Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Immunity
The Immunity
Uploaded by
Hamoud Al ThubyniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ImmunologyDocument15 pagesImmunologyAnik MazumderNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument41 pagesIntroductionworknehbethanyNo ratings yet
- FinaDocument19 pagesFinaZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- CH 1. Overview of The Immune SystemDocument23 pagesCH 1. Overview of The Immune SystemIbrahim MNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 MicroparaDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 16 MicroparaKathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- Micro Assignment Unit 3 Group BDocument12 pagesMicro Assignment Unit 3 Group Bnabeelpatras19No ratings yet
- Csa ExerciseDocument17 pagesCsa ExerciseBlack starNo ratings yet
- Immuno and InfectiousDocument17 pagesImmuno and Infectiousgreen_archerNo ratings yet
- MicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionDocument11 pagesMicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionRaven Joyce LabayenNo ratings yet
- 5 Immunological DisordersDocument22 pages5 Immunological DisordersPaula CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument5 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Immunology Lecturs 27Document27 pagesImmunology Lecturs 27Rolls SaeedNo ratings yet
- Control and Prevention of Communicable DiseasesDocument14 pagesControl and Prevention of Communicable DiseasesZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Specificity + Memory': Flexible Specific Immunological Memory Second ExposureDocument12 pagesSpecificity + Memory': Flexible Specific Immunological Memory Second ExposureRakin Bin RaihanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunityDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Immunityr.beqiraj22No ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument59 pagesImmunologyImran KhanNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument36 pagesImmunologyمروه عماد عيسى100% (1)
- ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (Rev - DR. Amoani)Document83 pagesADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (Rev - DR. Amoani)Boateng DerrickNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity Booklet AnswersDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity Booklet AnswersJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Micp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To InfectionDocument15 pagesMicp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To Infectioncaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument5 pagesIMMUNITYKebbewar KhaledNo ratings yet
- Crawford Hes Lec Sas 10Document6 pagesCrawford Hes Lec Sas 10Divo SkyeNo ratings yet
- Immunity Vaccination: Public HealthDocument41 pagesImmunity Vaccination: Public HealthBaraa AbosamraNo ratings yet
- Zoology6thSem PDFDocument88 pagesZoology6thSem PDFRouf MalikNo ratings yet
- Disease and The Immune SystemDocument44 pagesDisease and The Immune SystemBaydaa Hameed Al AbdaliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument6 pagesImmunitySahir Seemab ZafarNo ratings yet
- Immunometabolism IDocument29 pagesImmunometabolism IMatheus TavaresNo ratings yet
- Ayan Das 16401722005 BO-303Document4 pagesAyan Das 16401722005 BO-303Ayan DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3futnariNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Midterm Notes 2Document67 pagesNCM 112 Midterm Notes 2ljealou2002No ratings yet
- Task 1. Concept Analysis and DiagramDocument4 pagesTask 1. Concept Analysis and Diagramkristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- L 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDDocument15 pagesL 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Disease and Immunity NotesDocument8 pagesDisease and Immunity NotesFaeequa nasrahNo ratings yet
- Immunity and Immunization ProgramDocument11 pagesImmunity and Immunization ProgramĦajra KhaŋNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument4 pagesImmunityMiran HussienNo ratings yet
- 57 64Document7 pages57 64Airah Fate BrunoNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction of ImmunologyDocument6 pages2.introduction of Immunologyvivena1464No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Properties and Overview of Immune ResponsesDocument45 pagesChapter 1 Properties and Overview of Immune Responses13701319477No ratings yet
- 40 Definitions BioDocument3 pages40 Definitions BioJustin JamesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Innate ImmunityDocument8 pagesLecture 1 Innate ImmunityOfficial NgareNo ratings yet
- Immune ResponsesintissueDocument22 pagesImmune ResponsesintissueFahim AhmadNo ratings yet
- Immunologic and Infectious DisordersDocument38 pagesImmunologic and Infectious Disordersdarla ryanNo ratings yet
- Acquired Imm and Infection - BPTDocument15 pagesAcquired Imm and Infection - BPTKathal 66No ratings yet
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- IS LessonDocument30 pagesIS Lessonjohn dale duranoNo ratings yet
- 4 Immune DisordersDocument11 pages4 Immune DisorderscedonuliNo ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Document41 pagesDasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Olivia NurudhiyaNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology - IntroductionDocument51 pagesImmunopharmacology - IntroductionIsrat Jahan Surovy 2225400672No ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology - Sep2022Document31 pagesIntroduction To Immunology - Sep2022Esther WanjukiNo ratings yet
- Host Defence..Document23 pagesHost Defence..Nagendrappa MalipatilNo ratings yet
- Inmune SystemDocument8 pagesInmune Systemfranciscarivera09No ratings yet
- Biology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFDocument21 pagesBiology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFMichael John LozanoNo ratings yet
- B & T Cells (Immunity) (23-3-11)Document1 pageB & T Cells (Immunity) (23-3-11)harrisonwhiteNo ratings yet
- L1 - IntroductionDocument5 pagesL1 - IntroductionMiles NsgNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Immune SystemDocument13 pagesLesson 6 Immune SystemBrent PatarasNo ratings yet
- Immunization New ContentDocument11 pagesImmunization New ContentkrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- W8 Immunology and ImmunizationDocument9 pagesW8 Immunology and ImmunizationJamie De LunaNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument31 pagesImmunityattiarph23No ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
The Immunity
The Immunity
Uploaded by
Hamoud Al ThubyniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Immunity
The Immunity
Uploaded by
Hamoud Al ThubyniCopyright:
Available Formats
The Immunity
Student name : Hamoud Humidan
Computer number : 2910095
Introduction
Immune systems are generally characterized by their ability to distinguish between
self and non-self cells, tissues, or molecules, and to eliminate the non-self .
Or other definition is acquired by human ability to resist infection and overcome, the
defense of the human body against invading germs that cause disease
Type of immunity :
1) Passive immunity it is the transfer of active immunity, in the form of readymade
antibodies, from one individual to another. Passive immunity can occur naturally,
when maternal antibodies are transferred to the fetus through the placenta .
a) Natural acquired passive immunity
b) Artificially acquired passive immunity
c) Passive transfer of cell-mediated immunity
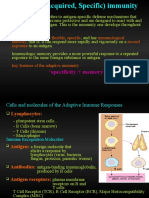
2) Active immunity .. When B cells and T cells are activated by a pathogen, memory
B-cells and T- cells develop. Throughout the lifetime of an animal these memory
cells will “remember” each specific pathogen encountered, and are able to mount
a strong response if the pathogen is detected again.
a) Naturally acquired active immunity
b) Artificially acquired active immunity
VIRAL IMMUNOLOGY
Viruses are strongly immunogenic and induces 2 types of immune responses; humoral
and cellular
Humoral response is responsible for blocking the infectivity of the virus
(neutralization)
cellular response kills the virus-infected cells expressing viral proteins on their
surfaces, such as the glycoproteins of enveloped viruses and sometimes core proteins
of these viruses
You might also like
- ImmunologyDocument15 pagesImmunologyAnik MazumderNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument41 pagesIntroductionworknehbethanyNo ratings yet
- FinaDocument19 pagesFinaZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- CH 1. Overview of The Immune SystemDocument23 pagesCH 1. Overview of The Immune SystemIbrahim MNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 MicroparaDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 16 MicroparaKathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- Micro Assignment Unit 3 Group BDocument12 pagesMicro Assignment Unit 3 Group Bnabeelpatras19No ratings yet
- Csa ExerciseDocument17 pagesCsa ExerciseBlack starNo ratings yet
- Immuno and InfectiousDocument17 pagesImmuno and Infectiousgreen_archerNo ratings yet
- MicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionDocument11 pagesMicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionRaven Joyce LabayenNo ratings yet
- 5 Immunological DisordersDocument22 pages5 Immunological DisordersPaula CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument5 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Immunology Lecturs 27Document27 pagesImmunology Lecturs 27Rolls SaeedNo ratings yet
- Control and Prevention of Communicable DiseasesDocument14 pagesControl and Prevention of Communicable DiseasesZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Specificity + Memory': Flexible Specific Immunological Memory Second ExposureDocument12 pagesSpecificity + Memory': Flexible Specific Immunological Memory Second ExposureRakin Bin RaihanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunityDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Immunityr.beqiraj22No ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument59 pagesImmunologyImran KhanNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument36 pagesImmunologyمروه عماد عيسى100% (1)
- ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (Rev - DR. Amoani)Document83 pagesADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (Rev - DR. Amoani)Boateng DerrickNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity Booklet AnswersDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity Booklet AnswersJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Micp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To InfectionDocument15 pagesMicp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To Infectioncaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument5 pagesIMMUNITYKebbewar KhaledNo ratings yet
- Crawford Hes Lec Sas 10Document6 pagesCrawford Hes Lec Sas 10Divo SkyeNo ratings yet
- Immunity Vaccination: Public HealthDocument41 pagesImmunity Vaccination: Public HealthBaraa AbosamraNo ratings yet
- Zoology6thSem PDFDocument88 pagesZoology6thSem PDFRouf MalikNo ratings yet
- Disease and The Immune SystemDocument44 pagesDisease and The Immune SystemBaydaa Hameed Al AbdaliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument6 pagesImmunitySahir Seemab ZafarNo ratings yet
- Immunometabolism IDocument29 pagesImmunometabolism IMatheus TavaresNo ratings yet
- Ayan Das 16401722005 BO-303Document4 pagesAyan Das 16401722005 BO-303Ayan DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3futnariNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Midterm Notes 2Document67 pagesNCM 112 Midterm Notes 2ljealou2002No ratings yet
- Task 1. Concept Analysis and DiagramDocument4 pagesTask 1. Concept Analysis and Diagramkristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- L 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDDocument15 pagesL 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Disease and Immunity NotesDocument8 pagesDisease and Immunity NotesFaeequa nasrahNo ratings yet
- Immunity and Immunization ProgramDocument11 pagesImmunity and Immunization ProgramĦajra KhaŋNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument4 pagesImmunityMiran HussienNo ratings yet
- 57 64Document7 pages57 64Airah Fate BrunoNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction of ImmunologyDocument6 pages2.introduction of Immunologyvivena1464No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Properties and Overview of Immune ResponsesDocument45 pagesChapter 1 Properties and Overview of Immune Responses13701319477No ratings yet
- 40 Definitions BioDocument3 pages40 Definitions BioJustin JamesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Innate ImmunityDocument8 pagesLecture 1 Innate ImmunityOfficial NgareNo ratings yet
- Immune ResponsesintissueDocument22 pagesImmune ResponsesintissueFahim AhmadNo ratings yet
- Immunologic and Infectious DisordersDocument38 pagesImmunologic and Infectious Disordersdarla ryanNo ratings yet
- Acquired Imm and Infection - BPTDocument15 pagesAcquired Imm and Infection - BPTKathal 66No ratings yet
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- IS LessonDocument30 pagesIS Lessonjohn dale duranoNo ratings yet
- 4 Immune DisordersDocument11 pages4 Immune DisorderscedonuliNo ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Document41 pagesDasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Olivia NurudhiyaNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology - IntroductionDocument51 pagesImmunopharmacology - IntroductionIsrat Jahan Surovy 2225400672No ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology - Sep2022Document31 pagesIntroduction To Immunology - Sep2022Esther WanjukiNo ratings yet
- Host Defence..Document23 pagesHost Defence..Nagendrappa MalipatilNo ratings yet
- Inmune SystemDocument8 pagesInmune Systemfranciscarivera09No ratings yet
- Biology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFDocument21 pagesBiology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFMichael John LozanoNo ratings yet
- B & T Cells (Immunity) (23-3-11)Document1 pageB & T Cells (Immunity) (23-3-11)harrisonwhiteNo ratings yet
- L1 - IntroductionDocument5 pagesL1 - IntroductionMiles NsgNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Immune SystemDocument13 pagesLesson 6 Immune SystemBrent PatarasNo ratings yet
- Immunization New ContentDocument11 pagesImmunization New ContentkrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- W8 Immunology and ImmunizationDocument9 pagesW8 Immunology and ImmunizationJamie De LunaNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument31 pagesImmunityattiarph23No ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet