Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Tramadol
Drug Study Tramadol
Uploaded by
Kersey Adricula Ricalde0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views2 pagesDRUG NAME
DOSAGE & ROUTE
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS/ ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
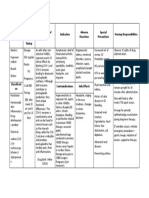
Ketorolac
30mg/amp1 amp IM
Toradol CLASSIFICATI ON: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents, nonopioid analagesics
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing peripherally mediated analgesia - Also has antipyretic and antiinflammatory properties. - Therapeutic effect:Decreased pain
Short term management of pain (not to exceed 5 days total for all routes combined
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDRUG NAME
DOSAGE & ROUTE
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS/ ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
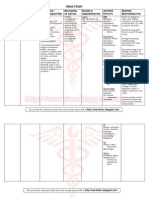
Ketorolac
30mg/amp1 amp IM
Toradol CLASSIFICATI ON: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents, nonopioid analagesics
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing peripherally mediated analgesia - Also has antipyretic and antiinflammatory properties. - Therapeutic effect:Decreased pain
Short term management of pain (not to exceed 5 days total for all routes combined
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views2 pagesDrug Study Tramadol
Drug Study Tramadol
Uploaded by
Kersey Adricula RicaldeDRUG NAME
DOSAGE & ROUTE
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS/ ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
Ketorolac
30mg/amp1 amp IM
Toradol CLASSIFICATI ON: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents, nonopioid analagesics
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing peripherally mediated analgesia - Also has antipyretic and antiinflammatory properties. - Therapeutic effect:Decreased pain
Short term management of pain (not to exceed 5 days total for all routes combined
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
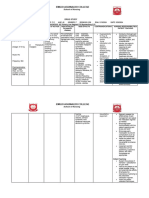
DRUG NAME DOSAGE & MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS/ NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
ROUTE ADVERSE REACTIONS
30mg/amp1 Inhibits Hypersensitivity CNS:drowsiness Patients who have asthma,
prostaglandin Short term - Cross-sensitivity abnormal thinking, aspirin-induced allergy, and
Ketorolac amp IM management of
synthesis, producing with other NSAIDs dizziness, euphoria, nasal polyps are at increased
peripherally pain (not to may exist¨Pre- or headache- risk for developing
mediated analgesia exceed 5 days perioperative use - RESP:asthma hypersensitivity reactions.
Toradol - Also has total for all - Known alcohol ,dyspnea Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and
antipyretic and anti- routes intoleranceUse - CV: urticaria.
inflammatory combined) cautiously in: edema - Assess pain (note type,
CLASSIFICATI properties. 1) History of GI pallor location, and intensity) prior to
ON: - Therapeutic bleeding vasodilation and 1-2 hr following
Nonsteroidal anti-
effect:Decreased 2) Renal impair- - GI: administration.
inflammatory
pain ment (dosage 1) GI Bleeding - Ketorolac therapy should
agents, nonopioid
reduction may be 2) abnormal taste always be given initially by the
analagesics
required) 3) diarrhea IM or IV route. Oral therapy
3) Cardiovascular 4) dry mouth should be used only as a
disease 5) dyspepsia continuation of parenteral
6) GI pain therapy.
7) nausea - Caution patient to avoid
GU: concurrent use of alcohol,
1) oliguria aspirin, NSAIDs,
2) renal toxicity acetaminophen, or other OTC
3) urinary medications without consulting
frequency health care professional.
- DERM: - Advise patient to consult if
1) pruritis rash, itching, visual
2) purpura disturbances, tinnitus, weight
3) sweating gain, edema, black stools,
4) urticaria persistent headche, or
- HEMAT: influenza-like syndromes
1) prolonged (chills,fever,muscles aches,
bleeding time pain) occur.
- LOCAL: - Effectiveness of therapy can
1) injection site be demonstrated by decrease
pain in severity of pain. Patients
- NEURO: who do not respond to one
1) paresthesia NSAIDs may respond to
- MISC: another.
1) allergic reaction,
anaphylaxis
You might also like
- Sparks Taylors Nursing Diagnosis Reference Manual 10th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesSparks Taylors Nursing Diagnosis Reference Manual 10th Edition Ebook PDFzelma.bennett128100% (42)
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument1 pageKetorolac Drug StudyRose100% (1)
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKetorolac Drug StudyIvan Liquiran Avenado71% (17)
- Oxford Handbook of Cardiac Nursing (PDFDrive) PDFDocument422 pagesOxford Handbook of Cardiac Nursing (PDFDrive) PDFvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKetorolac Drug StudyA.No ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument6 pagesName of DrugGail Leslie HernandezNo ratings yet
- Kedren Drug StudyDocument14 pagesKedren Drug StudyKedren Kent JawoodNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledALYSSA MARIE MATANo ratings yet
- Kedren Drug StudyDocument14 pagesKedren Drug StudyKedren Kent JawoodNo ratings yet
- Whole Case1 DoneDocument5 pagesWhole Case1 Donejovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug Study FormKuro Mufu100% (2)
- Mefenamic Acid Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug Study Form2C- VILLACARLOS, LEONA ROSE M.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyAmsh RosalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyEden Astred ObilloNo ratings yet
- DS KetorolacDocument3 pagesDS Ketorolackailu08No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Drug Studymarvinsanantonio0612No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudymaxynezolayvarNo ratings yet
- IX. Drug StudyDocument4 pagesIX. Drug StudykingpinNo ratings yet
- Pain and Palliative - Topic DiscussionDocument7 pagesPain and Palliative - Topic Discussionapi-535001113No ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Cotrimoxazole, AllopurinolDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Cotrimoxazole, Allopurinolpaupaulala89% (9)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamceian23No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJIESEL ACEBEDONo ratings yet
- Amiodarone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAmiodarone Drug StudyDexter Niel Ortilano CPAC-SNNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification and Mode of Action Adverse Effects/precautions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Classification and Mode of Action Adverse Effects/precautions Nursing ConsiderationsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument2 pagesAspirinBARRISTERFLOWERSEAURCHIN6No ratings yet
- Amh Summary 2019 İn One FileDocument220 pagesAmh Summary 2019 İn One FileTatenda BrunoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- Make A Drug Study On The Medications Given To JaneDocument2 pagesMake A Drug Study On The Medications Given To JaneYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Endo (Part 1) - 1Document12 pagesLec 4 Endo (Part 1) - 1Mohamed NabilNo ratings yet
- DrugstudyDocument2 pagesDrugstudyacissej_o3No ratings yet
- Balanced AnalgesicDocument37 pagesBalanced AnalgesicGia Bảo Thụy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- NCMB317: RupturedDocument12 pagesNCMB317: RupturedArmand Bong Santiago100% (1)
- Drug Study Hernandez 2nd SemDocument3 pagesDrug Study Hernandez 2nd SemhernandezmarianneroseNo ratings yet
- Bonilla Drug Study 2 20Document9 pagesBonilla Drug Study 2 20YLA KATRINA BONILLANo ratings yet
- Drug Study For SLEDocument28 pagesDrug Study For SLERomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessMaricon BautistaNo ratings yet
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyKarl Lourenz Deysolong100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY - AnticonvulsantsDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - AnticonvulsantsZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Case Study - Pre-Eclampsia Drugs:: Calcium Iron 2 Doses of Tetanus ToxoidDocument9 pagesWeek 3: Case Study - Pre-Eclampsia Drugs:: Calcium Iron 2 Doses of Tetanus ToxoidLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studytalia hamedNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument2 pagesDrug Study FinalFrancesca Marie CapawanNo ratings yet
- For MaDocument9 pagesFor MaKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco Logy Imm Une Syste M Drugs: Julia Leonor Huaringa Lagomarsino, RN February 13, 2009Document12 pagesPharmaco Logy Imm Une Syste M Drugs: Julia Leonor Huaringa Lagomarsino, RN February 13, 2009julialeoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drugs Actions Indications Contraindicatio NS Side/Adverse Effect Nsg. Responsibilities CelecoxibDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Drugs Actions Indications Contraindicatio NS Side/Adverse Effect Nsg. Responsibilities CelecoxibBella Nikki Tagaban PasianNo ratings yet
- Specific ActionDocument3 pagesSpecific Actionmoritashinobu2011No ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Ibuprofenanon-326479No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument5 pagesParacetamol Drug StudyMatty Jolbitado50% (2)
