Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care Plan
Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jose Mari F. EsguerraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case StudyDocument33 pagesPneumonia Case StudyArceo AbiGail100% (3)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Asthma Care PlanDocument3 pagesAsthma Care PlanSam ParkNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- Fluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringDocument24 pagesFluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringdrjriNo ratings yet
- NCP Alcoholic NeuropathyDocument5 pagesNCP Alcoholic NeuropathyPeachy Marie Anca100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Case Study OpdDocument35 pagesCase Study OpdMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- NCP Proper 1Document6 pagesNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- Peritonsillar AbscessDocument2 pagesPeritonsillar AbscessKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFAkeroNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document1 pageChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument25 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Communicable DiseaseDocument15 pagesCase Study On Communicable DiseaseThiradevi BalakrisnanNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesHyperthermiapamgee100% (11)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesNursing Care PlanZhel Geron MercadoNo ratings yet
- NCP Cough PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Cough PneumoniaAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plansapi-19762967No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia and Risk For AspirationDocument3 pagesHyperthermia and Risk For AspirationAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia Care Plan/OthersDocument11 pagesOsteomalacia Care Plan/OthersJill Jackson, RNNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Care Plan For GastrectomyDocument16 pagesCare Plan For GastrectomyPriyal ParikhNo ratings yet
- CcroupDocument53 pagesCcroupOlivia BernadiNo ratings yet
- PP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Document16 pagesPP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Ali RumiNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Respiratory Tract ProblemsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Respiratory Tract ProblemsDianeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: IndependentJay Mar BabateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan, Diagnosis, Interventions Hyperthermia, Fever, High TemperatureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan, Diagnosis, Interventions Hyperthermia, Fever, High TemperatureVanessa AbboudNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- BPN NCPDocument6 pagesBPN NCPJoart EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- 8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pages8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelDocument16 pagesOxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelAmrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightTrisha Lapid MatulaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryDocument13 pagesCare of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryRazel Kinette AzotesNo ratings yet
- NCP2 - DengueDocument4 pagesNCP2 - DengueSummer SuarezNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Ncp-SinusitisDocument2 pagesIdoc - Pub Ncp-SinusitisEdson John Demayo100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument7 pagesNCP TBLorraine CilloNo ratings yet
- NCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainEerie EraNo ratings yet
- NCPGDMDocument8 pagesNCPGDMChristopher LontocNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Ayu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing CareDocument4 pagesAyu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Careson hyejooNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument7 pagesChest PhysiotherapyNikhil Mohan100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- DOH AO No 2020 0019 Service Delibvey NetworkDocument15 pagesDOH AO No 2020 0019 Service Delibvey NetworkJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Irr Chapter II - Water SupplyDocument17 pagesIrr Chapter II - Water SupplyJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- RHU-Consignee Details - TCW-3043 SDD - Icelined Vaccine Ref1Document4 pagesRHU-Consignee Details - TCW-3043 SDD - Icelined Vaccine Ref1Jose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Public Health TemplatesDocument16 pagesPublic Health TemplatesJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CCMHDocument35 pagesDrug Study CCMHJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Mellor Thesis FinalDocument152 pagesJonathan Mellor Thesis FinalJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care Plan
Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jose Mari F. EsguerraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care Plan
Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jose Mari F. EsguerraCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING CARE PLAN
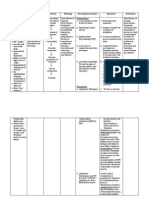
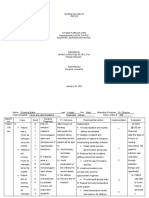
Patient Name: J.A. Age/Gender: 93 yrs. old / F Diagnosis: CAP with risk moderate HPN Ineffective airway clearance ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS SUBJECTIVE DATA: Nurse, nahihirapan akong huminga ngayon as verbalized by patient. OBJECTIVE DATA: Use of accessory muscle. Dyspnea Fatigue (+) alar flaring (+) intercostals retractions (+) wheezes @ both lung field (+) labored breathing V/S taken as follows: T: 37.3*C P: 80 bpm R: 31 cpm Bp: 120/80mmHg Ineffective airway clearance r/t increase bronchial secretion secondarty to pneumonia.
PLANNING After 8 hours of rendering of nursing intervention the patient will manifest effective breathing pattern.
INTERVENTION Independent: Elevate head of the bed, change position frequently.
