Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immunity
Immunity
Uploaded by
Hi HelloOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Immunity
Immunity
Uploaded by
Hi HelloCopyright:
Available Formats
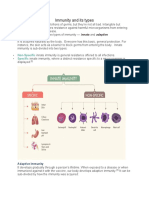
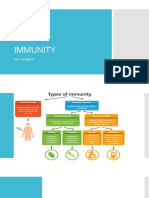
Immunity to be insusceptible or unaffected by a particular disease or condition.
the body s specific response/defense to particular substances, toxins, cells, proteins which the body perceives as foreign. 2 classifications: i) Natural Immunity ii) Artificial Immunity 4 types: Naturally acquired passive immunity Maternal passive immunity is a type of naturally acquired passive immunity, and refers to antibody-mediated immunity conveyed to a fetus by its mother during pregnancy Artificially acquired passive immunity see also: Temporarily-induced immunity Artificially acquired passive immunity is a short-term immunization induced by the transfer of antibodies, which can be administered in several forms; as human or animal blood plasma, as pooled human immunoglobulin for intravenous (IVIG) or intramuscular (IG) use. passive immunization lasts for only a short period of time, Naturally acquired active immunity For more details on this topic, see Immune system. Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when a person is exposed to a live pathogen, and develops a primary immune response, which leads to immunological memory. Artificially acquired active immunity Main articles: artificial induction of immunity and vaccination Artificially acquired active immunity can be induced by a vaccine, a substance that contains antigen. A vaccine stimulates a primary response against the antigen without causing symptoms of the disease.
You might also like
- Biologics 2 PDFDocument24 pagesBiologics 2 PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Immuno AssgtDocument2 pagesImmuno Assgtapi-3727388No ratings yet
- Immunity: Immunity Is The Balanced State ofDocument1 pageImmunity: Immunity Is The Balanced State ofCarolina GasperNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument17 pagesImmunityNAVEEN DHIMANNo ratings yet
- Acquired Imm and Infection - BPTDocument15 pagesAcquired Imm and Infection - BPTKathal 66No ratings yet
- KhelangbarDocument64 pagesKhelangbargayatri.murasingNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 Infection and Host Resistance PDFDocument22 pagesMODULE 3 Infection and Host Resistance PDFVillanueva, AbegailNo ratings yet
- Overview of Immunity and Its Different TypesDocument11 pagesOverview of Immunity and Its Different TypesPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument9 pagesImmunologyNivedita DasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 Specific Host Defense MechanismsDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 16 Specific Host Defense MechanismsedemcantosumjiNo ratings yet
- (PPT) DPC 1.4.2 Immunity and Disease - Dr. Cabanos PDFDocument83 pages(PPT) DPC 1.4.2 Immunity and Disease - Dr. Cabanos PDFJennifer Pisco LiracNo ratings yet
- Acquired Immunity: Dr. Mejbah Uddin AhmedDocument13 pagesAcquired Immunity: Dr. Mejbah Uddin Ahmedapi-19969058No ratings yet
- Immunity and Immunization ProgramDocument11 pagesImmunity and Immunization ProgramĦajra KhaŋNo ratings yet
- Immunity and Its TypesDocument3 pagesImmunity and Its TypesBenazir SheikhNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGICS LectureDocument36 pagesBIOLOGICS LectureRao Salman LatifNo ratings yet
- EPI Lesson TwoDocument10 pagesEPI Lesson Twomaryanruuney1212No ratings yet
- 2.0 Principles of Immunology and Immunization - April 20 2018Document13 pages2.0 Principles of Immunology and Immunization - April 20 2018Ranjan YadavNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITY - 5th FormDocument21 pagesIMMUNITY - 5th FormKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- KhelangbarDocument63 pagesKhelangbargayatri.murasingNo ratings yet
- Ayan Das 16401722005 BO-303Document4 pagesAyan Das 16401722005 BO-303Ayan DasNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument31 pagesImmunityattiarph23No ratings yet
- Types of Immunity: Presented byDocument12 pagesTypes of Immunity: Presented byGayathri deviNo ratings yet
- Immunity NewDocument17 pagesImmunity NewWijesiri D WNo ratings yet
- Comment On The Following ProverbsDocument4 pagesComment On The Following ProverbsArina CucuruzaNo ratings yet
- Immunity Vaccination: Public HealthDocument41 pagesImmunity Vaccination: Public HealthBaraa AbosamraNo ratings yet
- Micro Assignment Unit 3 Group BDocument12 pagesMicro Assignment Unit 3 Group Bnabeelpatras19No ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)Andhy Andha Dhyan HardhyantiNo ratings yet
- Immune System (Inn & Adapt)Document53 pagesImmune System (Inn & Adapt)Bushra Khan100% (1)
- Acquired Immunity - Edited.editedDocument4 pagesAcquired Immunity - Edited.editedMavokeNo ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)DindaalifiahNo ratings yet
- H.S.Z.H Govt (Autonomous) Unani Medical College Bhopal: Immunity and Immunization ScheduleDocument18 pagesH.S.Z.H Govt (Autonomous) Unani Medical College Bhopal: Immunity and Immunization ScheduleĦajra KhaŋNo ratings yet
- Infectious Epidemiology 2Document76 pagesInfectious Epidemiology 2Myself HereNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ImmunityDocument6 pagesAdaptive ImmunityAvinash SahuNo ratings yet
- MicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionDocument11 pagesMicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionRaven Joyce LabayenNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument3 pagesMICROBIOLOGYbritishsam57No ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument59 pagesImmunologyImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Active ImmunityDocument1 pageActive ImmunityshaliniNo ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)Dinda FirdasariNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument72 pagesImmunityAARYANo ratings yet
- A. ImunitasDocument1 pageA. Imunitasbaiq elmalia mislah putriNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument24 pagesImmunityrekha dehariyaNo ratings yet
- Innate Immunity: Is Present at The Time of Birth. There Are 4 Types of Barriers Present inDocument2 pagesInnate Immunity: Is Present at The Time of Birth. There Are 4 Types of Barriers Present inSTEFFY MARY JOHNSON 2031844No ratings yet
- Types of ImmunityDocument13 pagesTypes of ImmunityKailash Nagar100% (3)
- Zoology6thSem PDFDocument88 pagesZoology6thSem PDFRouf MalikNo ratings yet
- 9-3-23 Immunity, Epi, Disease Control, Delivered Lec by DR Shumaila Humayun, 09-03-23Document65 pages9-3-23 Immunity, Epi, Disease Control, Delivered Lec by DR Shumaila Humayun, 09-03-23Dr Sarah Bakhsh - Resident FCPS Community MedicineNo ratings yet
- Immunoprophylaxis and Immunotherapy: Dr. Mejbah Uddin AhmedDocument19 pagesImmunoprophylaxis and Immunotherapy: Dr. Mejbah Uddin Ahmedapi-19969058No ratings yet
- Che 224 Immunity and ImmunizationDocument54 pagesChe 224 Immunity and ImmunizationAbdullahi Bashir SalisuNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW CDC Govvaccinespubspinkbookdownloadsprinvac PDFDocument8 pagesHTTPSWWW CDC Govvaccinespubspinkbookdownloadsprinvac PDFSubash KhatiwadaNo ratings yet
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyArpita MishraNo ratings yet
- Acquired ImmunityDocument22 pagesAcquired ImmunityWilliam C ChishaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument41 pagesIntroductionworknehbethanyNo ratings yet
- l3 Immunization & Cold ChainDocument53 pagesl3 Immunization & Cold ChainNur AinaaNo ratings yet
- l2.1 Immunization Cold ChainDocument53 pagesl2.1 Immunization Cold Chainsinuaish syaNo ratings yet
- Virology Lecture 6 ImmunityDocument14 pagesVirology Lecture 6 Immunityao868598No ratings yet
- Immunity and Immunization, Vaccines and Their Role in Prevention of DiseaseDocument14 pagesImmunity and Immunization, Vaccines and Their Role in Prevention of Diseaseshivani.priyaNo ratings yet
- AQA Vaccinations - AS Level BiologyDocument3 pagesAQA Vaccinations - AS Level BiologymonkeysaltaccNo ratings yet
- Immunological Aspect of ImmunizationDocument18 pagesImmunological Aspect of ImmunizationDavid ChristianNo ratings yet
- Types of ImmunityDocument35 pagesTypes of ImmunityKailash NagarNo ratings yet