Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Area of Plane Doraha (B)
Area of Plane Doraha (B)
Uploaded by
api-3731257Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lecture 4 - QuadrilateralsDocument29 pagesLecture 4 - QuadrilateralsSandra Enn BahintingNo ratings yet
- Mensuration of Plane Figures (Triangle)Document5 pagesMensuration of Plane Figures (Triangle)Danica AguilarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document17 pagesLecture 01David OrtegaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Document10 pagesMensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Danica AguilarNo ratings yet
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- Plane Figures: Group 1Document49 pagesPlane Figures: Group 1Danielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IDocument21 pagesSolid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IAzha Clarice Villanueva100% (1)
- Plane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureDocument5 pagesPlane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureKasmawati FatirNo ratings yet
- GEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresDocument23 pagesGEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresPREFIX THAT IS LONG - Lester LoutteNo ratings yet
- The Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaDocument12 pagesThe Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaMolla DerbewNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals NotesDocument11 pagesQuadrilaterals NotesJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- POLYGONSDocument45 pagesPOLYGONSBlessa Mae100% (1)
- Area Perimeter FormulaDocument2 pagesArea Perimeter Formulasamsonf94100% (3)
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Topic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutDocument15 pagesTopic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutShine100% (1)
- Math HelpDocument8 pagesMath Helpatiggy05100% (1)
- Parallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelDocument25 pagesParallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelAdrianD.PalenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Maths NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Maths NotesViral DaftaryNo ratings yet
- Area Perimeter CircumferenceDocument2 pagesArea Perimeter CircumferenceMathnasium of BentonvilleNo ratings yet
- A About Area and PerimeterDocument11 pagesA About Area and PerimeterAmiel ColanoNo ratings yet
- Polygons 1 1Document32 pagesPolygons 1 1pcuaron100% (1)
- S (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CDocument3 pagesS (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CSaideep AryalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument100 pagesChapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsSushanta Singh100% (1)
- Mensuration FormulaDocument2 pagesMensuration FormulaSrijita SinhaNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument12 pagesGeometryJose Marviel JesoroNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesDocument34 pagesGeometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesVaseem Raza Mirza100% (1)
- Solid MensurationDocument60 pagesSolid MensurationBenePicar100% (2)
- Area Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaDocument12 pagesArea Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaPankaj Jirafe100% (1)
- Yr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCDocument412 pagesYr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCRichard Yang93% (14)
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesDocument40 pagesGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoNo ratings yet
- Geometry ProblemsDocument54 pagesGeometry Problemshvphatak80% (5)
- MENSURATION-I (Area & Perimeter)Document12 pagesMENSURATION-I (Area & Perimeter)sanjeevNo ratings yet
- Ariel Li Basic GeometryDocument5 pagesAriel Li Basic GeometryOmkar MandalNo ratings yet
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocument1 pageAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNo ratings yet
- Triangles: Here, Ab Ac B CDocument1 pageTriangles: Here, Ab Ac B CDavidkumar MoramNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Triangles: Learning Enhancement TeamDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Triangles: Learning Enhancement Teamthierry abaniNo ratings yet
- 5 1 A Geometricshapesarea LennonDocument23 pages5 1 A Geometricshapesarea Lennonapi-234212327No ratings yet
- QuadrilateralDocument18 pagesQuadrilateralIshaan PunjNo ratings yet
- of MensurationDocument18 pagesof MensurationSACHIN SHROTRI100% (1)
- Triangle Square: Heptagon OctagonDocument54 pagesTriangle Square: Heptagon OctagonJyotsna Rawal100% (1)
- My Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookDocument18 pagesMy Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookJhayNo ratings yet
