Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yc Yc
Yc Yc
Uploaded by
Yasaswy GunturiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yc Yc
Yc Yc
Uploaded by
Yasaswy GunturiCopyright:
Available Formats
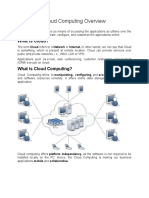
Cloud computing is a general term for anything that involves delivering hosted services over the Internet.
These services are broadly divided into three categories: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). The name cloud computing was inspired by the cloud symbol that's often used to represent the Internet in flowcharts and diagrams.
Characteristics
Cloud computing exhibits the following key characteristics:
y y y y y y y y y y
Agility Application Programming Interface (API) Cost Device and location independence Multi-tenancy Reliability Scalability Performance Security Maintenance
The term "cloud" is used as a metaphor for the Internet, based on the cloud drawing used in the past to represent the telephone network and later to depict the Internet in computer network diagrams as an abstraction of the underlying infrastructure it represents. A cloud can be private or public. A public cloud sells services to anyone on the Internet. (Currently, Amazon Web Services is the largest public cloud provider.) A private cloud is a proprietary network or a data center that supplies hosted services to a limited number of people. When a service provider uses public cloud resources to create their private cloud, the result is called a virtual private cloud. Private or public, the goal of cloud computing is to provide easy, scalable access to computing resources and IT services.
Research
Many universities, vendors and government organizations are investing in research around the topic of cloud computing:
In October 2007 the Academic Cloud Computing Initiative (ACCI) was announced as a multi-university project designed to enhance students' technical knowledge to address the challenges of cloud computing.
You might also like
- Cloud ComputingDocument11 pagesCloud ComputingLvenkatesh VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Definition 451Document2 pagesDefinition 451Ambekar NitinkumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument2 pagesCloud ComputingAnju NishadNo ratings yet
- Rajvardhan Oak ADM NO: 326615 Class: Xi EDocument17 pagesRajvardhan Oak ADM NO: 326615 Class: Xi ERaj OakNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument2 pagesCloud ComputingAmritendraNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing in A View: Cloud Computing Is A General Term For Anything That Involves DeliveringDocument9 pagesCloud Computing in A View: Cloud Computing Is A General Term For Anything That Involves DeliveringGrace ShankarNo ratings yet
- CC Evolution Od CloudDocument51 pagesCC Evolution Od CloudTushar MircheNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument25 pagesCloud ComputingANU_ECIMT100% (5)
- A Brief Introduction To Cloud Computing: Iaas (Infrastructure As Service)Document4 pagesA Brief Introduction To Cloud Computing: Iaas (Infrastructure As Service)Swagato RayNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesCloud ComputingkeyurNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Paper2Document4 pagesCloud Computing Paper2Akanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Architecture& Services: Manju Sharma, Sadia Husain, Halah ZainDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Architecture& Services: Manju Sharma, Sadia Husain, Halah Zainelangolatha5No ratings yet
- Zarmina DDB Ass#1Document13 pagesZarmina DDB Ass#1Meena JadoonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Cloud Computing ArchitectureDocument13 pagesUnit 2-Cloud Computing ArchitectureShristi PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument32 pagesCloud ComputingBala Subramanian100% (2)
- LESSON in ELECTIVE 4Document7 pagesLESSON in ELECTIVE 4GENED Bernadine GoyalNo ratings yet
- 2-Overview of Cloud ComputingDocument7 pages2-Overview of Cloud ComputinginderNo ratings yet
- RSA Data SecurityDocument5 pagesRSA Data Securitybikram160106No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Google Cloud Platform (GCP)Document1 pageCloud Computing: Google Cloud Platform (GCP)Michael Roy CimatuNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? AnsDocument8 pagesAssignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? Ansvashishttyagi91No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Basic ConceptDocument24 pagesCloud Computing: Basic ConceptGourav RanaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument13 pagesCloud ComputingJaskaranrehalNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument13 pagesCloud ComputingDamak SanaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - PrashantDocument6 pagesCloud Computing - PrashantSachin MauryaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Presented By: CHEOW KEVIN 1B4 20141081DIT NG MEE XUAN 1 B3 20141034DITDocument28 pagesCloud Computing: Presented By: CHEOW KEVIN 1B4 20141081DIT NG MEE XUAN 1 B3 20141034DITKevin CheowNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Impact On The Business Session 4Document17 pagesCloud Computing and Impact On The Business Session 4G D M SupriyaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesCloud ComputingtejuNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument15 pagesCloud ComputingHala GharibNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument20 pagesCloud ComputingxyzNo ratings yet
- Face RecognitionDocument36 pagesFace Recognitionkirankatke33No ratings yet
- 6LbN6J3C6PfMf19KYeAMbSDocument21 pages6LbN6J3C6PfMf19KYeAMbSAmol VermaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesCloud ComputingKarishma KumariNo ratings yet
- Saroj: Under The Guidance of Prof.Y.C.kulkarniDocument31 pagesSaroj: Under The Guidance of Prof.Y.C.kulkarniKalyan SinghNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document50 pagesBook 1Asad MoinuddinNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesCloud Computingsamiksha5singhalNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: MD Abul Kalam AzadDocument38 pagesCloud Computing: MD Abul Kalam AzadSaiful Islam Ony100% (1)
- Loud Computing: Download Now: Speech-to-Text Services: AWS vs. Microsoft vs. GoogleDocument26 pagesLoud Computing: Download Now: Speech-to-Text Services: AWS vs. Microsoft vs. GoogleVincent MoralesNo ratings yet
- UNIT2-Introduction To Cloud Computing4 PDFDocument95 pagesUNIT2-Introduction To Cloud Computing4 PDFjanuaryNo ratings yet
- Tawi Engineering College: Assignment 1 of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesTawi Engineering College: Assignment 1 of Cloud ComputingAmanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing OverviewDocument7 pagesCloud Computing OverviewALANNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesEvolution of Cloud Computinghiteshsharma01abuNo ratings yet
- Que-Explain The Framework Architecture of SPI For Cloud Computing?Document10 pagesQue-Explain The Framework Architecture of SPI For Cloud Computing?Vaibhav KukadiNo ratings yet
- Description of Cloud ComputingDocument1 pageDescription of Cloud Computing3 PNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: by Pragya Chakshoo (4067) To Prof. Narender Singh ChauhanDocument10 pagesAssignment On: by Pragya Chakshoo (4067) To Prof. Narender Singh ChauhanPragya ChakshooNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Aksa KalsoomDocument17 pagesCloud Computing: Aksa KalsoomlailaaabidNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument31 pagesCloud ComputingJayanth GsskNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and VirtualizationDocument29 pagesCloud Computing and VirtualizationPriyanka AggarwalNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingAnish SunchuNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 2Document28 pagesUnit 3 2rachananandhan3007No ratings yet
- Case Study Based On: Cloud Deployment and Service Delivery ModelsDocument10 pagesCase Study Based On: Cloud Deployment and Service Delivery ModelsNikunj JenaNo ratings yet
- Javed HallikeriDocument23 pagesJaved Hallikerifarukgoundi014No ratings yet
- Thesis On Cloud ComputingDocument71 pagesThesis On Cloud Computingashutoshsnp96No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing VocabularyDocument4 pagesCloud Computing VocabularyLuis Alfonso ChandíaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A General Term Used To Describe A New Class ofDocument7 pagesCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A General Term Used To Describe A New Class ofsori1No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument38 pagesCloud ComputingRanjan RajNo ratings yet
- Virtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationDocument5 pagesVirtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing.: By: Deepak Yadav B.Tech (H.C.S.T.)Document22 pagesCloud Computing.: By: Deepak Yadav B.Tech (H.C.S.T.)dips032No ratings yet
- Iaas Paas) Saas FlowchartDocument3 pagesIaas Paas) Saas FlowchartersharvanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet