosephNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Methods of PreparationDocument15 pagesAlcohols: Methods of PreparationKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Methods of PreparationDocument15 pagesAlcohols: Methods of PreparationKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 3Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3GundanNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquationsDocument1 pageIonic EquationssoniapuriNo ratings yet
- Identification of Unknown Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesIdentification of Unknown Organic CompoundsabhinickyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-2 Alcol PhenolDocument55 pagesLecture 1-2 Alcol PhenolLinh Giao Nguyễn TrầnNo ratings yet
- Reagents NBS SubstituionDocument10 pagesReagents NBS SubstituionPriyanshi JainNo ratings yet
- CH 1,2,3 Second Year EDocument2 pagesCH 1,2,3 Second Year EJauhar JauharabadNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument119 pagesAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsKashvi KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Oxidation - (Pharmaceutical Process Chemistry)Document34 pagesOxidation - (Pharmaceutical Process Chemistry)AnamIlyasNo ratings yet
- C P P S: Hemical Eriodicity Roperties UmmaryDocument1 pageC P P S: Hemical Eriodicity Roperties UmmaryHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Cetonas y Aldehidos - 19Document36 pagesCetonas y Aldehidos - 19Moisés ChucNo ratings yet
- ALCOHOLDocument47 pagesALCOHOLNhi Huỳnh YếnNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Selective Stripping of Molybdenum (VI) and Vanadium (IV) From Sulfuric Acid Solution Containing Aluminum (III), Cobalt (II), Nickel (II) and Iron (III) by LIX 63 in Exxsol D80Document9 pagesExtraction and Selective Stripping of Molybdenum (VI) and Vanadium (IV) From Sulfuric Acid Solution Containing Aluminum (III), Cobalt (II), Nickel (II) and Iron (III) by LIX 63 in Exxsol D80Prince GuptaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument56 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsjahiem wilsonNo ratings yet
- What Are Redox Titrations?Document7 pagesWhat Are Redox Titrations?Nidhi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Cations IdentificationsDocument39 pagesCations IdentificationsAndari RahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Oxidation RductionDocument34 pagesOxidation RductionEnkuan AbiyuNo ratings yet
- Reference Section: A - Inorganic Compounds and ElementsDocument10 pagesReference Section: A - Inorganic Compounds and ElementsHassan 2No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument22 pagesRedox ReactionsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument22 pagesRedox ReactionsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Oxidising Reducing AgentDocument3 pagesOxidising Reducing AgentAida Azira MohamedNo ratings yet
- Molybdenum and Its Compounds: 1 Characterization of The SubstanceDocument21 pagesMolybdenum and Its Compounds: 1 Characterization of The SubstanceThusith WijayawardenaNo ratings yet
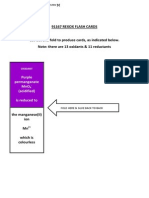
- Rexox Flash Cards: Purple Permanganate Mno (Acidified) Is Reduced ToDocument5 pagesRexox Flash Cards: Purple Permanganate Mno (Acidified) Is Reduced ToVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- BaeyerDocument1 pageBaeyerLivaashini NadarajanNo ratings yet
- Amines Bounceback One ShotDocument100 pagesAmines Bounceback One ShotShivadeep Vishwakarma0% (1)
- Ghubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085: AntacidsDocument2 pagesGhubaya College of Pharmacy 9485500085: AntacidsGhubaya CopNo ratings yet
- P'Chem-I Antacids PDFDocument2 pagesP'Chem-I Antacids PDFGhubaya CopNo ratings yet
- C10 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument55 pagesC10 Acids, Bases and SaltsKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Name: Hazel Nyaruai REGISTRATION NUMBER: ENM221-0244/2021 Course: Mechatronics Unit: Physical and Inorganic Chemistry Unit Code: SCH 2100Document4 pagesName: Hazel Nyaruai REGISTRATION NUMBER: ENM221-0244/2021 Course: Mechatronics Unit: Physical and Inorganic Chemistry Unit Code: SCH 2100Hazel WambuaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundDocument28 pagesCarbonyl CompoundZuhailimuna MudaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 1630993189Document56 pagesAlcohols 1630993189Sahisa MahatNo ratings yet
