Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscle Ion Table
Muscle Ion Table
Uploaded by
Meredith BarbOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Muscle Ion Table
Muscle Ion Table
Uploaded by
Meredith BarbCopyright:
Available Formats
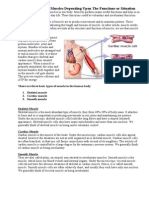
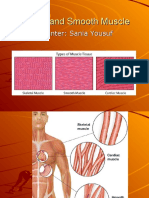
CHARACTERISTIC
SKELETAL Long, thin and cylindrical; also called muscle fibers; do NOT divide, new fibers are produced by stem cells called satellite cells- (not branched like cardiac)
CARDIAC Cardiac muscle cells are called cardiocytes; branching cells attached at intercalated discs -also called myocardium
SMOOTH Obviously different from skeletal and cardiacsmooth muscle cells are spindle shaped (small and tapered) and can divide
Cells
Striation (banded appearance) Number of Nuclei Controlled Voluntarily or Involuntarily
Obviously striated (myosin and actin help to Striated give muscle this appearance) Multinucleate (nuclei often pushed to edge) Uni- or binucleate Voluntary (conciously controlled)
None Uninucleate
Involuntary Involuntary (ANS) -no innervation is needed, -does not normally contract without the except for the regulation of rate, influence of nervous stimulation contractile strength because the myocardium has inherent -mainly innervated by the Somatic Nervous contractility (SA Node System (?) pacemaker) -while it can be stimulated to contract via the ANS, it doesnt need nervous stimulation and can contract rhythmically without it meat or flesh of body attached to skeletonFound only in heart; cardiocytes spindle-shaped cells with central forming large body muscles responsible for form a branching network at nuclei arranged closely to form body movements such as walking, also intercalated discsallow sheets support joints muscle cells to act as a unit - 40% of body mass in normal adults Moves limbs or other external body parts As it contracts, the heart acts as Typically has two layers running at a pump propelling the blood intoright angles to each other; thus its the blood vessels contraction can constrict or dilate the lumen (cavity) of an organ and propel substances along predetermined pathways Heart only Smooth musclealso called visceral muscle is found mainly in the walls of hollow organs (digestive and urinary tract organs, uterus and blood vessels)
Description
Result of Contraction
Location
In skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally to skin
You might also like
- CPT Top 500 Codes OB/GYN - Women's HealthDocument2 pagesCPT Top 500 Codes OB/GYN - Women's HealthMeredith Barb40% (10)
- Lab Manual SCOA 20 21Document37 pagesLab Manual SCOA 20 21Anuj Padmawar0% (1)
- Types of MusclesDocument1 pageTypes of Musclesapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Study GuideDocument11 pagesMedical Terminology Study GuideMeredith Barb100% (3)
- Cichlids From MadagascarDocument6 pagesCichlids From MadagascarderfalkeNo ratings yet
- Smooth and Cardiac MusclesDocument16 pagesSmooth and Cardiac MusclesNzau MuangeNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument11 pagesMuscle TissuemikkaNo ratings yet
- MuscularDocument33 pagesMusculargabriel joshua marronNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument23 pagesMuscular SystemAland BakrNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 pagesThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- Muscular System - TerminadoDocument2 pagesMuscular System - TerminadoCRISTOBAL JAVIER LOPEZ ALISTENo ratings yet
- Muscle Contraction: Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument44 pagesMuscle Contraction: Cardiovascular PhysiologyAira BellenNo ratings yet
- Muscular System AnatomyDocument23 pagesMuscular System Anatomymichaelryann madayagNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscles: Skeletal Muscles Are Attached Mainly To The Skeletal Bones But Some AreDocument1 pageTypes of Muscles: Skeletal Muscles Are Attached Mainly To The Skeletal Bones But Some Arehyttg thyNo ratings yet
- Ana 221 Muscle TissueDocument12 pagesAna 221 Muscle TissueAmadi CedarNo ratings yet
- Compact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesDocument27 pagesCompact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Muscular TissueDocument3 pagesStructure and Functions of Muscular TissueSheba Victoria RabagoNo ratings yet
- Muscles EngDocument3 pagesMuscles Engkaneki.ghoul1710No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesMuscular Systemchristianoliver.aceroNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: BFKT Ii Group 1 Alexandru Ioana Liana Avram Camelia Elena Barbu Alexandru Andrei Ioan-TeodorDocument3 pagesMuscular System: BFKT Ii Group 1 Alexandru Ioana Liana Avram Camelia Elena Barbu Alexandru Andrei Ioan-TeodorIulia ValentinaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)Document38 pagesSistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Muscular System 4Document4 pagesSummary of Muscular System 4api-253866502100% (1)
- HAP Lesson 3 (Muscular System)Document33 pagesHAP Lesson 3 (Muscular System)rodolfogallineroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 The Muscular SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 6 The Muscular Systemrafaelarmildez02No ratings yet
- ANA205 Muscular Tissue: Lecture Notes by Dr. Taiwo-OlaDocument31 pagesANA205 Muscular Tissue: Lecture Notes by Dr. Taiwo-OlaIbrahim BabatundeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Muscles Depending Upon The Functions or SituationDocument1 pageClassification of Muscles Depending Upon The Functions or SituationSyed Bilal HussainNo ratings yet
- 副本 - Classification of musclesDocument31 pages副本 - Classification of musclesTan Ting WeiNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument41 pagesMuscular SystemGem Rose UretaNo ratings yet
- E. Muscular System RevisedDocument41 pagesE. Muscular System RevisedGenelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument101 pagesMuscular Systemsheryl dungogNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth Muscle Cells-Myasthenia Gravis, Muscular Dystrophy and MyotoniaDocument51 pagesDisorders of Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth Muscle Cells-Myasthenia Gravis, Muscular Dystrophy and MyotoniaCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesWEEK 6 Muscular SystemMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Naw TrainingDocument34 pagesNaw Trainingganesh pNo ratings yet
- Cardiac and Smooth MusclesDocument15 pagesCardiac and Smooth MusclesDr Muhammad Abdul QadirNo ratings yet
- ArteriesDocument3 pagesArteriesShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Muscular SyastemDocument28 pagesMuscular SyastemKaizen Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Types of MusclesDocument1 pageTypes of Musclesapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Muscles: Skeletal MuscleDocument12 pagesMuscles: Skeletal MuscleLee Angelo BorbeNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System-251606Document8 pagesThe Muscular System-251606sselt gayNo ratings yet
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument22 pagesMuscular TissueZidane LassaadNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue and Nervous TissueDocument5 pagesMuscle Tissue and Nervous TissueChristine Angela ManguiatNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesThe Muscular SystemMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Reading: I. Brainstorm The Cloud Words Related To The Word Muscle'. How Do They Interact With Each Other?Document4 pagesPre-Reading: I. Brainstorm The Cloud Words Related To The Word Muscle'. How Do They Interact With Each Other?Victoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Nerve HistoPHysioDocument91 pagesMuscle and Nerve HistoPHysioashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesWEEK 6 Muscular SystemMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- How To Form A Healthy Lifestyle and Muscle GroupsDocument14 pagesHow To Form A Healthy Lifestyle and Muscle GroupsRhea SmithNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology Chapter 4 - EndDocument172 pagesHuman Physiology Chapter 4 - EndEmebet DebissaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsDocument4 pagesThe Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsNeil AdelanNo ratings yet
- Muscular System 101Document21 pagesMuscular System 101Rida IshaqNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 Unit1 Chapter2 (Animal Cells) 1Document26 pagesGenbio1 Unit1 Chapter2 (Animal Cells) 1Sofia EgbalicNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular Systemmary jane ventuleroNo ratings yet
- Katherine Pinto - Josué Zambrano: IntegrantesDocument12 pagesKatherine Pinto - Josué Zambrano: Integranteskatherinepinto673No ratings yet
- ANAPHY Overview of The SystemDocument56 pagesANAPHY Overview of The SystemLalajimNo ratings yet
- Reagan Body Systems Booklet 3-13Document76 pagesReagan Body Systems Booklet 3-13api-26963416No ratings yet
- The Muscular System NewDocument11 pagesThe Muscular System Newapi-338929411No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 1 13Document13 pagesIlovepdf Merged 1 13Abdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemMichelle Ann DomagtoyNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesMuscle TissueHesbone AneneNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument19 pagesThe Muscular SystemRETLAWNo ratings yet
- 04 Muscle 2022Document39 pages04 Muscle 2022AlkadafeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyFrom EverandAnatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Insulin PharmDocument21 pagesInsulin PharmMeredith Barb0% (1)
- Scribd PDF - Diabetic Teach PlanDocument7 pagesScribd PDF - Diabetic Teach PlanMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document23 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 2Jennifer CastilloNo ratings yet
- Take Charge of Your Diabetes: What About Medical Treatment?Document2 pagesTake Charge of Your Diabetes: What About Medical Treatment?Meredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Most Common Skin RashesDocument5 pagesDermatology Most Common Skin RashesMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity in Perspective: Starr/Taggart's BiologyDocument34 pagesBiodiversity in Perspective: Starr/Taggart's BiologyMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Common Skin RashesDocument8 pagesDermatology Common Skin RashesMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Common Skin RashesDocument5 pagesDermatology Common Skin RashesMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Meredith Barb Homework-2 (25 Points) Due On Sept. 24 by 5:00pmDocument5 pagesMeredith Barb Homework-2 (25 Points) Due On Sept. 24 by 5:00pmMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Degree PresentationDocument2 pagesDegree PresentationMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Social Interactions: Starr/Taggart's BiologyDocument37 pagesSocial Interactions: Starr/Taggart's BiologyMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Standard: Halâl Agriculture and Fisheries ProductsDocument26 pagesPhilippine National Standard: Halâl Agriculture and Fisheries ProductsGaily HontiverosNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1257) Willem F. Wolkers, Harriëtte Oldenhof (Eds.) - Cryopreservation and Freeze-Drying Protocols-Springer-Verlag New York (2015)Document505 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 1257) Willem F. Wolkers, Harriëtte Oldenhof (Eds.) - Cryopreservation and Freeze-Drying Protocols-Springer-Verlag New York (2015)Sebastián Lescano100% (1)
- Feminism and Gender - Making Anthropology PublicDocument9 pagesFeminism and Gender - Making Anthropology PublicPearl SkyNo ratings yet
- Nsca - Cscs QuestionsDocument2 pagesNsca - Cscs QuestionsKhaled Salhi100% (1)
- Jurnal Morfometrik, Meristik Dan Pola Pertumbuhan Ikan JULUNG-JULUNG (Hemirhamphodon Pogonognathus Bleeker, 1865) Dari Perairan Umum Universitas RiauDocument17 pagesJurnal Morfometrik, Meristik Dan Pola Pertumbuhan Ikan JULUNG-JULUNG (Hemirhamphodon Pogonognathus Bleeker, 1865) Dari Perairan Umum Universitas RiauGhefira NabilahNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers of PDDocument14 pagesBiomarkers of PDAmey MoreNo ratings yet
- NSEC Solved Paper 2012Document19 pagesNSEC Solved Paper 2012swapnil narayanNo ratings yet
- The Neuronal EnvironmentDocument428 pagesThe Neuronal EnvironmentPandaNo ratings yet
- NITROSAMINESDocument10 pagesNITROSAMINESRicha Arora100% (1)
- Kuliah Rickets PBLDocument43 pagesKuliah Rickets PBLNovasuryatiNo ratings yet
- 2013 DegradationDocument15 pages2013 Degradationratna cempaka linggaNo ratings yet
- Ginantara Ecoturism MangroveDocument12 pagesGinantara Ecoturism MangroveC2-89Henricus Rotarius Octavianus TariganNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of KoranDocument12 pagesThe Healing Power of Koranzahrein100% (6)
- Controversies in BiotechnologyDocument25 pagesControversies in BiotechnologyXian LeeNo ratings yet
- Plant RootsDocument4 pagesPlant Rootsjamjamae100% (3)
- BPak's MI40-X - CEP Training BlueprintDocument22 pagesBPak's MI40-X - CEP Training BlueprintJose Rincon75% (8)
- Mki 012Document4 pagesMki 012Sinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Yacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211Document5 pagesYacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211joeyacomine100% (1)
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell Sixth EditionDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell Sixth EditionMarie Villar100% (35)
- Nutrition in Plants Edexcel IGCSEDocument7 pagesNutrition in Plants Edexcel IGCSETZ AZNo ratings yet
- Behaviour and Ecology of The Ethiopian Wolf CanisDocument10 pagesBehaviour and Ecology of The Ethiopian Wolf CanisLelna NegaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Class 7TH ScienceDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Class 7TH ScienceGeeta BhattNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyDocument20 pagesUNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyHarsh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Merus Ring - Water Booklet PDFDocument14 pagesMerus Ring - Water Booklet PDFAmey Dhaygude100% (1)
- My Cvfor PrintDocument3 pagesMy Cvfor PrintUkwuma Michael ChijiokeNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Handling Filamentous and Viscous Wastewater SludgeDocument7 pagesChallenges of Handling Filamentous and Viscous Wastewater SludgeAlexNo ratings yet
- Samal GenesisDocument6 pagesSamal GenesisfordmayNo ratings yet
- Faces of Biophilia in Contemporary TurkishDocument108 pagesFaces of Biophilia in Contemporary TurkishBuse AslanNo ratings yet