Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proof of Gauss Law
Proof of Gauss Law
Uploaded by
Ayush MittalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 7.7kirchhoff Theor Y: P Ikr Ikr IkrDocument19 pages7.7kirchhoff Theor Y: P Ikr Ikr IkrMujibussalimNo ratings yet
- Math 103 Problem 2Document4 pagesMath 103 Problem 2Nicholas YeeNo ratings yet
- Network Synthesis - R SinghDocument76 pagesNetwork Synthesis - R SinghPritam Deb RoyNo ratings yet
- Controls FDocument15 pagesControls Fjerick garlejoNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueDocument21 pagesDokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueSolid Work and Mechanical software TutorialNo ratings yet
- Jacob 1Document3 pagesJacob 1PpaNo ratings yet
- 5 2postDocument3 pages5 2posteperlaNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC2 H2 Maths Prelim Eunoia Junior College AnswerDocument27 pages2019 JC2 H2 Maths Prelim Eunoia Junior College AnswerSalman ShethNo ratings yet
- I. Ossola-Papadopoulos-Pittau Integrand ReductionDocument12 pagesI. Ossola-Papadopoulos-Pittau Integrand ReductionRaoul DukeNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document6 pagesWeek 7Mohammad Hafiz MahadzirNo ratings yet
- 4.worked AnswersDocument14 pages4.worked AnswersArnaz BakytbekNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration and Quantum NumbersDocument41 pagesElectron Configuration and Quantum NumbersgallosaaronmatthewNo ratings yet
- FP2C8 Polar Coordinates 210221 OnlineDocument3 pagesFP2C8 Polar Coordinates 210221 OnlineLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Notes - Lesson 3 and Lesson 4Document1 pageWeek 2 Notes - Lesson 3 and Lesson 4Francis Ian VillacicaNo ratings yet
- Flux GausssolsDocument9 pagesFlux GausssolsaakashbalaprajapathiofficialNo ratings yet
- The Dihedral GroupsDocument2 pagesThe Dihedral GroupsUjjwal RastogiNo ratings yet
- Week 13Document17 pagesWeek 13JavierPaganLacambraNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields All DerivationsDocument9 pagesElectric Charges and Fields All DerivationsFlame kaiserNo ratings yet
- Tcu11 11 02exDocument3 pagesTcu11 11 02exPierre BerkshireNo ratings yet
- Math GTM QP 20-12-23Document4 pagesMath GTM QP 20-12-23sbpathuriNo ratings yet
- Mott AppendixDocument65 pagesMott AppendixAnonymous VhaFjpGrwNNo ratings yet
- Atomic OrbitalsDocument63 pagesAtomic Orbitalsmakondo.yhNo ratings yet
- BA224 Lec 7Document11 pagesBA224 Lec 7selimhany10107575No ratings yet
- Jackson 1.5 Homework Problem SolutionDocument3 pagesJackson 1.5 Homework Problem SolutionBangkit SudrajadNo ratings yet
- 10 5BDoneDocument3 pages10 5BDoneeperlaNo ratings yet
- P1 Solution EJCDocument15 pagesP1 Solution EJCtoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 3 Rules For Sketching The Root Locus K 0Document3 pages3 Rules For Sketching The Root Locus K 0Yassine DjillaliNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 1Document17 pagesIntegral Calculus 1Bosta AtsobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, Numerical Sequences and Series: S S S S SDocument58 pagesChapter 3, Numerical Sequences and Series: S S S S Swil1963No ratings yet
- Krishna Sir Physics DerivationsDocument80 pagesKrishna Sir Physics Derivationsrajeevbehera2006No ratings yet
- Surface IntegralDocument22 pagesSurface IntegralRATNADEEP DASNo ratings yet
- LAPLACE-TRANSFORMSDocument15 pagesLAPLACE-TRANSFORMSjaj jajaNo ratings yet
- Notes 15 PDFDocument5 pagesNotes 15 PDFJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 33 Quantum NumbersDocument14 pagesTUTORIAL 33 Quantum NumbersDYES Motion GraphicsNo ratings yet
- QA 05 Ratio-1Document39 pagesQA 05 Ratio-1Sunit SomuNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Root Locus and PID DesignDocument28 pages1.5 Root Locus and PID DesignEstudiante De la UniversidadNo ratings yet
- Couplers PrintedDocument30 pagesCouplers Printedmatt tNo ratings yet
- Cheena Francesca Luciano - WORKSHEET Q2 WK 2Document4 pagesCheena Francesca Luciano - WORKSHEET Q2 WK 2Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Problemset 3 ADocument6 pagesProblemset 3 AUnnamed1122No ratings yet
- Burgess NordicSchool2019Document75 pagesBurgess NordicSchool2019Angel NavaNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment2 Solutionsadityalm2004No ratings yet
- 9 Bbcollab Laplace-TransformsDocument18 pages9 Bbcollab Laplace-TransformsEkoms GamingNo ratings yet
- Class-10 - KB - October 2022Document40 pagesClass-10 - KB - October 2022Syed Munir HasanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation DARK MODEDocument19 pagesQuadratic Equation DARK MODESumatiNo ratings yet
- EASStart Up Maths Year 72017Document24 pagesEASStart Up Maths Year 72017arti.sharma11No ratings yet
- LT3 Solving Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesLT3 Solving Differential Equationssujayan2005No ratings yet
- Section 6.3 OnlineDocument17 pagesSection 6.3 Onlinecomc5288No ratings yet
- DCLec 10Document6 pagesDCLec 10AwadHilmyNo ratings yet
- Inverse Kinematics PPT (Pak Toni)Document14 pagesInverse Kinematics PPT (Pak Toni)herawanadifNo ratings yet
- Calculus Early Transcendentals, 10th Edition07Document1 pageCalculus Early Transcendentals, 10th Edition07LamiaNo ratings yet
- Part A - Topic 1 - WK 1 - WednesdayDocument28 pagesPart A - Topic 1 - WK 1 - WednesdayJosie.p.kellyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Electron StructuresDocument58 pagesPeriodic Table: Electron StructuresVimanan A/L S. VelangganiNo ratings yet
- Pet 531 FormulasDocument1 pagePet 531 FormulasIgbereyivwe TejiriNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityAbdalah Saleh Moustafa ElgholmyNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityahmed.sherif3400No ratings yet
- Chpater 1 - 1.1 Electronic ConfigurationDocument7 pagesChpater 1 - 1.1 Electronic ConfigurationSyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- Gauss LawDocument39 pagesGauss Lawapi-3728553100% (2)
- PageNo 7 19 Devesh PandeyDocument3 pagesPageNo 7 19 Devesh PandeyManas HiremathNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFRanjith M100% (1)
- CH 1 ElectrosataticsDocument61 pagesCH 1 ElectrosataticsHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- PS2 SolDocument9 pagesPS2 SolrteehaNo ratings yet
- Oscillatory Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocument14 pagesOscillatory Motion: Multiple ChoiceCamilo ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields: UNIT-I: Chapter-01Document18 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: UNIT-I: Chapter-01Teju tejasNo ratings yet
- Zain Ahmad 2019f-Mulbsswe-019: Sr. No Students Name Registration No Assignment TopicsDocument11 pagesZain Ahmad 2019f-Mulbsswe-019: Sr. No Students Name Registration No Assignment TopicsAli RazaNo ratings yet
- ER (P-I) - 18/NQ (TEPS) - 19/ET (P-I (TEA1) ) - 19/ER (P-I) - 20: Enthusiast CourseDocument5 pagesER (P-I) - 18/NQ (TEPS) - 19/ET (P-I (TEA1) ) - 19/ER (P-I) - 20: Enthusiast CourseRajat Verma X D 39No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 1electric Charges and FieldsDocument15 pagesNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 1electric Charges and FieldsVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Phy Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesPhy Sample Paper 1nidha.jasmine21No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Chapter 1 PDFDocument29 pagesElectrostatics Chapter 1 PDFarnav sagarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic FieldsDocument85 pagesElectrostatic