- Wiki Hidrolisis Dan Kco3Document3 pagesWiki Hidrolisis Dan Kco3Gift GiftNo ratings yet
- QA 2015 Part 4Document6 pagesQA 2015 Part 4FangZiWenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet Unit 10: The S-Block ElementsDocument1 pageChemistry Worksheet Unit 10: The S-Block ElementsDark DevilNo ratings yet
- Red-Ox Titrations, Permanganometry, Iodometry Etc.: Pabitra Kumar ManiDocument32 pagesRed-Ox Titrations, Permanganometry, Iodometry Etc.: Pabitra Kumar ManiJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Peer TeachingDocument20 pagesPeer TeachingF5A12 JimenaChuNo ratings yet
- Schulup Question SS3Document3 pagesSchulup Question SS3solomonchuks19No ratings yet
- L4 GgOxidising Alcohols 8-12-21Document19 pagesL4 GgOxidising Alcohols 8-12-21boobooNo ratings yet
- 1 - Synthesis of Alcohols and PhenolsDocument2 pages1 - Synthesis of Alcohols and PhenolsMohamad AzaniNo ratings yet
- Bahan Alam Mineral No Nama Umum Rumus Empirik Kegunaan Pemakaian Di Farmasi Metoda PerolehannyaDocument4 pagesBahan Alam Mineral No Nama Umum Rumus Empirik Kegunaan Pemakaian Di Farmasi Metoda PerolehannyaMizanul IslamNo ratings yet
- Suma PharmaDocument14 pagesSuma PharmaRamboNo ratings yet
- Account Information Sample Information Equipment InformationDocument2 pagesAccount Information Sample Information Equipment Informationdhavit wijayantoNo ratings yet
- Sceince Workbook 9Document191 pagesSceince Workbook 9kkz2nfwhsyNo ratings yet
- Us5270023 PDFDocument8 pagesUs5270023 PDFYustinus Selis ToronNo ratings yet
- Ca141 Cone 5 6 Glazes 2 SampleDocument21 pagesCa141 Cone 5 6 Glazes 2 SampleАндрей СNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SS2 Second TermDocument5 pagesChemistry SS2 Second TermKel FelixNo ratings yet
- TRANSISIDocument61 pagesTRANSISIAlanNo ratings yet
- MET 52 3 337 340 RudolfDocument4 pagesMET 52 3 337 340 RudolfEduardo FlorianoNo ratings yet
- Determination of Tin in Canned Fruit JuicesDocument4 pagesDetermination of Tin in Canned Fruit JuicesGerges SamirNo ratings yet
- AGROPLUS EVE Ecogrow Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageAGROPLUS EVE Ecogrow Technical Data SheetMorgan AquaNo ratings yet
- NGK Guass Marshal Cross ReferenceDocument2 pagesNGK Guass Marshal Cross ReferenceFelipe MuñozNo ratings yet
- Ans GP-Spec Heat WSDocument4 pagesAns GP-Spec Heat WSOthello64No ratings yet
- Stainless Steel in The Pharmaceutical Food and Beverages Industries PDFDocument2 pagesStainless Steel in The Pharmaceutical Food and Beverages Industries PDFEng.sh1994shhotmail.com EngNo ratings yet
- Safety First!: Coin Chemistry and CleaningDocument13 pagesSafety First!: Coin Chemistry and CleaningBiciin MarianNo ratings yet
- Unitor Maintenance and Repair Welding: The Solutions GuideDocument1 pageUnitor Maintenance and Repair Welding: The Solutions GuideNuzhat Ali100% (1)
- Guide To Types of Welding PDFDocument24 pagesGuide To Types of Welding PDFbhaskarjalanNo ratings yet
- Production of Browns Gas Using Hydroxy GeneratorDocument3 pagesProduction of Browns Gas Using Hydroxy GeneratorBoyan StoyanovNo ratings yet
- Titanium Book From Org PDFDocument45 pagesTitanium Book From Org PDFSuthirak SumranNo ratings yet
- Peak Blue Diesel Exhaust Fluid (Def)Document2 pagesPeak Blue Diesel Exhaust Fluid (Def)Erick VargasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The Main Group Elements Ii: Groups 18, 17, 16, 15 and HydrogenDocument22 pagesChemistry of The Main Group Elements Ii: Groups 18, 17, 16, 15 and Hydrogenkennethleo69No ratings yet
- Year 12 Homework Ideal Gas, Empirical Formula QuestionsDocument8 pagesYear 12 Homework Ideal Gas, Empirical Formula QuestionsCat ShannonNo ratings yet
- ASC CATALOGUE With DetailsDocument3 pagesASC CATALOGUE With DetailsAmardeep Steel SalesNo ratings yet
- 11.4. Sulphuric AcidDocument14 pages11.4. Sulphuric AcidIsheba WarrenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chapter 11 QuestionsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chapter 11 QuestionsRajeshNo ratings yet
- Ujian Topikal Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument6 pagesUjian Topikal Jadual Berkala UnsurNurul Hana BalqisNo ratings yet
- AntacidsDocument14 pagesAntacidsCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- DisinfectionDocument20 pagesDisinfectionSona Parveen FarooqueNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic TableSithanandan GanapathyNo ratings yet
- WaterpollutantsDocument21 pagesWaterpollutantsJulio MariscalNo ratings yet