- Generic:: Drug Study #1Document1 pageGeneric:: Drug Study #1Patricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Ceria Dorena Fe SeteraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IMDocument2 pagesDrug Study IMAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy ForcasestudyDocument22 pagesDrugstudy ForcasestudyRovic Selga TrisinioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyAda Eloisa AloveraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Pen G FuroDocument3 pagesDrug Study Pen G Furokuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Therapeutic: Contraindicated In: CNS: Seizures, Drug-To-DrugDocument6 pagesTramadol Therapeutic: Contraindicated In: CNS: Seizures, Drug-To-DrugApril nicolNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoDocument4 pagesDrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Analgesia and Anesthesia for the Ill or Injured Dog and CatFrom EverandAnalgesia and Anesthesia for the Ill or Injured Dog and CatNo ratings yet
- Methods of Data CollectionDocument30 pagesMethods of Data CollectionKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Eastern Laguna Medical Hospital: Antimicrobial Stewardship CommitteeDocument2 pagesEastern Laguna Medical Hospital: Antimicrobial Stewardship CommitteeKersey Adricula Ricalde100% (1)
- Study Protocol of A Quasi-Experimental DesignDocument17 pagesStudy Protocol of A Quasi-Experimental DesignKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain Post Op CSDocument3 pagesNCP Pain Post Op CSKersey Adricula Ricalde100% (1)
- Postpartum ExercisesDocument4 pagesPostpartum ExercisesKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- DyphenhadramineDocument1 pageDyphenhadramineKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Los Art AnDocument2 pagesLos Art AnKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- 10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateDocument2 pages10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateamitNo ratings yet
- Herbal Plants in Western MedicineDocument31 pagesHerbal Plants in Western MedicineAyZee RanjitNo ratings yet
- NURS185 Assessment 6Document3 pagesNURS185 Assessment 6no oneNo ratings yet
- MCQs 1 30Document5 pagesMCQs 1 30Qing Liang OngNo ratings yet
- Killer Whales (Orcas) That Died in Captivity by LocationDocument8 pagesKiller Whales (Orcas) That Died in Captivity by LocationThe Orca Project CorpNo ratings yet
- Taylor Study GuideDocument10 pagesTaylor Study GuideAngella sseruwagi100% (1)
- 3 s2.0 B9780323555128001769 Main PDFDocument65 pages3 s2.0 B9780323555128001769 Main PDFAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- NCD Risk Assessment FormDocument1 pageNCD Risk Assessment Formruiza corcino100% (4)
- EBM of DyspepsiaDocument228 pagesEBM of DyspepsiaxcalibursysNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PsychopharmacologyDocument99 pagesLecture 3 PsychopharmacologyPavan chowdaryNo ratings yet
- sg8.08 Reporting of AccidentsDocument4 pagessg8.08 Reporting of AccidentsMIKE HarwoodNo ratings yet
- Listening 2 SedefDocument9 pagesListening 2 SedefBal EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Jepbn 2023Document16 pagesJepbn 2023sarmin05012008No ratings yet
- Costochondritis - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment - by Owen Jones - MediumDocument1 pageCostochondritis - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment - by Owen Jones - MediumkamrevariNo ratings yet
- New Ishihara Color Plates - Set 38 PDFDocument13 pagesNew Ishihara Color Plates - Set 38 PDFSukarnoNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Assisting Sitz Bath: Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegesDocument2 pagesProcedure Checklist Assisting Sitz Bath: Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegesElaine Frances IlloNo ratings yet
- Plasmasthetics Plasma Pen TreatmentDocument3 pagesPlasmasthetics Plasma Pen Treatmentlovrata4550No ratings yet
- Lesson Plans k6Document13 pagesLesson Plans k6Regine Delfin AclaracionNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy (CP) : DR Raj Kumar Yadav Assist. Prof., PMR MBBS VI Sem. - 25/04/2019Document38 pagesCerebral Palsy (CP) : DR Raj Kumar Yadav Assist. Prof., PMR MBBS VI Sem. - 25/04/2019Anjali GuptaNo ratings yet
- Eczema: Pathogenesis. Atopic Dermatitis Depends On A Complex Interaction BetweenDocument5 pagesEczema: Pathogenesis. Atopic Dermatitis Depends On A Complex Interaction BetweenSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Clinical PresentationDocument10 pagesMeningitis Clinical PresentationAniwat NillakarnNo ratings yet
- DEPERSONALIZATIONDocument4 pagesDEPERSONALIZATION2100428No ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests InterpretationDocument12 pagesLaboratory Tests InterpretationKaloy Kamao100% (1)
- Sts Gene TherapyDocument2 pagesSts Gene TherapyDuane OrejolaNo ratings yet
- JANIACSADI-Myasthenic Crisis Guidelines For Prevention and Treatment-Journal of The Neurological Sciences-2007 - 2Document7 pagesJANIACSADI-Myasthenic Crisis Guidelines For Prevention and Treatment-Journal of The Neurological Sciences-2007 - 2Inbar Surya SeruNo ratings yet
- Compatibility TestingDocument45 pagesCompatibility TestingkatieNo ratings yet
- Massive HemorrhageDocument17 pagesMassive HemorrhageShannen Madrid Tindugan100% (1)
- 7 1 Breast EngorgementDocument10 pages7 1 Breast EngorgementSreyasri GhoshNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Special LearnersDocument50 pagesCharacteristics of Special LearnersMary Ann Rodil ManaloNo ratings yet