FieldsZaharudin Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Halliday, Resnick, and Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 10e Question AnswersDocument16 pagesHalliday, Resnick, and Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 10e Question Answershanane el basriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Capacitance (Practice Questions)Document37 pagesChapter 25 Capacitance (Practice Questions)Isa Al-NoaimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 2 - Gauss Law, Divergence and Curl of E - PHYS 331Document55 pagesChapter 2 - Part 2 - Gauss Law, Divergence and Curl of E - PHYS 331Taukeer KhanNo ratings yet
- HC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 Gauss LawDocument22 pagesHC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 Gauss Lawamitsarkar6536No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument17 pagesModule 2 - Electromagnetic WavesMahek KhushalaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Charges and Fields Chapter - 1 PhysicsDocument61 pagesElectrical Charges and Fields Chapter - 1 PhysicsPrasad PallaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument16 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsPRACHI GUPTANo ratings yet
- Krishna Sir Physics DerivationsDocument80 pagesKrishna Sir Physics Derivationsrajeevbehera2006No ratings yet
- E1a 121 s06txtDocument4 pagesE1a 121 s06txtBob TheBuilderNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Document39 pages1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Ma. Alleli ChuaNo ratings yet
- EM2 NotesDocument165 pagesEM2 NotesTaner YenerNo ratings yet
- Chap3 William HaytDocument15 pagesChap3 William HaytM Zafeer KhanNo ratings yet
- 22 Clicker QuestionsDocument12 pages22 Clicker QuestionsChris KovaleskiNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Ley de Gauss SerwayDocument5 pagesEjercicios Ley de Gauss SerwayJuan Pablo Rincón AguiarNo ratings yet
- II PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions, Important Questions and Answers For 2023 Exam by MANJUNATH B.Document53 pagesII PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions, Important Questions and Answers For 2023 Exam by MANJUNATH B.praveens.photos.2023No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 1 Study Material em 214019Document96 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 1 Study Material em 214019Aakaash C.K.33% (6)
- Gauss LawDocument41 pagesGauss LawArvita KaurNo ratings yet
- Gauss's Law. Solutions of Home Work Problems: 24.1 Problem 24.6 (In The Text Book)Document7 pagesGauss's Law. Solutions of Home Work Problems: 24.1 Problem 24.6 (In The Text Book)AldairEviltonChGNo ratings yet
- Xii Summer Vacation Homework 2024Document17 pagesXii Summer Vacation Homework 2024dydbloggersNo ratings yet
Proof of Gauss Law
Proof of Gauss Law
Uploaded by
Ayush MittalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Proof of Gauss Law
Proof of Gauss Law
Uploaded by
Ayush MittalCopyright:
Available Formats
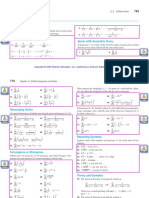
Derivation of Gauss Law
Case I - When charge is inside the Gaussian surface.
Consider a charge ‘q’ present at point A. Let P
be a point at a distance ‘r’ from A. Through ‘P’
consider a hypothetical surface ‘S’ enclosing the
charge ‘q’.
Due to charge ‘q’ intensity of electric field at ‘P’ is
1 ⎛q ⎞
E= ⎜ ⎟r̂
4πε ⎝ r
o
2
⎠
Surface integral of anr electric field over closed
surface ‘S’ will be ∫ E • dS . Now
r 1 q q dS cos θ
∫ E • dS =
4πε ∫r
S
r̂
2
• dS =
4πε ∫ r
S
2
o o
Here θ = angle between r̂ and normal to dS .
dS cos θ Normal area
Now 2
= = Solid angle (dω )
2
r r
Therefore
r q dS cos θ q q q
∫ E • dS =
4πε ∫ r
S
2
=
4πε ∫ dω =
S 4πε
.4π =
ε
o o o o
If many charges are present inside surface ‘S’ then
r 1
∑q
n
∫ E • dS =
ε i =1
i
o
Case II - When charge is outside the Gaussian surface.
Suppose charge ‘q’ be out side the Gaussian surface
‘S’. Due to charge ‘q’ let E , E , E & E be the 1 2 3 4
electric field intensities at dS , dS , dS 3 & dS 1 2 4
respectively.
r
∫ E • dS = ∫ E • dS + ∫ E • dS + ∫ E • dS + ∫ E • dS
1 1
S2
2 2
S3
3 3
S4
4 4
S
1
q 1 q 1 q 1
4πε o S∫1 r1 ∫S2 r 2 2 2 4πε S∫3 r 2 r̂3 • dS 3
= r̂ • dS + r̂ • dS +
4πε o
2 1 1
2 o 3
q 1
+ ∫
4πε o S4 r4
2
r̂4 • dS 4
q dS cos θ q dS cos θ q dS cos θ
4πε ∫ ∫ r ∫ r
= + 1 1 2
+ 2 3 3
4πε 4πε
2 2 2
r
o S1 1 o S2 2 o S3 3
q dS cos θ
4πε ∫
+ 4
2
4
r
o S4 4
r
∫ E • dS = 4πε [− 4π + 4π − 4π + 4π ] = 0
q
o
It means if charges are outside the surface the
normal flux or surface integral of electric field over
the surface is zero.
You might also like
- 7.7kirchhoff Theor Y: P Ikr Ikr IkrDocument19 pages7.7kirchhoff Theor Y: P Ikr Ikr IkrMujibussalimNo ratings yet
- Math 103 Problem 2Document4 pagesMath 103 Problem 2Nicholas YeeNo ratings yet
- Network Synthesis - R SinghDocument76 pagesNetwork Synthesis - R SinghPritam Deb RoyNo ratings yet
- Controls FDocument15 pagesControls Fjerick garlejoNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueDocument21 pagesDokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueSolid Work and Mechanical software TutorialNo ratings yet
- Jacob 1Document3 pagesJacob 1PpaNo ratings yet
- 5 2postDocument3 pages5 2posteperlaNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC2 H2 Maths Prelim Eunoia Junior College AnswerDocument27 pages2019 JC2 H2 Maths Prelim Eunoia Junior College AnswerSalman ShethNo ratings yet
- I. Ossola-Papadopoulos-Pittau Integrand ReductionDocument12 pagesI. Ossola-Papadopoulos-Pittau Integrand ReductionRaoul DukeNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document6 pagesWeek 7Mohammad Hafiz MahadzirNo ratings yet
- 4.worked AnswersDocument14 pages4.worked AnswersArnaz BakytbekNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration and Quantum NumbersDocument41 pagesElectron Configuration and Quantum NumbersgallosaaronmatthewNo ratings yet
- FP2C8 Polar Coordinates 210221 OnlineDocument3 pagesFP2C8 Polar Coordinates 210221 OnlineLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Notes - Lesson 3 and Lesson 4Document1 pageWeek 2 Notes - Lesson 3 and Lesson 4Francis Ian VillacicaNo ratings yet
- Flux GausssolsDocument9 pagesFlux GausssolsaakashbalaprajapathiofficialNo ratings yet
- The Dihedral GroupsDocument2 pagesThe Dihedral GroupsUjjwal RastogiNo ratings yet
- Week 13Document17 pagesWeek 13JavierPaganLacambraNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields All DerivationsDocument9 pagesElectric Charges and Fields All DerivationsFlame kaiserNo ratings yet
- Tcu11 11 02exDocument3 pagesTcu11 11 02exPierre BerkshireNo ratings yet
- Math GTM QP 20-12-23Document4 pagesMath GTM QP 20-12-23sbpathuriNo ratings yet
- Mott AppendixDocument65 pagesMott AppendixAnonymous VhaFjpGrwNNo ratings yet
- Atomic OrbitalsDocument63 pagesAtomic Orbitalsmakondo.yhNo ratings yet
- BA224 Lec 7Document11 pagesBA224 Lec 7selimhany10107575No ratings yet
- Jackson 1.5 Homework Problem SolutionDocument3 pagesJackson 1.5 Homework Problem SolutionBangkit SudrajadNo ratings yet
- 10 5BDoneDocument3 pages10 5BDoneeperlaNo ratings yet
- P1 Solution EJCDocument15 pagesP1 Solution EJCtoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 3 Rules For Sketching The Root Locus K 0Document3 pages3 Rules For Sketching The Root Locus K 0Yassine DjillaliNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 1Document17 pagesIntegral Calculus 1Bosta AtsobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, Numerical Sequences and Series: S S S S SDocument58 pagesChapter 3, Numerical Sequences and Series: S S S S Swil1963No ratings yet
- Krishna Sir Physics DerivationsDocument80 pagesKrishna Sir Physics Derivationsrajeevbehera2006No ratings yet
- Surface IntegralDocument22 pagesSurface IntegralRATNADEEP DASNo ratings yet
- LAPLACE-TRANSFORMSDocument15 pagesLAPLACE-TRANSFORMSjaj jajaNo ratings yet
- Notes 15 PDFDocument5 pagesNotes 15 PDFJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 33 Quantum NumbersDocument14 pagesTUTORIAL 33 Quantum NumbersDYES Motion GraphicsNo ratings yet
- QA 05 Ratio-1Document39 pagesQA 05 Ratio-1Sunit SomuNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Root Locus and PID DesignDocument28 pages1.5 Root Locus and PID DesignEstudiante De la UniversidadNo ratings yet
- Couplers PrintedDocument30 pagesCouplers Printedmatt tNo ratings yet
- Cheena Francesca Luciano - WORKSHEET Q2 WK 2Document4 pagesCheena Francesca Luciano - WORKSHEET Q2 WK 2Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Problemset 3 ADocument6 pagesProblemset 3 AUnnamed1122No ratings yet
- Burgess NordicSchool2019Document75 pagesBurgess NordicSchool2019Angel NavaNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment2 Solutionsadityalm2004No ratings yet
- 9 Bbcollab Laplace-TransformsDocument18 pages9 Bbcollab Laplace-TransformsEkoms GamingNo ratings yet
- Class-10 - KB - October 2022Document40 pagesClass-10 - KB - October 2022Syed Munir HasanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation DARK MODEDocument19 pagesQuadratic Equation DARK MODESumatiNo ratings yet
- EASStart Up Maths Year 72017Document24 pagesEASStart Up Maths Year 72017arti.sharma11No ratings yet
- LT3 Solving Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesLT3 Solving Differential Equationssujayan2005No ratings yet
- Section 6.3 OnlineDocument17 pagesSection 6.3 Onlinecomc5288No ratings yet
- DCLec 10Document6 pagesDCLec 10AwadHilmyNo ratings yet
- Inverse Kinematics PPT (Pak Toni)Document14 pagesInverse Kinematics PPT (Pak Toni)herawanadifNo ratings yet
- Calculus Early Transcendentals, 10th Edition07Document1 pageCalculus Early Transcendentals, 10th Edition07LamiaNo ratings yet
- Part A - Topic 1 - WK 1 - WednesdayDocument28 pagesPart A - Topic 1 - WK 1 - WednesdayJosie.p.kellyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Electron StructuresDocument58 pagesPeriodic Table: Electron StructuresVimanan A/L S. VelangganiNo ratings yet
- Pet 531 FormulasDocument1 pagePet 531 FormulasIgbereyivwe TejiriNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityAbdalah Saleh Moustafa ElgholmyNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityahmed.sherif3400No ratings yet
- Chpater 1 - 1.1 Electronic ConfigurationDocument7 pagesChpater 1 - 1.1 Electronic ConfigurationSyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- Gauss LawDocument39 pagesGauss Lawapi-3728553100% (2)
- PageNo 7 19 Devesh PandeyDocument3 pagesPageNo 7 19 Devesh PandeyManas HiremathNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFRanjith M100% (1)
- CH 1 ElectrosataticsDocument61 pagesCH 1 ElectrosataticsHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- PS2 SolDocument9 pagesPS2 SolrteehaNo ratings yet
- Oscillatory Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocument14 pagesOscillatory Motion: Multiple ChoiceCamilo ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields: UNIT-I: Chapter-01Document18 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: UNIT-I: Chapter-01Teju tejasNo ratings yet
- Zain Ahmad 2019f-Mulbsswe-019: Sr. No Students Name Registration No Assignment TopicsDocument11 pagesZain Ahmad 2019f-Mulbsswe-019: Sr. No Students Name Registration No Assignment TopicsAli RazaNo ratings yet
- ER (P-I) - 18/NQ (TEPS) - 19/ET (P-I (TEA1) ) - 19/ER (P-I) - 20: Enthusiast CourseDocument5 pagesER (P-I) - 18/NQ (TEPS) - 19/ET (P-I (TEA1) ) - 19/ER (P-I) - 20: Enthusiast CourseRajat Verma X D 39No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 1electric Charges and FieldsDocument15 pagesNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 1electric Charges and FieldsVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Phy Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesPhy Sample Paper 1nidha.jasmine21No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Chapter 1 PDFDocument29 pagesElectrostatics Chapter 1 PDFarnav sagarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic FieldsDocument85 pagesElectrostatic FieldsZaharudin Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Halliday, Resnick, and Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 10e Question AnswersDocument16 pagesHalliday, Resnick, and Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 10e Question Answershanane el basriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Capacitance (Practice Questions)Document37 pagesChapter 25 Capacitance (Practice Questions)Isa Al-NoaimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 2 - Gauss Law, Divergence and Curl of E - PHYS 331Document55 pagesChapter 2 - Part 2 - Gauss Law, Divergence and Curl of E - PHYS 331Taukeer KhanNo ratings yet
- HC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 Gauss LawDocument22 pagesHC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 Gauss Lawamitsarkar6536No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument17 pagesModule 2 - Electromagnetic WavesMahek KhushalaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Charges and Fields Chapter - 1 PhysicsDocument61 pagesElectrical Charges and Fields Chapter - 1 PhysicsPrasad PallaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument16 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsPRACHI GUPTANo ratings yet
- Krishna Sir Physics DerivationsDocument80 pagesKrishna Sir Physics Derivationsrajeevbehera2006No ratings yet
- E1a 121 s06txtDocument4 pagesE1a 121 s06txtBob TheBuilderNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Document39 pages1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Ma. Alleli ChuaNo ratings yet
- EM2 NotesDocument165 pagesEM2 NotesTaner YenerNo ratings yet
- Chap3 William HaytDocument15 pagesChap3 William HaytM Zafeer KhanNo ratings yet
- 22 Clicker QuestionsDocument12 pages22 Clicker QuestionsChris KovaleskiNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Ley de Gauss SerwayDocument5 pagesEjercicios Ley de Gauss SerwayJuan Pablo Rincón AguiarNo ratings yet
- II PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions, Important Questions and Answers For 2023 Exam by MANJUNATH B.Document53 pagesII PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions, Important Questions and Answers For 2023 Exam by MANJUNATH B.praveens.photos.2023No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 1 Study Material em 214019Document96 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 1 Study Material em 214019Aakaash C.K.33% (6)
- Gauss LawDocument41 pagesGauss LawArvita KaurNo ratings yet
- Gauss's Law. Solutions of Home Work Problems: 24.1 Problem 24.6 (In The Text Book)Document7 pagesGauss's Law. Solutions of Home Work Problems: 24.1 Problem 24.6 (In The Text Book)AldairEviltonChGNo ratings yet
- Xii Summer Vacation Homework 2024Document17 pagesXii Summer Vacation Homework 2024dydbloggersNo ratings yet