Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Promej Matematik SPM 2011
Promej Matematik SPM 2011
Uploaded by
Akim HogYokuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- UIL 4TH - 5TH Grade MATH Practice TestDocument10 pagesUIL 4TH - 5TH Grade MATH Practice TestKalpani Dissanayake0% (1)
- Developing Thinking in Geometry by Sue Johnston-Wilder, Professor John Mason PDFDocument285 pagesDeveloping Thinking in Geometry by Sue Johnston-Wilder, Professor John Mason PDFpietro265No ratings yet
- Perimeter & Luas SektorDocument3 pagesPerimeter & Luas Sektorzan izanNo ratings yet
- Mate Latih Tubi - Circle T4 PDFDocument2 pagesMate Latih Tubi - Circle T4 PDFcgnashNo ratings yet
- Area and PerimeterDocument16 pagesArea and PerimetershieydNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 II Arc Length & Area of Sector ENRICHDocument17 pagesChapter 3 II Arc Length & Area of Sector ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahim100% (1)
- Chapter 3 II Arc Length N Sector Area ENHANCEDocument21 pagesChapter 3 II Arc Length N Sector Area ENHANCENorliha JamilNo ratings yet
- Circle I and IIDocument5 pagesCircle I and IILEE HUE KEAN MoeNo ratings yet
- 8 Klon SPM Circular Measure 2007 - 2014Document14 pages8 Klon SPM Circular Measure 2007 - 2014Aidil-Nur ZainalNo ratings yet
- Waja Additional Mathematics SPM 2008 - Topic 6 Circular MeasureDocument7 pagesWaja Additional Mathematics SPM 2008 - Topic 6 Circular Measureput3norlidaNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Sukatan MembulatDocument24 pagesModul 1 Sukatan MembulatNova Adila ErizalNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Modul BaruDocument40 pagesPaper 2 Modul BaruFatimah Abdul KhalidNo ratings yet
- Arc and Area of SectorDocument5 pagesArc and Area of Sectorleena_louisNo ratings yet
- LAtihan F5Document9 pagesLAtihan F5rasidhaNo ratings yet
- F3circles PDF (Maths) PDFDocument4 pagesF3circles PDF (Maths) PDFDarshan NathNo ratings yet
- AMATH Circular MeasureDocument21 pagesAMATH Circular MeasureLene100% (1)
- Diagram 1 Shows A Sector AOB With Centre O A: Modul/Tingkatan Lima: Bab 1 (Sukatan Membulat)Document19 pagesDiagram 1 Shows A Sector AOB With Centre O A: Modul/Tingkatan Lima: Bab 1 (Sukatan Membulat)Norhapidah Mohd SaadNo ratings yet
- 1 Sukatan Membulat Kelas14feb 2020Document34 pages1 Sukatan Membulat Kelas14feb 2020Norhapidah Mohd SaadNo ratings yet
- 2°pd TrigonometriaDocument4 pages2°pd TrigonometriaEmily SaenzNo ratings yet
- Review Exercise 22 Objective)Document9 pagesReview Exercise 22 Objective)Vimalraj MoghanNo ratings yet
- Circles: CH CHDocument4 pagesCircles: CH CHJamaliah Daud100% (1)
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 2 Math Chapter 10velavanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - f4 - c8 - Circular - Measures - NewDocument10 pagesMicrosoft Word - f4 - c8 - Circular - Measures - NewRuban RubanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Maths Form 2 BulatanDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Maths Form 2 BulatanhafizahNo ratings yet
- Q14 Circles1Document6 pagesQ14 Circles1g-54230731No ratings yet
- Cycloid, Involute - SpiralDocument10 pagesCycloid, Involute - SpiralTariqNo ratings yet
- Area N PerimeterDocument9 pagesArea N Perimeteridaman2905No ratings yet
- Set Item Item Tambahan Tingkatan 5Document147 pagesSet Item Item Tambahan Tingkatan 5Amanina Edham Azree EdhamNo ratings yet
- IB Qns Arcs and SectorsDocument7 pagesIB Qns Arcs and SectorsDevNo ratings yet
- Sulit 1: Mathematics Paper 1 PMR Trial SBP 2009Document40 pagesSulit 1: Mathematics Paper 1 PMR Trial SBP 2009Suntheres MorganasundramNo ratings yet
- P1 - Ch. 7 - Supplementary Exercise 1Document2 pagesP1 - Ch. 7 - Supplementary Exercise 1TAN SHI LE CHARLOTTENo ratings yet
- MODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimeterDocument14 pagesMODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimetersyarelNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Mathematics Form 1 & 2 PMR 2012: SMK Taman Megah RiaDocument4 pagesUlangkaji Mathematics Form 1 & 2 PMR 2012: SMK Taman Megah Riapclim2010No ratings yet
- Question's PDFDocument19 pagesQuestion's PDFAyaan NaveedNo ratings yet
- Math Form5 Pertengahan TahunDocument7 pagesMath Form5 Pertengahan TahunMajidah NajihahNo ratings yet
- Plane Amp Solid Review Notes 2017 With Key PDF FreeDocument16 pagesPlane Amp Solid Review Notes 2017 With Key PDF FreeKimmy CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureBawani shanker100% (1)
- Q14 Circles2Document10 pagesQ14 Circles2g-54230731No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-17 at 20.02.58Document46 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-17 at 20.02.58ym6510147No ratings yet
- Sec 4 June Arc Sector Segment RevisionDocument15 pagesSec 4 June Arc Sector Segment RevisiontengjinghsuenNo ratings yet
- Circle: 1. 每年度有一题。 2. 一题大概 6 分!! 只是用 2 个 formula: Arc Length =Document3 pagesCircle: 1. 每年度有一题。 2. 一题大概 6 分!! 只是用 2 个 formula: Arc Length =Lim Lee JiunNo ratings yet
- D+D+D+D+D DDDDD: Section ADocument22 pagesD+D+D+D+D DDDDD: Section Aputri eva elinaNo ratings yet
- F 3 CirclesDocument4 pagesF 3 CirclesNur BainiNo ratings yet
- Deber#1 2P 2QTrigonometriaDocument7 pagesDeber#1 2P 2QTrigonometriaTommy Allen Ojeda PlúasNo ratings yet
- PPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre ODocument17 pagesPPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre OakuesukaNo ratings yet
- Shaded Area 4Document1 pageShaded Area 4danNo ratings yet
- A39 Mensuration 2D Shapes QuestionsDocument46 pagesA39 Mensuration 2D Shapes QuestionsThe KingpinNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ujian Selaras 1 Matematik Ting 3 & Skema JawapanDocument10 pagesSoalan Ujian Selaras 1 Matematik Ting 3 & Skema JawapanWawa Zameri100% (1)
- Circular Measure Past YrDocument3 pagesCircular Measure Past YrpizamNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure: Answer: .....................................Document8 pagesCircular Measure: Answer: .....................................Yogeswary GobalkrishnanNo ratings yet
- SM Pei Min 2021 1 Semester Exam Junior 3 Modern MathematicsDocument15 pagesSM Pei Min 2021 1 Semester Exam Junior 3 Modern MathematicsTeng Wei KiangNo ratings yet
- Mathematics10 Quarter2 Week5Document6 pagesMathematics10 Quarter2 Week5Jaymar AbetoNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions Subjective: 2 Hours 30 MinutesDocument19 pagesObjective Questions Subjective: 2 Hours 30 MinutesksganNo ratings yet
- Satprep Assignment: Circular Measurement 1.: Diagram Not To ScaleDocument5 pagesSatprep Assignment: Circular Measurement 1.: Diagram Not To ScaleJoel SohNo ratings yet
- 06 Circular MeasureDocument11 pages06 Circular MeasureTerence RileyNo ratings yet
- Tarea - Sector CircularDocument3 pagesTarea - Sector CirculareduxitoooNo ratings yet
- 06 Circular MeasureDocument10 pages06 Circular MeasureVivianne YongNo ratings yet
- Poligon Lukisan Kejuruteraan TIngkatan 4Document13 pagesPoligon Lukisan Kejuruteraan TIngkatan 4fara adhwaNo ratings yet
- I Love Maths Series Book 2 - Euclidean GeometryDocument113 pagesI Love Maths Series Book 2 - Euclidean Geometrylusandamelissa69No ratings yet
- Arc Length and Areas of SectorsDocument10 pagesArc Length and Areas of SectorsRafena MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Classifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92From EverandClassifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92No ratings yet
- Soal Uas Kelas 1 SD Saraswati 22Document3 pagesSoal Uas Kelas 1 SD Saraswati 22Nanda RusistaNo ratings yet
- 3D-Pythagoras and Trigonometry AnswersDocument3 pages3D-Pythagoras and Trigonometry Answersaidanzam13No ratings yet
- Math2412 Double Angle Power Reducing Half Angle IdentitiesDocument5 pagesMath2412 Double Angle Power Reducing Half Angle IdentitiesSylvia WilsonNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument69 pagesSimilarityavinandan chandraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A: Paper 3H Higher TierDocument24 pagesMathematics A: Paper 3H Higher Tierkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ProjectDocument8 pagesTrigonometry ProjectKiara Venice100% (1)
- Unit 2 Trigonometry LessonsDoneDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Trigonometry LessonsDoneNatasha MarieNo ratings yet
- Itf Marks BoosterDocument3 pagesItf Marks Boosterkunalff1638No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Extra Exercises 3.1: Pythagoras' TheoremDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Extra Exercises 3.1: Pythagoras' TheoremPh DeNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Undefined TermsDocument22 pagesGrade 7 Undefined Termskaren takasaNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL 2022 Complete PDFDocument251 pagesSSC CGL 2022 Complete PDFMG ConceptNo ratings yet
- Triangle Inequality TheoremDocument9 pagesTriangle Inequality TheoremCarlene MallariNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series: 12.1 Periodic FunctionsDocument35 pagesFourier Series: 12.1 Periodic Functionskishor nNo ratings yet
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya Sachin100% (1)
- 2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8Document7 pages2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8siyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Formula SheetDocument1 pageAP Calculus AB Formula SheetArad zeinaliNo ratings yet
- 01 Euclidean GeometryDocument23 pages01 Euclidean Geometrymiriam martinezNo ratings yet
- KMT Syllabus & PapersDocument2 pagesKMT Syllabus & PaperswutthicsaNo ratings yet
- ANGLEDocument37 pagesANGLEAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Geometry HistoryDocument2 pagesGeometry HistoryManilyn Requejo ObalNo ratings yet
- Online Week 5&6Document17 pagesOnline Week 5&6Rondex PabloNo ratings yet
- 01-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper-1Document7 pages01-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper-1SUB MOH MAYA HAI100% (1)
- Straight Line and Pair of Straight LinesDocument25 pagesStraight Line and Pair of Straight LinesHem kumarNo ratings yet
- A Generalization of The Spieker Circle and Nagel LineDocument8 pagesA Generalization of The Spieker Circle and Nagel LineMichael de VilliersNo ratings yet
- TSA Andvolume of SolidsDocument14 pagesTSA Andvolume of SolidsJairNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Properties of CirclesDocument17 pagesGeometrical Properties of CirclesJoann NgNo ratings yet
- Math Resources Geometry FormulasDocument2 pagesMath Resources Geometry FormulasMoslem GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- English Mathematics - 2022 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9: Formal Assessment Task Revision and Formal Assessment TaskDocument6 pagesEnglish Mathematics - 2022 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9: Formal Assessment Task Revision and Formal Assessment TaskThemba NyoniNo ratings yet
Promej Matematik SPM 2011
Promej Matematik SPM 2011
Uploaded by
Akim HogYokuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Promej Matematik SPM 2011
Promej Matematik SPM 2011
Uploaded by
Akim HogYokuCopyright:
Available Formats
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
SMK. KOTA KLIAS, BEAUFORT SABAH
PROMEJ - MATEMATIK SPM 2011 FASA I
DISUSUN OLEH: MOHD NAZAN B. KAMARUL ZAMAN
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
CONTENTS
SECTION A 1. LENGTH OF ARC AND AREA OF SECTOR
2.
VOLUME SOLID GEOMETRY
3. SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS 4. SETS 5. MATHEMATICAL REASONING 6. THE STRAIGHT LINE 7. LINES AND PLANES IN 3-DIMENSIONS
SECTION B 1. STATISTICS
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
1. LENGTH OF ARC AND AREA OF SECTOR
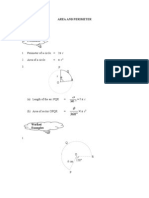
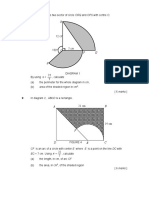
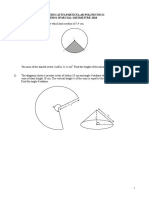
1. In the diagram below, O is the centre of the arc of the circle MNPQ and RSM is a quadrant with centre P. MOP is a straight line. M
S O Q R 14 cm P 240
o
22 Using = , calculate 7
a) the perimeter of the whole diagram, b) the area of the shaded region. marks] Answer :
[6
a) Perimeter of the whole diagram 90 22 2 14 = 360 7 = 58 cm =
180 22 2 7 360 7
+ 14
b) Area of the shaded region
90 22 142 360 7
128 1 cm2 3
60 22 2 7 360 7
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 Exercise 1. In Diagram 1, JKL is arc of circle with centre M. NML is a straight line and JN = NM = 7 cm. K J
DIAGRAM 1 N Using = 22 , calculate 7 M L
a. the area of the shaded region, in cm2, b. perimeter of the whole diagram, in cm. [6 marks]
2. In Diagram 2, O is the centre of the arc of the circle PQR and a quadrant STU. OSR is a straight line. P T 14 cm O 7 cm U DIAGRAM 2 45o S R Q
Using =
22 , calculate 7
a. perimeter of the whole shaded region, b. area of the whole shaded region. [6 marks]
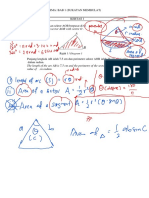
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 3. In Diagram 3, OAB, OCD and OEF are three sectors with same centre O.
