Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Or Tho
Or Tho
Uploaded by
dentist40Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Or Tho
Or Tho
Uploaded by
dentist40Copyright:
Available Formats
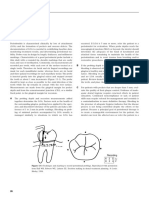
Fig. 115 Cephalometric landmarks and lines for Caucasians.
are then drawn between some of these landmarks. The angles between these can then be compared with standard values to indicate facial skeletal variations from normal. Digital photographic images may also be superimposed on the radiographic images and surgical predications carried out with the computer software. Typical Caucasian measurements are:
SNA SNB ANB
Clinical box Typical diagnosis for a dentofacial anomaly Class III skeletal relationship owing to both prognathic mandible and hypoplastic maxilla. Lower facial height increased. Competent lips and large tongue. Prominent nose and normal ears. Class III occlusal relationship with spaced lower incisors. Narrow maxillary intercanine width. All first molar teeth restored. No other restorations. Oral hygiene poor.
81 3 78 3 3 2
An ANB difference in a Negro patient of 5 is acceptable whereas in Oriental patients 3 or less is normal.
Diagnosis
For dentofacial anomalies, the diagnosis will describe the maxillary and mandibular base relationship relative to the skull together with a description of the dental occlusion and comments about general condition of the dentition and oral hygiene. The mandible and maxilla may be described as prognathic, hypoplastic or asymmetrical. The effect of these may be to produce a long face, open bite or short face. The chin may also be described using various classifications of excess (macrogenia),
hypoplasia (microgenia) and asymmetry. For craniofacial anomalies, the diagnosis will also describe the orbits, eyes, ears and other features and may suggest various syndromes in a differential diagnosis.
Treatment planning
Treatment planning usually consists of: 1. Preoperative orthodontic management to move teeth into a position for the best possible occlusion at operation. This may involve relief of crowding, flattening of the occlusal plane or other treatment.
139
You might also like
- Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning. Part I. G. William Arnett, DDS and Robert T. Bergman, DDS, MSDocument14 pagesFacial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning. Part I. G. William Arnett, DDS and Robert T. Bergman, DDS, MSdrimtiyaz123100% (1)
- Periodontal Treatment of Excessive Gingival DisplayDocument12 pagesPeriodontal Treatment of Excessive Gingival DisplayJuan Carlos CárcamoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0889540623002573 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0889540623002573 MainDANTE DELEGUERYNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery 1Document9 pagesOrthognathic Surgery 1c8vqyny865No ratings yet
- Mi Sympheal DODocument10 pagesMi Sympheal DOChhavi SinghalNo ratings yet
- 7 Articulo Bone-Anchored Maxillary Protraction in A Patient With Complete Cleft Lip and Palate: A Case ReportDocument8 pages7 Articulo Bone-Anchored Maxillary Protraction in A Patient With Complete Cleft Lip and Palate: A Case ReportErika NuñezNo ratings yet
- 2016 SergioDocument10 pages2016 SergioazizhamoudNo ratings yet
- Surgical OrthodonticsDocument301 pagesSurgical Orthodonticsdr_nilofervevai2360100% (4)
- Capel OzzaDocument6 pagesCapel OzzaDela MedinaNo ratings yet
- Open Bite, A Review of Etiology and Manageme PDFDocument8 pagesOpen Bite, A Review of Etiology and Manageme PDFVieussens JoffreyNo ratings yet
- Managing Oral Side Effects of Systemic Diseases: Prosthetic Rehabilitation With Amyloidosis of The TongueDocument17 pagesManaging Oral Side Effects of Systemic Diseases: Prosthetic Rehabilitation With Amyloidosis of The TongueRandy Ichsan AdlisNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Analysis: Dr. Ayushi Toley PG Ist YearDocument70 pagesSoft Tissue Analysis: Dr. Ayushi Toley PG Ist YearAyushi ToleyNo ratings yet
- Apert N CrouzonDocument13 pagesApert N CrouzonfayasyabminNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery Seminar 6 FinalDocument83 pagesOrthognathic Surgery Seminar 6 FinalNikhil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Intra Oral ExaminationDocument6 pagesLec 3 Intra Oral ExaminationMohammed JaberNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Treatment in Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly SyndromeDocument6 pagesOrthognathic Treatment in Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly Syndromehector rinconNo ratings yet
- Open Bite: A Review of Etiology and Management: Peter Ngan, DMD Henry W. Fields, DDS, MS, MSDDocument8 pagesOpen Bite: A Review of Etiology and Management: Peter Ngan, DMD Henry W. Fields, DDS, MS, MSDAzi Pertiwi HussainNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery RonalDocument56 pagesOrthognathic Surgery Ronaldrghempik100% (2)
- New StandardDocument5 pagesNew StandardMahar ErwidawanNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument16 pagesDownloadhasan nazzalNo ratings yet
- Lecrure 7 Clinical Diagnosis 4th StageDocument16 pagesLecrure 7 Clinical Diagnosis 4th StageIbrahim HysamNo ratings yet
- Functional Examination: Textbook of OrthodonticsDocument3 pagesFunctional Examination: Textbook of OrthodonticsndranNo ratings yet
- Mukherjee Et AlDocument5 pagesMukherjee Et AlSohaib ShujaatNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666430522000036 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S2666430522000036 MainDANTE DELEGUERYNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Arch Distalization Using Interradicular Miniscrews and The Lever-Arm ApplianceDocument8 pagesMaxillary Arch Distalization Using Interradicular Miniscrews and The Lever-Arm ApplianceJuan Carlos CárcamoNo ratings yet
- Clinical S - : Dr. K. S KumarDocument10 pagesClinical S - : Dr. K. S KumarDr. Neesu KumbhatNo ratings yet
- Noonan Syndrome: A Case Report: Muhammet E. Emral and Mehmet O. AkcamDocument6 pagesNoonan Syndrome: A Case Report: Muhammet E. Emral and Mehmet O. AkcamGabriela VillafañezNo ratings yet
- Manual Ao Cirurgia OrtognáticaDocument35 pagesManual Ao Cirurgia OrtognáticaAndre Luis CostaNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Occlusal Vertical Dimention in Eduntulos Patients Using Lateral CephalograamsDocument7 pagesDetermination of The Occlusal Vertical Dimention in Eduntulos Patients Using Lateral CephalograamsLeenMash'anNo ratings yet
- 740 PDFDocument7 pages740 PDFadriiianaiiioanaNo ratings yet
- Dentofacial Asymmetries: Challenging Diagnosis and Treatment PlanningDocument4 pagesDentofacial Asymmetries: Challenging Diagnosis and Treatment Planningblogger bloggerNo ratings yet
- Black TriangleDocument9 pagesBlack TriangleYasser MagramiNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Facial Morphology Following Surgical Repair of Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate in Patients After Nasoalveolar MoldingDocument7 pagesThree Dimensional Facial Morphology Following Surgical Repair of Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate in Patients After Nasoalveolar MoldingnoraveNo ratings yet
- Nine Steps To Occlusal Harmony FamdentDocument5 pagesNine Steps To Occlusal Harmony FamdentGhenciu Violeta100% (1)
- 12 ChapterDocument51 pages12 ChapterNaresh TeresNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie CleidocranianaDocument9 pagesBibliografie CleidocranianaMihaela ApostolNo ratings yet
- Scientific Dental Journal: Lower Facial Height and Soft Tissue Changes in Bimaxillary Protrusion CasesDocument7 pagesScientific Dental Journal: Lower Facial Height and Soft Tissue Changes in Bimaxillary Protrusion Casesyuni madjidNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Molar Distalization With Modified Trans Palatal Arch and Mini Implants PDFDocument6 pagesMaxillary Molar Distalization With Modified Trans Palatal Arch and Mini Implants PDFSoe San KyawNo ratings yet
