Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An Intranet
An Intranet
Uploaded by
Diksha GuptaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
An Intranet
An Intranet
Uploaded by
Diksha GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
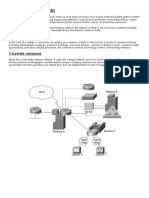
An intranet is a private computer network that uses Internet Protocol technology to securely
share any part of an organization's information or network operating system within that
organization. The term is used in contrast to internet, a network between organizations, and
instead refers to a network within an organization. Sometimes the term refers only to the
organization's internal website, but may be a more extensive part of the organization's
information technology infrastructure. It may host multiple private websites and constitute an
important component and focal point of internal communication and collaboration.
Characteristics
An intranet is built from the same concepts and technology used for the Internet, such as
client–server computing and the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP). Any of the well known
Internet protocols may be found in an intranet, such as HTTP (web services), SMTP (e-mail),
and FTP (file transfer protocol). Internet technologies are often deployed to provide modern
interfaces to legacy information systems hosting corporate data.
An intranet can be understood as a private analog of the Internet, or as a private extension of
the Internet confined to an organization. The first intranet websites and home pages began to
appear in organizations in 1996-1997. Although not officially noted, the term intranet first
became common-place among early adopters, such as universities and technology
corporations, in 1992.[dubious – discuss]
Intranets have also contrasted with extranets. While intranets are generally restricted to
employees of the organization, extranets may also be accessed by customers, suppliers, or
other approved parties.[1] Extranets extend a private network onto the Internet with special
provisions for access, authorization, and authentication (AAA protocol).
Intranets may provide a gateway to the Internet by means of a network gateway with a
firewall, shielding the intranet from unauthorized external access. The gateway often also
implements user authentication, encryption of messages, and often virtual private network
(VPN) connectivity for off-site employees to access company information, computing
resources and internal communication...
You might also like
- Intranet, Extranet, Internet, Wan Lan, ManDocument4 pagesIntranet, Extranet, Internet, Wan Lan, Manmaaheen100% (2)
- 1 4907038154730504391 PDFDocument116 pages1 4907038154730504391 PDFWILLIAM FERNANDO OCAMPO GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Intranet: Computer Network Internet Protocol Network Operating SystemDocument3 pagesIntranet: Computer Network Internet Protocol Network Operating SystemMANAPNo ratings yet
- Working of InternetDocument7 pagesWorking of InternetSaba JamalNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument14 pagesTypes of Networksm0rph1sNo ratings yet
- Internet 03Document13 pagesInternet 03Mano KaranNo ratings yet
- The IntranetDocument3 pagesThe IntranetM-soft solutionsNo ratings yet
- Intranet: Presented By: Urja Joshi Presented By: Urja JoshiDocument15 pagesIntranet: Presented By: Urja Joshi Presented By: Urja JoshiUrja JoshiNo ratings yet
- IT NotesDocument32 pagesIT Notesdordelderek the lastNo ratings yet
- To Intranet: Presented by - Isha Javed. MBA (G) Semester-1, Section-A. Enrollment No. 68Document6 pagesTo Intranet: Presented by - Isha Javed. MBA (G) Semester-1, Section-A. Enrollment No. 68Kunal ShahNo ratings yet
- E BusinessDocument29 pagesE BusinessTuryamureeba JuliusNo ratings yet
- Internet Vs IntranetDocument11 pagesInternet Vs IntranetSvb CharyNo ratings yet
- IntranetDocument6 pagesIntranetMayank MittalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Network LayerDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Network LayerFiromsa DineNo ratings yet
- Acme IncDocument1 pageAcme Incckxh9tw92zNo ratings yet
- E CommerceDocument2 pagesE CommerceLavi KukretiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Need of Develop An Intranet Based System When Internet Based System Is Possible? Explain With An Example. Answer 1Document4 pagesWhat Is The Need of Develop An Intranet Based System When Internet Based System Is Possible? Explain With An Example. Answer 1001nileshkNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Intranet Business-To-Business Business-To-Consumer DMZDocument16 pagesComputer Network Intranet Business-To-Business Business-To-Consumer DMZasingh18inNo ratings yet
