Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna Structure Glossary
Dna Structure Glossary
Uploaded by
FSM2010Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dna Structure Glossary
Dna Structure Glossary
Uploaded by
FSM2010Copyright:
Available Formats
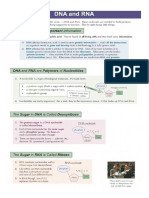
DNA STRUCTURE GLOSSARY
Term Definition/Explanation
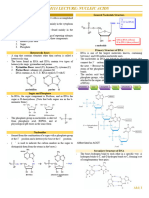
Deoxyribose
The pentose sugar that forms part of a nucleotide
Phosphate
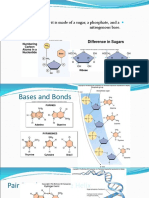
Nitrogenous These are the molecules that provide the “code” for DNA. They
Base do this by pairing with one another (G always pairs with C and
A always with T) to create a sequence of genetic information.
Purine Adenine and Guanine, These nitrogenous bases are two string
structures
Pyrimidine Cytosine and Thymine. Theses nitrogenous bases are single ring
structures
Phosphodiest The very strong covalent bond that a phosphate forms with two
er bond Deoxyribose sugars
Sugar The structure of alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate
Phosphate groups that forms the supporting structure of DNA
Backbone
Nucleotide The name for the combination of Phosphate a Deoxyribose
sugar and a nitrogenous base
Polynucleotid A strand of nucleotides (this is what DNA is constructed of)
e
Anti-Parallel The description of how one polynucleotide strand runs one way
while the other polynucleotide strand that makes up DNA runs
in the opposite direction
Helix A spiralling shape similar to that of a spring. DNA is structured
in a double helix.
Histone A protein which packages DNA so that it can be stored in the
nucleus of the cell.
Nucleosome A group of eight histones wrapped in linker DNA.
Chromatin This is made up of DNA and proteins. TI supercoils into
chromosomes prior to mitosis.
Exon The coding section of a gene
Intron The non-coding sections of a gene
3’ The Carbon atom which forms a bond with the phosphate
“down” the chain. It contains a Hydroxyl group
5’ The carbon atom which forms a bond with the phosphate “up”
the polynucleotide chain.
You might also like
- Cohort Critical AppraisalDocument5 pagesCohort Critical AppraisalViko Bagus LisephanoNo ratings yet
- Scanter 2001Document4 pagesScanter 2001anteysNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu General Ash7asc-W - 9710k1222Document16 pagesFujitsu General Ash7asc-W - 9710k1222Liuda Scutaru Zarisneac100% (2)
- Biology Nucleic A-Level OCR NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Nucleic A-Level OCR Notestbrook2017No ratings yet
- REPLICATIONDocument9 pagesREPLICATIONdineshNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) : - FemaleDocument4 pagesDNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) : - FemaleKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument46 pagesNucleic Acid - Britannica Online EncyclopediaBauza, Stephanie Dawn T.No ratings yet
- The Structure of DNADocument3 pagesThe Structure of DNAkalaysiahart01No ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5-GeneticsDocument9 pagesMODULE 5-GeneticsDivine Grace CincoNo ratings yet
- Remember It Is Made of A Sugar, A Phosphate, and A Nitrogenous BaseDocument26 pagesRemember It Is Made of A Sugar, A Phosphate, and A Nitrogenous BaseIbrahim EmadNo ratings yet
- Dna 053215Document13 pagesDna 053215Baninla NerusNo ratings yet
- Genetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Document20 pagesGenetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Hassan JavedNo ratings yet
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Document9 pagesDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument20 pagesFinals Reviewer20mintchocologistNo ratings yet
- 6.molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument62 pages6.molecular Basis of InheritanceSubhashakti BeheraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidAjagu ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science. Chapter 7Document21 pagesEarth and Life Science. Chapter 7veronicaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Document7 pagesWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA and RNA: StarterDocument24 pagesStructure of DNA and RNA: StarterChiara Manji100% (1)
- Molecular GeneticsDocument14 pagesMolecular GeneticsYitbarek TesfayeNo ratings yet
- NAT SCI 9 Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNAT SCI 9 Nucleic Acidskjgbitoon00125No ratings yet
- DNA Replication PDFDocument7 pagesDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidDocument33 pagesStructure and Function of Nucleic AcidLaiba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Om Prakash PPT BiologyDocument11 pagesOm Prakash PPT BiologyOm Prakash100% (1)
- 6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyDocument15 pages6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument50 pagesDNA StructureAngelo LucindoNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument62 pagesGenetic MaterialFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument31 pagesGenetic MaterialANBC- 24- Safa AfreenNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23Document3 pages3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23SiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Nucleic AcidsDocument62 pagesUnit 7 Nucleic AcidsGlory MuedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Suzette B. DoctoleroDocument67 pagesNucleic Acid: Suzette B. DoctoleroPojangNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiDocument14 pagesGenetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Replicationmeprabhatmishra99No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Fact SheetDocument1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheetasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Nucleic AcidsDocument19 pagesTopic 7 Nucleic AcidsSammy MicahNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument20 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritancetorin shahNo ratings yet
- Lecture. (1), Introduction & Structure of Nucleic AcidDocument64 pagesLecture. (1), Introduction & Structure of Nucleic Acidstudentactivity555No ratings yet
- 12 - Genetic CodeDocument19 pages12 - Genetic Codewhether913No ratings yet
- Share Xii-6-Molecular-Basis-Of-InheritanceDocument105 pagesShare Xii-6-Molecular-Basis-Of-InheritanceAman KumarNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Document29 pagesNucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Arslan AliNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument1 pageDna StructureAmirul ZackNo ratings yet
- Level of Structural OrganizationDocument15 pagesLevel of Structural OrganizationahmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Nucleic Acids Dna Genetic Code Transcription TranslationDocument16 pagesLecture 5 - Nucleic Acids Dna Genetic Code Transcription TranslationKendra SimonNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument54 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceLNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument3 pagesNucleic AcidSamraNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and ProteinDocument30 pagesDNA, RNA and Proteinsiti sarah amandaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisLaurence PriscillaNo ratings yet
- AS - Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesAS - Nucleic AcidsAraijan AbaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 DNA RNA Gen Structure Ade FKUI 2012Document44 pagesLecture 3 DNA RNA Gen Structure Ade FKUI 2012Faridah Yuwono 28No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and DiscoveryDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and Discoverybabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument8 pagesDna ReplicationIrma NeyraNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Rationalised 2023-24Document31 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance: Rationalised 2023-24Archana shuklaNo ratings yet
- Unit-9 Regression AnalysisDocument20 pagesUnit-9 Regression AnalysisPRASANT KUMAR SAMALNo ratings yet
- Mol Bio-DNA-bookbasedDocument8 pagesMol Bio-DNA-bookbasedElijah Mae MundocNo ratings yet
- 1 5kW Raum Energy System Specs 2009Document2 pages1 5kW Raum Energy System Specs 2009LucasZheNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Lead AcetateDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - Lead AcetateSwarnabha BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Database Design: Artificial, Composite, and Secondary UidsDocument17 pagesDatabase Design: Artificial, Composite, and Secondary UidsSladjan UgrenovicNo ratings yet
- List PPB Open 20221125Document8 pagesList PPB Open 20221125martaNo ratings yet
- Ceha PDFDocument17 pagesCeha PDFMIGUELNo ratings yet
- Steel Futures April 09Document4 pagesSteel Futures April 09whwy99No ratings yet
- PDMS Course SyllabusDocument3 pagesPDMS Course SyllabusBalu MuruganNo ratings yet
- 18 - Creating The Persistence Layer With TopLinkDocument42 pages18 - Creating The Persistence Layer With TopLinksuresh1130No ratings yet
- Power Tour Electric GuitarDocument12 pagesPower Tour Electric GuitarOmar SánchezNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of HVACDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment of HVACApurv Goyal100% (2)
- Kami Export - Jaden Mills - Angle VocabularyDocument3 pagesKami Export - Jaden Mills - Angle VocabularyJaden MillsNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesChristine SerranoNo ratings yet
- Joyseeker Tarot - Guidebook - SMDocument174 pagesJoyseeker Tarot - Guidebook - SMLinda100% (1)
- LBR JWB Sesi 1 - Medika Adijaya - 2021Document11 pagesLBR JWB Sesi 1 - Medika Adijaya - 2021NahmaKidsNo ratings yet
- 2020-21 Kps Summary FinalDocument5 pages2020-21 Kps Summary FinalWWMT100% (2)
- Antony Raj-ChennaiDocument1 pageAntony Raj-ChennaiRishap u.No ratings yet
- HiFly - A340 9H SUNDocument8 pagesHiFly - A340 9H SUNGustavo QueirozNo ratings yet
- A Discussion of The Life of Heinrich Friedrich Emil LenzDocument10 pagesA Discussion of The Life of Heinrich Friedrich Emil LenzJovan KuzmanovskiNo ratings yet
- Sex OnlineDocument15 pagesSex OnlineAlessandro ZarrellaNo ratings yet
- Kinds of ForgeryDocument24 pagesKinds of ForgeryQs DantesNo ratings yet
- Plastic Methods For Steel and Concrete StructuresDocument118 pagesPlastic Methods For Steel and Concrete Structurescall1986100% (1)
- The Strands That Are Woven Into Skilled WritingV2Document3 pagesThe Strands That Are Woven Into Skilled WritingV2Jeanine NyundoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 PSK DemodDocument18 pagesChapter 16 PSK DemodberkahNo ratings yet
- Student Affairs ResumeDocument6 pagesStudent Affairs Resumeusuoezegf100% (1)
- Diagonals of TilesDocument2 pagesDiagonals of TileskheyNo ratings yet
- Gender & Society 2Document7 pagesGender & Society 2John Roasa100% (1)
- Varivent Seat Valves Catalog 262492Document380 pagesVarivent Seat Valves Catalog 262492Thái Đạo Phạm LêNo ratings yet