- CirugiaDocument27 pagesCirugiaalexmtzgNo ratings yet
- 36 Cleft Lip and PalateDocument45 pages36 Cleft Lip and PalateCristian VieyraNo ratings yet
- Angle Class I Malocclusion Treated With Lower Incisor ExtractionDocument9 pagesAngle Class I Malocclusion Treated With Lower Incisor ExtractiondellalalaNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Reconstruction of The Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nasal Deformity: Abbé Flap RevisitedDocument9 pagesSimultaneous Reconstruction of The Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nasal Deformity: Abbé Flap RevisitedwulanbrurrNo ratings yet
- Cephalometrics in Orthodontics: University of SydneyDocument24 pagesCephalometrics in Orthodontics: University of SydneyMirek SzNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Surgical Orthodontic Treatment of Severe Skeletal Class IIDocument6 pagesCase Report: Surgical Orthodontic Treatment of Severe Skeletal Class IISebas Quiroga GNo ratings yet
- Correction of Severe Bimaxillary ProtrusionDocument37 pagesCorrection of Severe Bimaxillary ProtrusionRobbyRamadhonieNo ratings yet
- Disatalización Clase IIDocument13 pagesDisatalización Clase IIchristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Stalpers Am JOrthod Dentofac Orthop 2007132316323Document8 pagesStalpers Am JOrthod Dentofac Orthop 2007132316323thomas QuilangNo ratings yet
- DiagnosisDocument17 pagesDiagnosisAmr IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Management of Supernumerary Teeth-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesOrthodontic Management of Supernumerary Teeth-A Case ReportCalin CristianNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Maxillofacial Surgery FileDocument14 pagesPediatric Maxillofacial Surgery Filegroup1iiistomatologyNo ratings yet
- HAL 49 Critical Decision in PeriodontologyDocument1 pageHAL 49 Critical Decision in PeriodontologyUntuk TugasNo ratings yet
- Angle Orthod 2013 83 36-42Document7 pagesAngle Orthod 2013 83 36-42brookortontiaNo ratings yet
- 4278-Article Text-16560-2-10-20210520Document6 pages4278-Article Text-16560-2-10-20210520Shincia PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Digital Smile Design Concept PDFDocument18 pagesDigital Smile Design Concept PDFAndyRamosLopezNo ratings yet
- Gummy Smile017Document55 pagesGummy Smile017Shathra'a Hamza100% (1)
- Borderline Cases in Orthodontics-A ReviewDocument6 pagesBorderline Cases in Orthodontics-A ReviewShatabdi A ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- AJODO 1993 Mar 203-211 - Taken From The AJO-DO On CD-ROMDocument20 pagesAJODO 1993 Mar 203-211 - Taken From The AJO-DO On CD-ROMAndré MéndezNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0889540622006552 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0889540622006552 MainMarcos Gómez SosaNo ratings yet
- 0550262Document3 pages0550262Bagoes Ario BimoNo ratings yet
- 4 Endodontics. Definition - Methods of Medical and Instrumental Treatment of Root CanalsDocument33 pages4 Endodontics. Definition - Methods of Medical and Instrumental Treatment of Root Canalsayuna tresnaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management OF Acute Severe AsthmaDocument43 pagesAssessment and Management OF Acute Severe Asthmadentist40No ratings yet
- Asthma in ERDocument40 pagesAsthma in ERdentist40No ratings yet
- N24: Class #8 Obstructive and Inflammatory Lung Disease: Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis AsthmaDocument42 pagesN24: Class #8 Obstructive and Inflammatory Lung Disease: Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis Asthmadentist40No ratings yet
- PERICORONITIS5Document15 pagesPERICORONITIS5dentist40No ratings yet
- Rhinosinusitis Slides 060509Document36 pagesRhinosinusitis Slides 060509KURBULDKNo ratings yet
- Dental AlloysDocument2 pagesDental Alloysdentist40No ratings yet
- Precision AttachmentsDocument10 pagesPrecision Attachmentsdentist40No ratings yet