Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCCCC C CCCC C C
CCCCC C CCCC C C
Uploaded by
vgevgbrnhgCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Problems For Practice LCR CircuitDocument2 pagesProblems For Practice LCR CircuitNeha AttriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document2 pagesChapter 7Monisha RNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New SDocument4 pagesTutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New STan Nian HanNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3Document2 pagesAssignment#3allan mugishaNo ratings yet
- Problems 33Document12 pagesProblems 33Daniyar MuratovNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - 05-Subjective Unsolved (C.B.S.E.) LevelDocument2 pagesAlternating Current - 05-Subjective Unsolved (C.B.S.E.) LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledAnamika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - 06 - Subjective Unsolved Level-IIDocument3 pagesAlternating Current - 06 - Subjective Unsolved Level-IIRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet 6Document2 pagesPractice Sheet 6Utkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 Alternating Current CircuitDocument3 pagesTutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuithuijing966No ratings yet
- Class 12 AssignmentDocument3 pagesClass 12 AssignmentAMAN KUMAR SHAWNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Serway 6 e Problems 33Document12 pagesSerway 6 e Problems 33Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDocument3 pagesTutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems in SingleDocument1 pageSample Problems in SingleIvy Jude Panes GabalesNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesAlternating Current Important QuestionsArnav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ac and Emi MCQSDocument5 pagesAc and Emi MCQSGuru ki physicsNo ratings yet
- DPP01CH07C12PDocument3 pagesDPP01CH07C12PAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- ADCExmpDocument10 pagesADCExmpgromit948No ratings yet
- ECE 226 Chapter 1 Tutorial QuestionsDocument20 pagesECE 226 Chapter 1 Tutorial QuestionsFilbert OmbongiNo ratings yet
- EE103 Homework 4Document2 pagesEE103 Homework 4Hubert SemenianoNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits - WorksheetDocument2 pagesAC Circuits - WorksheetShiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Self Induction ProblemDocument1 pageSelf Induction ProblemSun SopheakNo ratings yet
- Phy 1Document4 pagesPhy 1Garlapati Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: AnswerDocument22 pagesAlternating Current: AnswersmsubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Success Study Circle Physics Test FM 20 Time 45minDocument1 pageSuccess Study Circle Physics Test FM 20 Time 45minashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Ac PDFDocument15 pagesAc PDFAAKASH RUSTAGINo ratings yet
- Bio Assign 1Document17 pagesBio Assign 1Gaurav ShekharNo ratings yet
- Kee-101 TutDocument2 pagesKee-101 TutsanidhyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 1Document1 pageTutorial - 1Shreyansh KashaudhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- Module2 Qbank 2023-24Document3 pagesModule2 Qbank 2023-24Aqsa MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Ac & DCDocument3 pagesProblem Set Ac & DCPaolo Steven PolintanNo ratings yet
- Circuits 22Document4 pagesCircuits 22Davis Spat TambongNo ratings yet
- Ch33 PHYS 205 Problems To Solve in Class Alternating Current CircuitsDocument3 pagesCh33 PHYS 205 Problems To Solve in Class Alternating Current CircuitsAllyson OffreyNo ratings yet
- Emi and Ac AssignmentDocument5 pagesEmi and Ac AssignmentMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetAJ REPECILONo ratings yet
- Acdpp 1633763219Document14 pagesAcdpp 1633763219atul kumarNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Bee Theory and Nuerical Question BankDocument7 pagesBee Theory and Nuerical Question BankC1 314 Krishna GavaneNo ratings yet
- An AC Voltage of The Form VDocument2 pagesAn AC Voltage of The Form VTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Key - ExerciseDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Key - Exercisevenkatalakshmi civilNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 7 [AC & AC Circuits]Document2 pagesProblems Set 7 [AC & AC Circuits]Matty MontshoNo ratings yet
- Electric NoteDocument6 pagesElectric NoteKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current ExerciseDocument17 pagesAlternating Current ExerciseCarzyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 INAC X1X2Document2 pagesAssignment 1 INAC X1X2Joyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Revision Worksheet 2 - Alternating CurrentDocument5 pagesChapter 7 - Revision Worksheet 2 - Alternating CurrentVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Circuits-SrkDocument2 pagesAlternating Current Circuits-SrkShiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Question and Answers With SolutionDocument16 pagesQuestion and Answers With SolutionYuan LabayNo ratings yet
- PHY102 Numerical-Problems-6 Summer2020Document1 pagePHY102 Numerical-Problems-6 Summer2020Ambrin AishaNo ratings yet
- Question and Answers OnlyDocument3 pagesQuestion and Answers OnlyYuan LabayNo ratings yet
- Acckt Single PhaseDocument6 pagesAcckt Single Phaseken peligrinoNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument2 pagesAC CircuitsShiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Abdallah LotfyNo ratings yet
- RLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZDocument3 pagesRLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZMoshotle InnocentNo ratings yet
- Test of Alternating CurrentDocument1 pageTest of Alternating CurrentmarvelxslayyNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits 1 Batch 13Document2 pagesAC Circuits 1 Batch 13Jan Henry JebulanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document1 pageAssignment 8Pavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
CCCCC C CCCC C C
CCCCC C CCCC C C
Uploaded by
vgevgbrnhgOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CCCCC C CCCC C C
CCCCC C CCCC C C
Uploaded by
vgevgbrnhgCopyright:
Available Formats
Alternating Current (Physics Paathshala)
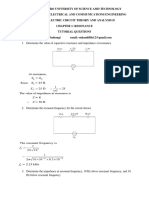
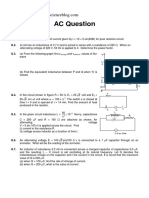
1. Find the time required for a 50 Hz alternating current to change its value from zero to the rms value. 2. The household supply of electricity is at 220 V (rms value) and 50 Hz. Find the peak voltage and the least possible time in which the voltage can change from the rms value to zero. 3. A bulb rated 60 W at 220 V is connected across a household supply of alternating voltage of 220 V. Calculate the maximum instantaneous current through the filament. 4. An electric bulb is designed to operate at 12 volts DC. If this bulb is connected to an AC source and gives normal brightness, what would be the peak voltage of the source ? 5. The peak power consumed by a resistive coil when connected to an AC source is 80 W. Find the energy consumed by the coil in 100 seconds which is many times larger than the time period of the source. 6. The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 x 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm 2 and plate separation 0.l0 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source which can be safely connected to this capacitor.
7. A capacitor of capacitance 10 F is connected to an oscillator giving an output voltage E = (10 V)sin t. Find the peak currents in the circuit for = 10 s-1 , 100 s-1 , 500 s-1, 1000 s-1. 8. A resistor of resistance 100 is connected to an AC source E = (12 V) sin (250 )t. Find the energy dissipated as heat during t = 0 to t = 1.0 ms.
9. In a series RC circuit with an AC source, R = 300 , C = 25 F, E0 = 50V and v = 50/ Hz. Find the peak current and the average power dissipated in the circuit. 10. A transformer has 50 turns in the primary and 100 in the secondary. If the primary is connected to a 220 V DC supply, what will be the voltage across the secondary ? 11. An AC source rated 100 V (rms) supplies a current of 10 A (rms) to a circuit. The average power delivered by the source (a) must be 1000 W (b) may be 1000 W (c) may be greater than 1000 W (d) may be less than 1000 W.
www.physicspaathshala.org
You might also like
- Problems For Practice LCR CircuitDocument2 pagesProblems For Practice LCR CircuitNeha AttriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document2 pagesChapter 7Monisha RNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New SDocument4 pagesTutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New STan Nian HanNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3Document2 pagesAssignment#3allan mugishaNo ratings yet
- Problems 33Document12 pagesProblems 33Daniyar MuratovNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - 05-Subjective Unsolved (C.B.S.E.) LevelDocument2 pagesAlternating Current - 05-Subjective Unsolved (C.B.S.E.) LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledAnamika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - 06 - Subjective Unsolved Level-IIDocument3 pagesAlternating Current - 06 - Subjective Unsolved Level-IIRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet 6Document2 pagesPractice Sheet 6Utkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 Alternating Current CircuitDocument3 pagesTutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuithuijing966No ratings yet
- Class 12 AssignmentDocument3 pagesClass 12 AssignmentAMAN KUMAR SHAWNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Serway 6 e Problems 33Document12 pagesSerway 6 e Problems 33Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDocument3 pagesTutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems in SingleDocument1 pageSample Problems in SingleIvy Jude Panes GabalesNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesAlternating Current Important QuestionsArnav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ac and Emi MCQSDocument5 pagesAc and Emi MCQSGuru ki physicsNo ratings yet
- DPP01CH07C12PDocument3 pagesDPP01CH07C12PAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- ADCExmpDocument10 pagesADCExmpgromit948No ratings yet
- ECE 226 Chapter 1 Tutorial QuestionsDocument20 pagesECE 226 Chapter 1 Tutorial QuestionsFilbert OmbongiNo ratings yet
- EE103 Homework 4Document2 pagesEE103 Homework 4Hubert SemenianoNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits - WorksheetDocument2 pagesAC Circuits - WorksheetShiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Self Induction ProblemDocument1 pageSelf Induction ProblemSun SopheakNo ratings yet
- Phy 1Document4 pagesPhy 1Garlapati Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: AnswerDocument22 pagesAlternating Current: AnswersmsubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Success Study Circle Physics Test FM 20 Time 45minDocument1 pageSuccess Study Circle Physics Test FM 20 Time 45minashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Ac PDFDocument15 pagesAc PDFAAKASH RUSTAGINo ratings yet
- Bio Assign 1Document17 pagesBio Assign 1Gaurav ShekharNo ratings yet
- Kee-101 TutDocument2 pagesKee-101 TutsanidhyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 1Document1 pageTutorial - 1Shreyansh KashaudhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- Module2 Qbank 2023-24Document3 pagesModule2 Qbank 2023-24Aqsa MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Ac & DCDocument3 pagesProblem Set Ac & DCPaolo Steven PolintanNo ratings yet
- Circuits 22Document4 pagesCircuits 22Davis Spat TambongNo ratings yet
- Ch33 PHYS 205 Problems To Solve in Class Alternating Current CircuitsDocument3 pagesCh33 PHYS 205 Problems To Solve in Class Alternating Current CircuitsAllyson OffreyNo ratings yet
- Emi and Ac AssignmentDocument5 pagesEmi and Ac AssignmentMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetAJ REPECILONo ratings yet
- Acdpp 1633763219Document14 pagesAcdpp 1633763219atul kumarNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Bee Theory and Nuerical Question BankDocument7 pagesBee Theory and Nuerical Question BankC1 314 Krishna GavaneNo ratings yet
- An AC Voltage of The Form VDocument2 pagesAn AC Voltage of The Form VTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Key - ExerciseDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Key - Exercisevenkatalakshmi civilNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 7 [AC & AC Circuits]Document2 pagesProblems Set 7 [AC & AC Circuits]Matty MontshoNo ratings yet
- Electric NoteDocument6 pagesElectric NoteKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current ExerciseDocument17 pagesAlternating Current ExerciseCarzyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 INAC X1X2Document2 pagesAssignment 1 INAC X1X2Joyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Revision Worksheet 2 - Alternating CurrentDocument5 pagesChapter 7 - Revision Worksheet 2 - Alternating CurrentVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Circuits-SrkDocument2 pagesAlternating Current Circuits-SrkShiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Question and Answers With SolutionDocument16 pagesQuestion and Answers With SolutionYuan LabayNo ratings yet
- PHY102 Numerical-Problems-6 Summer2020Document1 pagePHY102 Numerical-Problems-6 Summer2020Ambrin AishaNo ratings yet
- Question and Answers OnlyDocument3 pagesQuestion and Answers OnlyYuan LabayNo ratings yet
- Acckt Single PhaseDocument6 pagesAcckt Single Phaseken peligrinoNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument2 pagesAC CircuitsShiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Abdallah LotfyNo ratings yet
- RLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZDocument3 pagesRLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZMoshotle InnocentNo ratings yet
- Test of Alternating CurrentDocument1 pageTest of Alternating CurrentmarvelxslayyNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits 1 Batch 13Document2 pagesAC Circuits 1 Batch 13Jan Henry JebulanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document1 pageAssignment 8Pavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)









































![Problems Set 7 [AC & AC Circuits]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/747654362/149x198/2f30123c9a/1720029220?v=1)















