Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Datasheet FOUNDATIONof Energy
Datasheet FOUNDATIONof Energy
Uploaded by
api-37659360 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageThe document provides information relevant to an exam on the foundations of energy including:
1) The exam is 2 hours closed-book with only an approved calculator, writing utensils, and dictionary permitted for non-native English speakers.
2) Prefixes and unit conversions are provided such as kilo = 103 and 1 toe = 42 GJ.
3) Properties of materials like water, air, fuels, and ranges of heat transfer coefficients are included as reference tables.
4) Useful equations for ideal gases, isentropic processes, Stefan-Boltzmann law, hydraulic power, fluid current power, and nondimensional specific speed are listed.
Original Description:
Original Title
datasheetFOUNDATIONofEnergy
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information relevant to an exam on the foundations of energy including:
1) The exam is 2 hours closed-book with only an approved calculator, writing utensils, and dictionary permitted for non-native English speakers.
2) Prefixes and unit conversions are provided such as kilo = 103 and 1 toe = 42 GJ.
3) Properties of materials like water, air, fuels, and ranges of heat transfer coefficients are included as reference tables.
4) Useful equations for ideal gases, isentropic processes, Stefan-Boltzmann law, hydraulic power, fluid current power, and nondimensional specific speed are listed.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageDatasheet FOUNDATIONof Energy
Datasheet FOUNDATIONof Energy
Uploaded by
api-3765936The document provides information relevant to an exam on the foundations of energy including:
1) The exam is 2 hours closed-book with only an approved calculator, writing utensils, and dictionary permitted for non-native English speakers.
2) Prefixes and unit conversions are provided such as kilo = 103 and 1 toe = 42 GJ.
3) Properties of materials like water, air, fuels, and ranges of heat transfer coefficients are included as reference tables.
4) Useful equations for ideal gases, isentropic processes, Stefan-Boltzmann law, hydraulic power, fluid current power, and nondimensional specific speed are listed.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Typical examination data sheet
NB: The Foundations of Energy is a 2-hour exam which is a closed-book exam.
Apart from an approved calculator and writing utensils the only permitted material is a
standard dictionary for those whose main language is not English. All dictionaries will
need to be presented to the invigilators for checking.
However, this data sheet (or a modification thereof) will be provided as part of the
exam paper.
Prefixes and conversions
kilo: 103, mega: 106, giga: 109, tera: 1012, peta: 1015, exa: 1018,
1 toe = 42 GJ; 1kWh = 3.6 MJ
Fluid and fuel properties
–3
Water at 5 to 20°C : density 1000 kg m ; specific heat 4.2 kJ kg– 1 K– 1
Air at ground level and 0 to 40°C: density 1.225 kg m – 3 ; specific heat at constant
pressure 1.01 kJ kg– 1 K– 1, specific heat at constant volume 0.72 kJ kg– 1 K– 1,
Name Composition Molecular weight Energy content
(MJ / kg)
Methane CH4 16 55
Ethane C2H6 30 51
Octane C8H18 114 48
Cetane C16H34 226 48
Anthracite >~80% C 12 ~30
Lignite ~ 60% C 12 ~20
Biomass ~ Cx(H2O)y ~10 – ~20
Carbon dioxide CO2 44
Typical ranges of the heat transfer coefficient
Type of convection h W/m2/K
Free convection of gases 2 - 25
Free convection of liquids 10 - 1000
Forced convection of gases 25 - 250
Forced convection of liquids 50 - 20,000
Boiling and condensation 2,500 - 100,000
Useful equations
Ideal gas p = ρ RT with R = Cp – CV
Isentropic processes
p2 / p1 = ( ρ2 / ρ1 ) γ ; T2 / T1 = ( ρ2 / ρ1 ) γ −1
; T2 / T1 = ( p2 / p1 ) ( γ −1)/γ
with γ=
Cp / CV
Stefan-Boltzmann law: Q = ε σ A T 4 with σ= 5.67×10 – 8 W m–2 K–4
Hydraulic power PH = ρ g H Q
Fluid current power P = ½ ρ A U3
Nondimensional specific speed: KN = Ω (P/ρ) 1/2 (gH) – 5/4
You might also like
- Condenser CalculationsDocument9 pagesCondenser CalculationsAngelo Imbo100% (2)
- Chapter Three Working Fluids (A) Ideal Gas (Perfect Gas) :: Statement No. (1)Document16 pagesChapter Three Working Fluids (A) Ideal Gas (Perfect Gas) :: Statement No. (1)Bonifacio MifañaNo ratings yet
- Understand Temperature Change in Process Stream MixingDocument6 pagesUnderstand Temperature Change in Process Stream MixingAnonymous 1XHScfCI100% (1)
- Properties of Liquid SimpleDocument3 pagesProperties of Liquid SimpleOsadreuasa100% (3)
- Hydrological Investigation in Determining Subsurface ResourcesDocument47 pagesHydrological Investigation in Determining Subsurface ResourcesJohn Carlo AbalaNo ratings yet
- ChE ThermodynamicsDocument49 pagesChE ThermodynamicsMiguel FelisildaNo ratings yet
- Heat Effect & ThermochemistryDocument29 pagesHeat Effect & ThermochemistryRani TriwrdhNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perpindahan PanasDocument20 pagesTugas Perpindahan PanasLiyan Fajar GintaraNo ratings yet
- Me ThermodynamicsDocument63 pagesMe ThermodynamicsGlenn Ray ErasmoNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument14 pagesGas LawRoszelan Majid100% (1)
- Ex 2Document2 pagesEx 2Anas ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Adv Thermo 2018 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesAdv Thermo 2018 Tutorial 1Greg PolemanNo ratings yet
- 10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Problem Set DDocument2 pages10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Problem Set DPM SHNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Gas LawsDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Gas LawsAdamNo ratings yet
- Life Is A Huge Lab: Answers and Grading Schemes JULY 25, 2015 Baku, AzerbaijanDocument42 pagesLife Is A Huge Lab: Answers and Grading Schemes JULY 25, 2015 Baku, AzerbaijanLê Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- Final 2012 Chemical MetallurgyDocument7 pagesFinal 2012 Chemical MetallurgyRuby AdijayaNo ratings yet
- E233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasDocument16 pagesE233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasYingyote LubphooNo ratings yet
- Stream 18: H ∆ Ĥ f (l) + Cp Dt + Δp ṽDocument20 pagesStream 18: H ∆ Ĥ f (l) + Cp Dt + Δp ṽAhmed Qutb AkmalNo ratings yet
- 3010 Lec 3123Document25 pages3010 Lec 3123Mertcan AslanNo ratings yet
- Drying Tower & Sulphur BurnerDocument18 pagesDrying Tower & Sulphur BurnerAhmed Qutb AkmalNo ratings yet
- Problem 1 (20 PTS) .: P (V B) RT C C RDocument5 pagesProblem 1 (20 PTS) .: P (V B) RT C C RAriful RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - The First Law of Thermo Part 2Document25 pagesLecture 6 - The First Law of Thermo Part 2SaraNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine CyclesDocument60 pagesGas Turbine Cyclesالأردني JordanianNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 For 2022Document52 pagesUNIT 2 For 2022Rishan KundetyNo ratings yet
- Bsme 3-B: Me 114 - Heat Transfer Bachelor of Science in Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesBsme 3-B: Me 114 - Heat Transfer Bachelor of Science in Mechanical EngineeringJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Jethro Heat TransferDocument3 pagesJethro Heat Transferjethro ganeloNo ratings yet
- HHV, LHV, and Closed Systems.Document8 pagesHHV, LHV, and Closed Systems.RONIBAEL CORDOVANo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AlkynesDocument31 pagesSynthesis of AlkynesttinbddinNo ratings yet
- Steady Flow Energy Equation (SFEE) :) Z Z (+ G 2 C 2 C + H W H QDocument23 pagesSteady Flow Energy Equation (SFEE) :) Z Z (+ G 2 C 2 C + H W H QSams ArefinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Energy Balance: I Ki PiDocument13 pagesChapter 4: Energy Balance: I Ki PiAhmed Qutb AkmalNo ratings yet
- Thermally Double Coupled Reactor Coupling Aqueous Phase GlycerolDocument10 pagesThermally Double Coupled Reactor Coupling Aqueous Phase GlycerolMahdy HajienayatiNo ratings yet
- 314 CH 5Document26 pages314 CH 5reham khaledNo ratings yet
- Bsme 3-B: Me 114 - Heat Transfer Bachelor of Science in Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesBsme 3-B: Me 114 - Heat Transfer Bachelor of Science in Mechanical EngineeringJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Process 2 Enbal IncDocument43 pagesProcess 2 Enbal IncJULIA REESE REYESNo ratings yet
- Che 501 - TutorialsDocument7 pagesChe 501 - TutorialsIgnatius Setiadi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- 4.4.2 Energy Balance For Sulphur BurnerDocument5 pages4.4.2 Energy Balance For Sulphur BurnerAhmed Qutb AkmalNo ratings yet
- Combustion: Flame Theory and Heat Produced: Arthur Anconetani Oscar Castillo Everett HendersonDocument29 pagesCombustion: Flame Theory and Heat Produced: Arthur Anconetani Oscar Castillo Everett HendersonTommy Cha Yee WenNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Combustion For PublicationDocument30 pagesTopic 3 - Combustion For PublicationMuhammad Nur Fahmi NaimemNo ratings yet
- Fcto Infrastructure Workshop 2018 31 AhluwaliaDocument12 pagesFcto Infrastructure Workshop 2018 31 AhluwaliaFlogamagNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-1 PDFDocument21 pagesUnit 4-1 PDFkaushikNo ratings yet
- Products of CombustionDocument5 pagesProducts of CombustionAJ SiosonNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of FormationDocument11 pagesEnthalpy of FormationRONIBAEL CORDOVANo ratings yet
- MECH5265 Tutorial 04 SolutionsDocument6 pagesMECH5265 Tutorial 04 Solutionshnyjd2No ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR07 Set No. 2Samiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Equilibrium Composition of Flames: Niranjwan Chettiar 2010213041 ME. Energy Engineering Dr. NatarajanDocument28 pagesChapter 5: Equilibrium Composition of Flames: Niranjwan Chettiar 2010213041 ME. Energy Engineering Dr. NatarajanNiranjwan ChettiarNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Transducers 2012Document30 pagesSensors and Transducers 2012Anonymous AMjDOJ0lNo ratings yet
- Heat CalcDocument7 pagesHeat CalcasdfghjkNo ratings yet
- TOCK - 10JBB - BTLarticle - OwnlayoutDocument28 pagesTOCK - 10JBB - BTLarticle - OwnlayoutazNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet: Boyang Qin Date Created: Jan 2013Document3 pagesEquation Sheet: Boyang Qin Date Created: Jan 2013Boyang QinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes: (Revised 9/04)Document9 pagesChemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes: (Revised 9/04)shiv kr dubeyNo ratings yet
- Thermo Heat EffectsDocument61 pagesThermo Heat EffectsMayFifthNo ratings yet
- Fuel and CombustionDocument21 pagesFuel and CombustionAnil DubeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2022Document5 pagesAssignment 1 2022Katlego NathanNo ratings yet
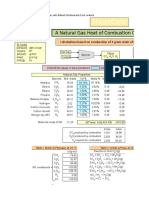
- Heatcalc: A Natural Gas Heat of Combustion CalculatorDocument7 pagesHeatcalc: A Natural Gas Heat of Combustion CalculatorMuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Note Ideal Gas TutorialDocument5 pagesNote Ideal Gas TutorialGnabryNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 - Gas Laws2Document19 pagesLecture3 - Gas Laws2lytonchirwa882No ratings yet
- Aula 5Document46 pagesAula 5hannibal_12No ratings yet
- L-9 Pure Substance Ideal Gases-IDocument25 pagesL-9 Pure Substance Ideal Gases-IShailin SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Nr-220802-Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - IDocument8 pagesNr-220802-Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - ISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Cith 35: O2 BalanceDocument11 pagesCith 35: O2 BalanceSecret SecretNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- CH 5 Heat Exchanger Design MethodsDocument30 pagesCH 5 Heat Exchanger Design Methodsapi-3765936100% (1)
- CH 4 Pressure Drop in Heat ExchangersDocument14 pagesCH 4 Pressure Drop in Heat Exchangersapi-3765936100% (5)
- Foundation of EnergyDocument121 pagesFoundation of Energyapi-3765936No ratings yet
- Foundations of Energy Past Paper 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesFoundations of Energy Past Paper 1 Solutionsapi-3765936No ratings yet
- Foe 4Document6 pagesFoe 4api-3765936No ratings yet
- Energy RevolutionDocument96 pagesEnergy RevolutionviskyseNo ratings yet
- Foe 0Document10 pagesFoe 0api-3765936No ratings yet
- Reduction of CO2 EemissionsDocument18 pagesReduction of CO2 Eemissionsapi-3765936No ratings yet
- Set 9 GroundwaterDocument5 pagesSet 9 GroundwaterFM burgosNo ratings yet
- Convective Mass TransferDocument21 pagesConvective Mass TransferRichardNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Fluid Mechanics Lesson 2 PRDocument4 pagesToaz - Info Fluid Mechanics Lesson 2 PRMark Lester NacarioNo ratings yet
- Turbomolecular PumpDocument10 pagesTurbomolecular PumpMustafa SayyedNo ratings yet
- Global Water Crisis OverviewDocument1 pageGlobal Water Crisis OverviewMisaki DragneelNo ratings yet
- Course: B.Tech Mechanical Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering Unit-1Document84 pagesCourse: B.Tech Mechanical Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering Unit-1Amogh VaishnavNo ratings yet
- 3 Students ANALYZING DATA Physical Properties of Gaseous Elements 1Document3 pages3 Students ANALYZING DATA Physical Properties of Gaseous Elements 1Jana AhmedNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With OneDriveDocument41 pagesGetting Started With OneDriveAijaz Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- AIGA 046 - 08 Periodic Inspection of Static Cryogenic Vessels - Reformated Jan 12Document28 pagesAIGA 046 - 08 Periodic Inspection of Static Cryogenic Vessels - Reformated Jan 12Abdullah FazilNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surrounding QRDocument48 pagesMatter in Our Surrounding QRomvjanapureNo ratings yet
- Cementing Across Massive Salt Formations J. Yearwood P. Drecq P. RaeDocument10 pagesCementing Across Massive Salt Formations J. Yearwood P. Drecq P. RaeCoolProphetNo ratings yet
- NGVF 2016 D1.T2.4.1 Gordon Farquharson WFI - New PH Eur Production Specification PDFDocument39 pagesNGVF 2016 D1.T2.4.1 Gordon Farquharson WFI - New PH Eur Production Specification PDFParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 3279106Document20 pagesGrundfosliterature 3279106Riski SuhardinataNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment System (Sistem Pengolahan Air Spa)Document38 pagesWater Treatment System (Sistem Pengolahan Air Spa)Tjen MolynaNo ratings yet
- DIP DIJ OB Pumps V4 1741102 ENDocument8 pagesDIP DIJ OB Pumps V4 1741102 ENsamant singhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 (Bubble Leak Testing)Document9 pagesCHAPTER 6 (Bubble Leak Testing)Samia IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Drinking-Water Guidelines - Chapter 4 Selection of Water Source and TreatmentDocument34 pagesDrinking-Water Guidelines - Chapter 4 Selection of Water Source and TreatmentMohamed KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Worksheet 3 - PVTN Problems: P T V N Initial Final EffectDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 3 - PVTN Problems: P T V N Initial Final EffectBillyNo ratings yet
- Ref PVC Schedule80 IPS PlasticPipeDocument1 pageRef PVC Schedule80 IPS PlasticPipesirajuddin khowajaNo ratings yet
- Irrigation System of Pakistan - CSS Pakistan Affairs NotesDocument2 pagesIrrigation System of Pakistan - CSS Pakistan Affairs NotesAar Tech Care100% (1)
- CELdek Tech Manual GB-0016-0400Document9 pagesCELdek Tech Manual GB-0016-0400maihuongxd100% (3)
- Applied Thermal Engg. 15ME52TDocument23 pagesApplied Thermal Engg. 15ME52TMr Omkar PatilNo ratings yet
- Vapour Absorption Chiller (VAM) - Working Principle in DetailDocument14 pagesVapour Absorption Chiller (VAM) - Working Principle in DetailUPENNo ratings yet
- Use of Preservation Chemicals Following Hydrostatic Testing of PipelinesDocument3 pagesUse of Preservation Chemicals Following Hydrostatic Testing of PipelinesAmirah AqilahNo ratings yet
- Bhs. Inggris Wajib XiDocument9 pagesBhs. Inggris Wajib XiElma Septiana0% (1)
- Proceeding 8th IMAT3Document118 pagesProceeding 8th IMAT3Edy SusantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Water Resource of Ethiopia: Drainage Systems and The Horn?Document23 pagesChapter Four: Water Resource of Ethiopia: Drainage Systems and The Horn?Bergude Gurzho100% (1)
- 1 QQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQDocument8 pages1 QQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQJeremy TatskiNo ratings yet