Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsPlant
Plant
Uploaded by
Royal RonaldoPlants obtain support through a variety of structures and tissues. Aquatic plants are supported by buoyancy from air spaces in their leaves and stems or broad, firm but flexible leaves that resist wave action. Terrestrial herbaceous plants get support from turgor pressure in their cells and thickened cell walls. Woody plants have additional support from sclerenchyma tissues like fibers and sclereids, as well as xylem tissues that undergo secondary thickening to form wood. Other structures providing plant support include buttress roots, vines, and lianas.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- Biology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesDocument51 pagesBiology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (4)
- UNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyDocument48 pagesUNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyMyreal Venice CrudaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Report Plant ANATOMYDocument9 pagesLab 3 Report Plant ANATOMYEizuwanEizuddin50% (2)
- Bio LabDocument13 pagesBio Labapi-3730385100% (9)
- Support and Movement Notes PDFDocument26 pagesSupport and Movement Notes PDFmark njeru ngigi88% (8)
- Type of Plant Adaptation Explanation: A) Submerged PlantsDocument2 pagesType of Plant Adaptation Explanation: A) Submerged PlantsReen1996No ratings yet
- 2.3 Support in PlantsDocument17 pages2.3 Support in PlantsMichelle ChinNo ratings yet
- Support in Aquatic PlantsDocument11 pagesSupport in Aquatic PlantsnewdirextionNo ratings yet
- Support and MovementsDocument44 pagesSupport and MovementsSohaib MalikNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation in PlantsDocument21 pagesCell Organisation in PlantsRajananthini PushpanathanNo ratings yet
- Support and MovementDocument96 pagesSupport and Movementmercynjesh20100% (2)
- PLANTDocument23 pagesPLANTAngelito HalmainNo ratings yet
- Ch35 PlantStructure&GrowthDocument5 pagesCh35 PlantStructure&GrowthCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- PLANT TISSUE AND SEC GROWTH For 9 11Document6 pagesPLANT TISSUE AND SEC GROWTH For 9 11Khushbu PandyaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Document79 pagesGen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Samantha AcostaNo ratings yet
- FBS 221 Lab - Edited With QuestionsDocument10 pagesFBS 221 Lab - Edited With QuestionsashleyNo ratings yet
- Botany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument47 pagesBotany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisManar AnwerNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology Classification of PlantsDocument28 pagesPlant Biology Classification of PlantsAhmet OnaltNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About The Part of A PlantDocument51 pagesThis Article Is About The Part of A PlantTess TubieronNo ratings yet
- k12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsDocument3 pagesk12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsJohn Matthew Jobo100% (1)
- Parts of A Plant and Its Functions: Jason L. Cabrigas BAT - 4Document6 pagesParts of A Plant and Its Functions: Jason L. Cabrigas BAT - 4Chona Janiola CastuloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneApostolos KoutsaftisNo ratings yet
- Plant BiologyDocument58 pagesPlant Biologypriyankalikhitha1183No ratings yet
- Describe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueIshaHenryNo ratings yet
- Vascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraDocument22 pagesVascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraGeorgia VasanthaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues 2Document43 pagesPlant Tissues 2Francis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 pagesTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- SAT 2 Biology - PlantsDocument22 pagesSAT 2 Biology - PlantsMido MidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Document9 pagesLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramNo ratings yet
- PRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4Document26 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Meristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and TissuesDocument8 pagesMeristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and Tissuessandy waskitoNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Chapters2Document60 pagesPlant Physiology Chapters2Mahad Ahmed HilowleNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue ARDocument34 pagesPlant Tissue ARAnna Grace Lobigas RanocoNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Document42 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Marcus LeeNo ratings yet
- PLANTYDocument27 pagesPLANTYbry uyNo ratings yet
- Reading Guide Answers PlantsDocument9 pagesReading Guide Answers PlantsNirmal PatelNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Typical Plant BodyDocument4 pagesTissues and Typical Plant BodyKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument6 pagesRevisionStefani KavangoNo ratings yet
- Botny TissuesDocument3 pagesBotny TissuesSamantha AbelloNo ratings yet
- The Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemDocument11 pagesThe Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemClarissa CuñaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues PDFDocument12 pagesPlant Tissues PDFenhlemsane945No ratings yet
- About Presentation Flower GrowthDocument2 pagesAbout Presentation Flower GrowthMedinaNo ratings yet
- Biozone 2 PG 342Document3 pagesBiozone 2 PG 342Ji-Soo KimNo ratings yet
