Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Turbines
Steam Turbines
Uploaded by
Vimal WoosyeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesRankine Cycledeepakkesri260% (1)
- SteamDocument24 pagesSteamsanju_17No ratings yet
- Experiment NoDocument5 pagesExperiment NoAbdullah UsmaniNo ratings yet
- Bhel TrainingDocument41 pagesBhel TrainingArun AroraNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument10 pagesSteam TurbineBilal Qasim50% (2)
- Thermal Power StationsDocument83 pagesThermal Power StationschdiNo ratings yet
- Types of Steam Turbines ReportDocument6 pagesTypes of Steam Turbines Reportalaa zahranNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbines: Presented By: Prof. Prabha Chand NIT Jamshedpur Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument44 pagesSteam Turbines: Presented By: Prof. Prabha Chand NIT Jamshedpur Department of Mechanical EngineeringArun Venkat100% (1)
- Experiment No 09Document3 pagesExperiment No 09Muhammad Zohaib ShahidNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine 2Document5 pagesSteam Turbine 2Pratibha PatelNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument58 pagesSteam TurbineJoy Prokash RoyNo ratings yet
- Class 4. Steam Power PlantDocument37 pagesClass 4. Steam Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
- '' Turbine - Nozzle - Diffuser - Compressor ''Document15 pages'' Turbine - Nozzle - Diffuser - Compressor ''Eng-Ahmed Salama100% (1)
- Steam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in ADocument13 pagesSteam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in AAnil Tandon100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant 1Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant 1ckissyou04No ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plantshamna AbdullaNo ratings yet
- AES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byDocument25 pagesAES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument47 pagesSteam Turbinegone gangasagarNo ratings yet
- BHEL Bhopal STM Training ReportDocument20 pagesBHEL Bhopal STM Training ReportMohit Assudani50% (2)
- Thermal Engineering - Ii: 111. What Is Steam Nozzle? How Are They Classified?Document61 pagesThermal Engineering - Ii: 111. What Is Steam Nozzle? How Are They Classified?karthiyuvenNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: HistoryDocument19 pagesChapter-1: HistoryraisNo ratings yet
- pptPPE (15&17)Document22 pagespptPPE (15&17)HarshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Power CyclesDocument23 pagesChapter 2-Power CyclesbaseakelNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesRankine CycleAshish GargNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine ReportDocument21 pagesSteam Turbine Reportchampbhushan82% (11)
- Turbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItDocument10 pagesTurbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: AdvantagesDocument6 pagesSteam Turbine: AdvantagesMahi100% (1)
- Steam Power Plants CyclesDocument4 pagesSteam Power Plants CyclesJohn Michael PioquintoNo ratings yet
- CollectionDocument7 pagesCollectionRohan RustagiNo ratings yet
- Nozzles Notes PDFDocument83 pagesNozzles Notes PDFAbubakkar Siddiq83% (6)
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclerr1819No ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument5 pagesRankine CycleRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument46 pagesSteam TurbinePOWERBOOKONE100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Power CycleDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Power CycleBese Mat100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument41 pagesThermodynamicsNicole Andrei BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesExperiment No.4: ObjectiveMahrukh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant PDFDocument47 pagesSteam Power Plant PDFSandeep Gupta100% (1)
- PGD 161018125619 PDFDocument47 pagesPGD 161018125619 PDFveerchetan007No ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)Document11 pagesRankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)bnida99No ratings yet
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument3 pagesSteam TurbineErAbdulRehmanNo ratings yet
- Extraction CondensingDocument3 pagesExtraction CondensingSharath Kota0% (1)
- A Gas Turbine UnitDocument9 pagesA Gas Turbine UnitTITU NATHNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: HistoryDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine: HistoryrikumohanNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclesbmmla100% (1)
- Chapter-5 Steam TurbineDocument26 pagesChapter-5 Steam Turbinehadush gebre100% (1)
- Vapor Power CyclesDocument8 pagesVapor Power CyclesGürel ÖzeşmeNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument12 pagesSteam TurbineMandeep Singh PannuNo ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Experiment No 1: Categories For Conventional Power Plants 1. Fossil Fuel Power Plants or Thermal PlantDocument8 pagesExperiment No 1: Categories For Conventional Power Plants 1. Fossil Fuel Power Plants or Thermal Plantmughees khanNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesFrom EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesFrom EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- The Steam Engine and Turbine - A Text Book for Engineering CollegesFrom EverandThe Steam Engine and Turbine - A Text Book for Engineering CollegesNo ratings yet
Steam Turbines
Steam Turbines
Uploaded by
Vimal WoosyeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Steam Turbines
Steam Turbines
Uploaded by
Vimal WoosyeCopyright:
Available Formats
Steam turbines
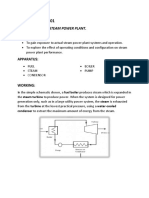
Steam turbines are devices which convert the energy stored in steam into rotational mechanical energy. The machines are widely used for the generation of electricity in a number of different cycles, such as: Rankine cycle Reheat cycle Regenerative cycle Combined cycle The steam turbine may consists of several stages. Each stage can be described by analysing the expansion of steam from a higher pressure to a lower pressure. The steam may be wet, dry saturated or superheated.
Considering the steam turbine s=cycle shown above. The output Power of the turbine at steady flow condition is; P = m (h1-h2) Where m is the mass flow of the steam through the turbine and h1 and h2 are specific enthalpy of the steam at inlet respective outlet of the turbine
The efficiency of the steam turbines is often described by the isentropic efficiency for expansion process. The presence of water droplets in the steam will reduce the efficiency of the turbine and cause physical erosion of the blades. Therefore the dryness fraction of the stream at the outlet of the turbine should not be less than 0.9
How a steam turbines operate.
In a steam turbine the high-pressure steam from the boiler expands in a set of Stationary blades or vanes (or nozzles). The high-velocity steam from the nozzles Strikes the set of moving blades .The kinetic energy of the steam is used to produce work on the turbine rotor. And Low-pressure steam then exhausts to the condenser. There are two classical types of turbine stage designs: the impulse stage the reaction stage. Steam turbines can be noncondensing or condensing. In noncondensing turbines (or backpressure turbines) steam exhausts at a pressure greater than atmospheric. Steam then leaves the turbine and is utilized in other parts of the plant that use the heat of the steam for other processes. The backpressure turbines have very high efciencies (range from 67% to 75%). A multi-stage condensing turbine is a turbine in which steam exhausts to a condenser and is condensed by air-cooled condensers. The exhaust pressure from the turbine is less than the atmospheric. In this turbine, cycle efciency is low because a large part of the steam energy is lost in the condenser.
You might also like
- Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesRankine Cycledeepakkesri260% (1)
- SteamDocument24 pagesSteamsanju_17No ratings yet
- Experiment NoDocument5 pagesExperiment NoAbdullah UsmaniNo ratings yet
- Bhel TrainingDocument41 pagesBhel TrainingArun AroraNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument10 pagesSteam TurbineBilal Qasim50% (2)
- Thermal Power StationsDocument83 pagesThermal Power StationschdiNo ratings yet
- Types of Steam Turbines ReportDocument6 pagesTypes of Steam Turbines Reportalaa zahranNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbines: Presented By: Prof. Prabha Chand NIT Jamshedpur Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument44 pagesSteam Turbines: Presented By: Prof. Prabha Chand NIT Jamshedpur Department of Mechanical EngineeringArun Venkat100% (1)
- Experiment No 09Document3 pagesExperiment No 09Muhammad Zohaib ShahidNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine 2Document5 pagesSteam Turbine 2Pratibha PatelNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument58 pagesSteam TurbineJoy Prokash RoyNo ratings yet
- Class 4. Steam Power PlantDocument37 pagesClass 4. Steam Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
- '' Turbine - Nozzle - Diffuser - Compressor ''Document15 pages'' Turbine - Nozzle - Diffuser - Compressor ''Eng-Ahmed Salama100% (1)
- Steam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in ADocument13 pagesSteam Turbine: A Rotor of A Modern Steam Turbine, Used in AAnil Tandon100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant 1Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant 1ckissyou04No ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plantshamna AbdullaNo ratings yet
- AES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byDocument25 pagesAES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument47 pagesSteam Turbinegone gangasagarNo ratings yet
- BHEL Bhopal STM Training ReportDocument20 pagesBHEL Bhopal STM Training ReportMohit Assudani50% (2)
- Thermal Engineering - Ii: 111. What Is Steam Nozzle? How Are They Classified?Document61 pagesThermal Engineering - Ii: 111. What Is Steam Nozzle? How Are They Classified?karthiyuvenNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: HistoryDocument19 pagesChapter-1: HistoryraisNo ratings yet
- pptPPE (15&17)Document22 pagespptPPE (15&17)HarshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Power CyclesDocument23 pagesChapter 2-Power CyclesbaseakelNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesRankine CycleAshish GargNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine ReportDocument21 pagesSteam Turbine Reportchampbhushan82% (11)
- Turbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItDocument10 pagesTurbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: AdvantagesDocument6 pagesSteam Turbine: AdvantagesMahi100% (1)
- Steam Power Plants CyclesDocument4 pagesSteam Power Plants CyclesJohn Michael PioquintoNo ratings yet
- CollectionDocument7 pagesCollectionRohan RustagiNo ratings yet
- Nozzles Notes PDFDocument83 pagesNozzles Notes PDFAbubakkar Siddiq83% (6)
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclerr1819No ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument5 pagesRankine CycleRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument46 pagesSteam TurbinePOWERBOOKONE100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Power CycleDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Power CycleBese Mat100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument41 pagesThermodynamicsNicole Andrei BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesExperiment No.4: ObjectiveMahrukh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant PDFDocument47 pagesSteam Power Plant PDFSandeep Gupta100% (1)
- PGD 161018125619 PDFDocument47 pagesPGD 161018125619 PDFveerchetan007No ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)Document11 pagesRankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)bnida99No ratings yet
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument3 pagesSteam TurbineErAbdulRehmanNo ratings yet
- Extraction CondensingDocument3 pagesExtraction CondensingSharath Kota0% (1)
- A Gas Turbine UnitDocument9 pagesA Gas Turbine UnitTITU NATHNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: HistoryDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine: HistoryrikumohanNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclesbmmla100% (1)
- Chapter-5 Steam TurbineDocument26 pagesChapter-5 Steam Turbinehadush gebre100% (1)
- Vapor Power CyclesDocument8 pagesVapor Power CyclesGürel ÖzeşmeNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument12 pagesSteam TurbineMandeep Singh PannuNo ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Experiment No 1: Categories For Conventional Power Plants 1. Fossil Fuel Power Plants or Thermal PlantDocument8 pagesExperiment No 1: Categories For Conventional Power Plants 1. Fossil Fuel Power Plants or Thermal Plantmughees khanNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesFrom EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesFrom EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- The Steam Engine and Turbine - A Text Book for Engineering CollegesFrom EverandThe Steam Engine and Turbine - A Text Book for Engineering CollegesNo ratings yet