Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inorganic Ions
Inorganic Ions
Uploaded by
Stuart PetersCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Transition Metal Ion Metal Aqua Ion With OH With Excess OHDocument1 pageTransition Metal Ion Metal Aqua Ion With OH With Excess OHsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Ion Metal-Aqua Ion With OHDocument2 pagesTransition Metal Ion Metal-Aqua Ion With OHsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Red/Brown PPT of Purple Solution ofDocument1 pageRed/Brown PPT of Purple Solution ofSusana Natsumy Apaza HuallpaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Salt Analysis (12th)Document15 pagesSolution of Salt Analysis (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Comparative Reactions of The Ammonium Sulfide GroupDocument2 pagesComparative Reactions of The Ammonium Sulfide GroupPharmaNo ratings yet
- Some Hydroxides Are A: Few Drops of Naoh Xs Naoh Few Drops of NH Xs NH (Conc.) Na Co (Aq) HCL (Conc.)Document1 pageSome Hydroxides Are A: Few Drops of Naoh Xs Naoh Few Drops of NH Xs NH (Conc.) Na Co (Aq) HCL (Conc.)FaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- Met Al Aqueous Ion Limited Naoh Limited NH Excess Naoh Excess NH Na Co HCLDocument2 pagesMet Al Aqueous Ion Limited Naoh Limited NH Excess Naoh Excess NH Na Co HCLZeenat AfrozeNo ratings yet
- VII. Observation Result Experiment 1Document12 pagesVII. Observation Result Experiment 1Anggraini Nugroho PNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument1 pageInorganic ChemistryMihindi WeligamageNo ratings yet
- Solution of Salt Analysis-13thDocument16 pagesSolution of Salt Analysis-13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution: Chemistry A-Level (7405)Document2 pagesReactions of Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution: Chemistry A-Level (7405)SAMANNo ratings yet
- Comparative Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide GroupDocument5 pagesComparative Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide GroupPATRICIA ROSE SORIANO100% (1)
- Aqueous Ion ColoursDocument1 pageAqueous Ion ColoursAnita OguniNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions Concise Chemistry For Class 10 Chapter 4Document6 pagesSelina Solutions Concise Chemistry For Class 10 Chapter 4Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter-4 - Analytical Chemistry Chemistry: Book Name: Selina ConciseDocument9 pagesClass X Chapter-4 - Analytical Chemistry Chemistry: Book Name: Selina ConciseKartik RavindranNo ratings yet
- Print Version: Lecture #20 Closed Systems II & AlkalinityDocument19 pagesPrint Version: Lecture #20 Closed Systems II & AlkalinityNermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- Downloading File:salt Analysis - Expt - 10 - 2024Document4 pagesDownloading File:salt Analysis - Expt - 10 - 2024Siddhi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Metal Aqua Ion Reactions OCRDocument2 pagesMetal Aqua Ion Reactions OCRAli AfaqNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-19 Qualitative AnalysisDocument4 pagesC Sol Ch-19 Qualitative Analysismysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- Prac 7 - Report SheetDocument4 pagesPrac 7 - Report SheetMthetheleli NxeleNo ratings yet
- CP 07 & CP 15 - Analysis of Unknown CompoundsDocument5 pagesCP 07 & CP 15 - Analysis of Unknown Compoundsdameesh9No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis (Answer) (12th)Document16 pagesSalt Analysis (Answer) (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals Part 3 (Reactions) EdexcelDocument6 pagesTransition Metals Part 3 (Reactions) EdexcelKevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- TabelDocument4 pagesTabelayu irsalinaNo ratings yet
- AS Level Qualitative AnalysisDocument8 pagesAS Level Qualitative AnalysismahahajNo ratings yet
- 2.6. Reactions of Inorganic Compounds in Aqueous SolutionDocument3 pages2.6. Reactions of Inorganic Compounds in Aqueous Solutionshafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument30 pagesQualitative AnalysisShivaprasadNo ratings yet
- Solution of Salt Analysis-13thDocument8 pagesSolution of Salt Analysis-13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 6 Revision Guide Reactions of Aqueous Ions AqaDocument3 pages2 6 Revision Guide Reactions of Aqueous Ions AqaGarfield AndyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise - 4Document9 pagesChapter - 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise - 4parijatbhattacharjee949No ratings yet
- Jee Main Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds Revision NotesDocument5 pagesJee Main Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds Revision Notessaisiddardha19No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument65 pagesChemistrybilalNo ratings yet
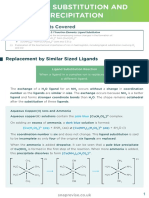
- Ligand Substitution and PrecipitationDocument9 pagesLigand Substitution and PrecipitationHadia RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical TestsDocument5 pagesChemical TestsChal WijeNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) Chapter 1.3 - Qualitative AnalysisDocument11 pages(CHEM) Chapter 1.3 - Qualitative AnalysisVijay Kumar NatteyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 10, 2024Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 10, 2024abcx87380No ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideDocument5 pagesQualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideJeremy TehNo ratings yet
- ch-4 Checm Class 10Document12 pagesch-4 Checm Class 10kipob56259No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 29, 2021Document6 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 29, 2021John DoeNo ratings yet
- Catholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Document13 pagesCatholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Clours of Different CompoundsDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - Clours of Different CompoundsMohit PanchalNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis CompleteDocument5 pagesSalt Analysis CompleteAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Colour of Compound - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesColour of Compound - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024subhamwork2006No ratings yet
- hoa-dai-cuong__acid-baseDocument45 pageshoa-dai-cuong__acid-basemydinh074No ratings yet
- (Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceDocument15 pages(Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceAbhay ManwalNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry Practical Salt AnalysisDocument13 pagesXii Chemistry Practical Salt AnalysisNupur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry PracticalDocument25 pagesXii Chemistry PracticalgamavilocityNo ratings yet
- (Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceDocument26 pages(Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceMeena QueenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 8 Group IIA Cations GROUP4 PCQADocument4 pagesWorksheet No. 8 Group IIA Cations GROUP4 PCQAAndrew CraigieNo ratings yet
- Notes of Unit 3Document12 pagesNotes of Unit 3saraNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 NotesDocument3 pagesTopic 9 Notesmarin tamNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 2Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 2jw wNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 1Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 1jw wNo ratings yet
- CP 8 - Analysis of Some Inorganic and Organic UnknownsDocument6 pagesCP 8 - Analysis of Some Inorganic and Organic UnknownsPOPNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sec 3 Qa Notes StudentsDocument11 pages2022 Sec 3 Qa Notes Studentsapi-628191203No ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-15 - The P-Block Elements (Group 13 To Group 18)Document9 pagesC - Sol - Ch-15 - The P-Block Elements (Group 13 To Group 18)mysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- RearrangementsDocument82 pagesRearrangementsjoy shruthiNo ratings yet
- COLOUR OF ALL IOC COMPOUNDS @HeyitsyashXDDocument2 pagesCOLOUR OF ALL IOC COMPOUNDS @HeyitsyashXDzehraNo ratings yet
Inorganic Ions
Inorganic Ions
Uploaded by
Stuart PetersOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inorganic Ions
Inorganic Ions
Uploaded by
Stuart PetersCopyright:
Available Formats
176
'---;C' , -,-.:'~ ~"-:~~ 'if¥::;-:'O"';~~~~ :-.
. ", ']. ,.~. :.:~f:!!~i'~Meta
• , • :e-..
!~~~.,~.
I-~g l!J a
~;J.t ~ -
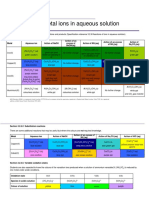
I Learn the Colours of All the Complex Ion Solutions and Precipitates I
This handy table summarises all the compo unds that are formed in the reactions on these pages.
You need to know the formulas of all the complex ions (so you can write ionic equations), and their colours. I
If you're doing OCR A, you only need the first two columns and first four rows of the table. AQA only
Metal-aqua ion With OH -(aq)or NH 3(aq) With excess OW(aq) With excess NH 3(aq) With Na 2C03(aq)
[Co(H 2O)6t Co(H 2O)4(OH)2 [Co(NH 3)6t CoC0 3
pink solution no change
blue-green precipitate straw coloured solution pink precipitate
[Cu(H 2O)6t CU(H,o)4(OH)2 [Cu(NH 3)4(H,o)2t CuC03
blue solution no change deep blue solution
blue precipitate green-blue precipitate
[Fe(H 2O)6t Fe(H,o)4(OH)2 FeC03
green solution no change no change
green precipitate green precipitate
[Fe(H 2O)6t Fe(H,o)3(OH)3 no change Fe(H 2O)3(OH)3
yellow solution no change
brown precipitate brown precipitate
[AI (H2O)6t AI(H 2O)3(OH)3 [AI(H 2O)2(O H)4r AI(H 2O)3(OH)3
colourless solution no change
white precipitate colourless solution white precipitate
[Cr(H 2O)6t Cr(H,o)3(OH)3 [Cr(OH)J3- [Cr(NH 3)6t Cr(H 2O)3(OH)3
violet solution green precipitate green solution purple solution green precipitate
[Mn(H,o)6t Mn(H,o)4(OH)2 no change no change
~ very pale pink solution brown precipitate
c:: If you're doing
-0
<li
\.J
~
[Ni(H 2O)6t
green solution
Ni(H 2O)4(OH)2
green precipitate
no change
[N i(NH 3)6t
blue solution
fdexcel, you can
ignore the cobalt
row at the top.
[Zn(H 2O)6t Zn(H,o)3(OH)3 [Zn(OH)4t [Zn(NH')4t
~ colourless solution white precipitate colourless solution colourless solution
I
I Practice Questions I
01 Explain why AICI 3 can act as a Lewis ac id.
02 Show by equations how AI(OH)3 can act as both a Br0nsted-Lowry acid and a Br0nsted-Lowry base.
03 What colour solution is formed when you add excess ammonia to a solution containing [Co(H 2 0)6F+ ions?
Exam Questions
I Explain why separate solutions ofiron(II) sulfate and iron(III) sulfate with equal concentrations
have different pH values. [4 marks]
2 Describe what you would see when ammonia solution is added slowly to a solution containing
copper(JI) sulfate until it is in excess. Write equations for each reaction that occurs. [8 marks]
3 Aqueous ammonia was added to an aqueous solution of chromium(III) sulfate.
a) Identify the chromium complex ion present in:
i) the aqueous chromium(III) sulfate. [I mark]
ii) the green precipitate initially formed when aqueous ammonia is added. [I mark]
iii) the purple solution when an excess of aqueous ammonia is added. [I mark]
b) Write an equation for the reaction in which the purple solution is formed from the green precipitate. [I mark]
4 a) Describe what you would observe when aqueous sodium carbonate is added to:
i) aqueous iron(JII) chloride. [1 mark]
ii) freshly-prepared aqueous iron (II) sulfate. [1 mark]
b) Write an equation for the reaction of the iron(II)-aqua ion with the carbonate ion. [I mark]
c) If iron(II) sulfate solution is left to stand overnight in an open beaker before the aqueous sodium carbonate
is added, then a different reaction is observed.
i) Describe the new observation. [I mark]
ii) Explain this change. [1 mark]
Test tube reactions - {lro{ler chemistr'£. at last...
50 many pretty colours. The only downside is that you have to remember them. But examiners do love to ask q uestions about
colours of solutions and precipitates. 50 lea rn them all, or come exam day you'll end up feeling blue. Or possibly blue-green ...
SECTION 77 - INORCANIC R EACTIONS
You might also like
- Transition Metal Ion Metal Aqua Ion With OH With Excess OHDocument1 pageTransition Metal Ion Metal Aqua Ion With OH With Excess OHsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Ion Metal-Aqua Ion With OHDocument2 pagesTransition Metal Ion Metal-Aqua Ion With OHsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Red/Brown PPT of Purple Solution ofDocument1 pageRed/Brown PPT of Purple Solution ofSusana Natsumy Apaza HuallpaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Salt Analysis (12th)Document15 pagesSolution of Salt Analysis (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Comparative Reactions of The Ammonium Sulfide GroupDocument2 pagesComparative Reactions of The Ammonium Sulfide GroupPharmaNo ratings yet
- Some Hydroxides Are A: Few Drops of Naoh Xs Naoh Few Drops of NH Xs NH (Conc.) Na Co (Aq) HCL (Conc.)Document1 pageSome Hydroxides Are A: Few Drops of Naoh Xs Naoh Few Drops of NH Xs NH (Conc.) Na Co (Aq) HCL (Conc.)FaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- Met Al Aqueous Ion Limited Naoh Limited NH Excess Naoh Excess NH Na Co HCLDocument2 pagesMet Al Aqueous Ion Limited Naoh Limited NH Excess Naoh Excess NH Na Co HCLZeenat AfrozeNo ratings yet
- VII. Observation Result Experiment 1Document12 pagesVII. Observation Result Experiment 1Anggraini Nugroho PNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument1 pageInorganic ChemistryMihindi WeligamageNo ratings yet
- Solution of Salt Analysis-13thDocument16 pagesSolution of Salt Analysis-13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution: Chemistry A-Level (7405)Document2 pagesReactions of Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution: Chemistry A-Level (7405)SAMANNo ratings yet
- Comparative Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide GroupDocument5 pagesComparative Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide GroupPATRICIA ROSE SORIANO100% (1)
- Aqueous Ion ColoursDocument1 pageAqueous Ion ColoursAnita OguniNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions Concise Chemistry For Class 10 Chapter 4Document6 pagesSelina Solutions Concise Chemistry For Class 10 Chapter 4Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter-4 - Analytical Chemistry Chemistry: Book Name: Selina ConciseDocument9 pagesClass X Chapter-4 - Analytical Chemistry Chemistry: Book Name: Selina ConciseKartik RavindranNo ratings yet
- Print Version: Lecture #20 Closed Systems II & AlkalinityDocument19 pagesPrint Version: Lecture #20 Closed Systems II & AlkalinityNermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- Downloading File:salt Analysis - Expt - 10 - 2024Document4 pagesDownloading File:salt Analysis - Expt - 10 - 2024Siddhi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Metal Aqua Ion Reactions OCRDocument2 pagesMetal Aqua Ion Reactions OCRAli AfaqNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-19 Qualitative AnalysisDocument4 pagesC Sol Ch-19 Qualitative Analysismysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- Prac 7 - Report SheetDocument4 pagesPrac 7 - Report SheetMthetheleli NxeleNo ratings yet
- CP 07 & CP 15 - Analysis of Unknown CompoundsDocument5 pagesCP 07 & CP 15 - Analysis of Unknown Compoundsdameesh9No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis (Answer) (12th)Document16 pagesSalt Analysis (Answer) (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals Part 3 (Reactions) EdexcelDocument6 pagesTransition Metals Part 3 (Reactions) EdexcelKevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- TabelDocument4 pagesTabelayu irsalinaNo ratings yet
- AS Level Qualitative AnalysisDocument8 pagesAS Level Qualitative AnalysismahahajNo ratings yet
- 2.6. Reactions of Inorganic Compounds in Aqueous SolutionDocument3 pages2.6. Reactions of Inorganic Compounds in Aqueous Solutionshafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument30 pagesQualitative AnalysisShivaprasadNo ratings yet
- Solution of Salt Analysis-13thDocument8 pagesSolution of Salt Analysis-13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 6 Revision Guide Reactions of Aqueous Ions AqaDocument3 pages2 6 Revision Guide Reactions of Aqueous Ions AqaGarfield AndyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise - 4Document9 pagesChapter - 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise - 4parijatbhattacharjee949No ratings yet
- Jee Main Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds Revision NotesDocument5 pagesJee Main Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds Revision Notessaisiddardha19No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument65 pagesChemistrybilalNo ratings yet
- Ligand Substitution and PrecipitationDocument9 pagesLigand Substitution and PrecipitationHadia RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical TestsDocument5 pagesChemical TestsChal WijeNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) Chapter 1.3 - Qualitative AnalysisDocument11 pages(CHEM) Chapter 1.3 - Qualitative AnalysisVijay Kumar NatteyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 10, 2024Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 10, 2024abcx87380No ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideDocument5 pagesQualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideJeremy TehNo ratings yet
- ch-4 Checm Class 10Document12 pagesch-4 Checm Class 10kipob56259No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 29, 2021Document6 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 29, 2021John DoeNo ratings yet
- Catholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Document13 pagesCatholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Clours of Different CompoundsDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - Clours of Different CompoundsMohit PanchalNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis CompleteDocument5 pagesSalt Analysis CompleteAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Colour of Compound - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesColour of Compound - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024subhamwork2006No ratings yet
- hoa-dai-cuong__acid-baseDocument45 pageshoa-dai-cuong__acid-basemydinh074No ratings yet
- (Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceDocument15 pages(Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceAbhay ManwalNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry Practical Salt AnalysisDocument13 pagesXii Chemistry Practical Salt AnalysisNupur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry PracticalDocument25 pagesXii Chemistry PracticalgamavilocityNo ratings yet
- (Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceDocument26 pages(Class Xii Chemistry Practicals) : Experiment - 1 Classification of Anions Group Reagent Observation InferenceMeena QueenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 8 Group IIA Cations GROUP4 PCQADocument4 pagesWorksheet No. 8 Group IIA Cations GROUP4 PCQAAndrew CraigieNo ratings yet
- Notes of Unit 3Document12 pagesNotes of Unit 3saraNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 NotesDocument3 pagesTopic 9 Notesmarin tamNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 2Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 2jw wNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 1Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 1jw wNo ratings yet
- CP 8 - Analysis of Some Inorganic and Organic UnknownsDocument6 pagesCP 8 - Analysis of Some Inorganic and Organic UnknownsPOPNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sec 3 Qa Notes StudentsDocument11 pages2022 Sec 3 Qa Notes Studentsapi-628191203No ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-15 - The P-Block Elements (Group 13 To Group 18)Document9 pagesC - Sol - Ch-15 - The P-Block Elements (Group 13 To Group 18)mysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- RearrangementsDocument82 pagesRearrangementsjoy shruthiNo ratings yet
- COLOUR OF ALL IOC COMPOUNDS @HeyitsyashXDDocument2 pagesCOLOUR OF ALL IOC COMPOUNDS @HeyitsyashXDzehraNo ratings yet