Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SKELETAL SYSTEM - Outline
SKELETAL SYSTEM - Outline
Uploaded by
Lind MondanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SKELETAL SYSTEM - Outline
SKELETAL SYSTEM - Outline
Uploaded by
Lind MondanoCopyright:
Available Formats
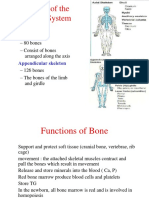
SKELETAL SYSTEM
Skeleton – gives shape and support to the body
-- protects the underlying organs from injury
. – aids in muscle movement and locomotion
exoskeleton – formed outside the animals body (insects, lobsters, and
snails)
endoskeleton – formed within the body (man and other vertabrates)
Vertebrate Skeleton
axial skeleton – includes the skull, backbone(vertebrae), ribs, and
breast bone(sternum)
o skull – made up of fused bones – the cranium or the body case
immediately around the brain and bones of the face.
o backbone – made up of thirty three separate vertebrae.
o ribs – series of flat bones which support the chest wall and keep it
from collapsing as the diaphragm contracts; twelve pairs: first
seven are attached ventrally to the breast bone, the next three are
attached indirectly by cartilages and the last two have no
attachments to the breast bone (floating ribs)
appendicular skeleton – includes the bones of the paired appendages
and pelvic girdles.
TOTAL NO. OF BONES OF CHILD = 213
TOTAL NO. OF BONES OF ADULT = 206
joint – point of junction between two bones.
immovable – as in skull
ball and socket – as in femur(thigh bone) to the hip bone
hinge joints – as in knee
pivot joints – as in the wrists and ankles
cartilage – reduces friction between two bones
tendons – attach muscles to the bones
ligaments – connect bones
Bone – building material of the skeleton
-- 25% water, 45% mineral deposits(mainly calcium combined with
either phosphate or carbonate)
bone formation is controlled by:
- hormones(parathyroid hormone)
- vitamin A, C, and D
- minerals like calcium
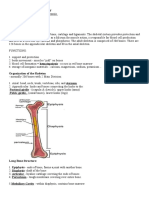
Structure of the long bone(such as the femur):
periosteum – outer tough covering
compast bone – under the periosteum; contains deposits of mineral
matter and protein fibers.
spongy bone – interior to the compact bone; composed of a network
or connective tissues.
marrow – hollow interiors and contain a soft tissue; richly supplied
with blood vessels and nerves
o red bone marrow – found in spongy bones and the end of long bones,
flat bones such as ribs and sternum, and in vertebrae; manufactures
red blood cells and white blood cells.
o yellow bone marrow – composed mostly of fat cells and nerves as
energy reserve; fills the shaft of long bone.
Bone Defects
arthritis – inflamed tissues around a joint
hypertrophied bones – toes that are larger than normal bones
rickets – lack of vitamin D
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 8aDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Module 8aJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument31 pagesSkeletal SystemZabeth ZabNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemmikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AnaphyDocument10 pagesChapter 5 AnaphyKryzell Ann HadcanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument15 pagesSkeletal SystemRaven LacsonNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument2 pagesBonesSherry SinghNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Priyanjali SainiDocument32 pagesPresented By:-Priyanjali SainiPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues Blood Vessels Blood MusclesDocument2 pagesConnective Tissues Blood Vessels Blood MusclesLeonard PlazaNo ratings yet
- Biology SkeletonDocument36 pagesBiology SkeletonHariPriya JothimeenakshiNo ratings yet
- K00429 - 20180831105725 - Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesK00429 - 20180831105725 - Skeletal Systemroesil juniNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System-ReviewerDocument12 pagesSkeletal System-ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Report PDFDocument86 pagesSkeletal System Report PDFMarian Elaine RufilaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- 2 Skeletal System HandoutDocument8 pages2 Skeletal System Handoutapi-302873465No ratings yet
- Premedical Biology: Motor MechanismDocument44 pagesPremedical Biology: Motor MechanismsheenaNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion-23-24Document3 pagesMovement and Locomotion-23-24Chintan ShahNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM-WPS OfficeAlan Gandidze MotifNo ratings yet
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesModule Skeletal SystemEMEM QUENNo ratings yet
- G-8 Skeletal SystemDocument30 pagesG-8 Skeletal SystemMarjun SalinasNo ratings yet
- Bones and Formation of The SkullDocument15 pagesBones and Formation of The SkullسالمNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PPT SMDVDocument81 pagesSkeletal System PPT SMDVPumpkin SpiceNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesSkeletal Systemsedrahamaamin512No ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMatthew YoungNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System AnatomyDocument6 pagesSkeletal System AnatomymanuelaristotleNo ratings yet
- (Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pages(Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemTrúc Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3 SkeletalDocument49 pagesAnatomy 3 SkeletalibrooavcNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesSkeletal SystemMaureen Tianson DomingoNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsDocument80 pagesNCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- The Human SkeletonDocument12 pagesThe Human SkeletonBJ Allon Mallari75% (4)
- NCMDocument2 pagesNCMHeherson_Taban_2403No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument13 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemGracia OmariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Musculoskeletal System 2012Document18 pagesIntroduction To Musculoskeletal System 2012Mandeep DhillonNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document2 pagesWa0002.Anne-CheilleNo ratings yet
- Bone AnatomyDocument11 pagesBone AnatomyLiam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- Movement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForDocument7 pagesMovement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Human Musculoskeletal System GotovoDocument10 pagesHuman Musculoskeletal System GotovonatalivaloNo ratings yet
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Dan ZagoreanuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System 1Document31 pagesSkeletal System 1Hannan AliNo ratings yet
- M2 DAN M3 ING Sistem RangkaDocument146 pagesM2 DAN M3 ING Sistem RangkaChloe LuNo ratings yet
- ACE CPT Chapter 9 Part 1 (Edition 6)Document6 pagesACE CPT Chapter 9 Part 1 (Edition 6)alishuuuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Integumentary SystemDocument20 pagesSkeletal and Integumentary SystemAbby Gaile LopezNo ratings yet
- Reading 3 The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesReading 3 The Skeletal Systemlephuongvy1406No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Tristan Joseph Cantillo BSN-RN, CRNDocument42 pagesThe Skeletal System: Tristan Joseph Cantillo BSN-RN, CRNMonico SalangusteNo ratings yet
- Osteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeDocument17 pagesOsteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeA CNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Skeletal SystemDocument45 pages7.0 Skeletal System[R2A] Khadijah Azlan100% (1)
- Anatomy Lecture 2Document5 pagesAnatomy Lecture 2Juli AprosoffNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Prelims ReviewerDocument11 pagesAnaphy Prelims ReviewerMariz Elizabeth TaytayNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument104 pagesSkeletal Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Part 5 - Human Skeletal System - UpdatedDocument30 pagesPart 5 - Human Skeletal System - UpdatedمحمدالسلمانNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal SystemBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahDocument60 pagesSekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahrameshkasinathanNo ratings yet
- PIOGADO - Anatomy ReportDocument11 pagesPIOGADO - Anatomy ReportJunaisah P. PangaponNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- A. Definition of SkeletonDocument6 pagesA. Definition of SkeletonNEIRA LENE SALONGANo ratings yet
- Muscular and Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular and Skeletal SystemPrasad WasteNo ratings yet
- Risk Characterization and EvaluationDocument86 pagesRisk Characterization and EvaluationTusabe FredNo ratings yet
- Maranatha University Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesMaranatha University Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyKojo Yeboah EnchillNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 1 Unit 9 WordlistDocument4 pagesMastermind 1 Unit 9 WordlistValentina CárdenasNo ratings yet
- IX Studying Sample PaperDocument15 pagesIX Studying Sample PaperEVERYDAY SCIENCE EXPERIMENTSNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology Childhood Adolescence 9th Edition Shaffer Test BankDocument25 pagesDevelopmental Psychology Childhood Adolescence 9th Edition Shaffer Test BankPatriciaGrantetab100% (65)
- Local Knowledge and Conservation of Seagrasses in The Tamil Nadu State of IndiaDocument17 pagesLocal Knowledge and Conservation of Seagrasses in The Tamil Nadu State of Indialisda syahrirNo ratings yet
- Final Apo Ipa SMPDocument11 pagesFinal Apo Ipa SMPRey BengrasNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Eye and EarDocument60 pagesSpecial Senses Eye and EarTosinNo ratings yet
- Free Download Advanced Fermentation and Cell Technology 2 Volume Set Byong H Lee Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesFree Download Advanced Fermentation and Cell Technology 2 Volume Set Byong H Lee Full Chapter PDFjennifer.holman559100% (23)
- 71-90 - Reading PracticeDocument20 pages71-90 - Reading PracticeNazarNo ratings yet
- Nadia Handayani - 2213091007 - Artikel InggrisDocument4 pagesNadia Handayani - 2213091007 - Artikel InggrisNadia HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Thalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDocument8 pagesThalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Linkage and Genetic Mapping EukaryotesDocument37 pagesLinkage and Genetic Mapping EukaryotesSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Research White PaperDocument28 pagesHuman Genetics Research White PaperrajeshbhramaNo ratings yet
- Poly-L-Lysine Solution (0.01%) : Cell Culture Reagent Cat. # A-005-C Pack Size: 100mLDocument2 pagesPoly-L-Lysine Solution (0.01%) : Cell Culture Reagent Cat. # A-005-C Pack Size: 100mLConstanza NegreteNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of GeneticsDocument20 pagesFundamentals of GeneticsKyra Lee EclarinalNo ratings yet
- Exam Practice 1Document1 pageExam Practice 1Evelyn CastillaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Bacteriology Methods and ProtocolsDocument265 pagesDiagnostic Bacteriology Methods and Protocolsrukman kiswariNo ratings yet
- Unit II Microbes Structure and MultiplicationDocument22 pagesUnit II Microbes Structure and MultiplicationSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Towards A General Definition of LifeDocument12 pagesTowards A General Definition of LifeFernandoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueDocument5 pagesChapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueAravind Shabu100% (1)
- Tissues Level OrganizationDocument60 pagesTissues Level OrganizationHilman YusriNo ratings yet
- E - Halder, Science, 1995, Pax6Document6 pagesE - Halder, Science, 1995, Pax6vietteNo ratings yet
- Midterm Mathayom 3Document8 pagesMidterm Mathayom 3AbdullohNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Marriages Families and Relationships Making Choices in A Diverse Society 11 Edition Mary Ann LamannaDocument41 pagesTest Bank For Marriages Families and Relationships Making Choices in A Diverse Society 11 Edition Mary Ann Lamannaparchisidewg0drNo ratings yet
- Biology Trivia IDocument3 pagesBiology Trivia IInday EbangNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Algorithms in Bioinformatics Theory and Implementation 1St Edition Gagniuc Paul A Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Algorithms in Bioinformatics Theory and Implementation 1St Edition Gagniuc Paul A Online PDF All Chapterbaligiainiey100% (17)
- Usp 1132Document21 pagesUsp 1132raulwang2015No ratings yet
- Test TOEFL 26 November 22Document10 pagesTest TOEFL 26 November 22محمد جوفريانتوNo ratings yet
- ACE Biology O'level Book@2021Document213 pagesACE Biology O'level Book@2021Duy100% (1)