RATIONALE
EVALUATION Goal Met:
Lowers diaphragm, promoting chest expansion and expectoration of secretions. Deep breathing facilitates maximum expansion of the lungs and smaller airways. Coughing is a natural self-cleaning mechanism. Splinting reduces chest discomfort, and an upright position favors deeper, more forceful cough effort.
After 8hours of rendering of nursing intervention patient able to manifest effective breathing pattern.
Assist patient with deep breathing exercises.
Demonstrate or help patient learn to perform activity like splinting chest and effective coughing while in upright position.
Force fluids to at least Fluids especially 3000 ml per day and warm liquids aid in offer warm, rather mobilization and than cold fluids. expectoration of secretions.
Auscultating patients chest
To monitor for the presence of abnormal breath sounds
Provide chest and back clapping with vibration
Chest physiotheraphy facilitates the loosening of secretions
Collaborative: Administers and titrates oxygen therapy as prescribed. Administer medications as prescribe: mucolytics or expectorants. Provide supplemental fluids. Support adequate body oxygenation of patient
Aids in reduction of bronchospasm and mobilization of secretions. Fluids are required to replace losses and aid in mobilization of secretions.
Assist respiratory therapist in performing nebulization of the patient
Nebulization is a favourable route of administering bronchodilators and aid in expectorating secretions, hence patients breathing
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case StudyDocument33 pagesPneumonia Case StudyArceo AbiGail100% (3)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Asthma Care PlanDocument3 pagesAsthma Care PlanSam ParkNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- Fluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringDocument24 pagesFluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringdrjriNo ratings yet
- NCP Alcoholic NeuropathyDocument5 pagesNCP Alcoholic NeuropathyPeachy Marie Anca100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Case Study OpdDocument35 pagesCase Study OpdMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- NCP Proper 1Document6 pagesNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- Peritonsillar AbscessDocument2 pagesPeritonsillar AbscessKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFAkeroNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document1 pageChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument25 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Communicable DiseaseDocument15 pagesCase Study On Communicable DiseaseThiradevi BalakrisnanNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesHyperthermiapamgee100% (11)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesNursing Care PlanZhel Geron MercadoNo ratings yet
- NCP Cough PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Cough PneumoniaAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plansapi-19762967No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia and Risk For AspirationDocument3 pagesHyperthermia and Risk For AspirationAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia Care Plan/OthersDocument11 pagesOsteomalacia Care Plan/OthersJill Jackson, RNNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Care Plan For GastrectomyDocument16 pagesCare Plan For GastrectomyPriyal ParikhNo ratings yet
- CcroupDocument53 pagesCcroupOlivia BernadiNo ratings yet
- PP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Document16 pagesPP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Ali RumiNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Respiratory Tract ProblemsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Respiratory Tract ProblemsDianeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: IndependentJay Mar BabateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan, Diagnosis, Interventions Hyperthermia, Fever, High TemperatureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan, Diagnosis, Interventions Hyperthermia, Fever, High TemperatureVanessa AbboudNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- BPN NCPDocument6 pagesBPN NCPJoart EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- 8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pages8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelDocument16 pagesOxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelAmrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightTrisha Lapid MatulaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryDocument13 pagesCare of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryRazel Kinette AzotesNo ratings yet
- NCP2 - DengueDocument4 pagesNCP2 - DengueSummer SuarezNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Ncp-SinusitisDocument2 pagesIdoc - Pub Ncp-SinusitisEdson John Demayo100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument7 pagesNCP TBLorraine CilloNo ratings yet
- NCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainEerie EraNo ratings yet
- NCPGDMDocument8 pagesNCPGDMChristopher LontocNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Ayu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing CareDocument4 pagesAyu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Careson hyejooNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument7 pagesChest PhysiotherapyNikhil Mohan100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- DOH AO No 2020 0019 Service Delibvey NetworkDocument15 pagesDOH AO No 2020 0019 Service Delibvey NetworkJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Irr Chapter II - Water SupplyDocument17 pagesIrr Chapter II - Water SupplyJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- RHU-Consignee Details - TCW-3043 SDD - Icelined Vaccine Ref1Document4 pagesRHU-Consignee Details - TCW-3043 SDD - Icelined Vaccine Ref1Jose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Public Health TemplatesDocument16 pagesPublic Health TemplatesJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CCMHDocument35 pagesDrug Study CCMHJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Mellor Thesis FinalDocument152 pagesJonathan Mellor Thesis FinalJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet