Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 - Additional - Definitions
Chapter 9 - Additional - Definitions
Uploaded by
Eliane Abou FaycalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Network HardwareDocument2 pagesNetwork HardwareChloe Madisyn DowneyNo ratings yet
- Network Commu DevicesDocument17 pagesNetwork Commu Deviceskudikala kalabharathiNo ratings yet
- Computer Network DevicesDocument8 pagesComputer Network DevicesDIONARRA DRUMMONDNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument5 pagesNetwork Devicesmitalee2502No ratings yet
- What Is A Network?Document9 pagesWhat Is A Network?amrit singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Network Hardware: LO 2:-Install and Configure Internet and ServicesDocument2 pagesNetwork Hardware: LO 2:-Install and Configure Internet and ServicesIsrael KifleNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document13 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12om100% (3)
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document14 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12Mohit HoodaNo ratings yet
- Lesson I - Network TopologyDocument32 pagesLesson I - Network Topologybrian estriNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument15 pagesNetwork DevicesShilpa PutanikarNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: Open SystemDocument6 pagesComputer Networking: Open SystemMd. AkramNo ratings yet
- Data Communication NewDocument15 pagesData Communication NewAagam JainNo ratings yet
- CN Lab2 102117105Document9 pagesCN Lab2 102117105kavya aggarwalNo ratings yet
- XII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesDocument30 pagesXII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesLakshya NayakNo ratings yet
- Router: Hardware Packets Network DropDocument8 pagesRouter: Hardware Packets Network DropDanilo CumpioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 SlidesDocument17 pagesLecture 2 SlidesAghaNo ratings yet
- Components of Computer Networks: Unit TwoDocument10 pagesComponents of Computer Networks: Unit Twosahan instituteNo ratings yet
- Netwrk DDocument11 pagesNetwrk Dcrasto999No ratings yet
- CN Pract-1Document21 pagesCN Pract-1Ur MnNo ratings yet
- DCN LabDocument6 pagesDCN LabBalaram Pratap KotyadaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Computer Networks and InternetDocument24 pagesIntroduction of Computer Networks and InternetChristy RagayNo ratings yet
- ST Anselm.'S SR Sec School, AjmerDocument9 pagesST Anselm.'S SR Sec School, Ajmermaanvendra singh rajawatNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology NetworkDocument62 pagesU3 Communication Technology NetworksurnewardsNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology A LevelDocument59 pagesU3 Communication Technology A LevelsurnewardsNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology Network A LevelDocument42 pagesU3 Communication Technology Network A LevelsurnewardsNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument9 pagesComputer NetworkNirmanyu SoodNo ratings yet
- DCCNDocument8 pagesDCCNHarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- 2 NetworkingDocument16 pages2 Networkinggiocel mercadoNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument2 pagesNetworkingAishwarya PradhanNo ratings yet
- Communication DevicesDocument16 pagesCommunication Devicesrajender564No ratings yet
- Hardware Componenets of NetworkDocument13 pagesHardware Componenets of NetworkZain AlyNo ratings yet
- 3 - Unit5 - Network DevicesDocument6 pages3 - Unit5 - Network DevicesShaunak SardesaiNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Module 1Document19 pagesComputer Networks Module 1scribdNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueDocument6 pagesNetwork Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueAbygayle IveyNo ratings yet
- Sharing Files, Data, and Information. in A NetworkDocument17 pagesSharing Files, Data, and Information. in A NetworkBharatNo ratings yet
- Web Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesDocument14 pagesWeb Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesNaina Kanojia91% (11)
- Network Devices: Repeater, Router, GatewayDocument11 pagesNetwork Devices: Repeater, Router, GatewayNikhilNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument28 pagesNetwork DevicesAdesh MahadaneNo ratings yet
- Practical:-1: AIM:-Study of Different Network Devices in Detail. HUBDocument3 pagesPractical:-1: AIM:-Study of Different Network Devices in Detail. HUBJencyShah 2045No ratings yet
- ICT Fundamentals ReportDocument49 pagesICT Fundamentals ReportJigs OlbesNo ratings yet
- Hardware Componenets of NetworkDocument13 pagesHardware Componenets of NetworkZain AlyNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document6 pagesLec 6kashyapmanas300No ratings yet
- Network Devices - TutorialspointDocument6 pagesNetwork Devices - TutorialspointThusharika ThilakaratneNo ratings yet
- Network Topology DevicesDocument33 pagesNetwork Topology DeviceshellomeranaamNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument20 pagesComputer NetworkyjnNo ratings yet
- Networking CSS 12Document11 pagesNetworking CSS 12Irene DausNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks KCDocument14 pagesComputer Networks KCKC ROCKNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab 1Document6 pagesComputer Networks Lab 1Haseeb Ur Rehman0% (1)
- Chapter 4-Network Layer: 4.1. Internetworking DevicesDocument26 pagesChapter 4-Network Layer: 4.1. Internetworking Devicesalish shrsethaNo ratings yet
- Netcom DA1 Vedant Kumar Khetan 20BCE0503Document40 pagesNetcom DA1 Vedant Kumar Khetan 20BCE0503Vedant KhetanNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Devices: Network Interface Card (NIC)Document9 pagesComputer Networking Devices: Network Interface Card (NIC)Kelvin KujoNo ratings yet
- Computer Network ComponentsDocument3 pagesComputer Network ComponentsRafayetNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument9 pagesNetwork DevicesMuse MohamedNo ratings yet
- Practical 10 IisDocument3 pagesPractical 10 IisKrishna FadaduNo ratings yet
- Mr. Nayneesh MishraDocument12 pagesMr. Nayneesh MishraPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESDocument73 pagesSection 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESgabriellestewart334No ratings yet
- Basic Computer Network PDFDocument35 pagesBasic Computer Network PDFTep TepNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNDocument6 pagesLab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNIqraJahanNo ratings yet
- CNC ExperimentDocument33 pagesCNC ExperimentNikita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
Chapter 9 - Additional - Definitions
Chapter 9 - Additional - Definitions
Uploaded by
Eliane Abou FaycalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9 - Additional - Definitions
Chapter 9 - Additional - Definitions
Uploaded by
Eliane Abou FaycalCopyright:
Available Formats
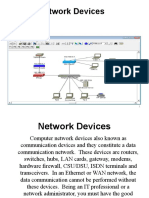
Chapter 9 – Additional Definitions
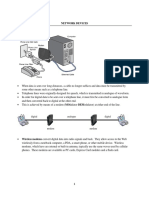
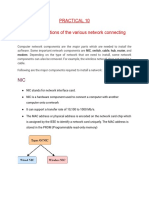
Network interface Card
Often abbreviated as NIC, an expansion board you insert into a computer so the computer
can be connected to a network. The card will handle sending, receiving and error
checking of transmitted data. Most NICs are designed for a particular type of network
although some can serve multiple networks.
Hub
A hub is used in a wired network to connect Ethernet cables from a number of devices
together. The hub allows each device to talk to the others. (Hubs aren't used in networks
with only wireless connections, since network devices such as routers and adapters
communicate directly with one another, with nothing in between.)
Hubs are such simple devices — they require no configuration, and have no manuals —
that their function is now included in other devices such as routers and modems.
Switch
A type of new routing that determines from the IP address sent with the data message
which output port to use for the next part of its trip to the intended destination. Although
the technology is new, it appears to be considerably faster than older router techniques.
Bridge
A device that connects similar networks and due to its hardware/software combination
recognizes the messages on the network and passes on those addressed to nodes in other
networks.
Gateway
A node on a network that serves as an entrance to another dissimilar network.
Technically a gateway converts signals from one network to signals understood by
the other dissimilar network. The gateway is associated with both a router, which use
headers and forwarding tables to determine where packets are sent, and a switch,
which provides the actual path for the packet in and out of the gateway.
Router
A device that forwards data messages along networks. A router is connected to at least
two networks, commonly two LANs or WANs or a LAN and its ISP’s network. Routers
use headers and forwarding tables to determine the best path for forwarding the
messages, and they communicate with each other and configure the best route between
any two hosts.
You might also like
- Network HardwareDocument2 pagesNetwork HardwareChloe Madisyn DowneyNo ratings yet
- Network Commu DevicesDocument17 pagesNetwork Commu Deviceskudikala kalabharathiNo ratings yet
- Computer Network DevicesDocument8 pagesComputer Network DevicesDIONARRA DRUMMONDNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument5 pagesNetwork Devicesmitalee2502No ratings yet
- What Is A Network?Document9 pagesWhat Is A Network?amrit singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Network Hardware: LO 2:-Install and Configure Internet and ServicesDocument2 pagesNetwork Hardware: LO 2:-Install and Configure Internet and ServicesIsrael KifleNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document13 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12om100% (3)
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document14 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12Mohit HoodaNo ratings yet
- Lesson I - Network TopologyDocument32 pagesLesson I - Network Topologybrian estriNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument15 pagesNetwork DevicesShilpa PutanikarNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: Open SystemDocument6 pagesComputer Networking: Open SystemMd. AkramNo ratings yet
- Data Communication NewDocument15 pagesData Communication NewAagam JainNo ratings yet
- CN Lab2 102117105Document9 pagesCN Lab2 102117105kavya aggarwalNo ratings yet
- XII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesDocument30 pagesXII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesLakshya NayakNo ratings yet
- Router: Hardware Packets Network DropDocument8 pagesRouter: Hardware Packets Network DropDanilo CumpioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 SlidesDocument17 pagesLecture 2 SlidesAghaNo ratings yet
- Components of Computer Networks: Unit TwoDocument10 pagesComponents of Computer Networks: Unit Twosahan instituteNo ratings yet
- Netwrk DDocument11 pagesNetwrk Dcrasto999No ratings yet
- CN Pract-1Document21 pagesCN Pract-1Ur MnNo ratings yet
- DCN LabDocument6 pagesDCN LabBalaram Pratap KotyadaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Computer Networks and InternetDocument24 pagesIntroduction of Computer Networks and InternetChristy RagayNo ratings yet
- ST Anselm.'S SR Sec School, AjmerDocument9 pagesST Anselm.'S SR Sec School, Ajmermaanvendra singh rajawatNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology NetworkDocument62 pagesU3 Communication Technology NetworksurnewardsNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology A LevelDocument59 pagesU3 Communication Technology A LevelsurnewardsNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology Network A LevelDocument42 pagesU3 Communication Technology Network A LevelsurnewardsNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument9 pagesComputer NetworkNirmanyu SoodNo ratings yet
- DCCNDocument8 pagesDCCNHarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- 2 NetworkingDocument16 pages2 Networkinggiocel mercadoNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument2 pagesNetworkingAishwarya PradhanNo ratings yet
- Communication DevicesDocument16 pagesCommunication Devicesrajender564No ratings yet
- Hardware Componenets of NetworkDocument13 pagesHardware Componenets of NetworkZain AlyNo ratings yet
- 3 - Unit5 - Network DevicesDocument6 pages3 - Unit5 - Network DevicesShaunak SardesaiNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Module 1Document19 pagesComputer Networks Module 1scribdNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueDocument6 pagesNetwork Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueAbygayle IveyNo ratings yet
- Sharing Files, Data, and Information. in A NetworkDocument17 pagesSharing Files, Data, and Information. in A NetworkBharatNo ratings yet
- Web Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesDocument14 pagesWeb Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesNaina Kanojia91% (11)
- Network Devices: Repeater, Router, GatewayDocument11 pagesNetwork Devices: Repeater, Router, GatewayNikhilNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument28 pagesNetwork DevicesAdesh MahadaneNo ratings yet
- Practical:-1: AIM:-Study of Different Network Devices in Detail. HUBDocument3 pagesPractical:-1: AIM:-Study of Different Network Devices in Detail. HUBJencyShah 2045No ratings yet
- ICT Fundamentals ReportDocument49 pagesICT Fundamentals ReportJigs OlbesNo ratings yet
- Hardware Componenets of NetworkDocument13 pagesHardware Componenets of NetworkZain AlyNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document6 pagesLec 6kashyapmanas300No ratings yet
- Network Devices - TutorialspointDocument6 pagesNetwork Devices - TutorialspointThusharika ThilakaratneNo ratings yet
- Network Topology DevicesDocument33 pagesNetwork Topology DeviceshellomeranaamNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument20 pagesComputer NetworkyjnNo ratings yet
- Networking CSS 12Document11 pagesNetworking CSS 12Irene DausNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks KCDocument14 pagesComputer Networks KCKC ROCKNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab 1Document6 pagesComputer Networks Lab 1Haseeb Ur Rehman0% (1)
- Chapter 4-Network Layer: 4.1. Internetworking DevicesDocument26 pagesChapter 4-Network Layer: 4.1. Internetworking Devicesalish shrsethaNo ratings yet
- Netcom DA1 Vedant Kumar Khetan 20BCE0503Document40 pagesNetcom DA1 Vedant Kumar Khetan 20BCE0503Vedant KhetanNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Devices: Network Interface Card (NIC)Document9 pagesComputer Networking Devices: Network Interface Card (NIC)Kelvin KujoNo ratings yet
- Computer Network ComponentsDocument3 pagesComputer Network ComponentsRafayetNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument9 pagesNetwork DevicesMuse MohamedNo ratings yet
- Practical 10 IisDocument3 pagesPractical 10 IisKrishna FadaduNo ratings yet
- Mr. Nayneesh MishraDocument12 pagesMr. Nayneesh MishraPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESDocument73 pagesSection 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESgabriellestewart334No ratings yet
- Basic Computer Network PDFDocument35 pagesBasic Computer Network PDFTep TepNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNDocument6 pagesLab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNIqraJahanNo ratings yet
- CNC ExperimentDocument33 pagesCNC ExperimentNikita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)