Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vroom
Vroom
Uploaded by
Reaz AllyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vroom
Vroom
Uploaded by
Reaz AllyCopyright:
Available Formats
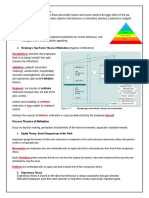
&/0; vroom's Expectancy Theory"
The Iocus oI Vroom`s 'Expectancy Theory is that an employee`s motivation to complete a task
is inIluenced by their personal views regarding:
1. The probability oI completing the task and
2. The possible outcome or consequence oI completing the task.
Expectancy Theory states that, individuals make decisions, which they believe will lead to
reward or reduce the likelihood oI pain. The ultimate goal does not matter, the important Iactor is
the impact that achieving the goal will have on the individual. An individual`s opinion is Iormed
by a combination oI three Iactors which Vroom categorised as Iollows
1. Expectancy Does the individual believe that they can achieve the task
2. Valence Does the individual believe that completing the task will beneIit them or cause
detriment.
3. Instrumentality What is the probability oI completing the task leading to an outcome desired
by the individual
1. Expectancy (Subjective Probability)
Expectancy is the individual`s belieI about whether they can achieve the task. This view will be
inIluenced by a number oI things including
- The type oI skills needed Ior the task,
- Support expectations oI co-workers and line managers,
- Type oI equipment/materials and
- Availability oI pertinent inIormation.
Another Iactor inIluencing expectancy is previous experience. II the task has been successIully
completed in the past then expectancy will be high but iI the task has Iailed in the past or was
diIIicult to perIorm then expectancy will be low.
O There is a positive correlation between eIIorts and perIormance,
O avourable perIormance will result in a desirable reward,
O The reward will satisIy an important need,
O The desire to satisIy the need is strong enough to make the eIIort worthwhile
II an individual Ieels that they can achieve the task then expectancy is measured as 1. On the
other hand iI they Ieel that the task can not be completed then expectancy is measured a 0. II the
individual Ieels that the task may be achievable then it will be categorised between 0 and 1.
Eg. A task measured as 0.75 is believed to be more achievable than one measured as 0.45.
You might also like
- Expectancy TheoryDocument3 pagesExpectancy TheoryJanice Amlon100% (1)
- Expectancy Theory: 2 Key ElementsDocument6 pagesExpectancy Theory: 2 Key ElementsAnonymous 7v9J4WaNo ratings yet
- 1541500836note VroomsTheoryofMotivationDocument8 pages1541500836note VroomsTheoryofMotivationnavinmichaeljohnsonNo ratings yet
- What Is It?Document17 pagesWhat Is It?RAHUL GUPTANo ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory of MotivationDocument4 pagesExpectancy Theory of MotivationIshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Expectancy TheoryDocument3 pagesExpectancy TheoryMeLodie Licudine EsquejoNo ratings yet
- Vrooms Expectancy Theory of MotivationDocument2 pagesVrooms Expectancy Theory of MotivationHazel OchiengNo ratings yet
- Victor Vrooms Expectancy TheoryDocument6 pagesVictor Vrooms Expectancy TheoryRVKotiaN100% (1)
- Expectancy Theory of MotivationDocument5 pagesExpectancy Theory of MotivationArmstrong BosantogNo ratings yet
- Vrooms Expectancy TheoryDocument3 pagesVrooms Expectancy Theoryswathi krishnaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Assignment MirriamDocument11 pagesPsychology Assignment MirriamBELENGA GEOFREYNo ratings yet
- PROCESS THEORIES OF MOTIVATION Original NotesDocument29 pagesPROCESS THEORIES OF MOTIVATION Original NotesignatiousmugovaNo ratings yet
- OuchiDocument3 pagesOuchiKatrina SamsonNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Vrooms Expectancy TheoryDocument9 pages2.2 - Vrooms Expectancy TheoryAnghaNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument7 pagesMotivationKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory of MotivationDocument7 pagesExpectancy Theory of MotivationAkanksha SinghNo ratings yet
- VROOMDocument2 pagesVROOMandycamille7No ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory Leadership and Management FinalDocument6 pagesExpectancy Theory Leadership and Management FinalMustafa ChowdriNo ratings yet
- Speed 18Document1 pageSpeed 18Tanisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Theories of MotivationDocument27 pagesContemporary Theories of MotivationAbhitosh SahNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Part 2Document8 pagesUnit 4 Part 2rauniyar97No ratings yet
- OB Motivation AdditionalDocument4 pagesOB Motivation AdditionalHazel Milca EstoqueNo ratings yet
- Victor VroomDocument9 pagesVictor VroomdyumnaNo ratings yet
- The Content Theories Look at What Motivates People at WorkDocument3 pagesThe Content Theories Look at What Motivates People at Workengr.caseresNo ratings yet
- Theories in OBDocument17 pagesTheories in OBSheikh Zain UddinNo ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory: Merged DiscussDocument4 pagesExpectancy Theory: Merged DiscussMuzaffar KcreativezNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument30 pagesMotivationZarak KhattakNo ratings yet
- Is The Result of The Interaction Between An Individual and A SituationDocument26 pagesIs The Result of The Interaction Between An Individual and A SituationMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Analyzing 2 Motivation Theories in Organizational BehaviorDocument13 pagesAnalyzing 2 Motivation Theories in Organizational BehaviorluongxphuNo ratings yet
- Porter LawlerDocument3 pagesPorter Lawlertiwariharshita85No ratings yet
- Process Perspectives On MotivationDocument4 pagesProcess Perspectives On Motivationanon_761113282100% (1)
- Vroomsexpectancytheoryofmotivation 120926122304 Phpapp01Document26 pagesVroomsexpectancytheoryofmotivation 120926122304 Phpapp01MainakMitraNo ratings yet
- Expectancy Theory Vroom HR MotivationDocument2 pagesExpectancy Theory Vroom HR MotivationGideon MoyoNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument5 pagesFinalkhalidNo ratings yet
- Vrooms Expectancy TheoryDocument3 pagesVrooms Expectancy Theoryazazel28No ratings yet
- Vroom's Expectancy Theory: "It's All About Expecting Something & Fulfilling That Expectation"Document10 pagesVroom's Expectancy Theory: "It's All About Expecting Something & Fulfilling That Expectation"Taimur AhmadNo ratings yet
- PART 5 - MotivationDocument11 pagesPART 5 - MotivationRose John SupranesNo ratings yet
- Expectancy TheoryDocument2 pagesExpectancy TheoryPratheek PsNo ratings yet
- "Motivating": - Stephen P RobbinsDocument5 pages"Motivating": - Stephen P RobbinsJill_xyinz14589No ratings yet
- 6 International Scientific Conference May 13-14, 2010, Vilnius, Lithuania Business and Management 2010 Selected Papers. Vilnius, 2010, Pp. 001-002Document7 pages6 International Scientific Conference May 13-14, 2010, Vilnius, Lithuania Business and Management 2010 Selected Papers. Vilnius, 2010, Pp. 001-002Youssef KhouadriNo ratings yet
- Process Theories: 1.vroom's Expectancy TheoryDocument6 pagesProcess Theories: 1.vroom's Expectancy TheoryDal.giNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management 2Document3 pagesEngineering Management 2Kay Leizlie Paredes100% (1)
- Theory of MotivationDocument11 pagesTheory of MotivationShreekumarNo ratings yet
- MC Gregors Theory X and Theory YDocument3 pagesMC Gregors Theory X and Theory Yswetha padmanaabanNo ratings yet
- Module OB 006Document25 pagesModule OB 006Abdullah Abbas JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Module (3) TDocument3 pagesModule (3) Ttuna dogNo ratings yet
- Role of Goal Setting Theory in Employee MotivationDocument14 pagesRole of Goal Setting Theory in Employee MotivationPawan RohidasNo ratings yet
- How Individual Beliefs Impact Individual Performance: EmailDocument19 pagesHow Individual Beliefs Impact Individual Performance: EmailRanjana BandaraNo ratings yet
- Victor VroomDocument5 pagesVictor VroomDileep Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Then I Will Perform Better) .: Expectancy Instrumentality ValenceDocument2 pagesThen I Will Perform Better) .: Expectancy Instrumentality Valenceaditya saiNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Vs Extrinsic Orientation and Job SatisfactionDocument2 pagesIntrinsic Vs Extrinsic Orientation and Job SatisfactionpoojaNo ratings yet
- DPGD PLPDocument7 pagesDPGD PLPSattwiki DeyNo ratings yet
- Motivation Concepts: Is The Result of The Interaction Between An Individual and A SituationDocument24 pagesMotivation Concepts: Is The Result of The Interaction Between An Individual and A Situationaqsa palijoNo ratings yet
- Reporter: Juanario J. Elejado Topic: Staff and Personnel Development Professor: Dr. Vilma H. ArazoDocument5 pagesReporter: Juanario J. Elejado Topic: Staff and Personnel Development Professor: Dr. Vilma H. ArazojeophilNo ratings yet
- Porter Lawler - Model of Motivation HandoutDocument3 pagesPorter Lawler - Model of Motivation HandoutPriyank Khokare100% (1)
- MotivationDocument23 pagesMotivationdazaik885No ratings yet
- Fiop Motivation AssignmentDocument6 pagesFiop Motivation AssignmentchehekNo ratings yet
- GRP. 4 - Motivation 002Document11 pagesGRP. 4 - Motivation 002hlpmefrmwthn143No ratings yet
- Presentation On Expectancy Theory of MotivationDocument13 pagesPresentation On Expectancy Theory of MotivationArjun AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceFrom EverandUnderstanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)