- Perform CalculationDocument30 pagesPerform CalculationDave FlautaNo ratings yet
- Monica Sant Monica Sant IX IX - A ADocument18 pagesMonica Sant Monica Sant IX IX - A AsrinivasvzmNo ratings yet
- Revcards SSMDocument12 pagesRevcards SSMapi-200177496No ratings yet
- MH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeDocument12 pagesMH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeNikhil Mahajan100% (1)
- Geometry Glossary of TermsDocument8 pagesGeometry Glossary of Termsapi-66400853No ratings yet
- Perimeter, Surface Area and VolumeDocument3 pagesPerimeter, Surface Area and Volumejoebloggs_comNo ratings yet
- RectangleDocument11 pagesRectangleapi-3731257No ratings yet
- 1705 - Week 5 Lesson Note For JSS3 Mathematics XXDocument5 pages1705 - Week 5 Lesson Note For JSS3 Mathematics XXimohammedpublicationsNo ratings yet
- Geometry Equations: Triangles Area Surface Area Perimeter & Circumference MiscellaneousDocument10 pagesGeometry Equations: Triangles Area Surface Area Perimeter & Circumference MiscellaneousSabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Geo7 HTMDocument4 pagesGeo7 HTMjhdmssNo ratings yet
- Geometric FormulasDocument7 pagesGeometric Formulasprince168No ratings yet
- 2dmensuration PDF 19 28Document10 pages2dmensuration PDF 19 28PRAKASH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasDocument10 pagesImportant Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasAmey GudigarNo ratings yet
- Class 10+2Document5 pagesClass 10+2api-3731257No ratings yet
- Govt. High. School Jhitan KalanDocument15 pagesGovt. High. School Jhitan Kalanapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Batch:-3 Phase - I Roll No.-34 Class-12 Subject: - General English Topic: - The Death of SocratesDocument13 pagesBatch:-3 Phase - I Roll No.-34 Class-12 Subject: - General English Topic: - The Death of Socratesapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Sarojini Naidu: The Nightingale of IndiaDocument9 pagesSarojini Naidu: The Nightingale of Indiaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- CH7 ForgettingDocument29 pagesCH7 Forgettingapi-3731257100% (1)
- Author:-J.L Nehru: JL Nehru Was 1 Prime Minister of IndiaDocument17 pagesAuthor:-J.L Nehru: JL Nehru Was 1 Prime Minister of Indiaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- General AidsDocument8 pagesGeneral Aidsapi-3731257No ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: Fasting As PenanceDocument10 pagesA Project Report ON: Fasting As Penanceapi-3731257No ratings yet
- GSSBANDALA English)Document14 pagesGSSBANDALA English)api-3731257No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 12 Class Topic Noun and VerbDocument18 pagesLesson Plan 12 Class Topic Noun and Verbapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Ghsmehma Amritsar Maori VillagesDocument10 pagesGhsmehma Amritsar Maori Villagesapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Ghsguruwali ForgettingDocument7 pagesGhsguruwali Forgettingapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Indian Weavers - Tarn Taran (G) - Tarn Taran (C)Document10 pagesIndian Weavers - Tarn Taran (G) - Tarn Taran (C)api-3731257No ratings yet
- No Men Are Foreign - Tarsikka - AmritsarDocument10 pagesNo Men Are Foreign - Tarsikka - Amritsarapi-3731257100% (1)
- Ghsmanawala - The School For SympathyDocument5 pagesGhsmanawala - The School For Sympathyapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Indian Weavers - Gaggobua) Tarn Taran (C)Document19 pagesIndian Weavers - Gaggobua) Tarn Taran (C)api-373125760% (5)
- Indian Weavers - Pandori Gola - Tarn Taran (A)Document13 pagesIndian Weavers - Pandori Gola - Tarn Taran (A)api-37312570% (1)
- Daffodils - Pandori Ran Singh - Tarn Taran (A)Document11 pagesDaffodils - Pandori Ran Singh - Tarn Taran (A)api-3731257No ratings yet
- Tolstoy's Home Sohian Khurd AmritsarDocument13 pagesTolstoy's Home Sohian Khurd Amritsarapi-3731257100% (2)
- On Saying Please Sanghana AmritsarDocument15 pagesOn Saying Please Sanghana Amritsarapi-3731257100% (2)
- The Lost Child Pakharpura AmritsarDocument5 pagesThe Lost Child Pakharpura Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Diamond Necklace Pakharpura AmritsarDocument8 pagesDiamond Necklace Pakharpura Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Leisure Nagkalan AmritsarDocument11 pagesLeisure Nagkalan Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Tense Nagkalan AmritsarDocument17 pagesTense Nagkalan Amritsarapi-3731257100% (1)
Area of Plane Doraha (B)
Area of Plane Doraha (B)
Uploaded by
api-3731257Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Area of Plane Doraha (B)
Area of Plane Doraha (B)
Uploaded by
api-3731257Copyright:
Available Formats
GOVT. SEN.SEC.
SCHOOL, DORAHA
Area of Plane Figure
The figures which can be drawn in one plane are called plane figures. For
example, triangles, quadrilaterals and circles etc. are plane figures.
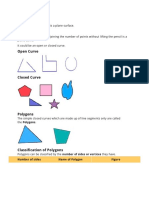
Polygon
A close plane figure formed by n line segments is called an n-sided polygon.
Thus, a closed figure of three sides is a triangle, a closed figure of four sides
is a quadrilateral and a closed figure of five sides is called a pentagon.
A polygon is called a regular polygon if all its sides and angles are equal.
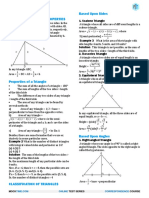
Triangle
A Closed figure obtained by joining three non-collinear point is called a
triangle.
In fig. ABCD a, b, c are sides, h altitude.
s= (a+b+c)/2
Area of triangle= ½(ch)
Right Triangle
A triangle, one of whose angle is a right angle i.e. of 90o is called a Right
Angled Triangle or Simply a Right Triangle.
In fig ABC d=√b²+h²
Area of Right Triangle =½(bh)
Isosceles Right Triangle
A triangle, one of whose angle is a right angle i.e. of 90o,with two equal
sides and two other equal angles always of 45°
In Fig. ABC d=a√2
Area of Isosceles Right Triangle= ½a²
Equilateral Triangle
A triangle having all three sides of equal length. The angles of an equilateral
triangle all measure 60 degrees.
In Fig. ABC h= √3/2a
Area of Equilateral Triangle= 1/2ah, √3/4a²
Rectangle
A four-sided polygon having all right angles. The sum of the angles of a
rectangle is 360 degrees
In Fig. ABCD a=length, b=breadth.
Area of Rectangle= a*b
Square
A four-sided polygon having equal-length sides meeting at right angles. The
sum of the angles of a square is 360 degrees.
In Fig. ABCD a= side
Area of Square= a²
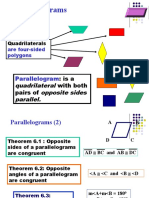
Parallelogram
A four-sided polygon with two pairs of parallel sides. The sum of the angles
of a parallelogram is 360 degrees.
In Fig. ABCD a= side, b=side, h=distance between parallel sides of
length a.
Area of Parallelogram= a*h
Rhombus
A four-sided polygon having all four sides of equal length. The sum of the
angles of a rhombus is 360 degrees.
In Fig. ABCD a=side, d1d2 -are the diagonals.
Area of Rhombus= ½ (d1*d2)
Trapezium
A four-sided polygon having exactly one pair of parallel sides. The two sides
that are parallel are called the bases of the trapezium. The sum of the angles
of a trapezium is 360 degrees.
In Fig. ABCD a, b= parallel sides, h=distance between them.
Area of Trapezium= ½(a+b) h
Circle
A circle is the collection of points in a plane that are all the same distance
from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the center. A line segment joining
the center to any point on the circle is called a radius.
In this fig. r-radius
Area of circle= π r2
BIBLIOGRAPHY
• TEXT BOK OF MATHEMETICS (P.S.E.B) OF CLASS 9TH
• TEXT BOK OF MATHEMETICS (P.S.E.B) OF CLASS 7TH
SOFTWARE USED
• MS-PAINT
• MS-WORD
You might also like
- Lecture 4 - QuadrilateralsDocument29 pagesLecture 4 - QuadrilateralsSandra Enn BahintingNo ratings yet
- Mensuration of Plane Figures (Triangle)Document5 pagesMensuration of Plane Figures (Triangle)Danica AguilarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document17 pagesLecture 01David OrtegaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Document10 pagesMensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Danica AguilarNo ratings yet
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- Plane Figures: Group 1Document49 pagesPlane Figures: Group 1Danielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IDocument21 pagesSolid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IAzha Clarice Villanueva100% (1)
- Plane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureDocument5 pagesPlane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureKasmawati FatirNo ratings yet
- GEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresDocument23 pagesGEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresPREFIX THAT IS LONG - Lester LoutteNo ratings yet
- The Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaDocument12 pagesThe Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaMolla DerbewNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals NotesDocument11 pagesQuadrilaterals NotesJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- POLYGONSDocument45 pagesPOLYGONSBlessa Mae100% (1)
- Area Perimeter FormulaDocument2 pagesArea Perimeter Formulasamsonf94100% (3)
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Topic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutDocument15 pagesTopic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutShine100% (1)
- Math HelpDocument8 pagesMath Helpatiggy05100% (1)
- Parallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelDocument25 pagesParallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelAdrianD.PalenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Maths NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Maths NotesViral DaftaryNo ratings yet
- Area Perimeter CircumferenceDocument2 pagesArea Perimeter CircumferenceMathnasium of BentonvilleNo ratings yet
- A About Area and PerimeterDocument11 pagesA About Area and PerimeterAmiel ColanoNo ratings yet
- Polygons 1 1Document32 pagesPolygons 1 1pcuaron100% (1)
- S (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CDocument3 pagesS (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CSaideep AryalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument100 pagesChapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsSushanta Singh100% (1)
- Mensuration FormulaDocument2 pagesMensuration FormulaSrijita SinhaNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument12 pagesGeometryJose Marviel JesoroNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesDocument34 pagesGeometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesVaseem Raza Mirza100% (1)
- Solid MensurationDocument60 pagesSolid MensurationBenePicar100% (2)
- Area Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaDocument12 pagesArea Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaPankaj Jirafe100% (1)
- Yr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCDocument412 pagesYr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCRichard Yang93% (14)
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesDocument40 pagesGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoNo ratings yet
- Geometry ProblemsDocument54 pagesGeometry Problemshvphatak80% (5)
- MENSURATION-I (Area & Perimeter)Document12 pagesMENSURATION-I (Area & Perimeter)sanjeevNo ratings yet
- Ariel Li Basic GeometryDocument5 pagesAriel Li Basic GeometryOmkar MandalNo ratings yet
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocument1 pageAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNo ratings yet
- Triangles: Here, Ab Ac B CDocument1 pageTriangles: Here, Ab Ac B CDavidkumar MoramNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Triangles: Learning Enhancement TeamDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Triangles: Learning Enhancement Teamthierry abaniNo ratings yet
- 5 1 A Geometricshapesarea LennonDocument23 pages5 1 A Geometricshapesarea Lennonapi-234212327No ratings yet
- QuadrilateralDocument18 pagesQuadrilateralIshaan PunjNo ratings yet
- of MensurationDocument18 pagesof MensurationSACHIN SHROTRI100% (1)
- Triangle Square: Heptagon OctagonDocument54 pagesTriangle Square: Heptagon OctagonJyotsna Rawal100% (1)
