Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Programming
Linear Programming
Uploaded by
Rolanda Williams BaldwinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linear Programming
Linear Programming
Uploaded by
Rolanda Williams BaldwinCopyright:
Available Formats
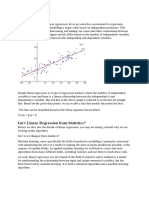
Linear Programming Linear programming is the process of taking various linear inequalities relating to some situation, and finding
the "best" value obtainable under those conditions. A typical example would be taking the limitations of materials and labor, and then determining the "best" production levels for maximal profits under those conditions. In "real life", linear programming is part of a very important area of mathematics called "optimization techniques". This field of study (or at least the applied results of it) are used every day in the organization and allocation of resources. These "real life" systems can have dozens or hundreds of variables, or more. In algebra, though, you'll only work with the simple (and graphable) two-variable linear case. Objective Function: The quantity modeled with the goal of finding the maximum or minimum. Constraints: Limits on the variables in the objective function, written as linear inequalities. Feasible Region: All the points the satisfy the constraints. Vertex Principle of Linear Programming: If there is a maximum or minimum of the linear objective function, it occurs at one or more vertices of the feasible region.
You might also like
- Project On Linear Programming ProblemsDocument29 pagesProject On Linear Programming ProblemsVinod Bhaskar67% (130)
- Project On Linear Programming ProblemsDocument32 pagesProject On Linear Programming ProblemsJeeban BaralNo ratings yet
- Vogue USA - January 2021Document94 pagesVogue USA - January 2021Andreea Dana100% (6)
- Multiobjective Optimization Scilab PDFDocument11 pagesMultiobjective Optimization Scilab PDFNiki Veranda Agil PermadiNo ratings yet
- Chemerinsky Points 01Document12 pagesChemerinsky Points 01Jared DerringerNo ratings yet
- Using graphical method to solve the linear programming.:ريرقتلا نساDocument5 pagesUsing graphical method to solve the linear programming.:ريرقتلا نساQUSI E. ABDNo ratings yet
- Rohit Oberoi - General A - Assignment 1Document6 pagesRohit Oberoi - General A - Assignment 1Rohit OberoiNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Graphical Methods: Presented By:-Ishant Soni Chitranshu KhareDocument8 pagesLinear Programming Graphical Methods: Presented By:-Ishant Soni Chitranshu KhareAlisa ConleyNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument25 pagesLinear ProgrammingEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Is A Mathematical Method For Optimizing Operations Given RestrictionsDocument10 pagesLinear Programming Is A Mathematical Method For Optimizing Operations Given RestrictionsJyoti SahuNo ratings yet
- LESSON 7 Vanjo BautistaDocument19 pagesLESSON 7 Vanjo BautistaChristian paul ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Operational ResearchDocument23 pagesOperational ResearchAyesha IqbalNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument20 pagesMaths ProjectChirag JoshiNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument23 pagesMaths ProjectAjay Vernekar100% (1)
- TheoryDocument5 pagesTheorysonali guptaNo ratings yet
- LP Quantitative TechniquesDocument29 pagesLP Quantitative TechniquesPrateek LoganiNo ratings yet
- Junal LPDocument25 pagesJunal LPGumilang Al HafizNo ratings yet
- Scan Doc0002Document9 pagesScan Doc0002jonty777No ratings yet
- Unit 4,5Document13 pagesUnit 4,5ggyutuygjNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis DocumentationsDocument13 pagesRegression Analysis DocumentationssaeedNo ratings yet
- Isn't Linear Regression From Statistics?Document4 pagesIsn't Linear Regression From Statistics?umang rajanNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression For BeginnersDocument4 pagesLinear Regression For BeginnersrajatNo ratings yet
- MGMT ScienceDocument35 pagesMGMT ScienceraghevjindalNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming: X in This Case) - The Inequalities Ax B and X 0 Are TheDocument5 pagesLinear Programming: X in This Case) - The Inequalities Ax B and X 0 Are TheUrbi Roy BarmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document21 pagesUnit 2Rebecca SanchezNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument8 pagesLinear ProgrammingbeebeeNo ratings yet
- Performance CH 4Document76 pagesPerformance CH 4Yasichalew sefineh100% (2)
- Quantitative Techniques - 5.Document9 pagesQuantitative Techniques - 5.Suneel Kumar100% (1)
- Operations Research 1&2Document23 pagesOperations Research 1&2Der Dereje100% (5)
- Application of Linear ProgrammingDocument18 pagesApplication of Linear ProgrammingrajvanshimanyaNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Linear ProgrammingDocument4 pagesMeaning of Linear ProgrammingYaimaran MaibamNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction To Operations Research Operations ResearchDocument45 pagesChapter One: Introduction To Operations Research Operations Researchtame kibruNo ratings yet
- Ch11 LPIntro PDFDocument31 pagesCh11 LPIntro PDFAnonymous jlLBRMAr3ONo ratings yet
- Theory: Assignment ProblemsDocument5 pagesTheory: Assignment Problemsnilkanth bhattNo ratings yet
- Models PDFDocument86 pagesModels PDFAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Problem (LPP)Document24 pagesLinear Programming Problem (LPP)Shrouk__Anas100% (1)
- Linear Programming ProblemDocument83 pagesLinear Programming ProblemAbdi NegassaNo ratings yet
- Vijay Maths ProjectDocument54 pagesVijay Maths ProjectVijay MNo ratings yet
- WRPM Assessment AnsDocument4 pagesWRPM Assessment Ansbiramoabinet59No ratings yet
- Op Tim IzationDocument4 pagesOp Tim Izationhashim_mokhtar9286No ratings yet
- Research Paper On Linear Programming Simplex MethodDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Linear Programming Simplex Methodnadevufatuz2No ratings yet
- Linear Programming ProblemDocument20 pagesLinear Programming Problemsravanicharitha MamidiNo ratings yet
- Linearprograming Chapter1Document21 pagesLinearprograming Chapter1rahul10janNo ratings yet
- AOR (Lecture 1) Part 1-1Document30 pagesAOR (Lecture 1) Part 1-1syedNo ratings yet
- BA 4201 QTDM Two Mark-1Document14 pagesBA 4201 QTDM Two Mark-1stalineantoNo ratings yet
- Thesis Linear ProgrammingDocument6 pagesThesis Linear Programmingnqvgequgg100% (2)
- Eem520l3 2023Document25 pagesEem520l3 2023Berkan TezcanNo ratings yet
- LLP IntroductionDocument13 pagesLLP IntroductionSIVARANJANI PNo ratings yet
- Define Operations Research: Applications of Management ScienceDocument5 pagesDefine Operations Research: Applications of Management ScienceShinjiNo ratings yet
- 5.6 - Linear Programming: DefinitionsDocument11 pages5.6 - Linear Programming: DefinitionsRamon VillarealNo ratings yet
- Optimisation and Optimal ControlDocument82 pagesOptimisation and Optimal ControlMona AliNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Simplex MethodDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Simplex Methodafmabbpoksbfdp100% (1)
- Ch06 Linear ProgrammingDocument35 pagesCh06 Linear ProgrammingRehan FarhatNo ratings yet
- Optimization Models HUSTDocument24 pagesOptimization Models HUSTLan - GV trường TH Trác Văn Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- Operations Research PDFDocument63 pagesOperations Research PDFHari ShankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument52 pagesChapter TwoMoti BekeleNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods OptimizationDocument19 pagesNumerical Methods Optimizationahmad ramdanNo ratings yet
- Optimization MathematicsDocument9 pagesOptimization MathematicsKrishna AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Business MathematicsDocument14 pagesBusiness MathematicsGirjesh Chouhan100% (1)
- CP Propeller Equipment PDFDocument22 pagesCP Propeller Equipment PDFHtet Myat SoeNo ratings yet
- MAR 851 - Advanced Marine Engines & Power Plants NEWDocument71 pagesMAR 851 - Advanced Marine Engines & Power Plants NEWViolet PellyNo ratings yet
- RITI HRM Diploma Handouts - Full VersionDocument246 pagesRITI HRM Diploma Handouts - Full Versionmohammed barghothiNo ratings yet
- Triplex HotDocument20 pagesTriplex HotСергей КартавицкийNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller For Embedded Systems RIC-651Document27 pagesMicrocontroller For Embedded Systems RIC-651এম.এস.এম রবিনNo ratings yet
- Malaysia ReportDocument136 pagesMalaysia ReportKhashayar NarooeiNo ratings yet
- ADB Annual Report 1999Document317 pagesADB Annual Report 1999Asian Development BankNo ratings yet
- Micro Project Report (English)Document13 pagesMicro Project Report (English)Chaitali KumbharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document47 pagesChapter 07Muhammad AzharNo ratings yet
- Unveiling Creative Advertising: Top Ad Agencies in Delhi NCR - APPPL COMBINEDocument2 pagesUnveiling Creative Advertising: Top Ad Agencies in Delhi NCR - APPPL COMBINEsairam.appplNo ratings yet
- Crafting Goals Objectives Vision and MisDocument19 pagesCrafting Goals Objectives Vision and MisJC Viacrucis JuaneroNo ratings yet
- Gamon Plus v. Campbell Soup - ComplaintDocument180 pagesGamon Plus v. Campbell Soup - ComplaintSarah BursteinNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Balance Sheet As at March 31, 2021Document4 pagesConsolidated Balance Sheet As at March 31, 2021shreyansh naharNo ratings yet
- t1l2 Vol.5.3 Lucrari de Drum (Det)Document176 pagest1l2 Vol.5.3 Lucrari de Drum (Det)RaduIS91No ratings yet
- 3WA11 DatashDocument9 pages3WA11 DatashsuadNo ratings yet
- IPCO IP Sulphur Processing and Handling 08 2019 v1.1 LO-RESDocument20 pagesIPCO IP Sulphur Processing and Handling 08 2019 v1.1 LO-RESyamen-691904No ratings yet
- 25 (G.R. No. 213207. February 15, 2022)Document43 pages25 (G.R. No. 213207. February 15, 2022)faith.dungca02No ratings yet
- The Declaration of IndependenceDocument20 pagesThe Declaration of IndependenceEdisonSambiliNo ratings yet
- 15A05602 Data Warehousing & MiningDocument2 pages15A05602 Data Warehousing & MiningChitra Madhuri YashodaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Potential Impact of Ototoxicant Exposure On Worker HealthDocument17 pagesEvaluating The Potential Impact of Ototoxicant Exposure On Worker Healthani putkaradzeNo ratings yet
- Life Insurance: A Project Report OnDocument58 pagesLife Insurance: A Project Report Onkhan danishNo ratings yet
- Carnaval Owners ManualDocument17 pagesCarnaval Owners Manualmike_net8903No ratings yet
- Sta ExaDocument12 pagesSta ExaNiño Jose A. Flores (Onin)No ratings yet
- Case Study Unit 2Document2 pagesCase Study Unit 2Nga LêNo ratings yet
- Moeller Datasheet NZM-XHI11L 266098Document3 pagesMoeller Datasheet NZM-XHI11L 266098Aziz Fauzi .No ratings yet
- Computer Science SSCDocument20 pagesComputer Science SSCsonicefuNo ratings yet
- Diy Sls 3d PrinterDocument32 pagesDiy Sls 3d PrinterTF Escritório MGNo ratings yet