- Lesson Overview: 23.3 StemsDocument29 pagesLesson Overview: 23.3 Stemslayan essamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document11 pagesChapter 8sheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyDocument11 pagesDokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyAin SufizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Biology - DynessDocument45 pagesBiology - DynessmalikachinyantaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- KELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Document3 pagesKELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Dewi Sekar MiasihNo ratings yet
- Bot 121Document12 pagesBot 121eirrehs ellaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of PlantsDocument21 pagesParts and Functions of PlantsRaz QuipedNo ratings yet
- Botany MidtermsDocument16 pagesBotany MidtermsAnisa AzisNo ratings yet
- The Primary and Secondary Growth of PlantDocument31 pagesThe Primary and Secondary Growth of PlantNOFAIZAH RAMLINo ratings yet
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document24 pages06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- 8 June Support and Transport Systems in PlantsDocument25 pages8 June Support and Transport Systems in Plantsmaduanekabelo08No ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 5 NotesDocument20 pagesBio Form 5 NotesNithyamathi KalimuthuNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
Plant
Plant
Uploaded by
Royal Ronaldo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesPlants obtain support through a variety of structures and tissues. Aquatic plants are supported by buoyancy from air spaces in their leaves and stems or broad, firm but flexible leaves that resist wave action. Terrestrial herbaceous plants get support from turgor pressure in their cells and thickened cell walls. Woody plants have additional support from sclerenchyma tissues like fibers and sclereids, as well as xylem tissues that undergo secondary thickening to form wood. Other structures providing plant support include buttress roots, vines, and lianas.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlants obtain support through a variety of structures and tissues. Aquatic plants are supported by buoyancy from air spaces in their leaves and stems or broad, firm but flexible leaves that resist wave action. Terrestrial herbaceous plants get support from turgor pressure in their cells and thickened cell walls. Woody plants have additional support from sclerenchyma tissues like fibers and sclereids, as well as xylem tissues that undergo secondary thickening to form wood. Other structures providing plant support include buttress roots, vines, and lianas.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesPlant
Plant
Uploaded by
Royal RonaldoPlants obtain support through a variety of structures and tissues. Aquatic plants are supported by buoyancy from air spaces in their leaves and stems or broad, firm but flexible leaves that resist wave action. Terrestrial herbaceous plants get support from turgor pressure in their cells and thickened cell walls. Woody plants have additional support from sclerenchyma tissues like fibers and sclereids, as well as xylem tissues that undergo secondary thickening to form wood. Other structures providing plant support include buttress roots, vines, and lianas.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
2.
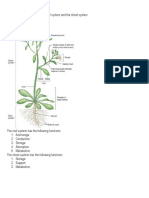
3 Support in Plants
1. Why?
a) Plant grows and it produces more leaves.
b) Grow tall therefore needs to withstand the forces of gravity.
c) Spreading of leaves and branches horizontally.
2. Aquatic plants are supported by buoyancy and support.
Support in aquatic and terrestrial plants
Submerged plants
1.Hydrilla sp. have thin, narrow and flexible leaves.
2. This type of leaves provide little resistance to water flows, plants can be tugged at
and pulled by water currents without being damaged.
3. Air sacs inside the leaves and stems keep the plant floating close to the surface to
obtain maximum sunlight.
4. Their stems have no woody tissues.
Floating plant
1. Water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes) have broad leaves that are firm but flexible
enough to resist tearing by wave action.
2. Aerenchyma tissues (spongy tissues with large air spaces between the cells) in the
stems and leaves provide buoyancy so that the plants can float on the surface of the
water.
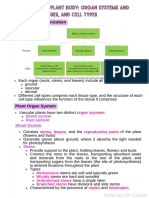
Herbaceous plants (Terresterial plants)
1. Support provided by the turgidity of the parenchyma and collenchyma cells.
2. Turgor pressure of the fluid content in the central vacuole pushes the cell
membrane and the cell contents against the cell wall, creating support for the stem,
root and leaves.
3. The thickening of the cell walls with cellulose and pectin in collenchyma cells
provide additional mechanical strength.
Woody plants
1. Support provided by sclerenchyma and xylem tissues.
2. Sclerenchyma tissue is composed of cells with secondary cell walls that are usually
lignified which support non-growing parts of plants.
3. Two types of sclerenchyma tissue:
a) fibres - long, straight and thin
- found around vascular tissues
b) sclereids – short, circular and irregular shaped
- found in fruit and seeds
4. During primary growth development, the cell walls of xylem vessels and tracheids
are thickened with lignin and forms vessels .
Form 5: Chapter 2 – Locomotion and Support
2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and Animals
5. Type of vessels:
a) annular (ring shaped) vessel
b) spiral vessel
c) scalariform (ladder like) vessel
d) pitted vessel
6. Secondary growth of xylem results in the formation of wood which makes the plant
stronger and and provides support..
7. Other supporting structures:
a) Buttress root – roots that come out from the lower part of the trunk and grow into
the ground, providing support for the tree.
b) Creepers, vines and lianas – use other trees for support.
You might also like
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- Biology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesDocument51 pagesBiology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (4)
- UNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyDocument48 pagesUNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyMyreal Venice CrudaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Report Plant ANATOMYDocument9 pagesLab 3 Report Plant ANATOMYEizuwanEizuddin50% (2)
- Bio LabDocument13 pagesBio Labapi-3730385100% (9)
- Support and Movement Notes PDFDocument26 pagesSupport and Movement Notes PDFmark njeru ngigi88% (8)
- Type of Plant Adaptation Explanation: A) Submerged PlantsDocument2 pagesType of Plant Adaptation Explanation: A) Submerged PlantsReen1996No ratings yet
- 2.3 Support in PlantsDocument17 pages2.3 Support in PlantsMichelle ChinNo ratings yet
- Support in Aquatic PlantsDocument11 pagesSupport in Aquatic PlantsnewdirextionNo ratings yet
- Support and MovementsDocument44 pagesSupport and MovementsSohaib MalikNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation in PlantsDocument21 pagesCell Organisation in PlantsRajananthini PushpanathanNo ratings yet
- Support and MovementDocument96 pagesSupport and Movementmercynjesh20100% (2)
- PLANTDocument23 pagesPLANTAngelito HalmainNo ratings yet
- Ch35 PlantStructure&GrowthDocument5 pagesCh35 PlantStructure&GrowthCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- PLANT TISSUE AND SEC GROWTH For 9 11Document6 pagesPLANT TISSUE AND SEC GROWTH For 9 11Khushbu PandyaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Document79 pagesGen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Samantha AcostaNo ratings yet
- FBS 221 Lab - Edited With QuestionsDocument10 pagesFBS 221 Lab - Edited With QuestionsashleyNo ratings yet
- Botany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument47 pagesBotany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisManar AnwerNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology Classification of PlantsDocument28 pagesPlant Biology Classification of PlantsAhmet OnaltNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About The Part of A PlantDocument51 pagesThis Article Is About The Part of A PlantTess TubieronNo ratings yet
- k12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsDocument3 pagesk12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsJohn Matthew Jobo100% (1)
- Parts of A Plant and Its Functions: Jason L. Cabrigas BAT - 4Document6 pagesParts of A Plant and Its Functions: Jason L. Cabrigas BAT - 4Chona Janiola CastuloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneApostolos KoutsaftisNo ratings yet
- Plant BiologyDocument58 pagesPlant Biologypriyankalikhitha1183No ratings yet
- Describe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueIshaHenryNo ratings yet
- Vascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraDocument22 pagesVascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraGeorgia VasanthaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues 2Document43 pagesPlant Tissues 2Francis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 pagesTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- SAT 2 Biology - PlantsDocument22 pagesSAT 2 Biology - PlantsMido MidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Document9 pagesLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramNo ratings yet
- PRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4Document26 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Meristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and TissuesDocument8 pagesMeristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and Tissuessandy waskitoNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Chapters2Document60 pagesPlant Physiology Chapters2Mahad Ahmed HilowleNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue ARDocument34 pagesPlant Tissue ARAnna Grace Lobigas RanocoNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Document42 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Marcus LeeNo ratings yet
- PLANTYDocument27 pagesPLANTYbry uyNo ratings yet
- Reading Guide Answers PlantsDocument9 pagesReading Guide Answers PlantsNirmal PatelNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Typical Plant BodyDocument4 pagesTissues and Typical Plant BodyKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument6 pagesRevisionStefani KavangoNo ratings yet
- Botny TissuesDocument3 pagesBotny TissuesSamantha AbelloNo ratings yet
- The Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemDocument11 pagesThe Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemClarissa CuñaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues PDFDocument12 pagesPlant Tissues PDFenhlemsane945No ratings yet
- About Presentation Flower GrowthDocument2 pagesAbout Presentation Flower GrowthMedinaNo ratings yet
- Biozone 2 PG 342Document3 pagesBiozone 2 PG 342Ji-Soo KimNo ratings yet
- Lesson Overview: 23.3 StemsDocument29 pagesLesson Overview: 23.3 Stemslayan essamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document11 pagesChapter 8sheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyDocument11 pagesDokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyAin SufizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Biology - DynessDocument45 pagesBiology - DynessmalikachinyantaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- KELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Document3 pagesKELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Dewi Sekar MiasihNo ratings yet
- Bot 121Document12 pagesBot 121eirrehs ellaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of PlantsDocument21 pagesParts and Functions of PlantsRaz QuipedNo ratings yet
- Botany MidtermsDocument16 pagesBotany MidtermsAnisa AzisNo ratings yet
- The Primary and Secondary Growth of PlantDocument31 pagesThe Primary and Secondary Growth of PlantNOFAIZAH RAMLINo ratings yet
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document24 pages06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- 8 June Support and Transport Systems in PlantsDocument25 pages8 June Support and Transport Systems in Plantsmaduanekabelo08No ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 5 NotesDocument20 pagesBio Form 5 NotesNithyamathi KalimuthuNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet