Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EquationsFLM400S Rev
EquationsFLM400S Rev
Uploaded by
Christo Malan LotzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 3Document81 pagesChapter 3Ricky Putra SiregarNo ratings yet
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 pagesFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Aero Basic FormulationDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Aero Basic FormulationNihar SamalNo ratings yet
- Physics 112 Formulae IIIDocument3 pagesPhysics 112 Formulae IIISaied RajehaNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet SPH 4U: DynamicsDocument3 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet SPH 4U: DynamicsNA TbNo ratings yet
- MIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Document15 pagesMIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Gavin BirlaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetMama PigNo ratings yet
- Canal Flow & Pipe Flow (Not Full) : 1. Hydraulic Depth Also Called Hydraulic Radius Different Shape and Sizes For CanalsDocument9 pagesCanal Flow & Pipe Flow (Not Full) : 1. Hydraulic Depth Also Called Hydraulic Radius Different Shape and Sizes For CanalsDLRauties100% (1)
- Formulario+i+parcial - 3Document2 pagesFormulario+i+parcial - 3NicolasNo ratings yet
- Formulario+i+parcial - 3Document2 pagesFormulario+i+parcial - 3NicolasNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasKristine BalansagNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Modern PhysicsDocument1 pageKinematics Modern PhysicsBoldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- Formula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵDocument5 pagesFormula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵPhemi2580No ratings yet
- Physics Grade 12 Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics Grade 12 Formula SheetLauren HongNo ratings yet
- Aa PDFDocument1 pageAa PDFmesfin DemiseNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics I Solution Manual 7 Question 1: Problem P3.158Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics I Solution Manual 7 Question 1: Problem P3.158cartoon_nateNo ratings yet
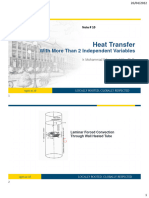
- PT #10 Temperature Profile With More Than One Independent Variables (Kelas A)Document17 pagesPT #10 Temperature Profile With More Than One Independent Variables (Kelas A)MUHAMMAD LUQMAN HAKIMI MOHD ZAMRINo ratings yet
- Formulae Part ThreeDocument5 pagesFormulae Part ThreeShiva SeshasaiNo ratings yet
- Phsi191 Mid Sem 2014Document8 pagesPhsi191 Mid Sem 2014gang gangNo ratings yet
- Useful Aerospace FormulasDocument1 pageUseful Aerospace FormulasRadj90No ratings yet
- Figure 1. Drag Coefficient As A Function of SphericityDocument9 pagesFigure 1. Drag Coefficient As A Function of SphericityPAULA ANDREA CARO BAEZNo ratings yet
- Equationsjhgg 77Document2 pagesEquationsjhgg 77harsh rajNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS & ANSWERS FOR AIEEE-2011 (11-05-2011) Version - B: Part A Physics 1. Ans: 2Document8 pagesSOLUTIONS & ANSWERS FOR AIEEE-2011 (11-05-2011) Version - B: Part A Physics 1. Ans: 2Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Formula 3Document3 pagesFormula 3OlexNo ratings yet
- SiFormulario HelicopterosDocument1 pageSiFormulario HelicopterosjuanNo ratings yet
- Fluid AssignmentDocument4 pagesFluid Assignment旭源吕No ratings yet
- EquationDocument2 pagesEquationDarrel HindoyNo ratings yet
- H SQP Physics-Relationships-DQPDocument4 pagesH SQP Physics-Relationships-DQPAaronNo ratings yet
- Equazioni Di Equilibrio Piastre: M Z H M Z HDocument5 pagesEquazioni Di Equilibrio Piastre: M Z H M Z HRiccardo CirulliNo ratings yet
- Physics Data Sheet: Useful ConstantsDocument2 pagesPhysics Data Sheet: Useful ConstantsReghan VersteegeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument13 pagesChapter 3 PDFNguyễn ThắngNo ratings yet
- Formularium R1-R2Document2 pagesFormularium R1-R2Mr KostjaNo ratings yet
- Formulario I ParcialDocument1 pageFormulario I Parcialseca cacaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Winter218Document6 pagesFormula Sheet Winter218Michael BarkerNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument10 pagesPhysics FormulasFaith Laurence Sarmiento100% (1)
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 pagesFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 pagesFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General Relativity Solutions 21-25Document5 pagesIntroduction To General Relativity Solutions 21-25daveNo ratings yet
- Old Thermo Exam Formula SheetDocument1 pageOld Thermo Exam Formula SheetjonahNo ratings yet
- Physics 40S Formula SheetDocument1 pagePhysics 40S Formula SheetWaleedSubhanNo ratings yet
- Math 55 Samplex 2 2013 (Answer Key) PDFDocument2 pagesMath 55 Samplex 2 2013 (Answer Key) PDFEdrien Dominick OfinaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - DynamicsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics - DynamicsMonique OrugaNo ratings yet
- Already Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkDocument3 pagesAlready Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkJon WestNo ratings yet
- Constantes & Principales FórmulasDocument7 pagesConstantes & Principales FórmulasJuan Diego PimientoNo ratings yet
- Relations and FormulaeDocument2 pagesRelations and FormulaeChiranjeevi KanikeNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet PH121Document1 pageFormula Sheet PH121menteNo ratings yet
- Formula Fis3Document1 pageFormula Fis3DANNA SOFIA LEDEZMA ARCOSNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Formula SheetDocument2 pages0.1 Formula Sheetbiggie cheeseNo ratings yet
- PW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsDocument13 pagesPW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsOfficers IasNo ratings yet
- Solutions JEEAdvanced2014 Paper2 Code-5Document35 pagesSolutions JEEAdvanced2014 Paper2 Code-5Vagarth AgrwalNo ratings yet
- Ytorres - 2021 04 04 Formulae CompendiumDocument7 pagesYtorres - 2021 04 04 Formulae CompendiumLeo Quintero PérezNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow: Speed of SoundDocument3 pagesCompressible Flow: Speed of SoundManu K VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Boundary LayerDocument3 pagesBoundary LayerPatrick Joseph RoblesNo ratings yet
- Formulario FiiiDocument1 pageFormulario FiiiJavier WolhersNo ratings yet
- Prénom: - Nom: - Feuille de Formule - Électricité Et MagnétismeDocument2 pagesPrénom: - Nom: - Feuille de Formule - Électricité Et MagnétismePhil L.No ratings yet
- Formulae Compendium Physics IV From Modern PhysicsDocument6 pagesFormulae Compendium Physics IV From Modern PhysicsErwing JF AnayaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Formula SheetDocument1 pagePhysics 11 Formula SheetJack Song S.YNo ratings yet
- 3 8 Solved ProblemsDocument1 page3 8 Solved ProblemsJim Lee LorenzoNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
EquationsFLM400S Rev
EquationsFLM400S Rev
Uploaded by
Christo Malan LotzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EquationsFLM400S Rev
EquationsFLM400S Rev
Uploaded by
Christo Malan LotzCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Mechanics IV – Equations Compressible isothermal flow
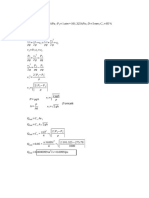
p 22 − p12 p2 p 4 fp12V12 L
Compressible flow − V12 1 ln 2 = −
γ
2 RT p1 2 DRT
γ −1 2 γ − 1 2 (γ −1) Dimensionless Groups
To = T 1 + M p 0 = p1 + M
2 2 V ρVl
γ Fr = Re =
1
lg µ
γ −1 (γ −1) p1 T1 γ −1
ρ 0 = ρ 1 + M2 =
2 p 2 T2 We =
ρV 2 l
Ca =
V2
V P σ ( K ρ)
a = γRT M = ρ= ∆p V
a RT Eu = M=
• ρV 2 c
m = ρAV
C p = ∆p CD = F
Normal shock − see tables 0,5 ρV 2 0,5ρV 2 l 2
Converging/diverging nozzle CL = F
γ +1 0,5 ρV 2 l 2
γ − 1 2 2(γ −1)
1 + M
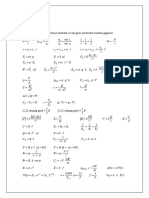
A 1 2 Flow over submerged objects
=
A∗ M γ +1
Re crit =
Vd ρVd
= F=
1
C D ρAV 2
ν µ 2
2
(γ +1) Sphere CD ≈ 0,2 (Re > 1×106)
• p0 A 2
∗ 2 (γ −1) Infinite cylinder CD ≈ 0,75 (Re > 6×106)
m=
RT0 γ + 1 fd 19,7
Str = = 0,1981 − 250 < Re < 2 × 10 5
Fanno flow V Re
aspect ratio = span / mean chord
L actual = L∗1 − L∗2
4 fL∗ 1 − M 2 γ + 1 γ + 1 2 γ − 1 2 Terminal velocity of falling spheres
= + ln M 1 + M 1
D γ 2γ 2 2 4 gd ρ s 2
Vt = − 1
4 fL* 4 fL* 4 fLactual 3C ρ
= + D
D 1 D 2 D
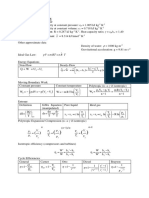
p 2M 2 γ − 1 2 Boundary layer flow
= 1 + M
p* γ + 1 2 Ux
−1
Re crit = crit
T γ +1 γ −1 2 ν
= 1 + M Laminar boundary layer
T* 2 2
4,91x 1,721x
γ +1 δ = δ∗ =
V γ + 1 γ − 1 2 −1 2(γ −1) 1
Re x 2
1
Re x 2
= M 1 + M
V* 2 2 1,328
CD = 1
γ +1
Re x 2
po 1 2 γ − 1 2 2(γ −1)
*
= 1 + M Laminar and Turbulent boundary layer
po M γ + 1 2 0,074 1742
CD = − (Recrit < ReL < 107)
Re1L5 Re L
Raleigh Flow
q = C P (T02 − T01 ) 0,455 1742
CD = − (107 < Rel)
p T V T0 p 0
(log10 Re L ) 2 ,58
Re L
; ; ; ; see tables F = 0,5ρU2b[(CD turbl) − (CD turbxcrit) + (CD lamxcrit)]
p ∗ T ∗ V ∗ T0∗ p 0∗
You might also like
- Chapter 3Document81 pagesChapter 3Ricky Putra SiregarNo ratings yet
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 pagesFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Aero Basic FormulationDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Aero Basic FormulationNihar SamalNo ratings yet
- Physics 112 Formulae IIIDocument3 pagesPhysics 112 Formulae IIISaied RajehaNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet SPH 4U: DynamicsDocument3 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet SPH 4U: DynamicsNA TbNo ratings yet
- MIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Document15 pagesMIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Gavin BirlaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetMama PigNo ratings yet
- Canal Flow & Pipe Flow (Not Full) : 1. Hydraulic Depth Also Called Hydraulic Radius Different Shape and Sizes For CanalsDocument9 pagesCanal Flow & Pipe Flow (Not Full) : 1. Hydraulic Depth Also Called Hydraulic Radius Different Shape and Sizes For CanalsDLRauties100% (1)
- Formulario+i+parcial - 3Document2 pagesFormulario+i+parcial - 3NicolasNo ratings yet
- Formulario+i+parcial - 3Document2 pagesFormulario+i+parcial - 3NicolasNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasKristine BalansagNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Modern PhysicsDocument1 pageKinematics Modern PhysicsBoldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- Formula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵDocument5 pagesFormula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵPhemi2580No ratings yet
- Physics Grade 12 Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics Grade 12 Formula SheetLauren HongNo ratings yet
- Aa PDFDocument1 pageAa PDFmesfin DemiseNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics I Solution Manual 7 Question 1: Problem P3.158Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics I Solution Manual 7 Question 1: Problem P3.158cartoon_nateNo ratings yet
- PT #10 Temperature Profile With More Than One Independent Variables (Kelas A)Document17 pagesPT #10 Temperature Profile With More Than One Independent Variables (Kelas A)MUHAMMAD LUQMAN HAKIMI MOHD ZAMRINo ratings yet
- Formulae Part ThreeDocument5 pagesFormulae Part ThreeShiva SeshasaiNo ratings yet
- Phsi191 Mid Sem 2014Document8 pagesPhsi191 Mid Sem 2014gang gangNo ratings yet
- Useful Aerospace FormulasDocument1 pageUseful Aerospace FormulasRadj90No ratings yet
- Figure 1. Drag Coefficient As A Function of SphericityDocument9 pagesFigure 1. Drag Coefficient As A Function of SphericityPAULA ANDREA CARO BAEZNo ratings yet
- Equationsjhgg 77Document2 pagesEquationsjhgg 77harsh rajNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS & ANSWERS FOR AIEEE-2011 (11-05-2011) Version - B: Part A Physics 1. Ans: 2Document8 pagesSOLUTIONS & ANSWERS FOR AIEEE-2011 (11-05-2011) Version - B: Part A Physics 1. Ans: 2Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Formula 3Document3 pagesFormula 3OlexNo ratings yet
- SiFormulario HelicopterosDocument1 pageSiFormulario HelicopterosjuanNo ratings yet
- Fluid AssignmentDocument4 pagesFluid Assignment旭源吕No ratings yet
- EquationDocument2 pagesEquationDarrel HindoyNo ratings yet
- H SQP Physics-Relationships-DQPDocument4 pagesH SQP Physics-Relationships-DQPAaronNo ratings yet
- Equazioni Di Equilibrio Piastre: M Z H M Z HDocument5 pagesEquazioni Di Equilibrio Piastre: M Z H M Z HRiccardo CirulliNo ratings yet
- Physics Data Sheet: Useful ConstantsDocument2 pagesPhysics Data Sheet: Useful ConstantsReghan VersteegeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument13 pagesChapter 3 PDFNguyễn ThắngNo ratings yet
- Formularium R1-R2Document2 pagesFormularium R1-R2Mr KostjaNo ratings yet
- Formulario I ParcialDocument1 pageFormulario I Parcialseca cacaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Winter218Document6 pagesFormula Sheet Winter218Michael BarkerNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument10 pagesPhysics FormulasFaith Laurence Sarmiento100% (1)
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 pagesFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- Formelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFDocument8 pagesFormelsammlung Strömungslehre PDFmaildesantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General Relativity Solutions 21-25Document5 pagesIntroduction To General Relativity Solutions 21-25daveNo ratings yet
- Old Thermo Exam Formula SheetDocument1 pageOld Thermo Exam Formula SheetjonahNo ratings yet
- Physics 40S Formula SheetDocument1 pagePhysics 40S Formula SheetWaleedSubhanNo ratings yet
- Math 55 Samplex 2 2013 (Answer Key) PDFDocument2 pagesMath 55 Samplex 2 2013 (Answer Key) PDFEdrien Dominick OfinaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - DynamicsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics - DynamicsMonique OrugaNo ratings yet
- Already Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkDocument3 pagesAlready Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkJon WestNo ratings yet
- Constantes & Principales FórmulasDocument7 pagesConstantes & Principales FórmulasJuan Diego PimientoNo ratings yet
- Relations and FormulaeDocument2 pagesRelations and FormulaeChiranjeevi KanikeNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet PH121Document1 pageFormula Sheet PH121menteNo ratings yet
- Formula Fis3Document1 pageFormula Fis3DANNA SOFIA LEDEZMA ARCOSNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Formula SheetDocument2 pages0.1 Formula Sheetbiggie cheeseNo ratings yet
- PW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsDocument13 pagesPW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsOfficers IasNo ratings yet
- Solutions JEEAdvanced2014 Paper2 Code-5Document35 pagesSolutions JEEAdvanced2014 Paper2 Code-5Vagarth AgrwalNo ratings yet
- Ytorres - 2021 04 04 Formulae CompendiumDocument7 pagesYtorres - 2021 04 04 Formulae CompendiumLeo Quintero PérezNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow: Speed of SoundDocument3 pagesCompressible Flow: Speed of SoundManu K VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Boundary LayerDocument3 pagesBoundary LayerPatrick Joseph RoblesNo ratings yet
- Formulario FiiiDocument1 pageFormulario FiiiJavier WolhersNo ratings yet
- Prénom: - Nom: - Feuille de Formule - Électricité Et MagnétismeDocument2 pagesPrénom: - Nom: - Feuille de Formule - Électricité Et MagnétismePhil L.No ratings yet
- Formulae Compendium Physics IV From Modern PhysicsDocument6 pagesFormulae Compendium Physics IV From Modern PhysicsErwing JF AnayaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Formula SheetDocument1 pagePhysics 11 Formula SheetJack Song S.YNo ratings yet
- 3 8 Solved ProblemsDocument1 page3 8 Solved ProblemsJim Lee LorenzoNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet