Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notations For Concentrations in Binary Systems
Notations For Concentrations in Binary Systems
Uploaded by
Carla SibalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notations For Concentrations in Binary Systems
Notations For Concentrations in Binary Systems
Uploaded by
Carla SibalCopyright:
Available Formats
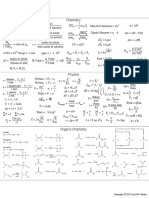
Notations for Concentrations in binary systems
ρ = ρ A + ρB = mass density of solution, g / cm 3
ρ = C A .M A = mass concentration of A, g / cm 3
ρ
wA = A = mass fraction of A
ρ
C = C A + C B = molar density of solution, g − mole / cm 3 , mole / cm 3
ρA
C= = molar concentration of A, g − mole / cm 3 , mole / cm 3
MA
ρ
M = = number-mean molecular weight of mixture
C
wA
MA
x A + xB = 1 ; M = x A .M A + xB .M B ; xA =
wA w
+ B
MA MB
1 w w x A .M A
wA + wB = 1 ; = A + B ; wA =
M MA MB x A .M A + xB .M B
ρ1 ρ
+ 2
M M 2 for binary liquids
Cave = 1 =
2
Dalton’s law of partial pressure and Raoult’s law:
P = PA + PB ;
PA PB
yA = ; yB = ; 1 = y A + y B ; y A = mole fraction of A in the vapor phase
P P
P P
xA = A ; xB = B ; 1 = x A + xB ; x A =mole fraction of A in the liquid phase
VPA VPB
PA nA
P.V = n.R.T ; PA .V = n A .R.T ; CA = ; CA = ; n = n A + nB
R.T V
PA .M A
ρA = C A .M A ; ρA = ; C A = C.x A ; ρA = ρ.wA
R.T
You might also like
- Thomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All ChapterDocument67 pagesThomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All Chapterramona.evans546100% (8)
- Geometry Formulas All Gathered On One Easy Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGeometry Formulas All Gathered On One Easy Cheat Sheetnatashkan100% (2)
- Answer Key NLM PDFDocument29 pagesAnswer Key NLM PDFYash ChaudhauryNo ratings yet
- Solved Assignment Colligative Properties-1Document8 pagesSolved Assignment Colligative Properties-1dhir.khushi.2005No ratings yet
- Uas PondasiDocument6 pagesUas PondasiAfif FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument5 pages5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassNo ratings yet
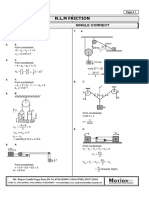
- Chemistry!: π ω Friction = F i Friction ≤ F i ΔL= αL ΔT ΔA= γ A ΔT P= Energy time I= Power SA Δf = v c Δ λ λ = v cDocument1 pageChemistry!: π ω Friction = F i Friction ≤ F i ΔL= αL ΔT ΔA= γ A ΔT P= Energy time I= Power SA Δf = v c Δ λ λ = v cjhhjjhNo ratings yet
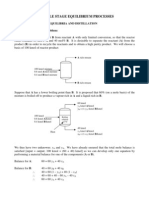
- Multiple Stage Equilibrium Processes: 1. Vapour Liquid Equilibria and Distillation Let Us Consider A Simple ProblemDocument23 pagesMultiple Stage Equilibrium Processes: 1. Vapour Liquid Equilibria and Distillation Let Us Consider A Simple Problemthesage100% (1)
- Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesLearning ObjectivesALEX CLEVER ALEJO HOYOSNo ratings yet
- Ecuación de GasesDocument5 pagesEcuación de GasesJuan Camilo Gil PardoNo ratings yet
- Ial Maths Pure 4 Ex7eDocument3 pagesIal Maths Pure 4 Ex7enasehaNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor Equations and Sample ProblemsDocument9 pagesBatch Reactor Equations and Sample ProblemsARIANA NICOLE RELIGIOSONo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Kinetics of Homogeneous Reactions (Part 2 of 3)Document19 pagesChapter 2 Kinetics of Homogeneous Reactions (Part 2 of 3)Molike HononoNo ratings yet
- CN2116-Unit 10-2022Document25 pagesCN2116-Unit 10-2022Carmen ChanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document32 pagesModule 2Henry Darius NamocNo ratings yet
- L NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP: D R D C D BDocument1 pageL NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP L NM O QP: D R D C D BragupaNo ratings yet
- Mass TransferDocument32 pagesMass TransferMichelle LiauNo ratings yet
- The Gaussian Elimination Method: Sarang S. SaneDocument49 pagesThe Gaussian Elimination Method: Sarang S. SaneMrTimbaktuNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formulas 2D and 3DDocument2 pagesMensuration Formulas 2D and 3Darvindsinghchauhan681No ratings yet
- Module 7Document27 pagesModule 7Henry Darius NamocNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Class 12 Imp Formula ND ReactionsDocument17 pagesChemistry - Class 12 Imp Formula ND Reactionsshurshtikarande18No ratings yet
- (L6) - (JLD 2.0) - Circular Motion - 29th September.Document48 pages(L6) - (JLD 2.0) - Circular Motion - 29th September.Aneek ChakrovartyNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For The DSATDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet For The DSATalt accNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetVaishnav VIPANCHIKANo ratings yet
- Materi - MEKANIKA TEKNIK IDocument3 pagesMateri - MEKANIKA TEKNIK Ifilia EdokudoNo ratings yet
- Kinetika Reaksi Kimia & KatalisisDocument6 pagesKinetika Reaksi Kimia & KatalisisFatmawati PutriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12, Solution 93Document1 pageChapter 12, Solution 93Sa-mer BeskalesNo ratings yet
- Booklet 5, CHG 806Document7 pagesBooklet 5, CHG 806ONAFUWA AyodeleNo ratings yet
- Two Component Phase Equilibria IDocument6 pagesTwo Component Phase Equilibria IRojo JohnNo ratings yet
- Tóm-tắt-công-thức-CK KTPUDocument13 pagesTóm-tắt-công-thức-CK KTPUHồng PhúcNo ratings yet
- Formula-Sheet-for-the-SAT MathsDocument4 pagesFormula-Sheet-for-the-SAT MathsYumon KoNo ratings yet
- Plane Kinematics of Rigid Bodies: Jump To First PageDocument17 pagesPlane Kinematics of Rigid Bodies: Jump To First Pagezoom^2No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: MFM 2P: W L P W L P LW ADocument2 pagesFormula Sheet: MFM 2P: W L P W L P LW AKIMIA PARNIANINo ratings yet
- Exer 1Document4 pagesExer 1RizwanbhatNo ratings yet
- General Case For Diffusion of Gases A & B Plus Bulk MovementDocument10 pagesGeneral Case For Diffusion of Gases A & B Plus Bulk MovementMayar H. HaggagNo ratings yet
- Co Ly Thuyet - Bai Tap Kinematics 2-1 - C4Document74 pagesCo Ly Thuyet - Bai Tap Kinematics 2-1 - C4Minh KhôiNo ratings yet
- Ca Foundation Maths Handbook by Raj AwateDocument60 pagesCa Foundation Maths Handbook by Raj AwateIpsheeta beheraNo ratings yet
- GibbsPhaseRule PDFDocument2 pagesGibbsPhaseRule PDFdeepak pandeyNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document4 pagesTask 4Julius CagampangNo ratings yet
- Tabel 2 Fixed End MomentDocument2 pagesTabel 2 Fixed End Momentsultanbona99No ratings yet
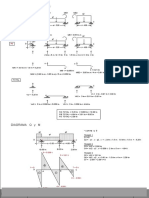
- Bending Moment Sign ConventionDocument14 pagesBending Moment Sign ConventionNeil WayneNo ratings yet
- Shear Forces and Bending Moments in Beams Sign Convention: MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsDocument14 pagesShear Forces and Bending Moments in Beams Sign Convention: MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsDogLifeNo ratings yet
- 1basics of Process Calculations by Dr. Chetan M. PatelDocument10 pages1basics of Process Calculations by Dr. Chetan M. PatelYash JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Viga Tres Tramos 2Document1 pageViga Tres Tramos 2cris heNo ratings yet
- Proofs Using VectorsDocument3 pagesProofs Using VectorsSophia ShiNo ratings yet
- ECH143 ProblemSetSol PDFDocument53 pagesECH143 ProblemSetSol PDFMohamed ElbehlilNo ratings yet
- Design Equations of Batch ReactorsDocument6 pagesDesign Equations of Batch ReactorsMaryaa Luwizaa AllauiganNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3B - Analysis of Batch Reactors (Aa +BB - P) PDFDocument6 pagesLecture 3B - Analysis of Batch Reactors (Aa +BB - P) PDFPAMELA TEJADANo ratings yet
- Formulario 3avaliacaoDocument2 pagesFormulario 3avaliacaoMarcelo Gimenez MagalhãesNo ratings yet
- Rotameter Equations and DerivationsDocument2 pagesRotameter Equations and DerivationsMariam flittyNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument5 pagesSolutionsSiya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Solucion Global ADocument5 pagesSolucion Global ARomel GomezNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Pose (Position and Orientation) of A Rigid BodyDocument34 pagesKinematics: Pose (Position and Orientation) of A Rigid Bodyknritm_10No ratings yet
- Equation Load Diagram W Shear-Force Diagram V Bending-Moment Diagram MDocument1 pageEquation Load Diagram W Shear-Force Diagram V Bending-Moment Diagram MAndres Felipe Prieto AlarconNo ratings yet
- Materi Mekanika Rekayasa - Simple BeamDocument13 pagesMateri Mekanika Rekayasa - Simple BeamAtalya PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Mt210 Quiz 10 Sample 1 Surname, Name:: Question 1. 3.2 Properties of DeterminantDocument1 pageMt210 Quiz 10 Sample 1 Surname, Name:: Question 1. 3.2 Properties of DeterminantahmedNo ratings yet
- Solutions: A A A BDocument3 pagesSolutions: A A A BRobin EappenNo ratings yet