Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Tincture Is An Alcoholic Extract
A Tincture Is An Alcoholic Extract
Uploaded by
Rey KesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Tincture Is An Alcoholic Extract
A Tincture Is An Alcoholic Extract
Uploaded by
Rey KesCopyright:
Available Formats
A tincture is an alcoholic extract (e.g. of leaves or other plant material) or solution of a non-volatile substance (e.g. of iodine, mercurochrome).
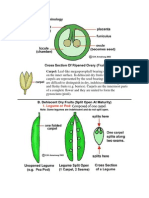
The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies (derived characteristics). These characteristics include flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds.
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos (), meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds (called ovules in their unfertilized state). Their naked condition stands in contrast to the seeds or ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed during pollination. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scale- or leaf-like appendages of cones, or at the end of short stalks (Ginkgo). The gymnosperms and angiosperms together comprise the spermatophytes or seed plants. By far the largest group of living gymnosperms are the conifers (pines, cypresses, and relatives), followed by cycads, Gnetales (Gnetophyta, Ephedra and Welwitschia), and Ginkgo (a single living species).
You might also like
- FLOWERDocument3 pagesFLOWERhendrix obcianaNo ratings yet
- Organoleptic Evaluation of The Different Parts of Plant (Flower, Fruits, and Seeds)Document13 pagesOrganoleptic Evaluation of The Different Parts of Plant (Flower, Fruits, and Seeds)Joanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Seed-Producing Plants Conifers Cycads Gnetophytes Greek Ovules Flowering Plants Ovary ConesDocument1 pageSeed-Producing Plants Conifers Cycads Gnetophytes Greek Ovules Flowering Plants Ovary ConesRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- gymnospermos γσμνόσπερμος: gymnospermsDocument1 pagegymnospermos γσμνόσπερμος: gymnospermsslyothersNo ratings yet
- Seed-Producing Plants Conifers Cycads Gnetales Greek Ovules: GinkgoDocument5 pagesSeed-Producing Plants Conifers Cycads Gnetales Greek Ovules: GinkgoRockyLagishettyNo ratings yet
- Vascular Plants: Group 5: Jessa Mae Mirador Kyla Mansarate Dianne FraginalDocument17 pagesVascular Plants: Group 5: Jessa Mae Mirador Kyla Mansarate Dianne FraginalIrvin EcalnirNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4.2 Class GymnospermaeDocument1 page2.2.4.2 Class GymnospermaeDiane EmpenoNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of GymnospermsDocument10 pagesGeneral Characteristics of GymnospermsJoules BillonesNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument2 pagesFlowering PlantsSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Vascular PlantDocument11 pagesVascular PlantSaad and ObaidNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm or GymnospermDocument2 pagesAngiosperm or Gymnospermtuti_ron_007100% (1)
- Advantages of GymnospermDocument2 pagesAdvantages of GymnospermKuyaMars Lorga AidadNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Report Outline: Overview (Supnet)Document4 pagesAngiosperm Report Outline: Overview (Supnet)Genghis SupnetNo ratings yet
- Nazmirafa Effendi A1F019039 Food Science and TechnologyDocument2 pagesNazmirafa Effendi A1F019039 Food Science and TechnologyNazmirafa EffendiNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant - WikipediaDocument125 pagesFlowering Plant - WikipediaBiology ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Topic: Angiosperm: DescriptionDocument12 pagesTopic: Angiosperm: DescriptionVINDHYA SHANKERNo ratings yet
- GRade 11 ScienceDocument3 pagesGRade 11 SciencePROx HUNTERzNo ratings yet
- What Are Angiosperms?Document5 pagesWhat Are Angiosperms?Yolo WoloNo ratings yet
- 4.what Is The Difference Between Gymnosperms and Angiosperms ? What Advantages Ids Angiosperms Have Over Gymnosperms ?Document2 pages4.what Is The Difference Between Gymnosperms and Angiosperms ? What Advantages Ids Angiosperms Have Over Gymnosperms ?Dat HoangNo ratings yet
- Which Is Not A Characteristic of The GymnospermsDocument9 pagesWhich Is Not A Characteristic of The Gymnospermsarissa noorNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlanTAEDocument26 pagesKingdom PlanTAEBaltazar EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Fruit: Botanic Fruit and Culinary FruitDocument5 pagesFruit: Botanic Fruit and Culinary FruitGrety IancuNo ratings yet
- (Class 11) Angiosperm Chapter 3Document8 pages(Class 11) Angiosperm Chapter 3Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Carmela VergaraDocument3 pagesCarmela Vergaracarmela vergaraNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant - WikipediaDocument75 pagesFlowering Plant - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms General CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesGymnosperms General Characteristicsrax dear100% (1)
- Anatomy of Seed and FruitDocument24 pagesAnatomy of Seed and FruitMonica LumbantobingNo ratings yet
- Cycadophyta: General CharactersDocument15 pagesCycadophyta: General CharactersagromamarvelNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantDocument1 pageClassification of PlantJeethin LevineNo ratings yet
- Fruit - WikipediaDocument53 pagesFruit - WikipediaOrigami toturial by AbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm: Seed Plants. Produce Reproductive Structures Called and - Angiosperms Are Also Known AsDocument11 pagesAngiosperm: Seed Plants. Produce Reproductive Structures Called and - Angiosperms Are Also Known AsazuitazoolkiflieNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument12 pagesBiologysakadynamites041No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- ApricotsDocument2 pagesApricotsArriane Joy Yturalde InsularNo ratings yet
- Division Spermatophyta 2012Document68 pagesDivision Spermatophyta 2012tomatasiin10No ratings yet
- 05 Plant KingdomDocument88 pages05 Plant Kingdomlucia.benito.sanz12No ratings yet
- BOT 101 Lecture Note On SpermatophytesDocument36 pagesBOT 101 Lecture Note On SpermatophytesAtoloye Favour100% (1)
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument59 pagesPerpetuation of LifeJhon Jeyno Rabia CabanteNo ratings yet
- Flower EssayDocument5 pagesFlower EssayallthingswaltNo ratings yet
- Project in Biology: Types of FruitsDocument10 pagesProject in Biology: Types of FruitsHannah Jean TinioNo ratings yet
- Dse V Sem Practical 3 Eng + HindiDocument9 pagesDse V Sem Practical 3 Eng + Hindimohitpatel18032003No ratings yet
- Bio Lab 13Document49 pagesBio Lab 13Jackie Swift FuntanillaNo ratings yet
- Seed Plant NotesDocument2 pagesSeed Plant NotesDesalegn WakshumaNo ratings yet
- GymnospermDocument5 pagesGymnospermAakash YadavNo ratings yet
- SUMMARDocument1 pageSUMMARMpho MathoboNo ratings yet
- Project in Biology: Types of FruitsDocument8 pagesProject in Biology: Types of FruitsHannah Jean TinioNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsATHIRA PNo ratings yet
- Vascular PlantDocument1 pageVascular PlantPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Land Plants Seed-Producing Plants Gymnosperms Synapomorphies Characteristics Flowers Endosperm FruitsDocument2 pagesLand Plants Seed-Producing Plants Gymnosperms Synapomorphies Characteristics Flowers Endosperm FruitsNimrod CabreraNo ratings yet
- Biology - February 2016Document1 pageBiology - February 2016Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant Life CycleDocument5 pagesFlowering Plant Life CycleTze XienNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm PDFDocument2 pagesAngiosperm PDFLiza Mortel CoralesNo ratings yet
- Fruit - WikipediaDocument62 pagesFruit - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- PteridophytesDocument5 pagesPteridophytesAsif SultanNo ratings yet
- Aggregate FruitsDocument2 pagesAggregate FruitsRamNo ratings yet
- Plant Geograph DefinitionsDocument2 pagesPlant Geograph DefinitionsSoraya FathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Points To RememberDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4No ratings yet
- Types of PlantsDocument2 pagesTypes of PlantsArt Justin SahagunNo ratings yet
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet