Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Greenhouse Effect: A Quick Review
The Greenhouse Effect: A Quick Review
Uploaded by
Alan Clarke0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views11 pagesThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that keeps the Earth's surface habitable by trapping heat from the Sun in the lower atmosphere. Greenhouse gases like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere absorb and emit infrared radiation emitted from the Earth's surface, preventing it from escaping into space and maintaining an average global temperature of around 60°F. Human activity has increased the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect and contributing to rising global temperatures.
Original Description:
Original Title
Greenhouse Effect
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that keeps the Earth's surface habitable by trapping heat from the Sun in the lower atmosphere. Greenhouse gases like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere absorb and emit infrared radiation emitted from the Earth's surface, preventing it from escaping into space and maintaining an average global temperature of around 60°F. Human activity has increased the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect and contributing to rising global temperatures.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views11 pagesThe Greenhouse Effect: A Quick Review
The Greenhouse Effect: A Quick Review
Uploaded by
Alan ClarkeThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that keeps the Earth's surface habitable by trapping heat from the Sun in the lower atmosphere. Greenhouse gases like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere absorb and emit infrared radiation emitted from the Earth's surface, preventing it from escaping into space and maintaining an average global temperature of around 60°F. Human activity has increased the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect and contributing to rising global temperatures.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
The Greenhouse Effect
A quick review
The Greenhouse Effect
A natural process that keeps the surface
of the earth at a habitable temperature.
Without the greenhouse effect, surface temperatures would be about 60 F colder. There would be NO liquid water!
How does it work?
Image source: kids.earth.NASA.gov
How does it work?
Short wavelength (ultraviolet) radiation from
Sun reaches Earth Earth warms and emits long wavelength (infrared) radiation back towards space Greenhouse gases in Earths atmosphere trap some of the infrared radiation near Earth
Think of your car on a sunny day: the sunlight enters through the closed windows and warms the car interior. That heat cant escape back out through the glass.
What are the main Greenhouse Gases?
Water vapor (H2O) Carbon dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous oxide (N2O) These were all present in atmosphere before humans, but we are adding more
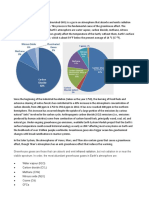
Greenhouse Gases allow ~75% of short wavelength energy from Sun to reach Earth.
Only 15-30% of the energy re-radiated by Earth escapes back through greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Image created by Robert A. Rohde / Global Warming Art http://www.globalwarmingart.com/wiki/File:Atmospheric_Transmission_png
Greenhouse Gas Efficiency
Gas Relative greenhouse efficiency per molecule Concentration in Relative the atmosphere efficiency x (ppm) concentration (ppm) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Ozone (O3) Chlorofluoro carbons (CFCs)
1 30 160 2000 21,000
350 1.7 0.31 0.06 0.00026
350 51 49.6 120 5.46
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Sources
Methane (CH4) Buuurp!
Enteric fermentation (cow burps!) Landfill emissions Rice cultivation Natural gas use Melting of permafrost in Arctic Agricultural processes (fertilizers)
Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Sources
What about CFCs? Very powerful greenhouse gas, but people have been very successful at reducing emissions (Montreal Protocol)
Effect on Upper Atmosphere
The Greenhouse Effect causes warming at
Earths surface, but cooling in upper atmosphere
If more of Earths emitted longwave radiation is held close to the surface, it is not available to cause warming in the upper atmosphere More noctilucent cloud formation in the Mesosphere? (see Noctilucent Clouds.ppt)
You might also like
- Effects of Green House Gases (Chemistry Project Class-11)Document15 pagesEffects of Green House Gases (Chemistry Project Class-11)Anujeet Saha88% (8)
- Greenhouse Effect-Acid Rain-Ozone Layer..Document66 pagesGreenhouse Effect-Acid Rain-Ozone Layer..Raiyan Zaman AdreyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact of Fuel Cell: Dr. Sammia ShahidDocument94 pagesEnvironmental Impact of Fuel Cell: Dr. Sammia ShahidJaggaJattNo ratings yet
- Module For Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesModule For Climate ChangeReina DionsonNo ratings yet
- Carbon SequestrationDocument45 pagesCarbon SequestrationSakshi TripathiNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument6 pagesGreen House EffectVir PatelNo ratings yet
- ADITI VERMA (Assignment 1, SUSTAINABLE ARCHITECTURE)Document30 pagesADITI VERMA (Assignment 1, SUSTAINABLE ARCHITECTURE)Sani SahaniNo ratings yet
- Cma433 Topics 2Document55 pagesCma433 Topics 2Muhammad AizatNo ratings yet
- The Greenhouse Effect and Global WarmingDocument20 pagesThe Greenhouse Effect and Global WarmingNimra KhalidNo ratings yet
- Outline For Report ENVIRONDocument6 pagesOutline For Report ENVIRONJoshua MacaraegNo ratings yet
- RA L9 Global Warming 9Document29 pagesRA L9 Global Warming 9md.daud.ul.islamNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument65 pages1.1 - Global Warming and Climate ChangeMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse GassDocument4 pagesGreenhouse GassBella Yunita100% (1)
- Presentation 10Document15 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- Activity 3 Answer The Following Questions BelowDocument3 pagesActivity 3 Answer The Following Questions BelowMicca Ella VinoyaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument33 pagesClimate ChangeKhiZra ShahZad100% (2)
- Greenhouse Effect: Learning OutcomeDocument16 pagesGreenhouse Effect: Learning OutcomeJames WongNo ratings yet
- Carbon Footprints: A Presentation OnDocument49 pagesCarbon Footprints: A Presentation OnKalsoom RazaNo ratings yet
- Zeu 1223 Proficiency English 2 Topic: Greenhouse EffectDocument22 pagesZeu 1223 Proficiency English 2 Topic: Greenhouse EffectJuni CellaNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument21 pagesAir PollutionstephanievogelNo ratings yet
- Introduction Climate Change ScienceDocument75 pagesIntroduction Climate Change ScienceJadiel Adrián Gómez GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Greenhouse Effect Acid RainDocument30 pagesGlobal Warming: Greenhouse Effect Acid RainSajib IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Climate-Greenhouse EffectDocument29 pagesClimate-Greenhouse Effecttheanuuradha1993gmaiNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectsDocument8 pagesGreen House Effectssme chemistryNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text Global WarmingDocument12 pagesExplanation Text Global WarmingEggi Marcelleno100% (1)
- LECTURE 5 - Green House Effect and Global WarmingDocument22 pagesLECTURE 5 - Green House Effect and Global WarmingArjit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument50 pagesGlobal WarmingLeah Oljol RualesNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry As It IsDocument57 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry As It Isatr030108No ratings yet
- Global Climate Change: What Is It?Document42 pagesGlobal Climate Change: What Is It?raghonittyNo ratings yet
- A Report On Global WarmingDocument33 pagesA Report On Global WarmingAbdullah Al ZobayerNo ratings yet
- Student Notes - Unit 9Document10 pagesStudent Notes - Unit 9T ANo ratings yet
- 08-Climate Change R0323Document52 pages08-Climate Change R0323abbicox.stlNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesGreenhouse EffectAldo S. ArizaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument10 pagesGlobal WarmingYashraj RathiNo ratings yet
- TDATDocument24 pagesTDATMagali MeacaNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument30 pagesGreenhouse EffectFernan SibugNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle StepsDocument20 pagesThe Carbon Cycle StepsBigLove100% (1)
- The EarthDocument3 pagesThe EarthloheesNo ratings yet
- Global Warming-A Gretest Environmental ThreatDocument21 pagesGlobal Warming-A Gretest Environmental Threatvj2713No ratings yet
- PowerPoint PresentationDocument45 pagesPowerPoint PresentationmonekaNo ratings yet
- Global Worming and Greenhose Gases PDFDocument5 pagesGlobal Worming and Greenhose Gases PDFShubham Raj SanuNo ratings yet
- 1579172394environment Science TechDocument213 pages1579172394environment Science TechAman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming FhsDocument28 pagesGlobal Warming FhsTiChristi TiJesuNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle and The Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesCarbon Cycle and The Greenhouse Effectapi-235669157No ratings yet
- 1611757209environment Science TechDocument205 pages1611757209environment Science TechWanderer InneverlandNo ratings yet
- BIOL 002 Global Warming: Beirut Arab University Faculty of Science Department of BiologyDocument65 pagesBIOL 002 Global Warming: Beirut Arab University Faculty of Science Department of BiologyYoumna ShatilaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Reasons For Global Warming?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Reasons For Global Warming?manirathinaNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere RevisionDocument33 pagesAtmosphere RevisionChaos InsurgencyNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect Global WarmingDocument2 pagesGreenhouse Effect Global Warmingrajaafif LcNo ratings yet
- EngrCritique - Agw Science.v4.3Document98 pagesEngrCritique - Agw Science.v4.3Ander SanderNo ratings yet
- Pollution Ozone GHGDocument33 pagesPollution Ozone GHGChisama SichoneNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument42 pagesClimate ChangeDela Cruz Honey Rose RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse GasDocument5 pagesGreenhouse Gastanzim444No ratings yet
- Lec-12-Env. Pollution IssueDocument46 pagesLec-12-Env. Pollution Issuezeshan habibNo ratings yet
- Group 2aDocument24 pagesGroup 2aPrince Abu100% (1)
- Global Warming: Department of Chemistry National Institute of Technology, RaipurDocument22 pagesGlobal Warming: Department of Chemistry National Institute of Technology, RaipurrajuNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Gases BiologyDocument6 pagesGreenhouse Gases BiologyDeadly ChillerNo ratings yet
- Environment: Climate ChangeDocument33 pagesEnvironment: Climate ChangeHằng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Cautions For A Finite WorldDocument26 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Cautions For A Finite WorldPutri Imarotul MuttaqiNo ratings yet