Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Worth ITIL
Blood Worth ITIL
Uploaded by
mbahardeenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Worth ITIL
Blood Worth ITIL
Uploaded by
mbahardeenCopyright:
Available Formats
Defining Effective ITIL Key Performance Indicators
By Diane Bloodworth and David Herron
The success of a process improvement initiative is dependent upon four key factors. First,
there must be a reason for initiating the improvement activity. This usually takes the form
of a business case focused on objectives relating reducing costs, improving delivery, and
improving quality. Second, a well thought out plan of action needs to be developed. An
action plan highlights timeframes, priorities, deliverables and risks. Next, the proper
resources need to be committed to the achievement of the improvement program’s goals
and objectives. This commitment should be made at the senior manager level. And
finally, there needs to be a clear set of measures that can be used to monitor progress and
track the achievement of the stated goals and objectives of the program.
In this article we will discuss an approach to defining effective Key Performance
Indicators (KPIs) in support of the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL).
ITIL is a set of best practices improvement framework focused on the management of IT
service processes. The purpose of ITIL is to promote quality and efficiency in the use of
IT by aligning IT services with business needs thereby improving the quality of IT
services and reducing the long-term cost of IT services. Service Management is one of
the best practices areas within the ITIL framework. Service Management is composed of
ten practice areas divided into two primary groups – Service Delivery and Service
Support. It is within these ten practice areas that we will discuss the need for Key
Performance Indicators that align with service and business (organization) measures and
the process used for establishing these measures.
Role of Measurement in Process Improvement
As noted earlier, one of the success factors for a process improvement initiative is having
the ability to measure outcomes. The ITIL framework is focused on providing services
that are supported by computer systems that require the maintenance of both the software
and hardware so as to have a minimal impact on the business. Therefore a quantifiable set
of measures needs to be established that will identify the performance and behavior of the
ITIL practice areas that support Service Management.
Guiding the IT organization towards improved Service Management practices using the
ITIL framework is a process improvement journey. Therefore this improvement process
is an ongoing activity and as such the Key Performance Indicators are being established
to monitor and guide the continued improvement of the various practice areas. They are
established so as to identify when goals and objectives are met. However, they should
also serve the purpose of guiding and directing activities as practices areas are being fine
tuned to continuously improve.
© 2007 David Consulting Group Page 1 February 2007
Measurement Practices Within the ITIL Framework
Identifying the appropriate measures, creating a process for collecting and analyzing the
data and effectively using the results to guide and direct continued improvement are
essential to establishing a successful measurement process.
The following is an outlined approach for implementing ITIL. There are four phases. The
essential activities for each phase are identified. Within each phase the measurement
activity necessary to create, analyze and report on KPIs has also been identified.
The “Initiate” Phase.
• Define the scope of the ITIL effort; includes the groups, functions, and processes
that are targeted and included in the effort.
• Link the ITIL objectives to the organization’s business objectives.
• Define the success criteria for the ITIL initiative – ‘How will we know that we
have achieved success?’
• KPI Measurement activity – Define priorities
Determine quality parameters
Establish value criteria
Business case or ROI for implementing ITIL
The “Assess” Phase.
• Document a description of the Current State for the functions or processes that are
included in the scope of the ITIL effort.
• Identify the Desired Future State by comparing the Current State to the Best
Practices in ITIL.
• Report strengths as well as gaps or weaknesses that should be addressed.
• KPI Measurement activity – Baseline performance
Evaluate performance
Identify supporting data
Identify data gaps
The “Plan” Phase.
• Plan improvements for the Gaps from the Assess Phase based on the
organization’s timeline and available resources.
• KPI Measurement activity – Develop measurements
Define metrics
Develop Measurement collection process
The “Implement” Phase.
• Designed, developed, and rolled out the future state solution.
• Determine if the success criteria has been achieved.
• KPI Measurement activity – Evaluate information
Id process impacts
Define improvements
© 2007 David Consulting Group Page 2 February 2007
Creating Key Performance Indicators
To define meaningful KPI measures that align with the goals of the organization, the
following questions need to be asked:
• What are the business / organization measures?
• How do these translate into IT service measures?
• How does a process support the IT service measures?
• How will I collect and analyze the measure?
Noted below we have included an example of KPI measures and the corresponding
definitions and goals.
Process Goal (Critical Measure Measurement
Success Factor) Definition Architecture
Service Level Improve ability to Percentage increase Tracked through
Management track and meet or decrease in Incident
service levels meeting service level Management and
agreed to with targets reported monthly
client
Change Reduce incidents Percentage reduction Tracked through
Management caused by in the number of Incident
unauthorized incidents resulting Management and
changes from unauthorized Change
changes Management and
reported monthly
Effectively Using Key Performance Indicators
Once the measures are defined and linked to the various business goals the focus of the
measurement activity is on the measurement process itself. How the data is going to be
collected, analyzed and reported needs to defined. The measurement program will
identify the sources of data and who is responsible for the measurement activity. The
overall intent is to use the measures to evaluate and improve the processes.
The KPIs should provide insight into:
1. Quality – How well is the process working? Are we improving toward goals that
were established for this process?
2. Efficiency – Is the throughput of the process sufficient?
3. Compliance – Is the process being followed?
4. Value – Are we doing what we are supposed to be doing?
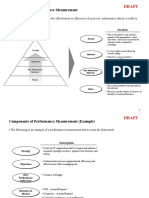
An overview of the measurement activity is noted below.
© 2007 David Consulting Group Page 3 February 2007
Establish Metrics
Goals
Develop
Measures and
Processes
Define Priorities Baseline
Determine Quality Performance
Parameters
Identify KPIs
Establish value Improvement
criteria Develop measurements
Define metrics Initiatives
Identify supporting data
Identify data gaps Benchmark model Scorecard
Evaluate performance
Develop measurement
collection processes
Evaluate information
Id process impacts
Evaluate performance Clarify criteria
Evaluate alignment Define relationship
Communicate improvements
achievement
Improve model
In Summary
Defining and establishing effective ITIL Key Performance Indicators requires a rigorous
measurement process. As the ITIL framework is being planned and implemented KPIs
are being defined in parallel. The measures must support the needs of the business and
provide insight as to how the various improvement processes within ITIL are performing.
Along with the ITIL framework, a well defined measurement activity must be
established.
© 2007 David Consulting Group Page 4 February 2007
You might also like
- Key Performance Indicators For Internal Audit FunctionDocument10 pagesKey Performance Indicators For Internal Audit FunctionarfianNo ratings yet
- KPIs ImplementationDocument30 pagesKPIs Implementationtelegwana flow100% (3)
- ITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5Document38 pagesITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5danrodd100% (1)
- 2.2 Performance Management System (Part 2)Document41 pages2.2 Performance Management System (Part 2)nashwaelsayedq2020No ratings yet
- KPI: Individual Performance To Make Organization GreatDocument28 pagesKPI: Individual Performance To Make Organization GreatMetoo ChyNo ratings yet
- ITIL - Foundation NewDocument155 pagesITIL - Foundation NewAnonymous zWUrYoc2VNo ratings yet
- Performance Kpi MetricsDocument16 pagesPerformance Kpi MetricsNausheen Fatima100% (1)
- Jorge Higueros - Making KPIs Component Work For You With NagiosDocument48 pagesJorge Higueros - Making KPIs Component Work For You With Nagiosmohamed_abueiss9815100% (1)
- Performance MeasurementDocument12 pagesPerformance Measurementharshit kasliwal100% (4)
- ISO 9001:2008 Quality Management System TrainingDocument46 pagesISO 9001:2008 Quality Management System Trainingprafull26No ratings yet
- KPI Approach For EG v1.0Document5 pagesKPI Approach For EG v1.0Ashish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Optimizing For Success Metrics For Enterprise ITDocument16 pagesOptimizing For Success Metrics For Enterprise ITOdira MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Group 12 CBMEDocument42 pagesGroup 12 CBMEReynaNo ratings yet
- Quality Management & Iso 9001 Standard: Aim Single Ecar Qms - 14 MARCH, 2016 (ANTIGUA)Document69 pagesQuality Management & Iso 9001 Standard: Aim Single Ecar Qms - 14 MARCH, 2016 (ANTIGUA)EllieNo ratings yet
- SCM - 16 - Performance MeasurementDocument28 pagesSCM - 16 - Performance MeasurementVishesh khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PerfMetricsDocument82 pagesModule 3 PerfMetricsBalaji SekarNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis From Theoretical To Implementation Using Excel, Python and FlourishDocument25 pagesData Analysis From Theoretical To Implementation Using Excel, Python and Flourishmohamed100% (1)
- Quality Management System RequirementsDocument70 pagesQuality Management System RequirementsinfojavedNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument35 pagesBalanced ScorecardAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Metrics Framwork RolloutDocument6 pagesMetrics Framwork RolloutAashirtha SNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Strategy Evaluation - Implementation and BSCDocument25 pagesModule 5 Strategy Evaluation - Implementation and BSCSidharth ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- United International University: Key Performance IndicatorDocument13 pagesUnited International University: Key Performance IndicatorRazaul IslamNo ratings yet
- 3.2 KPI Typology & Taxonomy (Paert 2)Document42 pages3.2 KPI Typology & Taxonomy (Paert 2)nashwaelsayedq2020No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Performance ManagementDocument33 pagesSupply Chain Performance ManagementDebashishDolon100% (1)
- Internal Audit Key Performance IndicatorsDocument21 pagesInternal Audit Key Performance IndicatorsHenry James Nepomuceno100% (1)
- Control of Management Reviews Procedure Sample PDFDocument4 pagesControl of Management Reviews Procedure Sample PDFMadan R HonnalagereNo ratings yet
- Key Performance Indicators Fast Easy OverviewDocument20 pagesKey Performance Indicators Fast Easy Overviewcarte_blueNo ratings yet
- BA DeptDocument14 pagesBA DeptAnirban GhoshNo ratings yet
- 5.2 CSI Process (E Next - In)Document24 pages5.2 CSI Process (E Next - In)Saurabh YadavNo ratings yet
- IT Management Development Center (IT-MDC) : Sesi 11: Continual Service ImprovementDocument33 pagesIT Management Development Center (IT-MDC) : Sesi 11: Continual Service ImprovementAhmad Abdul Haq100% (1)
- Basics of BSCDocument34 pagesBasics of BSCSushma SelaNo ratings yet
- Continual Service ImprovementDocument22 pagesContinual Service ImprovementShierdy Lynn E. NorialNo ratings yet
- Improved Quality Decreased Costs Fewer Mistakes and Delays Better Use of ResourcesDocument26 pagesImproved Quality Decreased Costs Fewer Mistakes and Delays Better Use of ResourcesAnup MeshramNo ratings yet
- Standard MS ISO 9001 2015Document54 pagesStandard MS ISO 9001 2015ras defgNo ratings yet
- Ims (3)Integrated Management System ImplementationDocument68 pagesIms (3)Integrated Management System ImplementationJustin B NickafNo ratings yet
- TWP BP For Stats Gather 12c 1967354Document46 pagesTWP BP For Stats Gather 12c 1967354ZarunKumarNo ratings yet
- Business FoundationDocument71 pagesBusiness FoundationBrian FurmanNo ratings yet
- Irqb Guideline 1 Kpi Final VersionDocument16 pagesIrqb Guideline 1 Kpi Final VersionDelong KongNo ratings yet
- HR Scorecard 2 - BSC OverviewDocument59 pagesHR Scorecard 2 - BSC Overviewphilip_kockNo ratings yet
- Measuring ITSM - Are Your Processes Making The GradeDocument17 pagesMeasuring ITSM - Are Your Processes Making The GradeMoe SulimanNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 CSI - Continual Service ImprovementDocument4 pagesITIL V3 CSI - Continual Service ImprovementAbdul Salam NMNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar SCM 13Document18 pagesBahan Ajar SCM 13Budy AriyantoNo ratings yet
- KPI (Key Performance Indicators)Document5 pagesKPI (Key Performance Indicators)ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Itil V3Document138 pagesItil V3Saurav TripathyNo ratings yet
- Chp. 11 Performance Measurement FIXDocument25 pagesChp. 11 Performance Measurement FIXKevin SijabatNo ratings yet
- Internal Quality Audit trainingDocument122 pagesInternal Quality Audit trainingmelkamu tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Construction Performance and Resource Optimization Chapter One Overview of Construction Performance ManagementDocument62 pagesConstruction Performance and Resource Optimization Chapter One Overview of Construction Performance Managementhaile mulunehNo ratings yet
- 6 ISO 9000 ImplementationDocument30 pages6 ISO 9000 ImplementationIgnou DelhiNo ratings yet
- Webinar-1. Understanding Japanese Management - A Tale of Three Gemba (Watson, 2021)Document59 pagesWebinar-1. Understanding Japanese Management - A Tale of Three Gemba (Watson, 2021)taghavi1347No ratings yet
- KPI's TrainingDocument29 pagesKPI's TrainingMohamed Hadjkacem100% (3)
- TQMSix Sigma LeanDocument82 pagesTQMSix Sigma Leanamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Guia Implantacion ISO 9001 2015Document12 pagesGuia Implantacion ISO 9001 2015Angelo Max Macarlupú ChavezNo ratings yet
- C KpiDocument6 pagesC KpivortegabNo ratings yet
- Performance Management, Evaluation, and Data AnalysisDocument24 pagesPerformance Management, Evaluation, and Data AnalysiscandraNo ratings yet
- Performance Measurement: Lesson StructureDocument9 pagesPerformance Measurement: Lesson StructureAnkur DhirNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Implementation GuideDocument12 pagesISO 9001 Implementation GuideKalish kumarNo ratings yet
- Ey Financial Process AnalyticsDocument20 pagesEy Financial Process AnalyticsccmehtaNo ratings yet
- Streamline Success: Harness the Power of Flowcharts to Develop Relevant KPIsFrom EverandStreamline Success: Harness the Power of Flowcharts to Develop Relevant KPIsNo ratings yet