Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Architecture - Cs1251 Unit I
Computer Architecture - Cs1251 Unit I
Uploaded by
Elven SepdracodeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Math10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionDocument32 pagesMath10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionChaz grant borromeo89% (9)
- Daimler Ir Mercedes Benz Strategy Update 2020 PresentationDocument79 pagesDaimler Ir Mercedes Benz Strategy Update 2020 PresentationabcdNo ratings yet
- CA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerDocument112 pagesCA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerOmprakash DNo ratings yet
- CS2253 - Computerorganization Architecture-QbDocument54 pagesCS2253 - Computerorganization Architecture-QbVaishnavi RaveNo ratings yet
- Coa-2-Marks-Q & ADocument30 pagesCoa-2-Marks-Q & AArup RakshitNo ratings yet
- Two Marks Question Bank CS2253 - Computer Organization & ArchitectureDocument22 pagesTwo Marks Question Bank CS2253 - Computer Organization & ArchitecturePeArL PiNkNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument7 pagesUnit IHarinath Ramamoorthy100% (1)
- CO UNIT1 Topic 3,4,5,6&7Document50 pagesCO UNIT1 Topic 3,4,5,6&7Suresh Reddy KambamNo ratings yet
- CA 2marksDocument41 pagesCA 2marksJaya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 16 MarksDocument28 pagesComputer Architecture 16 MarksBalachandar2000100% (1)
- Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument29 pagesTwo Mark Questions and Answerssuganrhithu9389No ratings yet
- Computer Science Notes - Software ConceptsDocument12 pagesComputer Science Notes - Software Conceptsgautham28No ratings yet
- SS VVFGC NewDocument84 pagesSS VVFGC NewArthiNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 2 MarksDocument32 pagesComputer Architecture 2 MarksArchanavgs0% (1)
- Computer Organization: Bus StructuresDocument4 pagesComputer Organization: Bus Structuressalman khanNo ratings yet
- Operating System Interview QuestionsDocument22 pagesOperating System Interview QuestionsKasab Hu maiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer TypesDocument10 pagesChapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer Typesachaparala4499No ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document18 pagesWa0000.h.hyadav8881No ratings yet
- Aca Univ 2 Mark and 16 MarkDocument20 pagesAca Univ 2 Mark and 16 MarkmenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document67 pagesUnit 1ராஜலிங்கம் பாலகிருஷ்ணன்No ratings yet
- CSC 403 Lecture 2Document16 pagesCSC 403 Lecture 2koredekayode2023No ratings yet
- System Programming Question BankDocument22 pagesSystem Programming Question BankShrunkhala Wankhede Badwaik50% (2)
- CS6303 Computer Architecture Two MarksDocument19 pagesCS6303 Computer Architecture Two Markskayalvizhimurugan80% (5)
- Os FaqDocument14 pagesOs Faqd_dharaNo ratings yet
- Cycle 2Document8 pagesCycle 2ireneNo ratings yet
- Operating System:: Franz Vallerie B. Bueno BS Computer Engineering 4-2dDocument11 pagesOperating System:: Franz Vallerie B. Bueno BS Computer Engineering 4-2dFranz Vallerie Brutas BuenoNo ratings yet
- CA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerDocument109 pagesCA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerJagadeesh Mohan100% (1)
- Draw The Block Diagram of Simple Microprocessor-Based System and Explain The Function of Each Block (You Can Use MS Word or Google Docs)Document8 pagesDraw The Block Diagram of Simple Microprocessor-Based System and Explain The Function of Each Block (You Can Use MS Word or Google Docs)Riza Pahama MananaongNo ratings yet
- NMLT Quiz Chapter 1Document9 pagesNMLT Quiz Chapter 1Hoàng HuyNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Computers - 1Document6 pagesBasic Structure of Computers - 1SwatiNo ratings yet
- Functional UnitsDocument15 pagesFunctional UnitssasisakthiNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organisation NotesDocument18 pagesComputer Architecture and Organisation NotesVED MISHRANo ratings yet
- CS8493 2marks PDFDocument36 pagesCS8493 2marks PDFSparkerz S Vijay100% (1)
- Computer OrganisationDocument17 pagesComputer Organisationkijanavictor96No ratings yet
- SS & MP Lab Viva QuestiionsDocument33 pagesSS & MP Lab Viva QuestiionsT A AsmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Computer: 1.2. Functional UnitDocument15 pagesBasic Structure of Computer: 1.2. Functional Unitprathuasharao2017No ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document11 pagesAssignment 7ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- DPCO Unit3 2mark Q&ADocument11 pagesDPCO Unit3 2mark Q&Akanimozhi rajasekarenNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science and EngineeringDocument32 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and Engineeringjexehif3730% (1)
- 2.1 Hardware and Communication TextBook (Theteacher - Info)Document42 pages2.1 Hardware and Communication TextBook (Theteacher - Info)AhmadNo ratings yet
- Network TheoryDocument31 pagesNetwork TheoryPradeep M NNo ratings yet
- Midterm CADocument5 pagesMidterm CAKashan AhmedNo ratings yet
- IT2Document23 pagesIT2rameshNo ratings yet
- 11th Opearting System July 2022Document7 pages11th Opearting System July 2022baljitNo ratings yet
- Mca 301Document7 pagesMca 301logicballiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer TypesDocument10 pagesChapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer TypesvinoliamanoharNo ratings yet
- 18csc203j - Coa Unit 1Document25 pages18csc203j - Coa Unit 1Rishabh ShahNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument13 pagesSoftwareAyug RaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Comp314Document6 pagesAssignment 1 Comp314Lam DerekNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2: CC118 Computer Organisation and ArchitectureDocument3 pagesTutorial 2: CC118 Computer Organisation and Architecturesajan gcNo ratings yet
- Cit309 Summary With Past QuestionsDocument7 pagesCit309 Summary With Past QuestionsShamsuddeenMuhammadAbubakarShamarNo ratings yet
- Sri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering CollegeDocument21 pagesSri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering Collegenaveenraj_mtechNo ratings yet
- Lec 02Document18 pagesLec 02mmmhasyNo ratings yet
- CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III Semester 2 Marks Unit-I Overview & InstructionsDocument18 pagesCS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III Semester 2 Marks Unit-I Overview & InstructionssathishNo ratings yet
- Ca Question BankDocument51 pagesCa Question Bankrsk20480No ratings yet
- Ge2112 Fundamentals of Computing and Programming: Introduction To ComputersDocument25 pagesGe2112 Fundamentals of Computing and Programming: Introduction To ComputerssanjeevnokiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ImpDocument15 pagesUnit 1 ImpGautham SajuNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation Chapter - 1 Basic Structure of ComputersDocument11 pagesComputer Organisation Chapter - 1 Basic Structure of ComputersMurali DharanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Ans 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1 Ans 1SLIM SHADYNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
- "Unleashing the Power of Assembly Language: Mastering the World's Most Efficient Code"From Everand"Unleashing the Power of Assembly Language: Mastering the World's Most Efficient Code"No ratings yet
- The Art of Comic Book Inking PDFDocument194 pagesThe Art of Comic Book Inking PDFElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Basic Unix CommandsDocument2 pagesBasic Unix CommandsElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: Parallel DatabasesDocument43 pagesChapter 21: Parallel DatabasesElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22: Distributed DatabasesDocument91 pagesChapter 22: Distributed DatabasesElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Altyre - Bard 3 Fight 1Document2 pagesAltyre - Bard 3 Fight 1Kris PitmanNo ratings yet
- BlueSky EXo2 ManualDocument18 pagesBlueSky EXo2 ManualCiho SebastianNo ratings yet
- Cortex Xsiam Admin GuideDocument1,003 pagesCortex Xsiam Admin Guidescribd.r514iNo ratings yet
- Tài liệu Biến tần LS IP5ADocument48 pagesTài liệu Biến tần LS IP5AchinhNo ratings yet
- Urschel DicerDocument268 pagesUrschel DicerGoker UyarerNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document7 pagesCH 3AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Kapselmutter: Ausgabe/Edition 2005-11Document9 pagesKapselmutter: Ausgabe/Edition 2005-11Ravi VermaNo ratings yet
- CSE408Document1 pageCSE408BHAVESHNo ratings yet
- Mranank ResumeDocument2 pagesMranank ResumeDeepak SinghalNo ratings yet
- Presentation Johan Van DorpDocument43 pagesPresentation Johan Van Dorpatilio martinezNo ratings yet
- Communication Basics SEILDocument36 pagesCommunication Basics SEILNaga potha raoNo ratings yet
- Texaco Meropa 320 Eng M0010Document2 pagesTexaco Meropa 320 Eng M0010Ady MihailaNo ratings yet
- Offers July 2012 PowerstormDocument16 pagesOffers July 2012 PowerstormMuhammad MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- BPP Proposal FormDocument4 pagesBPP Proposal FormRebecca VidelaNo ratings yet
- Cexrtcjng4Qw: Professional Regulation Commission Order of Payment Archives and Records DivisionDocument1 pageCexrtcjng4Qw: Professional Regulation Commission Order of Payment Archives and Records DivisionJames Anthony R. ParidoNo ratings yet
- Crit BondsDocument125 pagesCrit Bondsdidodad248No ratings yet
- 18.internationalization (I18N)Document3 pages18.internationalization (I18N)intjar AhmadNo ratings yet
- r17 M.tech Eee Model PapersDocument28 pagesr17 M.tech Eee Model PaperslvijayanandNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Session, The Students Are Expected ToDocument25 pagesAt The End of The Session, The Students Are Expected ToRYSON ARMADA100% (1)
- Handout 10379 DE10379Document25 pagesHandout 10379 DE10379Deeivid E.S.No ratings yet
- Computer Graphics VTUDocument65 pagesComputer Graphics VTUManju VinoNo ratings yet
- 20220627Document4,131 pages20220627Michii FloresNo ratings yet
- Installing XAMPP: Step 1: DownloadDocument13 pagesInstalling XAMPP: Step 1: DownloadShashank UttraniNo ratings yet
- MCC VFDDocument26 pagesMCC VFDAdam smithNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Section 1Document31 pagesWEEK 1 - Section 1Doktor CintaNo ratings yet
- Normalization in DBMS - 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF With ExamplesDocument26 pagesNormalization in DBMS - 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF With ExamplesHon seif MwabegeNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning MatrixDocument1 pageDistance Learning MatrixRuth PetrosNo ratings yet
- Confluence Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesConfluence Interview Questions and AnswerssayraNo ratings yet
Computer Architecture - Cs1251 Unit I
Computer Architecture - Cs1251 Unit I
Uploaded by
Elven SepdracodeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Architecture - Cs1251 Unit I
Computer Architecture - Cs1251 Unit I
Uploaded by
Elven SepdracodeCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE -CS1251
UNIT I
1.What is cache memory?
The small and fast RAM units are called as caches.when the execution of an
instruction calls for data located in the main memory,the data are fetched and a copy is
placed in the cache.Later if the same data is required it is read directly from the cache.
2. What is the function of ALU?
Most of the computer operations(arithmetic and logic) are performed in ALU.The
data required for the operation is brought by the processor and the operation is performed
by the ALU.
3. What is the function of CU?
The control unit acts as the nerve center,that coordinates all the computer
operations. It issues timing signals that governs the data transfer.
4. What are basic operations of a computer?
The basic operations are READ and WRITE.
5. What are the registers generally contained in the processor?
MAR-Memory Address Register
MDR-Memory Data Register
IR-Instruction Register
R0-Rn-General purpose Registers
PC-Program Counter
6. What are the steps in executing a program?
1.Fetch
2.Decode
3.Execute
4.Store
7. Define interrupt and ISR?
An interrupt is a request from an I/O device for service by the processor. The
processor provides the requested service by executing the interrupt service routine.
8. Define Bus?
A group of lines that serves as a connecting path for several devices is called a
bus.
9. What is the use of buffer register?
The buffer register is used to avoid speed mismatch between the I/O device and
the processor.
10. Compare single bus structure and multiple bus structure?
A system that contains only one bus(i.e only one transfer at a time) is called as a
single bus structure. A system is called as multiple bus structure if it contains multiple
buses.
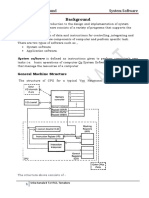
11. What is System Software? Give an example?
It is a collection of programs that are executed as needed to perform functions
such as
o Receiving and interpreting user commands
o Entering and editing application programs and storing them as files
in secondary storage devices.
Ex: Assembler, Linker, Compiler etc
12.What is Application Software? Give an example?
Application programs are usually written in a high-level programming language,
in which the programmer specifies mathematical or text-processing operations. These
operations are described in a format that is independent of the particular computer used to
execute the program.
Ex: C, C++, JAVA
13. What is a compiler?
A system software program called a compiler translates the high-level language
program into a suitable machine language program containing instructions such as the
Add and Load instructions.
14. What is text editor?
It is used for entering and editing application programs. The user of this program
interactively executes command that allow statements of a source program entered at a
keyboard to be accumulated in a file.
15. Discuss about OS as system software?
OS is a large program,or actually a collection of routines,that is used to control
the sharing of and interaction among various computer units as they execute application
programs.The OS routines perform the tasks required to assign computer resources to
individual application programs.
16. What is multiprogrraming or multitasking?
The operating system manages the concurrent execution of several application
programs to make the best possible uses of computer resources.this pattern of
concurrent execution is called multiprogrraming or multitasking.
17.What is elapsed time of computer system?
The total time to execute the total program is called elapsed time.it is affected by
the speed of the processor,the disk and the printer.
18. What is processor time of a program?
The periods during which the processor is active is called processor time of a
programIt depends on the hardware involved in the execution of individual machine
instructions.
19. Define clock rate?
The clock rate is given by,
R=1/P,where P is the length of one clock cycle.
20. Write down the basic performance equation?
T=N*S/R
T=processor time
N=no of instructions
S=no of steps
R=clock rate
21.What is pipelining?
The overlapping of execution of successive instructions is called pipelining.
22. What is byte addressable memory?
The assignment of successive addresses to successive byte locations in the
memory is called byte addressable memory.
23. What is big endian and little endian format?
The name big endian is used when lower byte addresses are used for the more
significiant of the word.The name little endian is used for the less significiant bytes of the
word.
24. What is a branch instruction?
Branch instruction is a type of instruction which loads a new value
into the program counter.
25. What is branch target?
As a result of branch instructions , the processor fetches and executes
the instruction at a new address called branch target, instead of the instruction at
the location that follows the branch instruction in sequential address order.
26.What are condition code flags?
The processor keep track of information about the results of various
operations for use by subsequent conditional branch instructions. This is
accomplished by recording the required information in individual bits, often
called condition code flags.
27.Define addressing mode.
The different ways in which the location of an operand is
specified in an instruction are referred to as addressing modes.
Thank you for evaluating AnyBizSoft PDF to Word.
You can only convert 3 pages with the trial version.
To get all the pages converted, you need to purchase the software from:
http://www.anypdftools.com/buy/buy-pdf-to-word.html
You might also like
- Math10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionDocument32 pagesMath10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionChaz grant borromeo89% (9)
- Daimler Ir Mercedes Benz Strategy Update 2020 PresentationDocument79 pagesDaimler Ir Mercedes Benz Strategy Update 2020 PresentationabcdNo ratings yet
- CA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerDocument112 pagesCA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerOmprakash DNo ratings yet
- CS2253 - Computerorganization Architecture-QbDocument54 pagesCS2253 - Computerorganization Architecture-QbVaishnavi RaveNo ratings yet
- Coa-2-Marks-Q & ADocument30 pagesCoa-2-Marks-Q & AArup RakshitNo ratings yet
- Two Marks Question Bank CS2253 - Computer Organization & ArchitectureDocument22 pagesTwo Marks Question Bank CS2253 - Computer Organization & ArchitecturePeArL PiNkNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument7 pagesUnit IHarinath Ramamoorthy100% (1)
- CO UNIT1 Topic 3,4,5,6&7Document50 pagesCO UNIT1 Topic 3,4,5,6&7Suresh Reddy KambamNo ratings yet
- CA 2marksDocument41 pagesCA 2marksJaya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 16 MarksDocument28 pagesComputer Architecture 16 MarksBalachandar2000100% (1)
- Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument29 pagesTwo Mark Questions and Answerssuganrhithu9389No ratings yet
- Computer Science Notes - Software ConceptsDocument12 pagesComputer Science Notes - Software Conceptsgautham28No ratings yet
- SS VVFGC NewDocument84 pagesSS VVFGC NewArthiNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 2 MarksDocument32 pagesComputer Architecture 2 MarksArchanavgs0% (1)
- Computer Organization: Bus StructuresDocument4 pagesComputer Organization: Bus Structuressalman khanNo ratings yet
- Operating System Interview QuestionsDocument22 pagesOperating System Interview QuestionsKasab Hu maiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer TypesDocument10 pagesChapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer Typesachaparala4499No ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document18 pagesWa0000.h.hyadav8881No ratings yet
- Aca Univ 2 Mark and 16 MarkDocument20 pagesAca Univ 2 Mark and 16 MarkmenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document67 pagesUnit 1ராஜலிங்கம் பாலகிருஷ்ணன்No ratings yet
- CSC 403 Lecture 2Document16 pagesCSC 403 Lecture 2koredekayode2023No ratings yet
- System Programming Question BankDocument22 pagesSystem Programming Question BankShrunkhala Wankhede Badwaik50% (2)
- CS6303 Computer Architecture Two MarksDocument19 pagesCS6303 Computer Architecture Two Markskayalvizhimurugan80% (5)
- Os FaqDocument14 pagesOs Faqd_dharaNo ratings yet
- Cycle 2Document8 pagesCycle 2ireneNo ratings yet
- Operating System:: Franz Vallerie B. Bueno BS Computer Engineering 4-2dDocument11 pagesOperating System:: Franz Vallerie B. Bueno BS Computer Engineering 4-2dFranz Vallerie Brutas BuenoNo ratings yet
- CA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerDocument109 pagesCA 2mark and 16 Mark With AnswerJagadeesh Mohan100% (1)
- Draw The Block Diagram of Simple Microprocessor-Based System and Explain The Function of Each Block (You Can Use MS Word or Google Docs)Document8 pagesDraw The Block Diagram of Simple Microprocessor-Based System and Explain The Function of Each Block (You Can Use MS Word or Google Docs)Riza Pahama MananaongNo ratings yet
- NMLT Quiz Chapter 1Document9 pagesNMLT Quiz Chapter 1Hoàng HuyNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Computers - 1Document6 pagesBasic Structure of Computers - 1SwatiNo ratings yet
- Functional UnitsDocument15 pagesFunctional UnitssasisakthiNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organisation NotesDocument18 pagesComputer Architecture and Organisation NotesVED MISHRANo ratings yet
- CS8493 2marks PDFDocument36 pagesCS8493 2marks PDFSparkerz S Vijay100% (1)
- Computer OrganisationDocument17 pagesComputer Organisationkijanavictor96No ratings yet
- SS & MP Lab Viva QuestiionsDocument33 pagesSS & MP Lab Viva QuestiionsT A AsmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Computer: 1.2. Functional UnitDocument15 pagesBasic Structure of Computer: 1.2. Functional Unitprathuasharao2017No ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document11 pagesAssignment 7ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- DPCO Unit3 2mark Q&ADocument11 pagesDPCO Unit3 2mark Q&Akanimozhi rajasekarenNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science and EngineeringDocument32 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and Engineeringjexehif3730% (1)
- 2.1 Hardware and Communication TextBook (Theteacher - Info)Document42 pages2.1 Hardware and Communication TextBook (Theteacher - Info)AhmadNo ratings yet
- Network TheoryDocument31 pagesNetwork TheoryPradeep M NNo ratings yet
- Midterm CADocument5 pagesMidterm CAKashan AhmedNo ratings yet
- IT2Document23 pagesIT2rameshNo ratings yet
- 11th Opearting System July 2022Document7 pages11th Opearting System July 2022baljitNo ratings yet
- Mca 301Document7 pagesMca 301logicballiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer TypesDocument10 pagesChapter - 1: Basic Structure of Computers: Computer TypesvinoliamanoharNo ratings yet
- 18csc203j - Coa Unit 1Document25 pages18csc203j - Coa Unit 1Rishabh ShahNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument13 pagesSoftwareAyug RaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Comp314Document6 pagesAssignment 1 Comp314Lam DerekNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2: CC118 Computer Organisation and ArchitectureDocument3 pagesTutorial 2: CC118 Computer Organisation and Architecturesajan gcNo ratings yet
- Cit309 Summary With Past QuestionsDocument7 pagesCit309 Summary With Past QuestionsShamsuddeenMuhammadAbubakarShamarNo ratings yet
- Sri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering CollegeDocument21 pagesSri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering Collegenaveenraj_mtechNo ratings yet
- Lec 02Document18 pagesLec 02mmmhasyNo ratings yet
- CS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III Semester 2 Marks Unit-I Overview & InstructionsDocument18 pagesCS6303 Computer Architecture Regulation 2013 BE-Computer Science and Engineering III Semester 2 Marks Unit-I Overview & InstructionssathishNo ratings yet
- Ca Question BankDocument51 pagesCa Question Bankrsk20480No ratings yet
- Ge2112 Fundamentals of Computing and Programming: Introduction To ComputersDocument25 pagesGe2112 Fundamentals of Computing and Programming: Introduction To ComputerssanjeevnokiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ImpDocument15 pagesUnit 1 ImpGautham SajuNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation Chapter - 1 Basic Structure of ComputersDocument11 pagesComputer Organisation Chapter - 1 Basic Structure of ComputersMurali DharanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Ans 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1 Ans 1SLIM SHADYNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
- "Unleashing the Power of Assembly Language: Mastering the World's Most Efficient Code"From Everand"Unleashing the Power of Assembly Language: Mastering the World's Most Efficient Code"No ratings yet
- The Art of Comic Book Inking PDFDocument194 pagesThe Art of Comic Book Inking PDFElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Basic Unix CommandsDocument2 pagesBasic Unix CommandsElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: Parallel DatabasesDocument43 pagesChapter 21: Parallel DatabasesElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22: Distributed DatabasesDocument91 pagesChapter 22: Distributed DatabasesElven SepdracodeNo ratings yet
- Altyre - Bard 3 Fight 1Document2 pagesAltyre - Bard 3 Fight 1Kris PitmanNo ratings yet
- BlueSky EXo2 ManualDocument18 pagesBlueSky EXo2 ManualCiho SebastianNo ratings yet
- Cortex Xsiam Admin GuideDocument1,003 pagesCortex Xsiam Admin Guidescribd.r514iNo ratings yet
- Tài liệu Biến tần LS IP5ADocument48 pagesTài liệu Biến tần LS IP5AchinhNo ratings yet
- Urschel DicerDocument268 pagesUrschel DicerGoker UyarerNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document7 pagesCH 3AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Kapselmutter: Ausgabe/Edition 2005-11Document9 pagesKapselmutter: Ausgabe/Edition 2005-11Ravi VermaNo ratings yet
- CSE408Document1 pageCSE408BHAVESHNo ratings yet
- Mranank ResumeDocument2 pagesMranank ResumeDeepak SinghalNo ratings yet
- Presentation Johan Van DorpDocument43 pagesPresentation Johan Van Dorpatilio martinezNo ratings yet
- Communication Basics SEILDocument36 pagesCommunication Basics SEILNaga potha raoNo ratings yet
- Texaco Meropa 320 Eng M0010Document2 pagesTexaco Meropa 320 Eng M0010Ady MihailaNo ratings yet
- Offers July 2012 PowerstormDocument16 pagesOffers July 2012 PowerstormMuhammad MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- BPP Proposal FormDocument4 pagesBPP Proposal FormRebecca VidelaNo ratings yet
- Cexrtcjng4Qw: Professional Regulation Commission Order of Payment Archives and Records DivisionDocument1 pageCexrtcjng4Qw: Professional Regulation Commission Order of Payment Archives and Records DivisionJames Anthony R. ParidoNo ratings yet
- Crit BondsDocument125 pagesCrit Bondsdidodad248No ratings yet
- 18.internationalization (I18N)Document3 pages18.internationalization (I18N)intjar AhmadNo ratings yet
- r17 M.tech Eee Model PapersDocument28 pagesr17 M.tech Eee Model PaperslvijayanandNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Session, The Students Are Expected ToDocument25 pagesAt The End of The Session, The Students Are Expected ToRYSON ARMADA100% (1)
- Handout 10379 DE10379Document25 pagesHandout 10379 DE10379Deeivid E.S.No ratings yet
- Computer Graphics VTUDocument65 pagesComputer Graphics VTUManju VinoNo ratings yet
- 20220627Document4,131 pages20220627Michii FloresNo ratings yet
- Installing XAMPP: Step 1: DownloadDocument13 pagesInstalling XAMPP: Step 1: DownloadShashank UttraniNo ratings yet
- MCC VFDDocument26 pagesMCC VFDAdam smithNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Section 1Document31 pagesWEEK 1 - Section 1Doktor CintaNo ratings yet
- Normalization in DBMS - 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF With ExamplesDocument26 pagesNormalization in DBMS - 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF With ExamplesHon seif MwabegeNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning MatrixDocument1 pageDistance Learning MatrixRuth PetrosNo ratings yet
- Confluence Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesConfluence Interview Questions and AnswerssayraNo ratings yet