Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and Ketones
Test Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and Ketones
Uploaded by
Mj WeakCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BIO - Lab Report 5 - FoodDocument13 pagesBIO - Lab Report 5 - FoodNor Ashikin Ismail50% (2)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Minutes of Regular Meeting Held Last July 10Document3 pagesMinutes of Regular Meeting Held Last July 10Mj Weak97% (32)
- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueDocument28 pagesAldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueMissy NalaunanNo ratings yet
- Ace T AldehydeDocument5 pagesAce T AldehydeAlfa FallurinNo ratings yet
- Qualitative TestDocument4 pagesQualitative TestSwati KaushalNo ratings yet
- Identification of AlcoholsDocument26 pagesIdentification of Alcoholspupu_wowNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For Environmental HealthDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry For Environmental HealthASYRANI ZULAIKHANo ratings yet
- Chem 503 - Activity 5Document7 pagesChem 503 - Activity 5Aries Jay ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chem31.1 Finals NotesDocument8 pagesChem31.1 Finals NotesElla YapNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestDocument20 pagesQualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestFRANCEEN LEANNA KATIGBAKNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 3Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3GundanNo ratings yet
- Pre Laboratory AssignmentDocument44 pagesPre Laboratory AssignmentJr Montero100% (3)
- Chemistry VIVADocument3 pagesChemistry VIVAtanvir shahriarNo ratings yet
- Experiment N0.6 - Aldehydes and Ketones-1Document3 pagesExperiment N0.6 - Aldehydes and Ketones-1Vida HumadasNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1Document93 pagesAldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1jjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde-Ketone TestsDocument3 pagesAldehyde-Ketone TestsNorazma ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- 12Document6 pages12NathaLie Sta ElenaNo ratings yet
- 2 5352688982180245339Document11 pages2 5352688982180245339حسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- A Positive Result Is A Red-Orange Precipitate of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazoneDocument3 pagesA Positive Result Is A Red-Orange Precipitate of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazoneBianca Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Expt 5 8 ResultsDocument4 pagesExpt 5 8 ResultsAdrian SantolomaNo ratings yet
- Detection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesDetection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsKiran PatroNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17Document28 pagesReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17angeline medallo100% (1)
- Labreport 8 OrganicDocument12 pagesLabreport 8 OrganicHajarul AjiehahNo ratings yet
- BALDONADO, LESLEY JOY - Activity On Aldehydes and KetonesDocument3 pagesBALDONADO, LESLEY JOY - Activity On Aldehydes and KetonesLesley Joy T. BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesDanluidQMalintadNo ratings yet
- BC Lab (Carbohydrates)Document4 pagesBC Lab (Carbohydrates)Cassandra HerreraNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument9 pagesAldehydesNadine Jamih100% (2)
- Theory 3 Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesTheory 3 Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesColor Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesRüveyda AkçinNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument19 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidPraneel BhattNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compound Khaled AlhiagemDocument14 pagesCarbonyl Compound Khaled Alhiagemkhfgf;lNo ratings yet
- Benedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesBenedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochem Lab ReviewerDarlin Maree JamonNo ratings yet
- Lab 6-283gDocument11 pagesLab 6-283gAnonymous 4KuItFhNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument40 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsMiguelNo ratings yet
- Lelm108 Pages 8Document1 pageLelm108 Pages 8ABCNo ratings yet
- Lab Expts 5-7 ReviewDocument6 pagesLab Expts 5-7 ReviewKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Report 4Document7 pagesChemistry Report 4Lih XuanNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compound-2Document20 pagesCarbonyl Compound-2fishindasea00No ratings yet
- Chem-No.-13 2Document5 pagesChem-No.-13 2ho laNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument119 pagesAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsKashvi KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Report SheetDocument21 pagesExperiment 7 Report SheetDiane Princess SultanNo ratings yet
- Iodoform OrganicDocument14 pagesIodoform OrganicJefy Liapril100% (2)
- FM7 Labreport 2Document12 pagesFM7 Labreport 2Jei y’allNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 3Document11 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 3wmaximoff426No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesDocument58 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Test For Carbohydrates: CHY 47.1 Biochemistry LaboratoryDocument11 pagesExercise 4 Test For Carbohydrates: CHY 47.1 Biochemistry LaboratorycamilleNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates LabBernardMarkMateoNo ratings yet
- Test For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalDocument31 pagesTest For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- 46.1.06 AOAC Official Surplus Method 920.209 Natural Coloring Matters Identification by Color Reactions First Action Surplus 1970Document3 pages46.1.06 AOAC Official Surplus Method 920.209 Natural Coloring Matters Identification by Color Reactions First Action Surplus 1970Khaled KayaliNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Expt 10Document4 pagesLab Report Expt 10Eyvette GoNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument5 pages4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsFin BrickmanNo ratings yet
- EXPE9Document8 pagesEXPE9K-yanVehraaYomomaNo ratings yet
- 3.theory Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesDocument11 pages3.theory Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 2Document16 pagesPractical No. 2shahbazNo ratings yet
- A Volumetric Analysis (Redox Titration) of Hypochlorite in BleachDocument5 pagesA Volumetric Analysis (Redox Titration) of Hypochlorite in Bleachskrim240No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- The National Teachers CollegeDocument4 pagesThe National Teachers CollegeMj WeakNo ratings yet
- Insect SterilizationDocument19 pagesInsect SterilizationMj WeakNo ratings yet
- Is The Internet Making Us StupidDocument2 pagesIs The Internet Making Us StupidMj WeakNo ratings yet
Test Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and Ketones
Test Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and Ketones
Uploaded by
Mj WeakOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and Ketones
Test Specific Purpose of The Test Principle Involved: Aldehydes and Ketones
Uploaded by
Mj WeakCopyright:
Available Formats
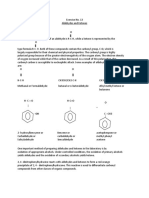
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Test SCHIFFS TEST Specific Purpose of the Test Test for aldehydes Principle Involved
RedOx reaction; Leucosulfunic acid is unstable and loses sulfurous acid when treated with an aldehyde, resulting to a violet-purple quinoid dye Equations
(nasa baba, Shriner, ang sa taas, nakita ko lang sa mga files dito)
Visible Results Aldehydes => violet purple color (+) with characteristic blue cast Ketones => faint color (-) since no characteristic blue cast Species Responsible
QUINOID DYE Disposal Neutralize with Sodium Carbonate, dilute with 10-15mL H20 => sink Other details Reacts more with aldehydes Reagent should not be heated and solution should not be alkaline Regeneration of pink color of fuchsin Is not enough; needs to have blue cast bordering on a violet or purple Reagents and Special Treatments Schiffs Reagent (bis-N-sulfinic acid of p-rosaline hydrochloride) aka fuchsin-aldehyde reagent or Leucosulfonic acid To prepare: dissolve 0.05 g of certified basic fuchsin (4-rosaline hydrochloride) 50 mLDW + 2mL saturated sodium bisulfate solution Sit for 1 h + 1mL HCl, stand overnight => colorless reagent and sensitive Test IODOFORM TEST FOR METHYL KETONES Specific Purpose of the Test Presence of methyl ketones Principles Involved Iodination, Hydrolysis, Substitution reaction, cleavage Equations
Visible Results Formation of yellow foul-smelling precipitate Species Responsible CHI3 (iodoform)
Disposal Add drops of acetone to destroy unreacted I2-KI solution until the liquid remains yellow Remove Iodoform by suction filtration, => halogenated waste Filtrate => sink Other details 1. Removal of proton from alpha poition to give an enolate ion (stabilized by anion with considerable proportion of charge on O 2. Enol/enoloate combine with halogen (I) to give alpha haloketone 3. Formation of trihaloketone since other Hs are made more acidic by e- attaching effect of halogen 4. Easily attacked by base at the C-C bond Reagents and Special Treatments 10% NaOH, I2-KI Solution, heated to 60oC
You might also like
- BIO - Lab Report 5 - FoodDocument13 pagesBIO - Lab Report 5 - FoodNor Ashikin Ismail50% (2)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Minutes of Regular Meeting Held Last July 10Document3 pagesMinutes of Regular Meeting Held Last July 10Mj Weak97% (32)
- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueDocument28 pagesAldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueMissy NalaunanNo ratings yet
- Ace T AldehydeDocument5 pagesAce T AldehydeAlfa FallurinNo ratings yet
- Qualitative TestDocument4 pagesQualitative TestSwati KaushalNo ratings yet
- Identification of AlcoholsDocument26 pagesIdentification of Alcoholspupu_wowNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For Environmental HealthDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry For Environmental HealthASYRANI ZULAIKHANo ratings yet
- Chem 503 - Activity 5Document7 pagesChem 503 - Activity 5Aries Jay ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chem31.1 Finals NotesDocument8 pagesChem31.1 Finals NotesElla YapNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestDocument20 pagesQualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestFRANCEEN LEANNA KATIGBAKNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 3Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3GundanNo ratings yet
- Pre Laboratory AssignmentDocument44 pagesPre Laboratory AssignmentJr Montero100% (3)
- Chemistry VIVADocument3 pagesChemistry VIVAtanvir shahriarNo ratings yet
- Experiment N0.6 - Aldehydes and Ketones-1Document3 pagesExperiment N0.6 - Aldehydes and Ketones-1Vida HumadasNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1Document93 pagesAldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1jjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde-Ketone TestsDocument3 pagesAldehyde-Ketone TestsNorazma ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- 12Document6 pages12NathaLie Sta ElenaNo ratings yet
- 2 5352688982180245339Document11 pages2 5352688982180245339حسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- A Positive Result Is A Red-Orange Precipitate of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazoneDocument3 pagesA Positive Result Is A Red-Orange Precipitate of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazoneBianca Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Expt 5 8 ResultsDocument4 pagesExpt 5 8 ResultsAdrian SantolomaNo ratings yet
- Detection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesDetection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsKiran PatroNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17Document28 pagesReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17angeline medallo100% (1)
- Labreport 8 OrganicDocument12 pagesLabreport 8 OrganicHajarul AjiehahNo ratings yet
- BALDONADO, LESLEY JOY - Activity On Aldehydes and KetonesDocument3 pagesBALDONADO, LESLEY JOY - Activity On Aldehydes and KetonesLesley Joy T. BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesDanluidQMalintadNo ratings yet
- BC Lab (Carbohydrates)Document4 pagesBC Lab (Carbohydrates)Cassandra HerreraNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument9 pagesAldehydesNadine Jamih100% (2)
- Theory 3 Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesTheory 3 Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesColor Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesRüveyda AkçinNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument19 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidPraneel BhattNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compound Khaled AlhiagemDocument14 pagesCarbonyl Compound Khaled Alhiagemkhfgf;lNo ratings yet
- Benedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesBenedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochem Lab ReviewerDarlin Maree JamonNo ratings yet
- Lab 6-283gDocument11 pagesLab 6-283gAnonymous 4KuItFhNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument40 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsMiguelNo ratings yet
- Lelm108 Pages 8Document1 pageLelm108 Pages 8ABCNo ratings yet
- Lab Expts 5-7 ReviewDocument6 pagesLab Expts 5-7 ReviewKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Report 4Document7 pagesChemistry Report 4Lih XuanNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compound-2Document20 pagesCarbonyl Compound-2fishindasea00No ratings yet
- Chem-No.-13 2Document5 pagesChem-No.-13 2ho laNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument119 pagesAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsKashvi KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Report SheetDocument21 pagesExperiment 7 Report SheetDiane Princess SultanNo ratings yet
- Iodoform OrganicDocument14 pagesIodoform OrganicJefy Liapril100% (2)
- FM7 Labreport 2Document12 pagesFM7 Labreport 2Jei y’allNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 3Document11 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 3wmaximoff426No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesDocument58 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Test For Carbohydrates: CHY 47.1 Biochemistry LaboratoryDocument11 pagesExercise 4 Test For Carbohydrates: CHY 47.1 Biochemistry LaboratorycamilleNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates LabBernardMarkMateoNo ratings yet
- Test For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalDocument31 pagesTest For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- 46.1.06 AOAC Official Surplus Method 920.209 Natural Coloring Matters Identification by Color Reactions First Action Surplus 1970Document3 pages46.1.06 AOAC Official Surplus Method 920.209 Natural Coloring Matters Identification by Color Reactions First Action Surplus 1970Khaled KayaliNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Expt 10Document4 pagesLab Report Expt 10Eyvette GoNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument5 pages4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsFin BrickmanNo ratings yet
- EXPE9Document8 pagesEXPE9K-yanVehraaYomomaNo ratings yet
- 3.theory Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesDocument11 pages3.theory Biochemical Tests For CarbohydratesAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 2Document16 pagesPractical No. 2shahbazNo ratings yet
- A Volumetric Analysis (Redox Titration) of Hypochlorite in BleachDocument5 pagesA Volumetric Analysis (Redox Titration) of Hypochlorite in Bleachskrim240No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- The National Teachers CollegeDocument4 pagesThe National Teachers CollegeMj WeakNo ratings yet
- Insect SterilizationDocument19 pagesInsect SterilizationMj WeakNo ratings yet
- Is The Internet Making Us StupidDocument2 pagesIs The Internet Making Us StupidMj WeakNo ratings yet