Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polarisation: Antenna and Wave Propogation
Polarisation: Antenna and Wave Propogation
Uploaded by
Manish SahaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polarisation: Antenna and Wave Propogation
Polarisation: Antenna and Wave Propogation
Uploaded by
Manish SahaCopyright:
Available Formats
ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPOGATION
MU Aligarh
POLARISATION
WE ARE:-
Presented To:Mr. Sudheer Sharma (HOD of EC)
Pulkit Jain:- 2009UEC077 Navneet :- 2009UEC074 Ekansh jaiN:- 2009UEC078
POLARISATION
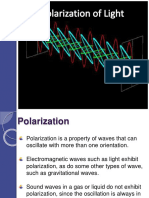
The polarization of an electromagnetic wave is defined as the orientation of the electric field vector.
Polarization (also polarisation) is a property of certain types of waves that describes the orientation of their oscillations. Electomagnetic waves, such as light, and gravitational waves exhibit polarization
Types Of Polarisation:1. Linear Polarisation
2. Circullar Polarisation 3. Ellipstical polarisation
Types of Polarisation
Linear Polarisation:A plane electromagnetic (EM) wave is characterized by travelling in a single direction (with no field variation in the two orthogonal directions). In this case, the electric field and the magnetic field are perpendicular to each other and to the direction the plane wave is propagating.
Kinds Of Linear Polarisation:1. VERTICAL POLARISATION
An antenna is said to be vertically polarized (linear) when its electric field is perpendicular to the Earth's surface. An example of a vertical antenna is a broadcast tower for AM radio or the "whip" antenna on an automobile.
2.HORIZONTAL POLARISATION:-
Horizontally polarized (linear) antennas have their electric field parallel to the Earth's surface. Television transmissions in the USA use horizontal polarization.
Circullar Polarisation:A circular polarized wave radiates energy in both the horizontal and vertical planes and all planes in between.
Ellipstical Polarisation:Elliptically polarizationconsists of two perpendicular waves of unequal amplitude which differ in phase by 90. The illustration shows right- elliptically polarized light.
THANK YOU..
You might also like
- Prepared by Habtamu WegariDocument12 pagesPrepared by Habtamu WegariAnonymous fYS62EVNo ratings yet
- EM Presentation (Types of Polarization)Document9 pagesEM Presentation (Types of Polarization)Avinash JadhavNo ratings yet
- Polarization of LightDocument7 pagesPolarization of Lightjunaid ahmadNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Electromagnetic WavesDocument13 pages1.7 Electromagnetic WavessfwongNo ratings yet
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocument28 pagesB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDhyey DESAIIINo ratings yet
- Exp5 - Polarization of Light PDFDocument10 pagesExp5 - Polarization of Light PDFSwarnava SanyalNo ratings yet
- Coralia AntenasDocument3 pagesCoralia AntenasALEX_125No ratings yet
- PolarizationDocument2 pagesPolarizationJaykrishnan ChembakaseriNo ratings yet
- Polarization PresentationDocument17 pagesPolarization PresentationMuhammad Ahkam KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 8: Polarization of Light: Figure 1: (A) Oscillation of E Vector, (B) An Electromagnetic FieldDocument10 pagesLab 8: Polarization of Light: Figure 1: (A) Oscillation of E Vector, (B) An Electromagnetic Fieldpankajpnd1No ratings yet
- EM Wave Propagation and PolarisationDocument13 pagesEM Wave Propagation and PolarisationSurya Prakash Singh100% (1)
- Unit IV Quantum ComputingDocument25 pagesUnit IV Quantum ComputingAnirudha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Polarization of Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pagePolarization of Electromagnetic WavesRana SaleemNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationBiswajit MohantyNo ratings yet
- Polarization (Waves)Document12 pagesPolarization (Waves)Leo HuangNo ratings yet
- Polarization RajuDocument61 pagesPolarization Rajuhibonow281No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsAparna ArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Polarization of Light and Its ManipulationDocument7 pagesPolarization of Light and Its ManipulationMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Lecture Notes PDFDocument9 pagesUNIT I Lecture Notes PDFAyush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PolarizationoteDocument14 pagesPolarizationoteOvijit KarmokarNo ratings yet
- Properties of Light 1Document23 pagesProperties of Light 1shafiulNo ratings yet
- Polarization WavesDocument37 pagesPolarization WavesNil TaiiayNo ratings yet
- Document Polarisation of LightDocument9 pagesDocument Polarisation of LightKunal KashyapNo ratings yet
- Z02120000220144012Session 20-21Document30 pagesZ02120000220144012Session 20-21tasyawijayaNo ratings yet
- MR of SP's Assignment On 2205Document16 pagesMR of SP's Assignment On 2205meenhaz7096No ratings yet
- Unit-1fundamentals of ElectromagneticDocument91 pagesUnit-1fundamentals of Electromagneticmuvin236No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Optical Fiber Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument11 pagesUnit 1 - Optical Fiber Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMainak NaskarNo ratings yet
- Classification of PolarizationDocument2 pagesClassification of Polarizationather_88No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics ProjectAkash NarayanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electricity and MagnetismDocument81 pagesUnit 1 Electricity and Magnetismeric appiahNo ratings yet
- Blaze - Radiation PressureDocument11 pagesBlaze - Radiation PressureDr. John BeveridgeNo ratings yet
- Machine1 Houndout FullDocument145 pagesMachine1 Houndout Fullkifle203No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductonDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic InductonAishwarya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Magnetite: Electrical Machines I (Eec 123) Lecture Notes For ND I (Prepared by Engr Aminu A.A.)Document26 pagesMagnetite: Electrical Machines I (Eec 123) Lecture Notes For ND I (Prepared by Engr Aminu A.A.)Micah AlfredNo ratings yet
- 0465 FB 1892452195Document7 pages0465 FB 1892452195Daudi Erasto MlangiNo ratings yet
- PolarizationDocument38 pagesPolarizationMazaya NoveriwaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic WavessomarshidubeyNo ratings yet
- PolarisationDocument5 pagesPolarisationandykym52No ratings yet
- PolarizationDocument8 pagesPolarizationYashmeen KaurNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Document10 pagesClass X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Mohammad RezaullahNo ratings yet
- Polarization of LightDocument46 pagesPolarization of LightTanvi MathurNo ratings yet
- 11th WeekDocument6 pages11th WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- PolarizationDocument17 pagesPolarizationHussein DahirNo ratings yet
- 3 Polarisation Chem Eng April 2022 DR Paul V3Document54 pages3 Polarisation Chem Eng April 2022 DR Paul V3Vaidik SomjiyaniNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Plan INTGRDocument4 pagesMagnetism Plan INTGRعالم المسلسلاتNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument22 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric CurrentAnurag Tiwari100% (1)
- PolarizationDocument10 pagesPolarizationVinnu ChNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document12 pagesCH 13charanNo ratings yet
- What Is LightDocument26 pagesWhat Is LightAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Isotropic Indicatrix: INDICATRIX - A 3 Dimensional Geometric Figure On Which The IndexDocument22 pagesIsotropic Indicatrix: INDICATRIX - A 3 Dimensional Geometric Figure On Which The IndexFajar Rohmala100% (1)
- Zeeman and Paschen-Back EffectDocument12 pagesZeeman and Paschen-Back EffectKamanpreet Singh100% (1)
- Light Orbital Angular Momentum - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesLight Orbital Angular Momentum - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamaheshnrmNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument30 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentEmil MammenNo ratings yet
- 13 Magnetic Effects of Electricity 1Document28 pages13 Magnetic Effects of Electricity 1Ranvijay RajputNo ratings yet
- PH 201 Optics & Lasers: Lecture - Polarization - 1Document24 pagesPH 201 Optics & Lasers: Lecture - Polarization - 1Selvi RNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field PDFDocument29 pagesMagnetic Field PDFPuran BistaNo ratings yet
- SDASDASDSADocument17 pagesSDASDASDSAAkash BidhuriNo ratings yet
- LEC6Document18 pagesLEC6emad zedanNo ratings yet