- My Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookDocument18 pagesMy Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookJhayNo ratings yet
- Perform CalculationDocument30 pagesPerform CalculationDave FlautaNo ratings yet
- Monica Sant Monica Sant IX IX - A ADocument18 pagesMonica Sant Monica Sant IX IX - A AsrinivasvzmNo ratings yet
- Revcards SSMDocument12 pagesRevcards SSMapi-200177496No ratings yet
- MH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeDocument12 pagesMH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeNikhil Mahajan100% (1)
- Geometry Glossary of TermsDocument8 pagesGeometry Glossary of Termsapi-66400853No ratings yet
- Perimeter, Surface Area and VolumeDocument3 pagesPerimeter, Surface Area and Volumejoebloggs_comNo ratings yet
- RectangleDocument11 pagesRectangleapi-3731257No ratings yet
- 1705 - Week 5 Lesson Note For JSS3 Mathematics XXDocument5 pages1705 - Week 5 Lesson Note For JSS3 Mathematics XXimohammedpublicationsNo ratings yet
- Geometry Equations: Triangles Area Surface Area Perimeter & Circumference MiscellaneousDocument10 pagesGeometry Equations: Triangles Area Surface Area Perimeter & Circumference MiscellaneousSabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Geo7 HTMDocument4 pagesGeo7 HTMjhdmssNo ratings yet
- Geometric FormulasDocument7 pagesGeometric Formulasprince168No ratings yet
- 2dmensuration PDF 19 28Document10 pages2dmensuration PDF 19 28PRAKASH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasDocument10 pagesImportant Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasAmey GudigarNo ratings yet
- Class 10+2Document5 pagesClass 10+2api-3731257No ratings yet
- Govt. High. School Jhitan KalanDocument15 pagesGovt. High. School Jhitan Kalanapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Batch:-3 Phase - I Roll No.-34 Class-12 Subject: - General English Topic: - The Death of SocratesDocument13 pagesBatch:-3 Phase - I Roll No.-34 Class-12 Subject: - General English Topic: - The Death of Socratesapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Sarojini Naidu: The Nightingale of IndiaDocument9 pagesSarojini Naidu: The Nightingale of Indiaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- CH7 ForgettingDocument29 pagesCH7 Forgettingapi-3731257100% (1)
- Author:-J.L Nehru: JL Nehru Was 1 Prime Minister of IndiaDocument17 pagesAuthor:-J.L Nehru: JL Nehru Was 1 Prime Minister of Indiaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- General AidsDocument8 pagesGeneral Aidsapi-3731257No ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: Fasting As PenanceDocument10 pagesA Project Report ON: Fasting As Penanceapi-3731257No ratings yet
- GSSBANDALA English)Document14 pagesGSSBANDALA English)api-3731257No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 12 Class Topic Noun and VerbDocument18 pagesLesson Plan 12 Class Topic Noun and Verbapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Ghsmehma Amritsar Maori VillagesDocument10 pagesGhsmehma Amritsar Maori Villagesapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Ghsguruwali ForgettingDocument7 pagesGhsguruwali Forgettingapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Indian Weavers - Tarn Taran (G) - Tarn Taran (C)Document10 pagesIndian Weavers - Tarn Taran (G) - Tarn Taran (C)api-3731257No ratings yet
- No Men Are Foreign - Tarsikka - AmritsarDocument10 pagesNo Men Are Foreign - Tarsikka - Amritsarapi-3731257100% (1)
- Ghsmanawala - The School For SympathyDocument5 pagesGhsmanawala - The School For Sympathyapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Indian Weavers - Gaggobua) Tarn Taran (C)Document19 pagesIndian Weavers - Gaggobua) Tarn Taran (C)api-373125760% (5)
- Indian Weavers - Pandori Gola - Tarn Taran (A)Document13 pagesIndian Weavers - Pandori Gola - Tarn Taran (A)api-37312570% (1)
- Daffodils - Pandori Ran Singh - Tarn Taran (A)Document11 pagesDaffodils - Pandori Ran Singh - Tarn Taran (A)api-3731257No ratings yet
- Tolstoy's Home Sohian Khurd AmritsarDocument13 pagesTolstoy's Home Sohian Khurd Amritsarapi-3731257100% (2)
- On Saying Please Sanghana AmritsarDocument15 pagesOn Saying Please Sanghana Amritsarapi-3731257100% (2)
- The Lost Child Pakharpura AmritsarDocument5 pagesThe Lost Child Pakharpura Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Diamond Necklace Pakharpura AmritsarDocument8 pagesDiamond Necklace Pakharpura Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Leisure Nagkalan AmritsarDocument11 pagesLeisure Nagkalan Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Tense Nagkalan AmritsarDocument17 pagesTense Nagkalan Amritsarapi-3731257100% (1)