Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theory of Constructivism
Theory of Constructivism
Uploaded by
Mohamad Tarmizi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesConstructivism proposes that children learn through generating meaning from their own experiences, and the teacher's role is to help connect new concepts to what students already know. Key principles of constructivism include that children view the world through established beliefs that filter new information, and challenging a child's beliefs requires effort as they are emotionally attached to their views. Constructivist classrooms encourage discussion, knowledge is viewed as dynamic and changing with experiences, and assessment considers students' work, observations, and perspectives in addition to testing.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConstructivism proposes that children learn through generating meaning from their own experiences, and the teacher's role is to help connect new concepts to what students already know. Key principles of constructivism include that children view the world through established beliefs that filter new information, and challenging a child's beliefs requires effort as they are emotionally attached to their views. Constructivist classrooms encourage discussion, knowledge is viewed as dynamic and changing with experiences, and assessment considers students' work, observations, and perspectives in addition to testing.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesTheory of Constructivism
Theory of Constructivism
Uploaded by
Mohamad TarmiziConstructivism proposes that children learn through generating meaning from their own experiences, and the teacher's role is to help connect new concepts to what students already know. Key principles of constructivism include that children view the world through established beliefs that filter new information, and challenging a child's beliefs requires effort as they are emotionally attached to their views. Constructivist classrooms encourage discussion, knowledge is viewed as dynamic and changing with experiences, and assessment considers students' work, observations, and perspectives in addition to testing.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
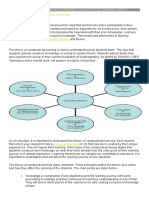
Theory of Constructivism
Constructivism proposes that all children learn as a result of their personal
generation of meaning from experiences. The fundamental role of a teacher is to
help children generate connections between what is to be learned and what the
children already know or believe.
Principles that make up Theory of Constructivism:
• Children come into classroom with an established world-view, formed by
years of prior experience and learning.
• Even as it evolves, a child’s world-view filters all experiences and affects
their interpretation of observations.
• Children are emotionally attached to their world-view and will not give up
their world-view easily.
• Challenging, revising and restructuring one’s world-view requires much
effort.
Constructivist Class
• Teachers have discuss with their students and help them construct their
own knowledge.
• Teacher’s role is interactive, rooted in negotiation
• Knowledge is seen as dynamic, ever changing with experiences
• Students work primarily in groups
• Assessment includes students’ works, observation, and points of view, as
well testing. Process is as important as product
Constructivism is a synthesis of methods by psychologist, philosophers and
educationist. The important contributions include development of schemata and
cognitive learning process by Piaget, discovery learning by Bruner, formation of
meaningful mental structures by Ausubel and emphasis on learning domain by
Gagne. Factors that affect how well a child learns science and what types of
science experiences should occur in the classroom.
You might also like
- Constructivist Learning TheoryDocument6 pagesConstructivist Learning TheoryFrancis Dave Nagum Mabborang II75% (4)
- K To 12 Pedagogical ApproachesDocument109 pagesK To 12 Pedagogical ApproachesDianne Permejo del Prado100% (3)
- LESSON 2 Learning Theories and Their Impact To EPP TeachingDocument9 pagesLESSON 2 Learning Theories and Their Impact To EPP Teachingjonah faye mabanglo92% (26)
- ConstructivismDocument24 pagesConstructivismgiancarloguiananislerNo ratings yet
- Constructivist ApproachDocument21 pagesConstructivist ApproachDaffodils100% (2)
- Math 116 PDFDocument6 pagesMath 116 PDFPELAEZ, JOANNA MAY L.No ratings yet
- Constructivism 1Document27 pagesConstructivism 1Critical ViewNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCTIVISM Report Aubrey AnnEdang Ronnie EllanicDocument33 pagesCONSTRUCTIVISM Report Aubrey AnnEdang Ronnie EllanicPatrick anthony ValesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-Constructivist-Theory-In-Teaching-Social-StudiesDocument34 pagesLesson 4-Constructivist-Theory-In-Teaching-Social-StudiesAdrian Jay JavierNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning - Module 14 Constructivism 1dfDocument31 pagesFacilitating Learning - Module 14 Constructivism 1dfMaureen Mae Estanol100% (4)
- PPT3 Constructivist Theory in Teaching Social StudiesDocument34 pagesPPT3 Constructivist Theory in Teaching Social StudiesJocelyn Caleza100% (1)
- Constructivism-Theory-In-Teaching-Science - Group-2 Flaviano General Obispo Gonzales AbivaDocument26 pagesConstructivism-Theory-In-Teaching-Science - Group-2 Flaviano General Obispo Gonzales Abivadavevince511No ratings yet
- 1.3.5 Constructivist Theory of LearningDocument18 pages1.3.5 Constructivist Theory of LearningMohamad NasirNo ratings yet
- ConstrutivismDocument22 pagesConstrutivismJohn Michael Padilla Romero100% (1)
- Constructivism in Science EducationDocument10 pagesConstructivism in Science EducationJayaraju BattulaNo ratings yet
- Technology in Constructivist Learning EnvironmentDocument26 pagesTechnology in Constructivist Learning EnvironmentAbegail Ebio TodioNo ratings yet
- Cooperative and Experiential LearningDocument46 pagesCooperative and Experiential LearningCedie MercadoNo ratings yet
- Reference Material Module 1 PPT Slide 64 To 97Document34 pagesReference Material Module 1 PPT Slide 64 To 97Sunshine BorerNo ratings yet
- (EDES113) : An Introduction To The Study of EducationDocument21 pages(EDES113) : An Introduction To The Study of EducationAfika NtandaNo ratings yet
- En - Wikipedia.org Wiki Constructivist Teaching Methods PDFDocument9 pagesEn - Wikipedia.org Wiki Constructivist Teaching Methods PDFbersam05100% (1)
- Construcitivist NeedhamDocument15 pagesConstrucitivist NeedhamAmirah HusnaNo ratings yet
- SCI 102 ConstructivismDocument43 pagesSCI 102 ConstructivismAGNES TUBOLA100% (1)
- Constructivism & CceDocument11 pagesConstructivism & CceamanNo ratings yet
- Educ 402 Report (Constructivism)Document23 pagesEduc 402 Report (Constructivism)Jenz Aria VillaNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument16 pagesConstructivismKhoiruddin Bashori50% (2)
- Facilitating Learning - Module 14 ConstructivismDocument33 pagesFacilitating Learning - Module 14 ConstructivismMaureen Mae Estanol88% (8)
- Theory of ConstructivismDocument28 pagesTheory of Constructivismzahabia k.bNo ratings yet
- Karthik 160720194603Document16 pagesKarthik 160720194603Nur islamiyahNo ratings yet
- Theory of ConstructivismDocument10 pagesTheory of ConstructivismBulan Ialah KamarulNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument13 pagesConstructivismIntan Syafina RosliNo ratings yet
- Theory of Constructivism 2Document6 pagesTheory of Constructivism 2Zivia LingNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument31 pagesConstructivismKawie MaxKawie100% (1)
- CONSTRUCTIVISMDocument32 pagesCONSTRUCTIVISMNur Naiemah Mohd Ibrahim100% (1)
- Technology in A Constructivist EnvironmentDocument19 pagesTechnology in A Constructivist EnvironmentRyanBaileNo ratings yet
- Good Evening: Integrative Teaching StrategiesDocument44 pagesGood Evening: Integrative Teaching StrategiesNick YanezNo ratings yet
- What Is ConstructivismDocument4 pagesWhat Is Constructivismapi-254210572No ratings yet
- Constructivism: Piaget Vygotsky GagneDocument7 pagesConstructivism: Piaget Vygotsky GagneLeoben GalimaNo ratings yet
- Constructivist Model of Working Together: The Advantages & Disadvantages of Constructivism in The ClassroomDocument11 pagesConstructivist Model of Working Together: The Advantages & Disadvantages of Constructivism in The Classroomria medialdiaNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories of Constructivism AND Cognitive Constructivism by Jean PiagetDocument17 pagesLearning Theories of Constructivism AND Cognitive Constructivism by Jean PiagetPatrizzia Ann Rose OcbinaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Prof Ed)Document8 pagesReviewer (Prof Ed)Jan Roldan GiducosNo ratings yet
- Constructivism As A Paradigm For Teaching and LearningDocument13 pagesConstructivism As A Paradigm For Teaching and LearningAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument31 pagesConstructivismLaila SyedNo ratings yet
- Curriculum - 20231113 185900 0000Document38 pagesCurriculum - 20231113 185900 0000SCIENCE Benjie AvecillaNo ratings yet
- Constructivism and Socio-Constructivism TEACHING 1: Fall 2022 3 WeekDocument25 pagesConstructivism and Socio-Constructivism TEACHING 1: Fall 2022 3 WeekhibaNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument44 pagesConstructivismlaguerta.mk2002No ratings yet
- Constructive Learning Design: Submitted To: Submitted By: Prachi Shukla B.A.B.Ed., 6 SemesterDocument13 pagesConstructive Learning Design: Submitted To: Submitted By: Prachi Shukla B.A.B.Ed., 6 SemesterParag ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Constructivism: Philosophical Foundation of EducationDocument11 pagesConstructivism: Philosophical Foundation of EducationVinella SantosNo ratings yet
- Tuto 3Document6 pagesTuto 3Siti Noor WahidaNo ratings yet
- ConstructivistDocument6 pagesConstructivistJeffrey DreoNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument20 pagesConstructivismClarissa HugasanNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument23 pagesConstructivismJennifer Jorge AquinoNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument17 pagesConstructivismWhella LazatinNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of EdDocument17 pagesPhilosophy of EdsikuetNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument17 pagesConstructivismGerry Mae TejaresNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Unit III April 16 Ppt1Document43 pagesWeek 6 Unit III April 16 Ppt1Narayan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- U2 A2 Overview of Learning Theories ReadingDocument3 pagesU2 A2 Overview of Learning Theories ReadingHạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Republic Act No. 10533Document5 pagesObjectives: Republic Act No. 10533JERIC A. REBULLOSNo ratings yet
- Learning and TeachingDocument26 pagesLearning and TeachingkhaledNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Socio Cultural and Behavioral Learning TheoriesDocument93 pagesCognitive Socio Cultural and Behavioral Learning TheoriesAngelica OlivarNo ratings yet