B
7 cm
E C 40 O D 40 21 cm F
22 , calculate 7 DIAGRAM 3
Given AOF, OCB and ODE are straight lines. Using = a. the area of sector OCD, b. the perimeter of the whole diagram.
[6 marks ]
4. Diagram 4 shows three quadrants OPQ, TQR and URS. POUS is a straight line and TOUR is a square. Q
T R P Using S 14 cm O T
R DIAGRAM 4 U S
22 , calculate 7
a) the perimeter of the whole diagram, Q P 7 cm b) the area of the whole diagram.
U [6 marks ]
5. In Diagram 5, QR and TU are two arc of circles with the same centre O. QPOU and RSTO are straight lines.
DIAGRAM 5
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
Using = a)
22 , calculate 7
O R Q ,
b) area of the shaded sector OTU, c) perimeter of the whole diagram. [6 marks]
2.VOLUME OF SOLIDS
10 cm 5 cm 5 cm DIAGRAM 1 1. Diagram 1 shows the tip of a cone touches the top of the cuboid and the base rests on the base of the cuboid. If the cone is taken out of the solid. Calculate the volume, in cm3, of the remaining solid. Use = 22 . 7
10 7
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
DIAGRAM 2 2 Diagram 2 shows a hemisphere resting on top of a cylinder, both having bases of identical area. The height of cylinder is 10 cm and the diameter of the cylinder is 7 cm. Find the volume, in cm3, of the composite object. Use = 22 . 7
Diagram 3 3 Diagram 3 shows a solid formed by combining a right prism with a half cylinder on the rectangular ABCD. BF = CE = 10 cm , FG = EH = 8 cm and BC = 13cm. Calculate the volume,in cm 3 , of the solid. [use = 22 ] 7
13 cm
5 cm
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
Diagram 4
4 Diagram 4 shows a solid formed by combining a cone with a hemisphere.Find the volume of the composite in cm3. [use = 22 ]. 7
12 cm
10 cm 15 cm Diagra m5 5 Diagram 5 shows a solid cuboid . A cylinder with radius 4 cm and height 7 cm is taken out of the solid. Calculate the volume, in cm 3 , of the remaining solid. [use =
22 ]. 7
3.SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS
1
Calculate the values of r and s that satisfy the following simultaneous linear equations : 5r + 2s = 20 and 2r 3s = 11 s = 5) (Ans : r = 2,
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
Calculate the value of v and of w that satisfy the following simultaneous linear equations : 2v + 3w = 8 and + w = 10 3v v = w = 4) 2, (Ans :
Calculate the values of m and u that satisfy the following simultaneous linear equations : m + 4u = 2
1 m + 7u = 1 4
(Ans : m =
1 u=4 ) 3,
Calculate the value of m and of n that satisfy the following simultaneous linear equations :
1 n =5 3
2m
3m n = 9 2, n = 3)
(Ans : m =
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
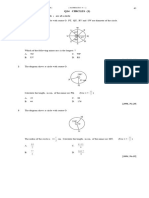
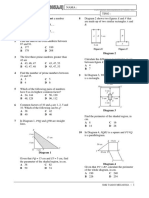
4.SETS
1. The Venn diagram in the answer space shows sets A, B and C. Given that = A B C. On the diagram provided in the answer spaces, shade the area of , (a) C (A B) (b) (A C) (B C)
Answer :
2.
A
7 8-x 9-x 8 7-x 9
Given that = A B C and that n() = 34 , find (a) (b) the value of x
n( A B C ' )
3.
The Venn diagrams below show set P, Q and R. Given that the universal set, = P Q R . On the diagrams, shade Q Q (a) P P P Q (b) P R '
R R
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
(c)
P ' R ' Q
Q R
4.
Given the universal set,
= {x :1 x0 2 , x 5
is an integer}
Set P = {x : x is a prime number} Set Q = {x : x is a multiple of 4} and Set R = {x: x is a number where one of its digits is more than 7} (a) (b) (c) Find the elements of set P Find the elements of set P R. Find n( P Q R ).
5. MATHEMATICAL REASONING
1) i: State whether the following statement is true or false.
9 > 6 and 42 = 8 ii : Complete the premise in the following argument. Premise 1 : If JKL is an equilateral triangle, then the value of its interior angle is 60o Premise 2 : ______________________________________________________ Conclusion : The value of the interior angle of JKL is 60o. iii : Write down two implications based on the following sentence.
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 x > y if and only if x y > 0
Implication 1 : . Implication II : .
2) i : Is the sentence below a statement or a non-statement ? 5 is an even number ii : Write down two implications based on the following sentence. PQR is a right-angled triangle if and only if PR2 = PQ2 + QR2 Implication 1 : . Implication II : iii : Based on the information below, make a general conclusion by induction regardingThe sum of the interior angles of triangle ABC = the sum of 180o the interior angles of a triangle. The sum of the interior angles of triangle JKL = 180o The sum of the interior angles of triangle PQR = 180o General conclusion :
3. a) Determine whether the following statement is true or false. 5 34 = 12 or = 1.25 4 b) Write two implications from the statement given below.
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
x = 4 if and only if x3 = 64 Implication I:
Implication II:
c) Complete the premise in the following argument. Premise 1 : If 2y = 10, then y = 5. Premise 2 : .. Conclusion : 2y 10.
4. a) Complete the conclusion in the following argument. Premise 1 : All regular hexagons have 6 equal sides. Premise 2 : ABCDEF is a regular hexagon. Conclusion : b) Make a conclusion by induction for a list of numbers 9,29, 57, 93,that follow the patterns below : 9 = 4(2)2 7 29 = 4(3)2 7 57 = 4(4)2 7 93 = 4(5)2 7
c) Combine the two statements given below to form a true statement. i) 15
( 5) = 5
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 ii) 32 is a multiple of 8.
6. THE STRAIGHT LINE
1.In the diagram, PQRS is a parallelogram.
y
The gradient of RS is (a) (b)
1 . 3
Find (Ans : 3) (Ans : y = 1x 2) 3 [5marks]
the y-intercept of the straight line RS, the equation of the straight line PQ.
2. In the diagram, the straight line PQ is parallel to the straight line ST. O is the origin.
y Q (3,
R (5, 8)
Given the gradient of RS is Find 2. (a) the equation of the straight line PQ, (Ans : y = + 14) 2x
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 (b) the x-intercept of the straight line RS. (Ans : 1) [5 marks] 3. In the diagram, OPQR is a parallelogram and O is the origin.
y
Find (a) (b) the gradient of the straight line PQ, the equation of the straight line QR.
P (3, 6)
(Ans : 3 ) 5 (Ans : y = 2x 7) [5 marks]
4. In the diagram, OPQR is a parallelogram and O is the origin.
R (5, 3)
O
Find (a) (b)
R (4
(Ans : y = 3x 15) (Ans : 20)
the equation of the straight line PQ, the y-intercept of the straight line QR.
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 [5 marks]
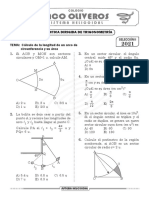
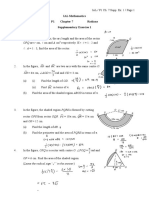
7. LINES AND PLANES IN 3-DIMENSIONS
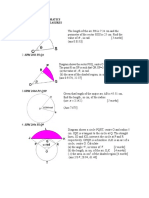
1.The diagram shows a cuboid with a horizontal rectangular base PQRS.
T
Calculate the angle between the plane PQW and the base PQRS. 38 ) (Ans : 41 2.The diagram shows a cuboid resting on a horizontal plane PQRS. M is the midpoint of PS
U
Given PS = 16 cm, SR = 10 cm, and CR = 6 cm. between the plane CMR and the plane CDSR.
Calculate the angle
(Ans : 38 40 ) 3.The diagram shows a right prism. Right angled triangle PQR is the uniform cross section of the prism.
A 5 cm P
U
T 12 cm
12 Q
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 Calculate the angle between the plane RTU and the base PQTU. 3341 ) (Ans :
[4 marks]
4.The diagram shows a right prism. The base PQRS is a horizontal rectangle. Right angled triangle QRU is the uniform cross section of the prism. V is the midpoint of PS.
T S
Identify and calculate the angle between the line UV and the plane 31.61)
U 5 cm R (Ans : RSTU.
16 cm
5.
The diagram shows a right prism with a right-angled triangle BFC as its uniform cross section. P is the midpoint of DC and DC = 10 cm.
12 cm
A
Calculate the angle between the line BP and the base CDEF. (Ans : 21 2 )
6. The diagram shows a right prism with an equilateral triangle PRS as its uniform cross section. M and N are
the midpoints of RS and WT respectively.
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011
If RM = 5 cm and ST = 12 cm, calculate the angle between the line PT and the base RSTW. (Ans : 3340 )
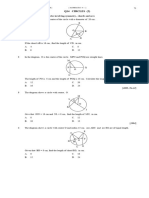
SECTION B STATISTICS
1.The data shows the ages, in years, of 30 workers in a carpenter factory. 21 48 38 (a) 38 29 34 25 34 24 39 45 26 31 23 20 31 29 36 43 40 33 27 47 31 32 28 20 25
W S
[4 marks] Upper Boundary
R
28
26
State the range of the data. [1 mark]
(Ans : 28)
(b)
Based on the data above and by using a class interval of 5 years, complete the table in the answer space.
Age (years) 20 24 25 29
Frequency
Mid-point
(c)
Based on the table in (b), (i) state the modal class, (Ans : 25 29)
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 (ii) calculate the estimated mean ages of the workers and given your answer correct to 3 decimal places. (Ans : 31.667) [3 marks] (d) For this part of the question, use the graph paper provided on the next page. By using a scale of 2 cm to 5 years on the x-axis and 2 cm to one worker on the y-axis, draw a histogram for the data. [4 marks]
2. The data shows the distribution of heights, in cm, of 40 students in a class. 17 8 17 4 17 2 17 3 17 6 15 4 16 2 15 1 15 9 17 7 17 5 17 6 17 1 17 9 15 3 15 6 160 158 167 178 16 6 16 8 16 7 15 2 16 4 16 7 15 5 16 3 17 1 17 4 16 8 16 0 17 4 16 9 17 3 17 2 154 164 169 154
(a) Using data above, complete the table in the answer space based on the class interval of the same size. [4 marks] Height (cm) 145 149 Frequency, f Mid-point, x
(b)
Based on the table in (a),
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 (i) (ii) state the modal class, (Ans : 170 174)
calculate the mean height of the students in the class and give your answer correct to two decimal palces. (Ans : 165.88) [4 marks]
(c)
For this part of the question, use the graph paper provided on the next page.
By using a scale of 2 cm to 5 cm on the horizontal axis and 2 cm to one student on the vertical axis, draw a frequency polygon for the data. [4 marks]
3. The table shows the distribution of heights, in cm, of 92 students in a school. Height 120 125 130 135 140 145 150 155 (a) (cm) 124 129 134 139 144 149 154 159 Mid-point Frequency 4 10 26 24 17 7 3 1
(i) Based on the table above, complete the table (a) in the answer space. (ii) Hence, calculate the mean height of the students. 136.239) [3 marks] (Ans :
(b) Upper Boundrary Cumulative Frequency 119. 5 159. 5
A+ Mathematics SPM 2011 (i) Based on the table in (a), complete the table in (b) in the answer space. (ii) For this part of the question, use the graph paper provided on the next page. By using a scale of 2 cm to 5 cm on the x-axis and 2 cm to 10 students on the y-axis, draw an ogive for the data. (iii) From the ogive, find the interquartile range for the data. (Ans : 9)
(iv) The students whose height is above 152 cm are chosen as basketball player. Find the number of students who are chosen. (Ans : 2) [9 marks]
You might also like
- UIL 4TH - 5TH Grade MATH Practice TestDocument10 pagesUIL 4TH - 5TH Grade MATH Practice TestKalpani Dissanayake0% (1)
- Developing Thinking in Geometry by Sue Johnston-Wilder, Professor John Mason PDFDocument285 pagesDeveloping Thinking in Geometry by Sue Johnston-Wilder, Professor John Mason PDFpietro265No ratings yet
- Perimeter & Luas SektorDocument3 pagesPerimeter & Luas Sektorzan izanNo ratings yet
- Mate Latih Tubi - Circle T4 PDFDocument2 pagesMate Latih Tubi - Circle T4 PDFcgnashNo ratings yet
- Area and PerimeterDocument16 pagesArea and PerimetershieydNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 II Arc Length & Area of Sector ENRICHDocument17 pagesChapter 3 II Arc Length & Area of Sector ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahim100% (1)
- Chapter 3 II Arc Length N Sector Area ENHANCEDocument21 pagesChapter 3 II Arc Length N Sector Area ENHANCENorliha JamilNo ratings yet
- Circle I and IIDocument5 pagesCircle I and IILEE HUE KEAN MoeNo ratings yet
- 8 Klon SPM Circular Measure 2007 - 2014Document14 pages8 Klon SPM Circular Measure 2007 - 2014Aidil-Nur ZainalNo ratings yet
- Waja Additional Mathematics SPM 2008 - Topic 6 Circular MeasureDocument7 pagesWaja Additional Mathematics SPM 2008 - Topic 6 Circular Measureput3norlidaNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Sukatan MembulatDocument24 pagesModul 1 Sukatan MembulatNova Adila ErizalNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Modul BaruDocument40 pagesPaper 2 Modul BaruFatimah Abdul KhalidNo ratings yet
- Arc and Area of SectorDocument5 pagesArc and Area of Sectorleena_louisNo ratings yet
- LAtihan F5Document9 pagesLAtihan F5rasidhaNo ratings yet
- F3circles PDF (Maths) PDFDocument4 pagesF3circles PDF (Maths) PDFDarshan NathNo ratings yet
- AMATH Circular MeasureDocument21 pagesAMATH Circular MeasureLene100% (1)
- Diagram 1 Shows A Sector AOB With Centre O A: Modul/Tingkatan Lima: Bab 1 (Sukatan Membulat)Document19 pagesDiagram 1 Shows A Sector AOB With Centre O A: Modul/Tingkatan Lima: Bab 1 (Sukatan Membulat)Norhapidah Mohd SaadNo ratings yet
- 1 Sukatan Membulat Kelas14feb 2020Document34 pages1 Sukatan Membulat Kelas14feb 2020Norhapidah Mohd SaadNo ratings yet
- 2°pd TrigonometriaDocument4 pages2°pd TrigonometriaEmily SaenzNo ratings yet
- Review Exercise 22 Objective)Document9 pagesReview Exercise 22 Objective)Vimalraj MoghanNo ratings yet
- Circles: CH CHDocument4 pagesCircles: CH CHJamaliah Daud100% (1)
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 2 Math Chapter 10velavanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - f4 - c8 - Circular - Measures - NewDocument10 pagesMicrosoft Word - f4 - c8 - Circular - Measures - NewRuban RubanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Maths Form 2 BulatanDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Maths Form 2 BulatanhafizahNo ratings yet
- Q14 Circles1Document6 pagesQ14 Circles1g-54230731No ratings yet
- Cycloid, Involute - SpiralDocument10 pagesCycloid, Involute - SpiralTariqNo ratings yet
- Area N PerimeterDocument9 pagesArea N Perimeteridaman2905No ratings yet
- Set Item Item Tambahan Tingkatan 5Document147 pagesSet Item Item Tambahan Tingkatan 5Amanina Edham Azree EdhamNo ratings yet
- IB Qns Arcs and SectorsDocument7 pagesIB Qns Arcs and SectorsDevNo ratings yet
- Sulit 1: Mathematics Paper 1 PMR Trial SBP 2009Document40 pagesSulit 1: Mathematics Paper 1 PMR Trial SBP 2009Suntheres MorganasundramNo ratings yet
- P1 - Ch. 7 - Supplementary Exercise 1Document2 pagesP1 - Ch. 7 - Supplementary Exercise 1TAN SHI LE CHARLOTTENo ratings yet
- MODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimeterDocument14 pagesMODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimetersyarelNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Mathematics Form 1 & 2 PMR 2012: SMK Taman Megah RiaDocument4 pagesUlangkaji Mathematics Form 1 & 2 PMR 2012: SMK Taman Megah Riapclim2010No ratings yet
- Question's PDFDocument19 pagesQuestion's PDFAyaan NaveedNo ratings yet
- Math Form5 Pertengahan TahunDocument7 pagesMath Form5 Pertengahan TahunMajidah NajihahNo ratings yet
- Plane Amp Solid Review Notes 2017 With Key PDF FreeDocument16 pagesPlane Amp Solid Review Notes 2017 With Key PDF FreeKimmy CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureBawani shanker100% (1)
- Q14 Circles2Document10 pagesQ14 Circles2g-54230731No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-17 at 20.02.58Document46 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-17 at 20.02.58ym6510147No ratings yet
- Sec 4 June Arc Sector Segment RevisionDocument15 pagesSec 4 June Arc Sector Segment RevisiontengjinghsuenNo ratings yet
- Circle: 1. 每年度有一题。 2. 一题大概 6 分!! 只是用 2 个 formula: Arc Length =Document3 pagesCircle: 1. 每年度有一题。 2. 一题大概 6 分!! 只是用 2 个 formula: Arc Length =Lim Lee JiunNo ratings yet
- D+D+D+D+D DDDDD: Section ADocument22 pagesD+D+D+D+D DDDDD: Section Aputri eva elinaNo ratings yet
- F 3 CirclesDocument4 pagesF 3 CirclesNur BainiNo ratings yet
- Deber#1 2P 2QTrigonometriaDocument7 pagesDeber#1 2P 2QTrigonometriaTommy Allen Ojeda PlúasNo ratings yet
- PPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre ODocument17 pagesPPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre OakuesukaNo ratings yet
- Shaded Area 4Document1 pageShaded Area 4danNo ratings yet
- A39 Mensuration 2D Shapes QuestionsDocument46 pagesA39 Mensuration 2D Shapes QuestionsThe KingpinNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ujian Selaras 1 Matematik Ting 3 & Skema JawapanDocument10 pagesSoalan Ujian Selaras 1 Matematik Ting 3 & Skema JawapanWawa Zameri100% (1)
- Circular Measure Past YrDocument3 pagesCircular Measure Past YrpizamNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure: Answer: .....................................Document8 pagesCircular Measure: Answer: .....................................Yogeswary GobalkrishnanNo ratings yet
- SM Pei Min 2021 1 Semester Exam Junior 3 Modern MathematicsDocument15 pagesSM Pei Min 2021 1 Semester Exam Junior 3 Modern MathematicsTeng Wei KiangNo ratings yet
- Mathematics10 Quarter2 Week5Document6 pagesMathematics10 Quarter2 Week5Jaymar AbetoNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions Subjective: 2 Hours 30 MinutesDocument19 pagesObjective Questions Subjective: 2 Hours 30 MinutesksganNo ratings yet
- Satprep Assignment: Circular Measurement 1.: Diagram Not To ScaleDocument5 pagesSatprep Assignment: Circular Measurement 1.: Diagram Not To ScaleJoel SohNo ratings yet
- 06 Circular MeasureDocument11 pages06 Circular MeasureTerence RileyNo ratings yet
- Tarea - Sector CircularDocument3 pagesTarea - Sector CirculareduxitoooNo ratings yet
- 06 Circular MeasureDocument10 pages06 Circular MeasureVivianne YongNo ratings yet
- Poligon Lukisan Kejuruteraan TIngkatan 4Document13 pagesPoligon Lukisan Kejuruteraan TIngkatan 4fara adhwaNo ratings yet
- I Love Maths Series Book 2 - Euclidean GeometryDocument113 pagesI Love Maths Series Book 2 - Euclidean Geometrylusandamelissa69No ratings yet
- Arc Length and Areas of SectorsDocument10 pagesArc Length and Areas of SectorsRafena MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Classifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92From EverandClassifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92No ratings yet
- Soal Uas Kelas 1 SD Saraswati 22Document3 pagesSoal Uas Kelas 1 SD Saraswati 22Nanda RusistaNo ratings yet
- 3D-Pythagoras and Trigonometry AnswersDocument3 pages3D-Pythagoras and Trigonometry Answersaidanzam13No ratings yet
- Math2412 Double Angle Power Reducing Half Angle IdentitiesDocument5 pagesMath2412 Double Angle Power Reducing Half Angle IdentitiesSylvia WilsonNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument69 pagesSimilarityavinandan chandraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A: Paper 3H Higher TierDocument24 pagesMathematics A: Paper 3H Higher Tierkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ProjectDocument8 pagesTrigonometry ProjectKiara Venice100% (1)
- Unit 2 Trigonometry LessonsDoneDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Trigonometry LessonsDoneNatasha MarieNo ratings yet
- Itf Marks BoosterDocument3 pagesItf Marks Boosterkunalff1638No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Extra Exercises 3.1: Pythagoras' TheoremDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Extra Exercises 3.1: Pythagoras' TheoremPh DeNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Undefined TermsDocument22 pagesGrade 7 Undefined Termskaren takasaNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL 2022 Complete PDFDocument251 pagesSSC CGL 2022 Complete PDFMG ConceptNo ratings yet
- Triangle Inequality TheoremDocument9 pagesTriangle Inequality TheoremCarlene MallariNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series: 12.1 Periodic FunctionsDocument35 pagesFourier Series: 12.1 Periodic Functionskishor nNo ratings yet
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya Sachin100% (1)
- 2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8Document7 pages2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8siyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Formula SheetDocument1 pageAP Calculus AB Formula SheetArad zeinaliNo ratings yet
- 01 Euclidean GeometryDocument23 pages01 Euclidean Geometrymiriam martinezNo ratings yet
- KMT Syllabus & PapersDocument2 pagesKMT Syllabus & PaperswutthicsaNo ratings yet
- ANGLEDocument37 pagesANGLEAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Geometry HistoryDocument2 pagesGeometry HistoryManilyn Requejo ObalNo ratings yet
- Online Week 5&6Document17 pagesOnline Week 5&6Rondex PabloNo ratings yet
- 01-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper-1Document7 pages01-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper-1SUB MOH MAYA HAI100% (1)
- Straight Line and Pair of Straight LinesDocument25 pagesStraight Line and Pair of Straight LinesHem kumarNo ratings yet
- A Generalization of The Spieker Circle and Nagel LineDocument8 pagesA Generalization of The Spieker Circle and Nagel LineMichael de VilliersNo ratings yet
- TSA Andvolume of SolidsDocument14 pagesTSA Andvolume of SolidsJairNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Properties of CirclesDocument17 pagesGeometrical Properties of CirclesJoann NgNo ratings yet
- Math Resources Geometry FormulasDocument2 pagesMath Resources Geometry FormulasMoslem GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- English Mathematics - 2022 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9: Formal Assessment Task Revision and Formal Assessment TaskDocument6 pagesEnglish Mathematics - 2022 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9: Formal Assessment Task Revision and Formal Assessment TaskThemba NyoniNo ratings yet