- The SPB College of Business Administration: Use of Internet in Various FieldDocument13 pagesThe SPB College of Business Administration: Use of Internet in Various FieldhemalpandyaNo ratings yet
- Internet Intranet and ExtranetDocument3 pagesInternet Intranet and ExtranetANUJ GIRINo ratings yet
- Intranet and ExtranetDocument11 pagesIntranet and ExtranetShashank ParmarNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument44 pagesSeminar ReportShubham KhotkarNo ratings yet
- Networks Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesNetworks Seminar ReportHarshaAchyutuni100% (1)
- Internet: Difference Between Extranet, Internet and Intranet?Document5 pagesInternet: Difference Between Extranet, Internet and Intranet?Rinku SharmaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Electronic ReportDocument12 pagesDefinition of Electronic ReportZain Ul AbdeenNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument2 pagesComputer NetworkMadison SmithNo ratings yet
- Teleconferences: Uses of The IntranetDocument14 pagesTeleconferences: Uses of The IntranetAniket SharmaNo ratings yet
- CONTENTS FOR E-CommerceDocument5 pagesCONTENTS FOR E-CommerceThe PaletteNo ratings yet
- IntranetDocument15 pagesIntranetdikshitnaikNo ratings yet
- Adamu Abubakar Abdulrazak AssignDocument4 pagesAdamu Abubakar Abdulrazak AssignAbdullahi AwwalNo ratings yet
- IntranetDocument3 pagesIntranetKhyati PatelNo ratings yet
- Extranet: Computer NetworkDocument4 pagesExtranet: Computer NetworkkhawasikarNo ratings yet
- E Business NotesDocument10 pagesE Business NotesvandanaNo ratings yet
- Internet, Intranet, ExtranetDocument35 pagesInternet, Intranet, ExtranetFarah Atika Ar Azmi100% (1)
- Web PortalDocument13 pagesWeb PortalSreyasi RoyNo ratings yet
- Intranet: Private Computer Network Within That OrganizationDocument2 pagesIntranet: Private Computer Network Within That Organizationvijayab7No ratings yet
- Introdution: Dubious - DiscussDocument10 pagesIntrodution: Dubious - DiscussKushal TibrewalNo ratings yet
- QUES.24 - What Is Intranet? Discuss The Features and Architecture of Intranet With The Help of A DiagramDocument17 pagesQUES.24 - What Is Intranet? Discuss The Features and Architecture of Intranet With The Help of A Diagramanil rajputNo ratings yet
- Internet, Intranet and Extranets: Presentation ByDocument25 pagesInternet, Intranet and Extranets: Presentation BysurbhibarveNo ratings yet
- Abubakar Hudu AssignmentDocument4 pagesAbubakar Hudu AssignmentAbdullahi AwwalNo ratings yet
- Internetintranetandextranet 121207230205 Phpapp01Document12 pagesInternetintranetandextranet 121207230205 Phpapp01api-231294003No ratings yet
- ExtranetDocument2 pagesExtranetHeavenStudio TimisoaraNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document29 pagesModule 3Aditi KuteNo ratings yet
- Notes On Information TechnologyDocument7 pagesNotes On Information Technologyronny ronNo ratings yet
- Internet, Intranet and ExtranetDocument11 pagesInternet, Intranet and Extranetktkalai selviNo ratings yet
- Basics of Internet, Intranet and Extranet: "Everything Is Connected To Everything"Document31 pagesBasics of Internet, Intranet and Extranet: "Everything Is Connected To Everything"ankitpareekNo ratings yet
- Intranet: Uses Benefits Planning and Creation MaintenanceDocument6 pagesIntranet: Uses Benefits Planning and Creation MaintenanceBonnie ThompsonNo ratings yet
- About InternetDocument88 pagesAbout InternetLokesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Internet HandoutDocument66 pagesInternet HandoutImrana mannirNo ratings yet
- E BusinessDocument22 pagesE Businessneo sirgeNo ratings yet
- What Is Network DiagramDocument7 pagesWhat Is Network DiagramOundo SamNo ratings yet
- Internet, Intranet, ExtranetDocument14 pagesInternet, Intranet, Extranetmotz100% (8)
- UNIT-3: Telecommunication and NetworksDocument13 pagesUNIT-3: Telecommunication and NetworksSameer YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Information: Presented By: Hoang Phan NguyenDocument27 pagesUnit 3: Information: Presented By: Hoang Phan NguyenShinigami MusicNo ratings yet
- E Commerce (L5)Document24 pagesE Commerce (L5)Jawad AliNo ratings yet
- Module 3newDocument46 pagesModule 3newAditi KuteNo ratings yet
- Internet, Intranet and ExtranetsDocument20 pagesInternet, Intranet and ExtranetsPRAO6005No ratings yet
- Internet, Intranets and ExtranetsDocument20 pagesInternet, Intranets and ExtranetsPRAO6005100% (7)
- Internet, Intranet and ExtranetDocument12 pagesInternet, Intranet and ExtranetJehra Mae Sevillano ÜNo ratings yet